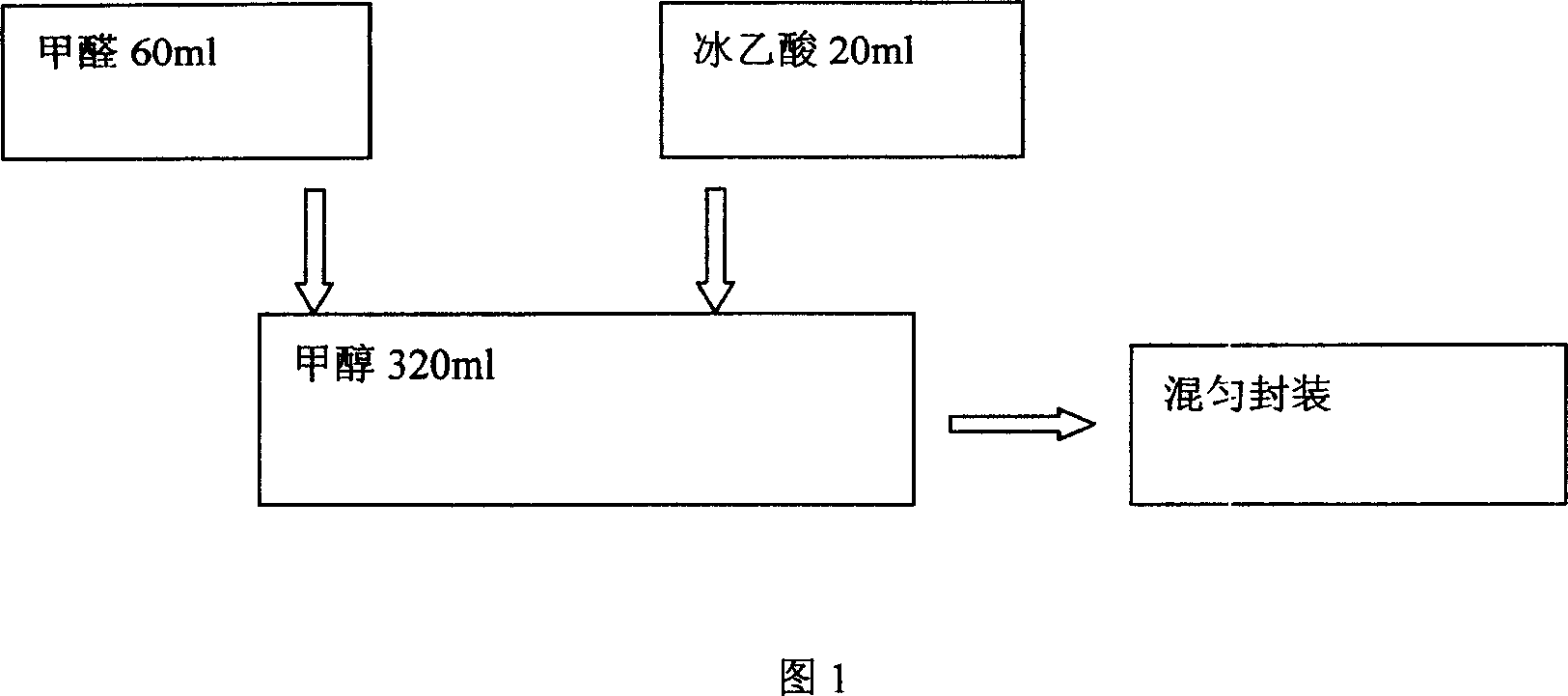
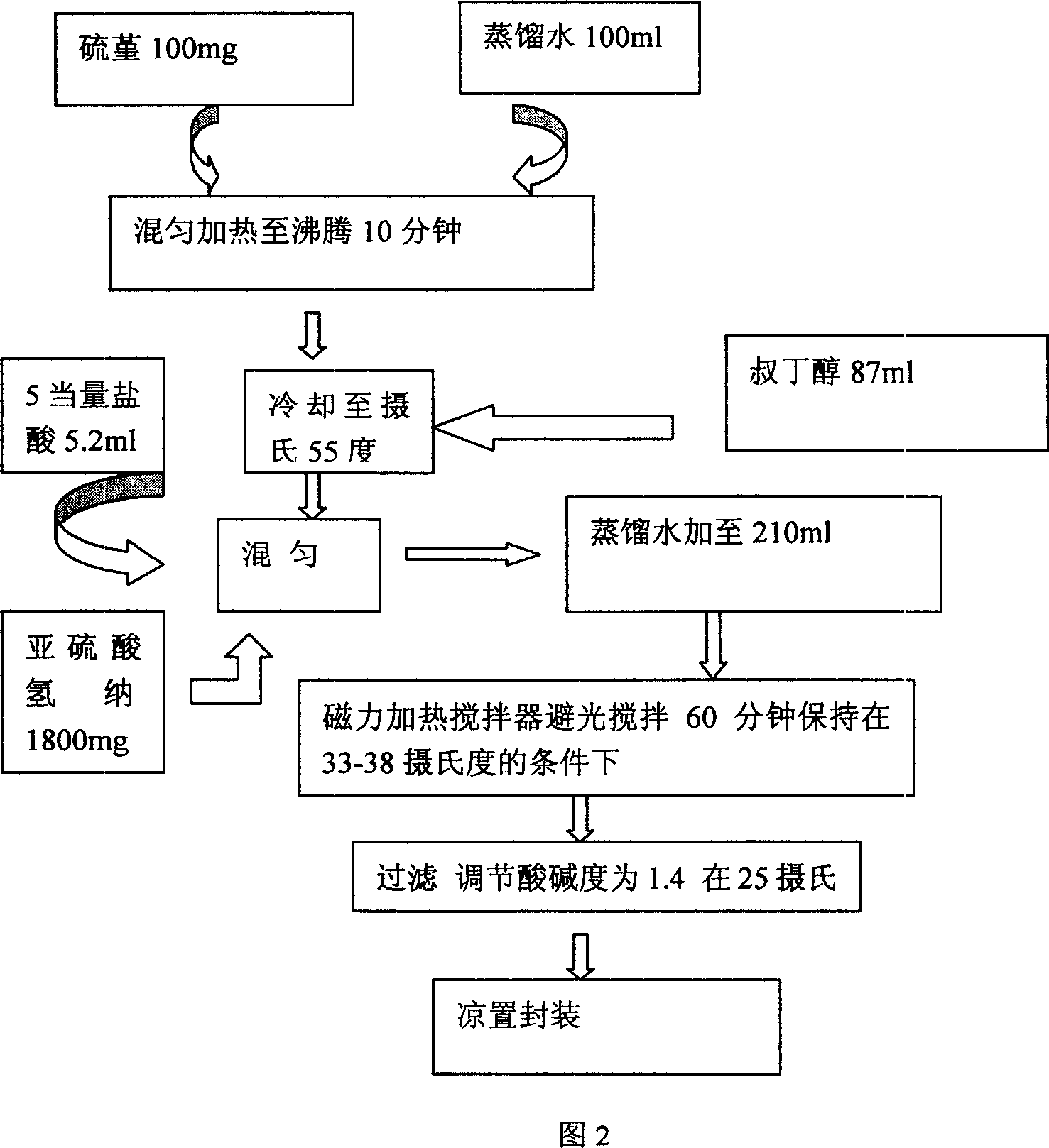
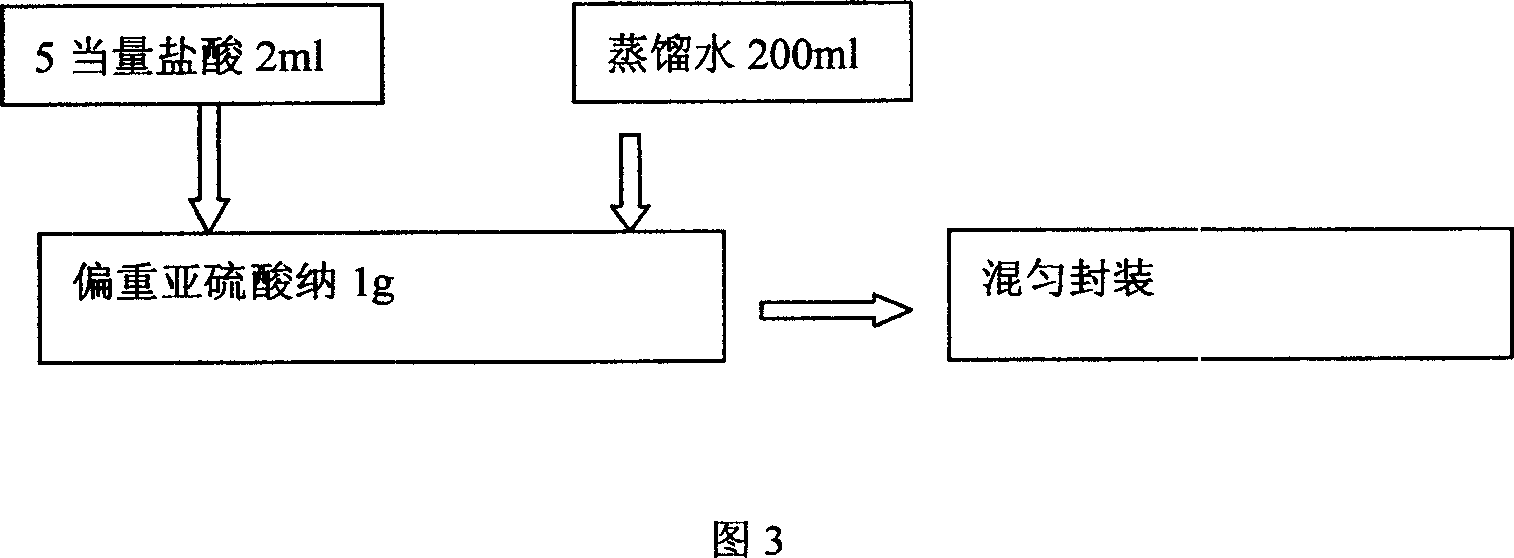
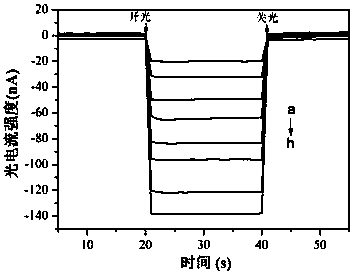
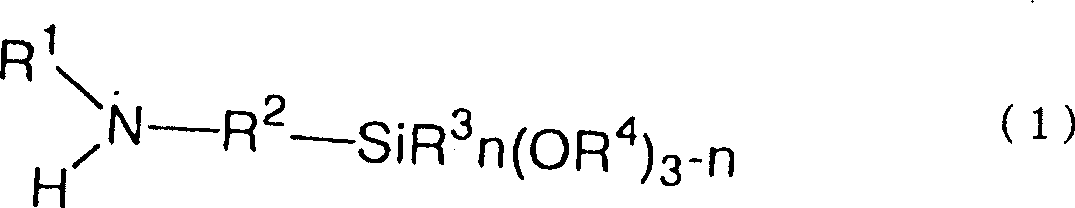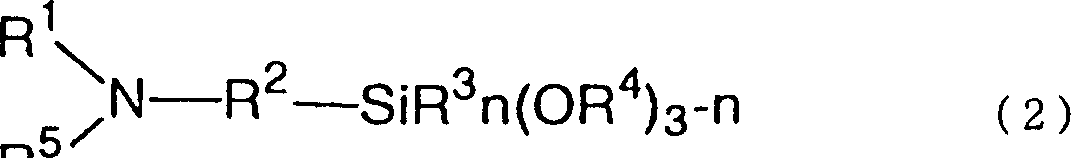Patents
Literature
46 results about "Dna immobilization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
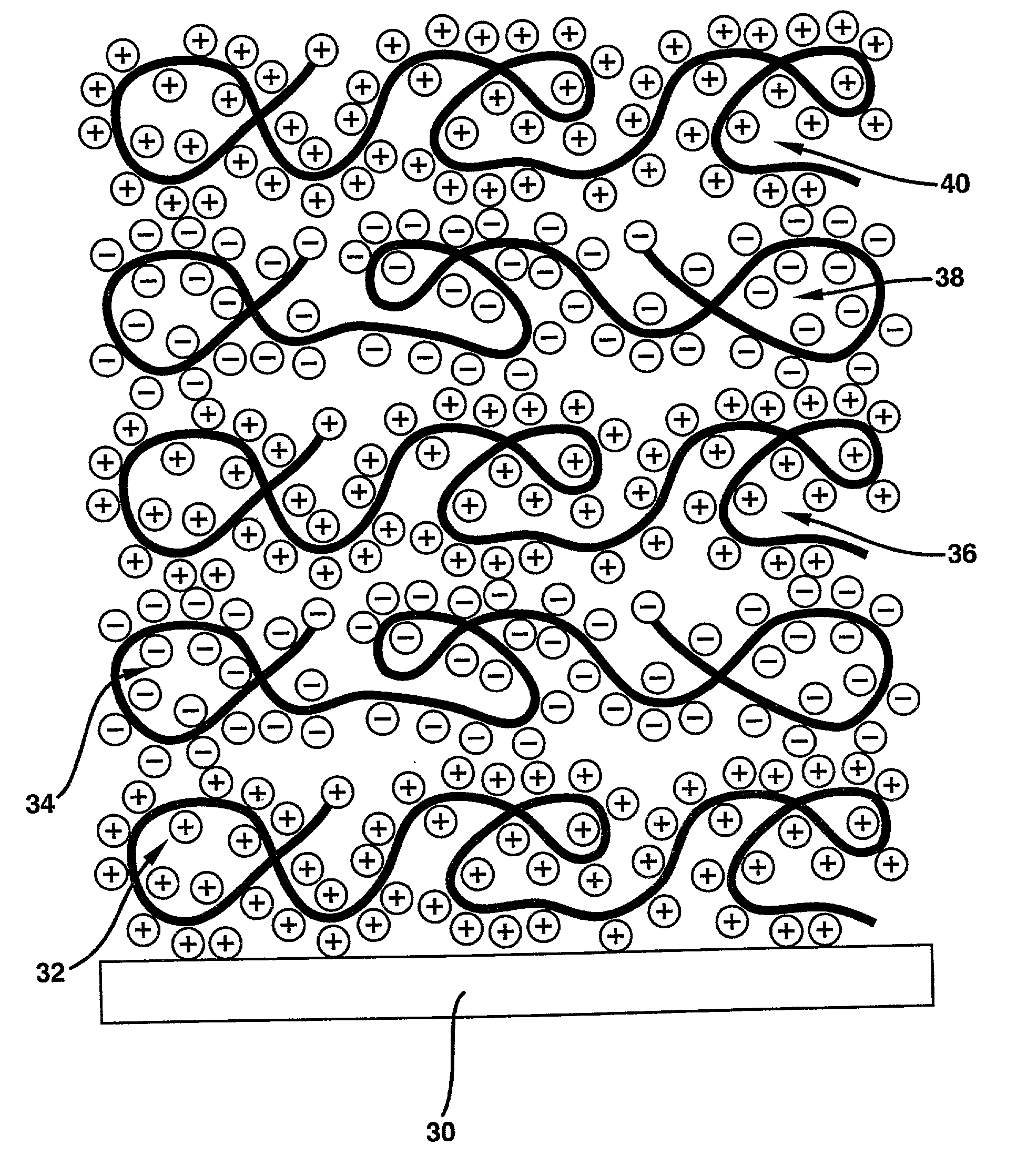
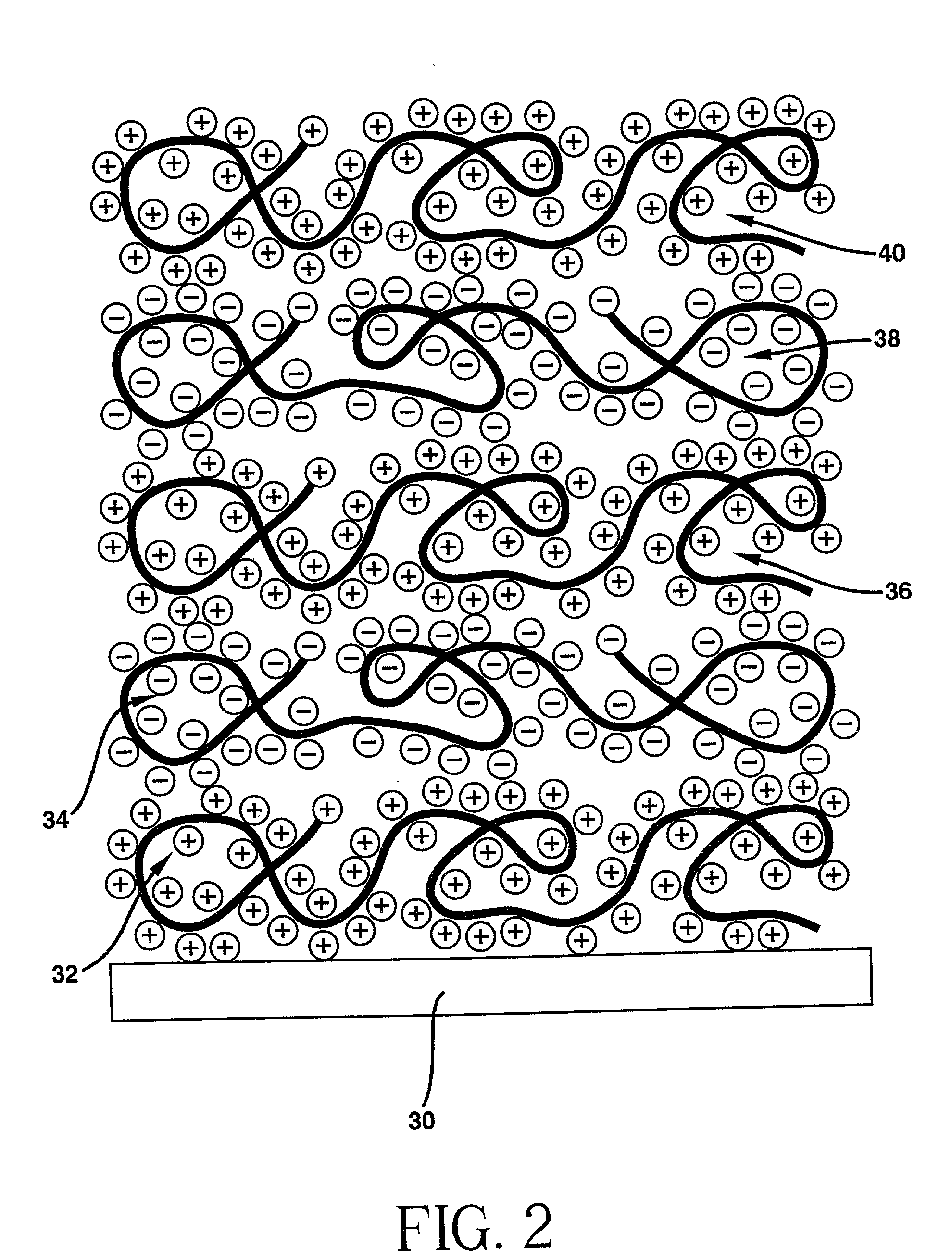
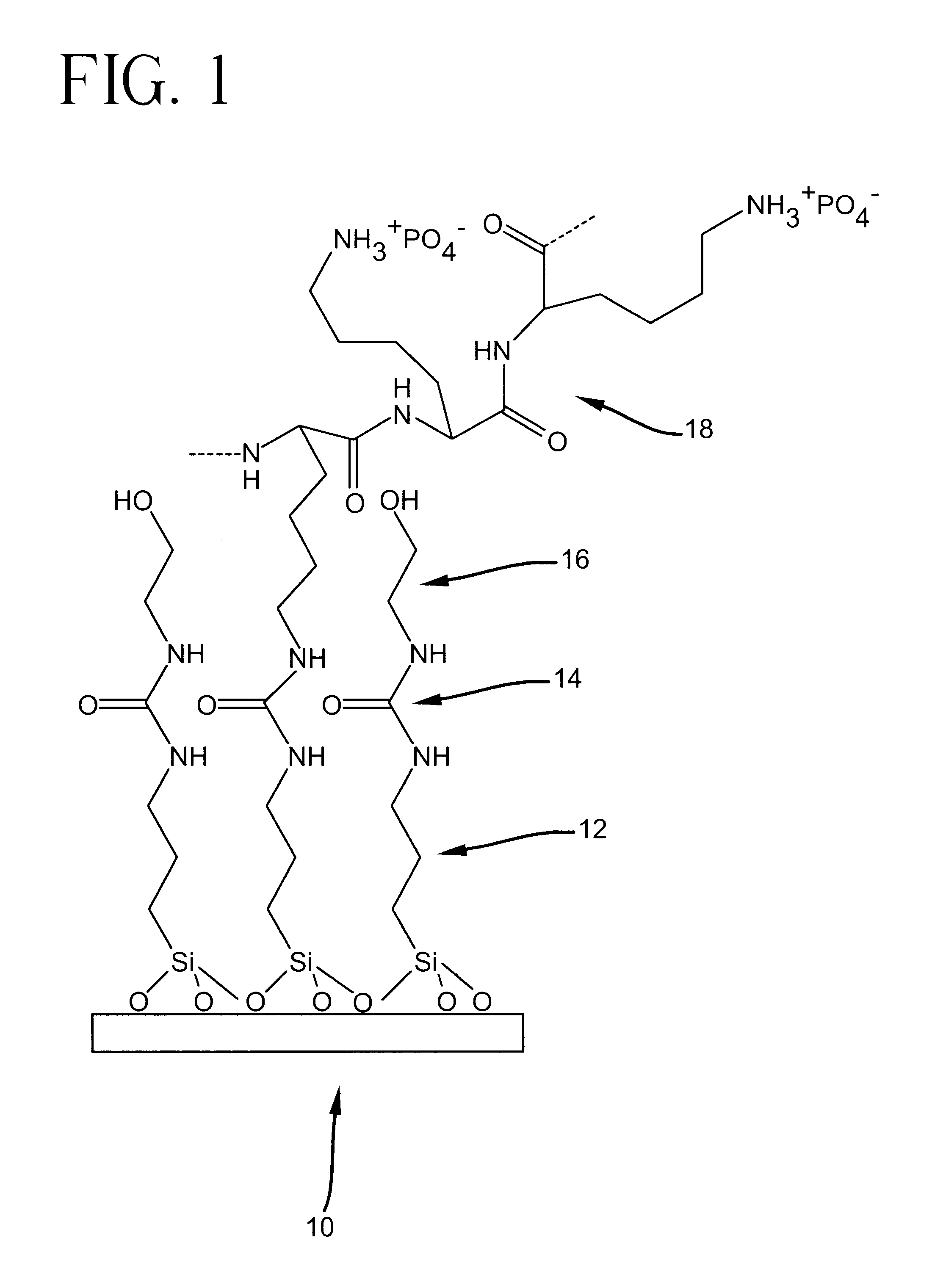
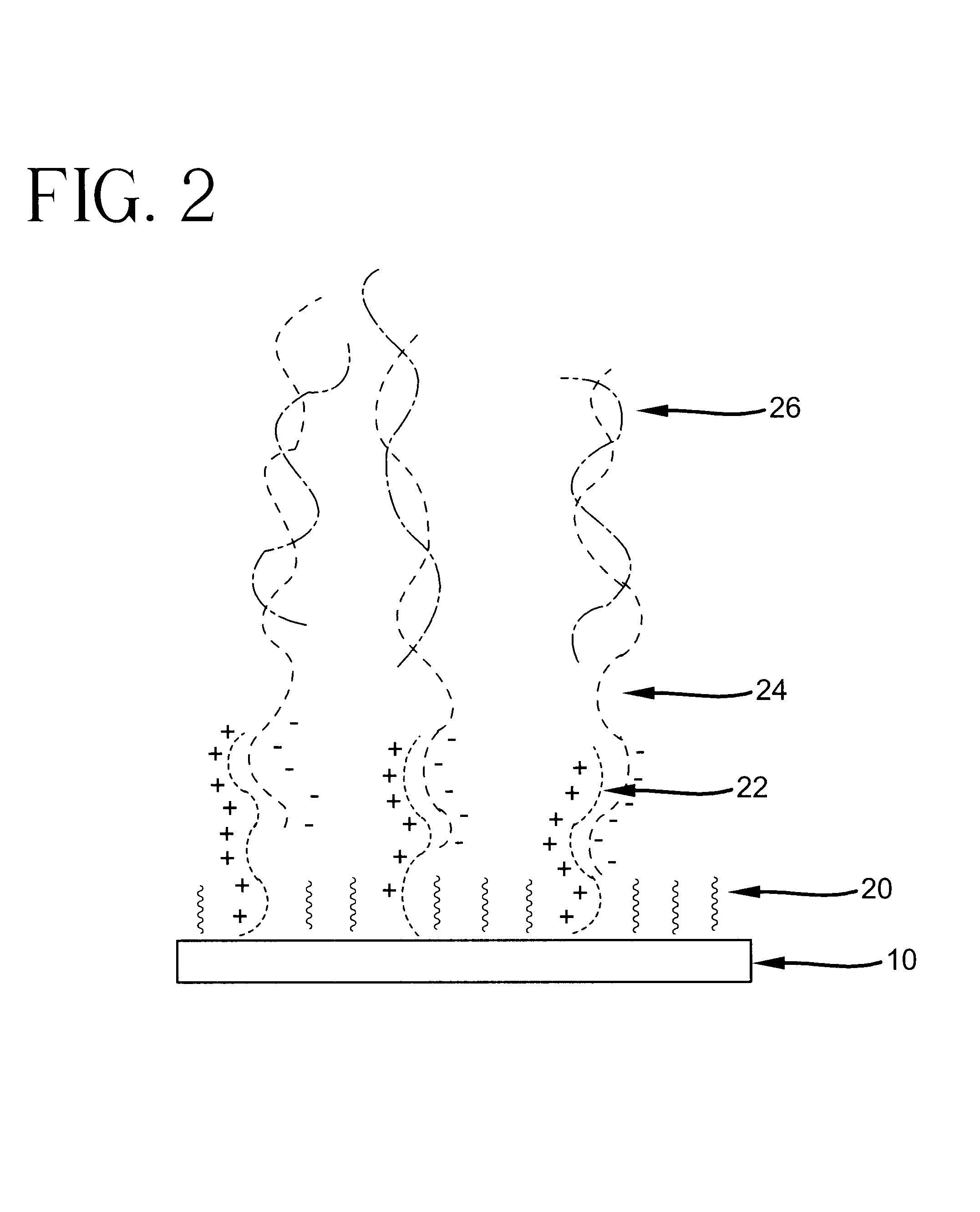
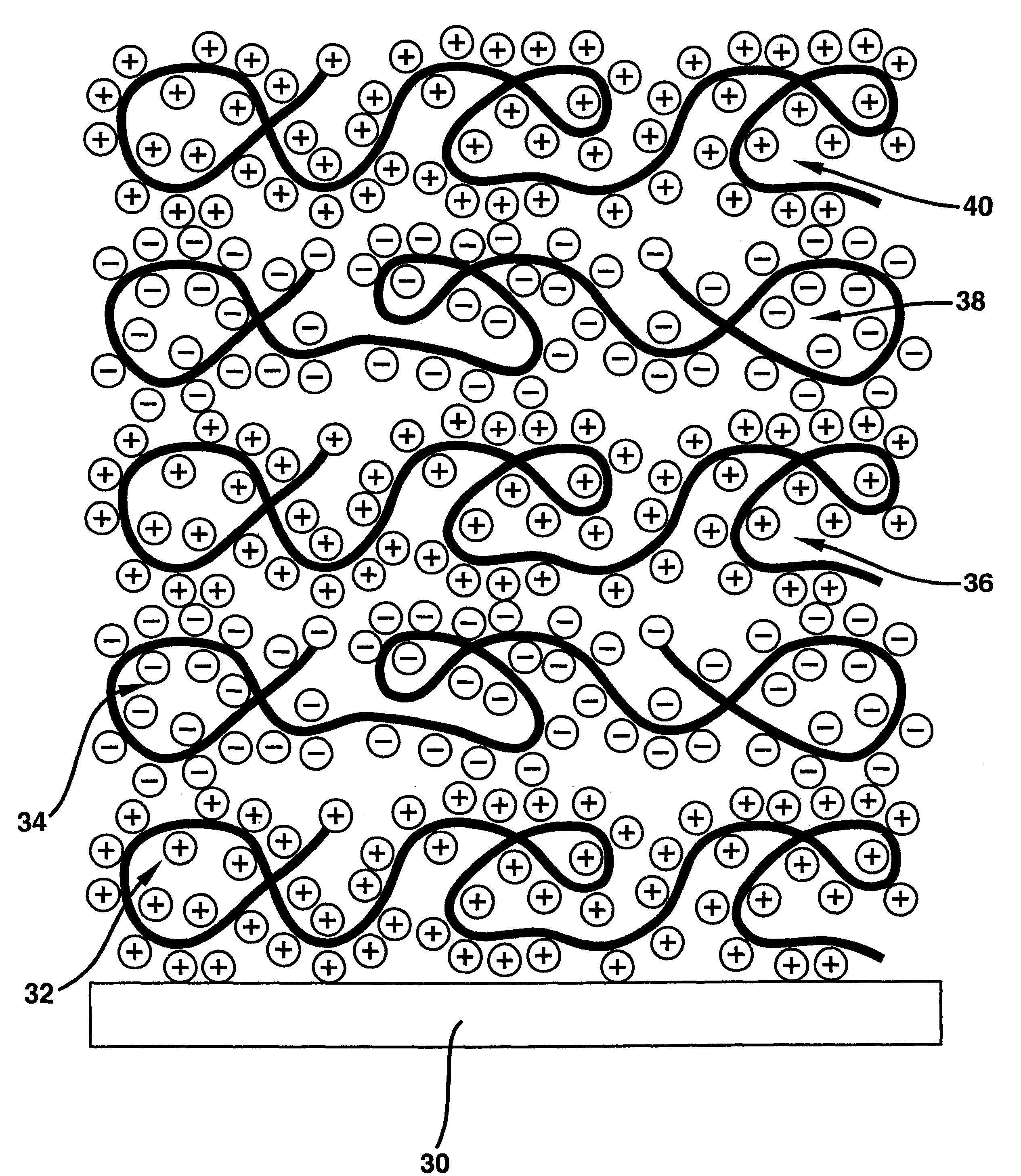
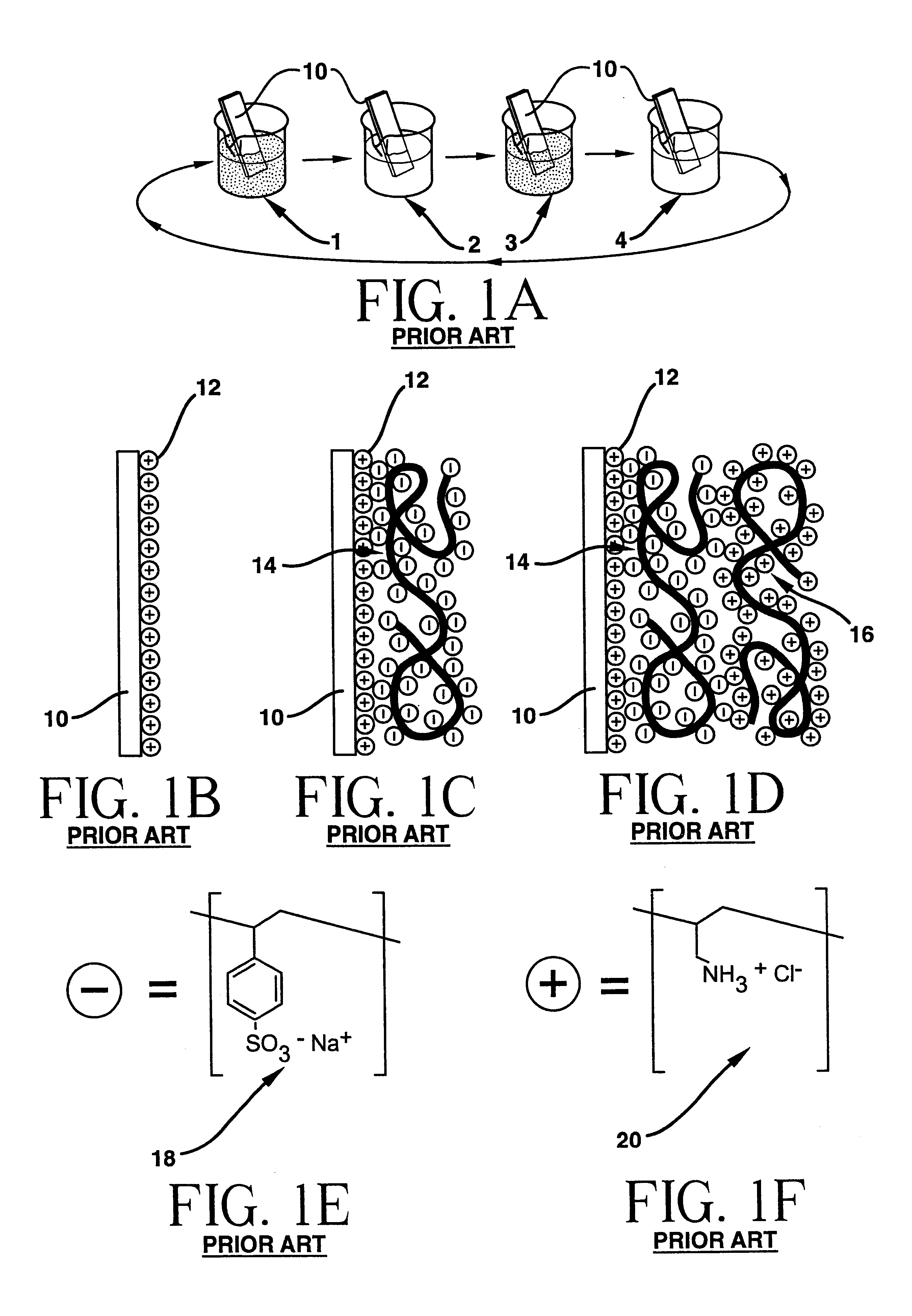
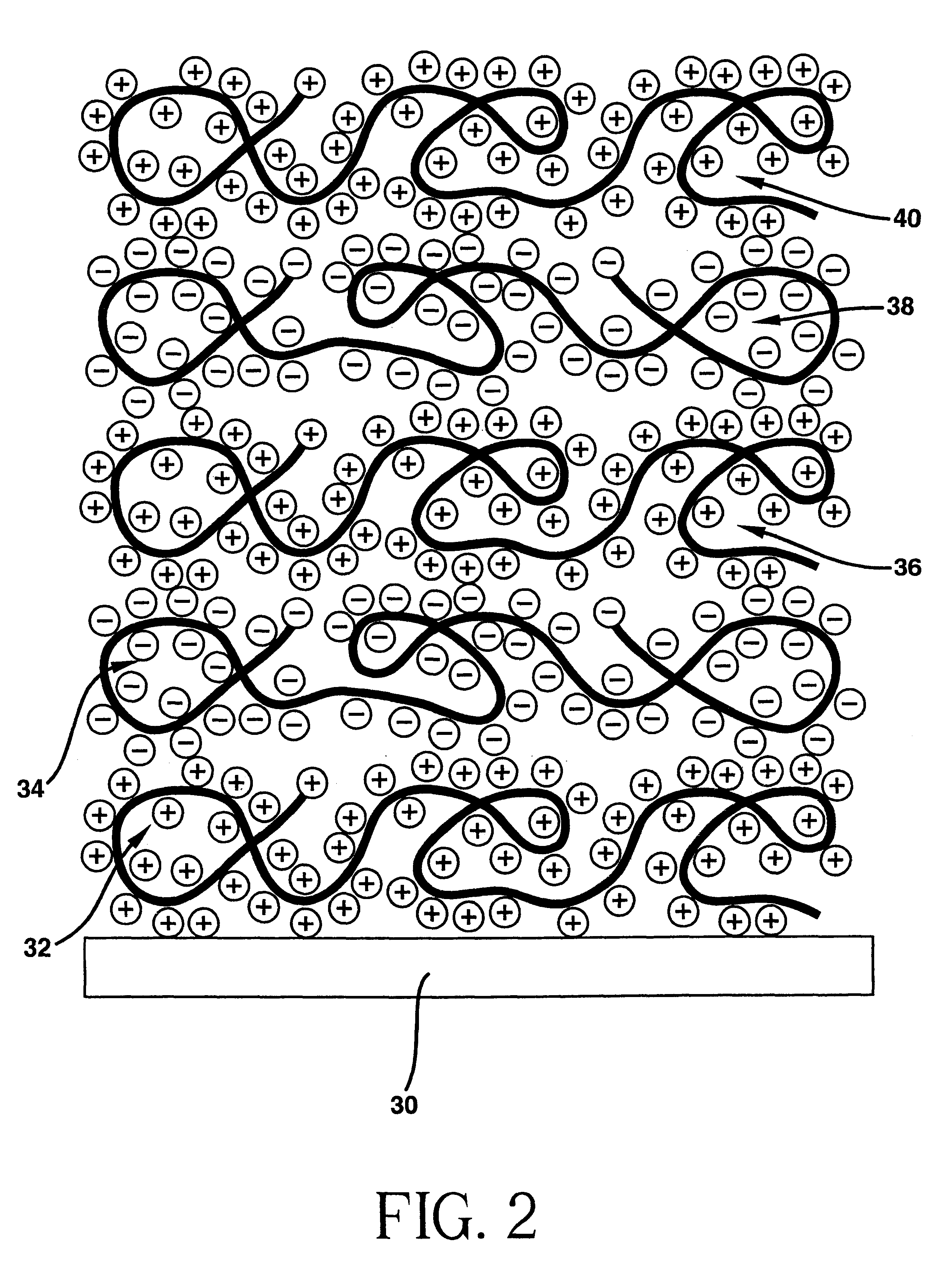
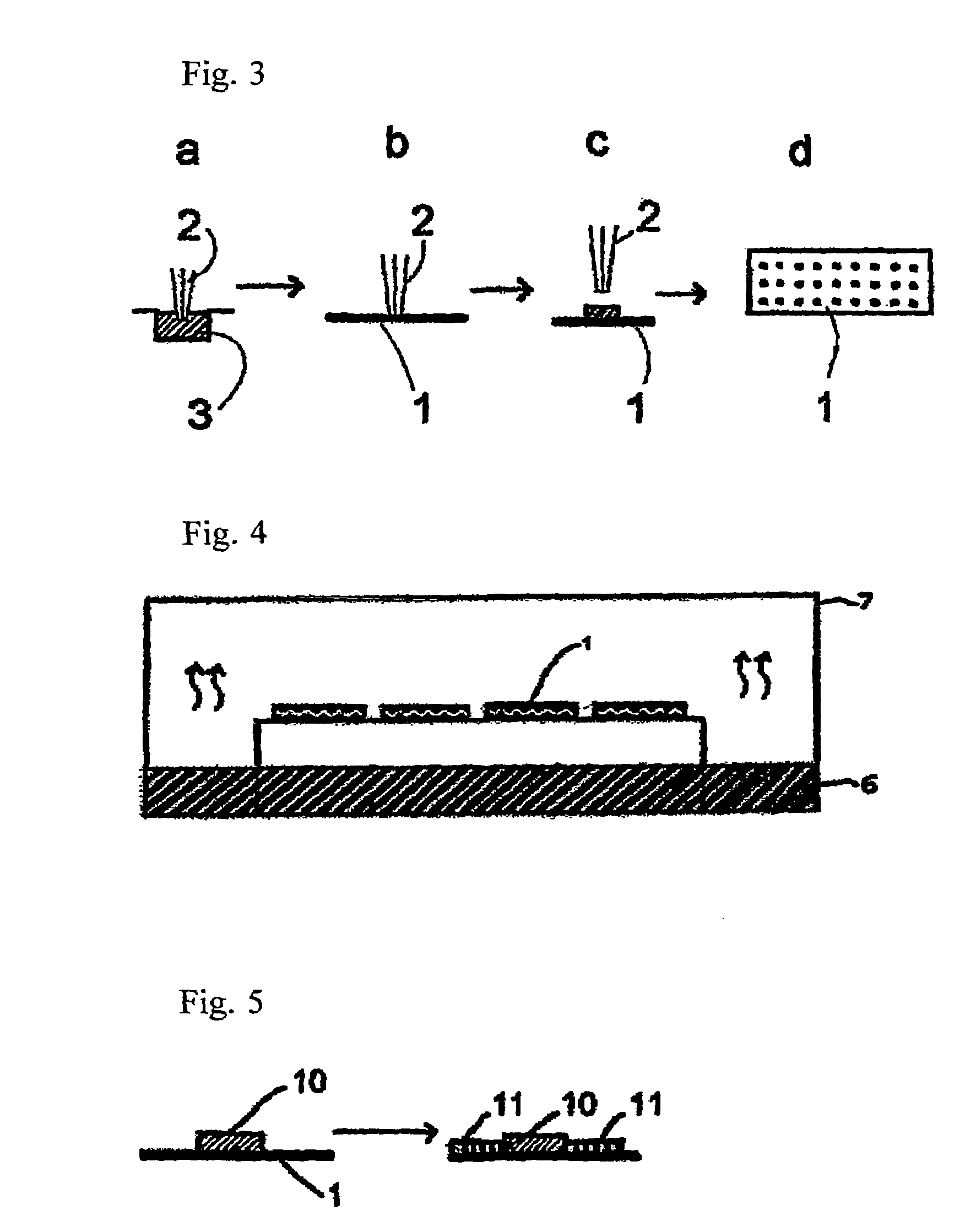
Polyanion/polycation multilayer film for DNA immobilization
Owner:CORNING INC
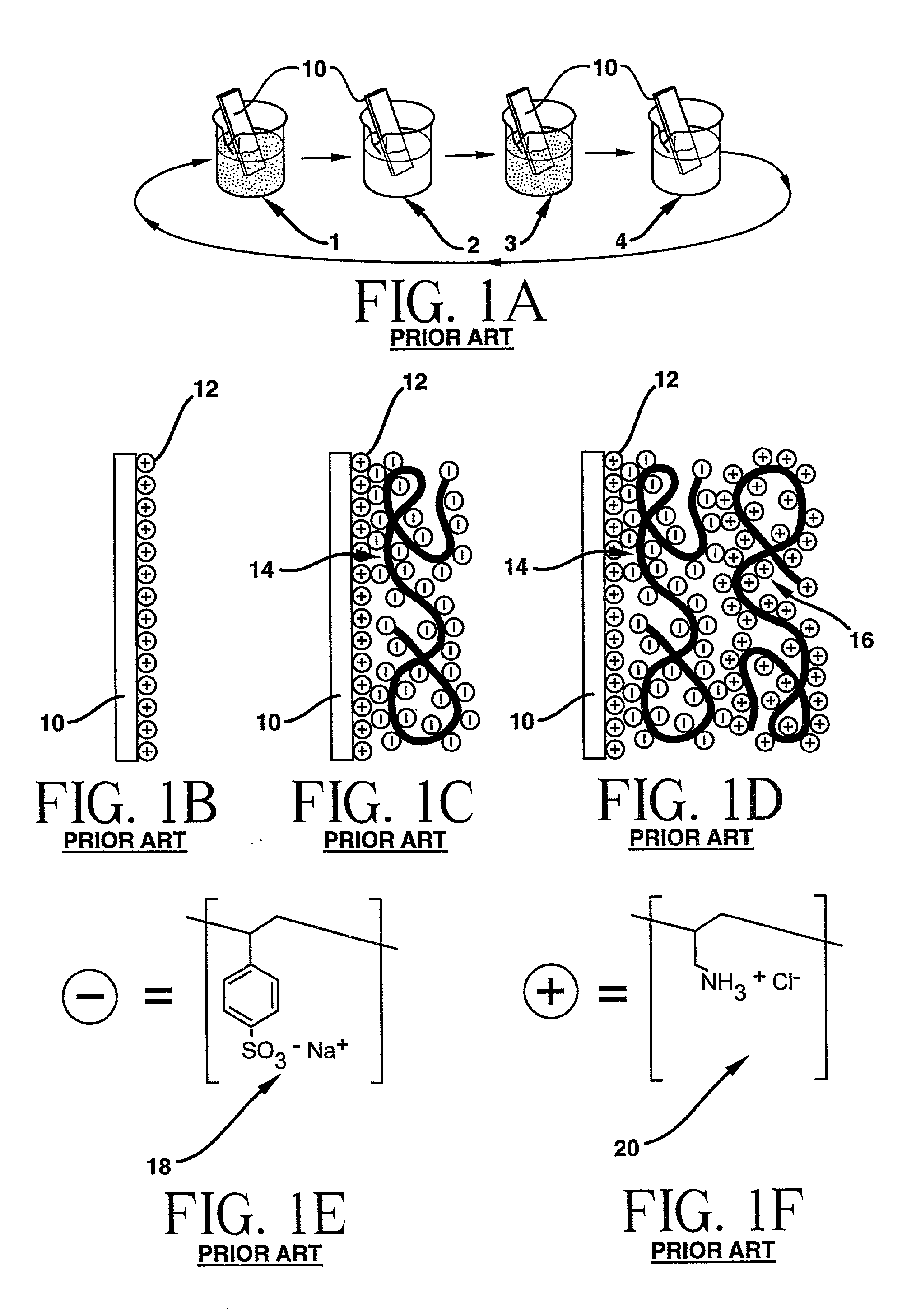
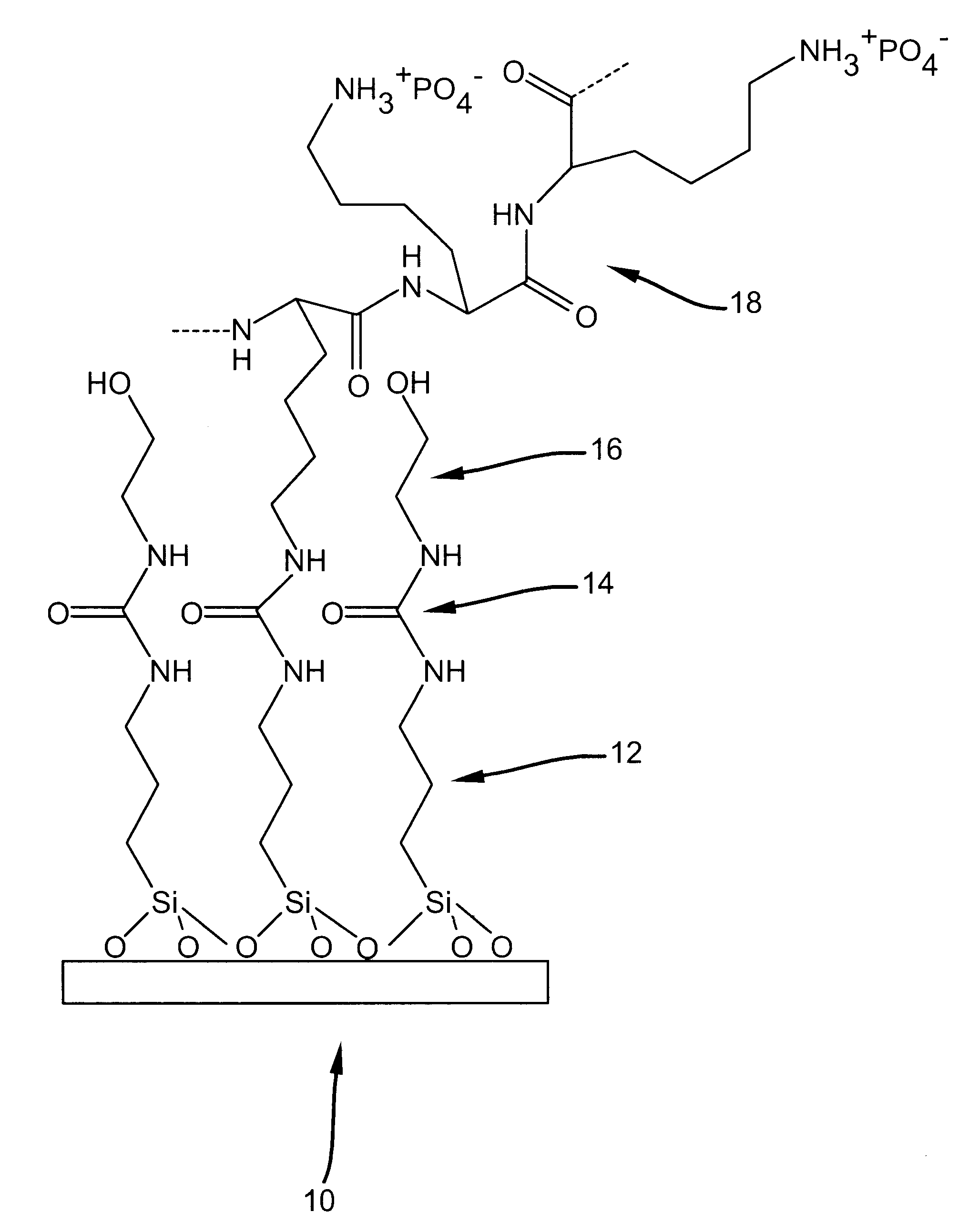
Polymer support for DNA immobilization
InactiveUS6528264B1Durable and stable attachmentRemarkable effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyEthylenediamineHigh density
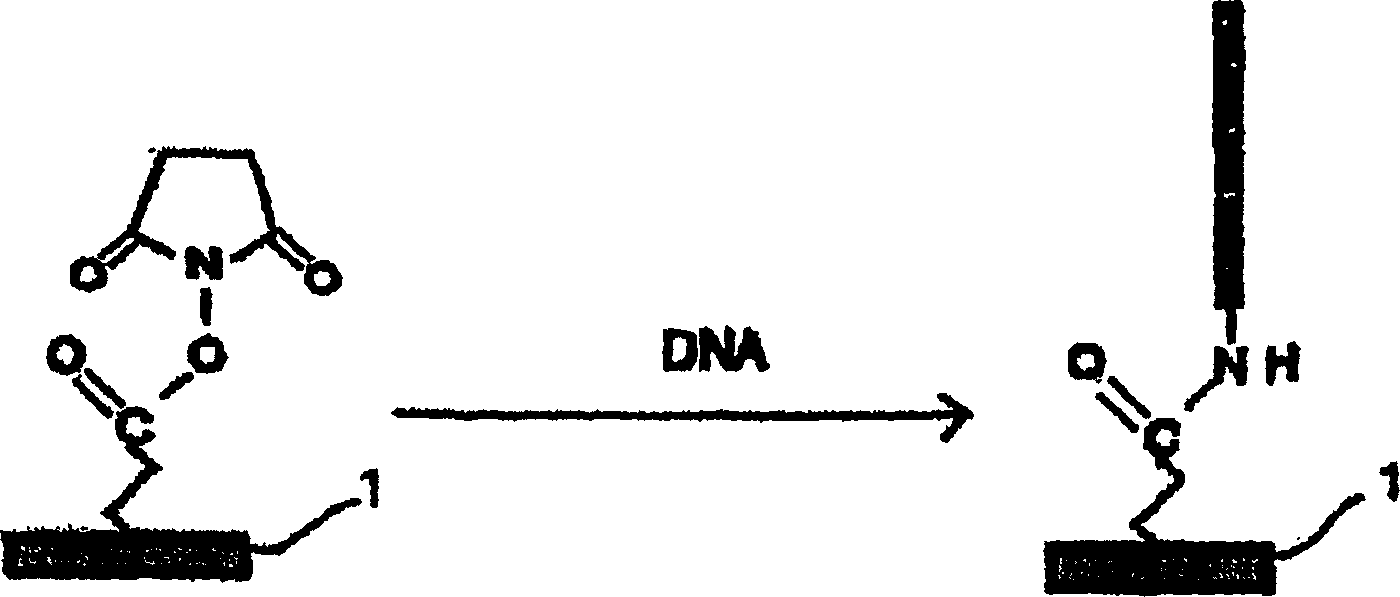
This invention relates to substrates for use in immobilizing biomolecules. More particularly, the invention relates to substrates (e.g. glass slides) having a coating of polylysine covalently attached to a silane layer coating the slide, wherein the polylysine compound has a functional NH2 group which can be coupled directly, indirectly, covalently, or non-covalently to a biomolecule (e.g., a DNA or RNA molecule). Even more particularly, the invention relates to specific prescribed addition of ethanalomine to the polylysine thereby forming a mixture which dramatically enhances the effectiveness of the polylysine for immobilizing DNA. Among other applications, the polylysine coated substrates can be used in the preparation of high density arrays for performing hybridization assays
Owner:CORNING INC
Polyanion/polycation multilayer film for DNA immobilization
Owner:CORNING INC
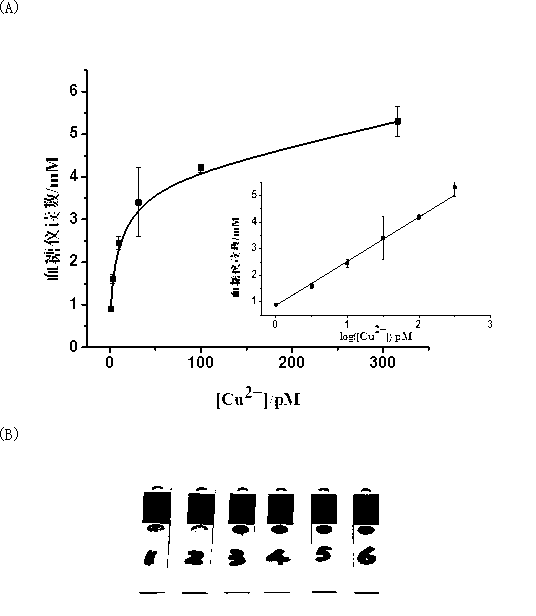
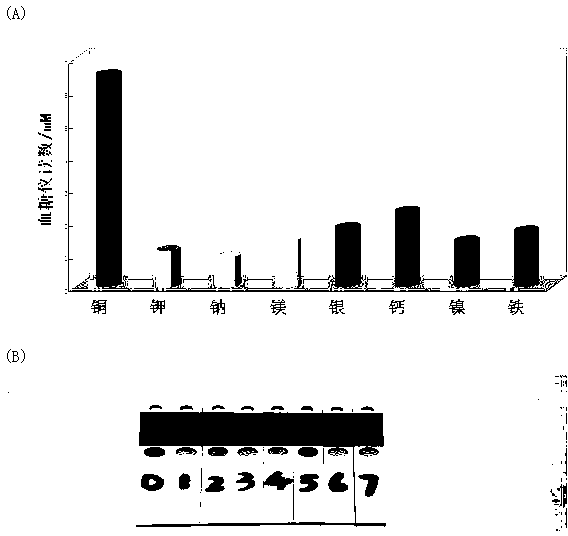
Portable copper ion concentration detection method based on click chemistry
ActiveCN103163130AGood linear responseEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDNA/RNA fragmentationMagnetic beadSodium ascorbate
The invention provides a portable copper ion concentration detection method based on click chemistry and belongs to the field of analytical chemistry. Under the condition that sodium ascorbate reduces cupric into cuprous as a catalyst, a 1,3-dipole cycloaddition reaction is carried out between NDA modified with an azide group and DNA modified with an alkynyl group, so that DNA modified with cane sugar invertase is fixed on magnetic beads; The magnetic beads are separated from a solution, the cleaned magnetic beads are dissolved into a cane sugar solution to carry out enzymatic hydrolysis, and then a reaction solution after enzymatic hydrolysis is measured by adopting a blood glucose meter, so that copper ion concentration can be detected. The portable copper ion concentration detection method provided by the invention takes the blood glucose meter as a platform and can portably and quickly detect the copper ion concentration on site; and the portable copper ion concentration detection method can be applied to copper ion detection in a human body serum sample, and the portable copper ion concentration detection method has the advantages of easy operation, low cost, high sensitivity and good specificity.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
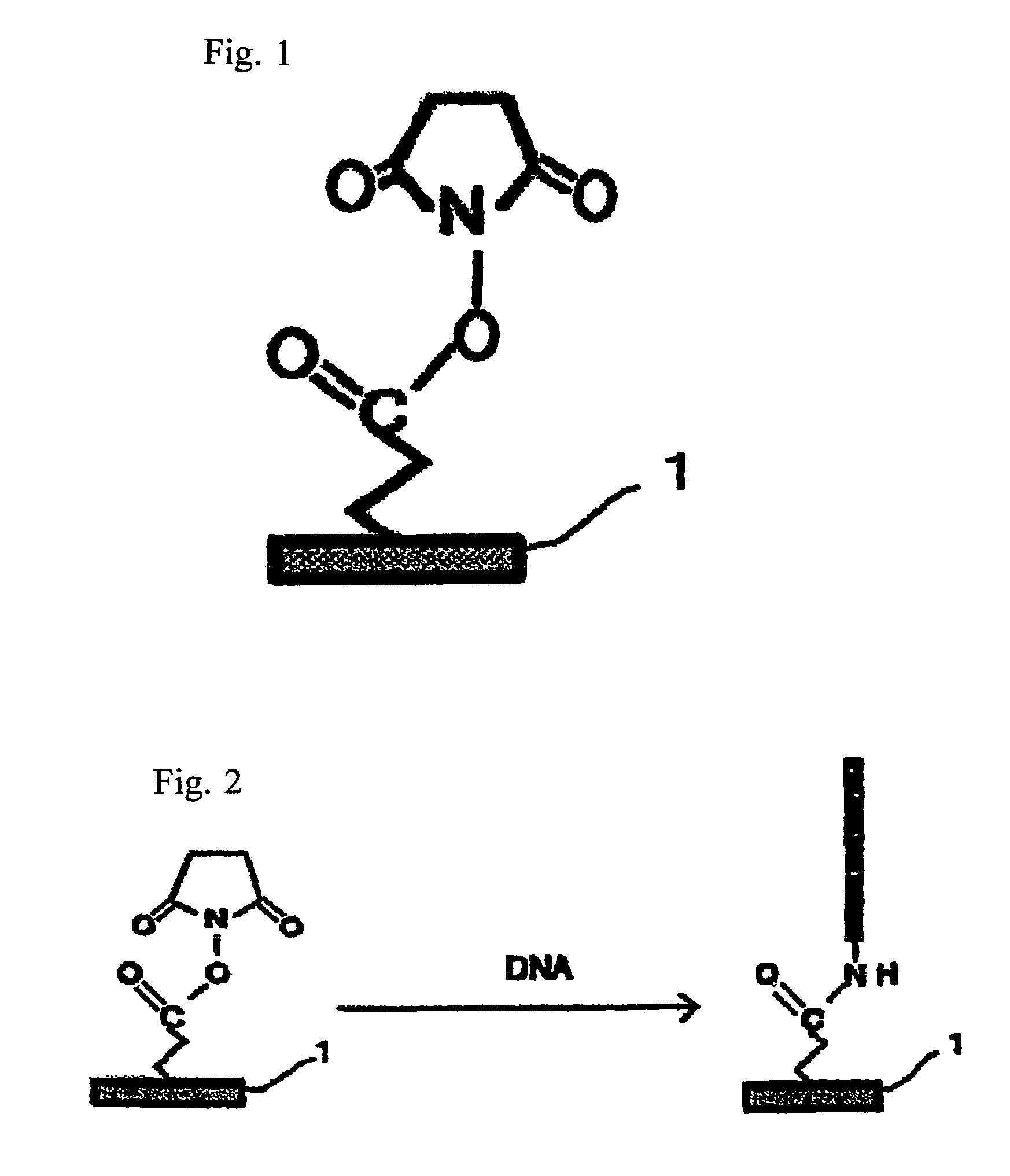
Substrate activation kit and method for detecting DNA and the like using the same
InactiveUS7078172B1Accurate detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh densityFluorescence
It is intended to provide a method whereby DNA can be conveniently and rigidly immobilized on a substrate at such a high density as achieved by the conventional methods and a method of accurately detecting DNA. A substrate activation kit comprising a phosphate buffer (pH6), a solution A (an aqueous solution) of N-hydroxysuccinimide and a solution B (a dioxide solution) of 1-[3-(dimethylamino) propyl]3-ethylcarbodiimide; and a method of detecting DNA characterized by comprising spotting DNA on a substrate having been activated by using the above activation kit and then hybridizing the spotted DNA with fluorescence labeled DNA.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
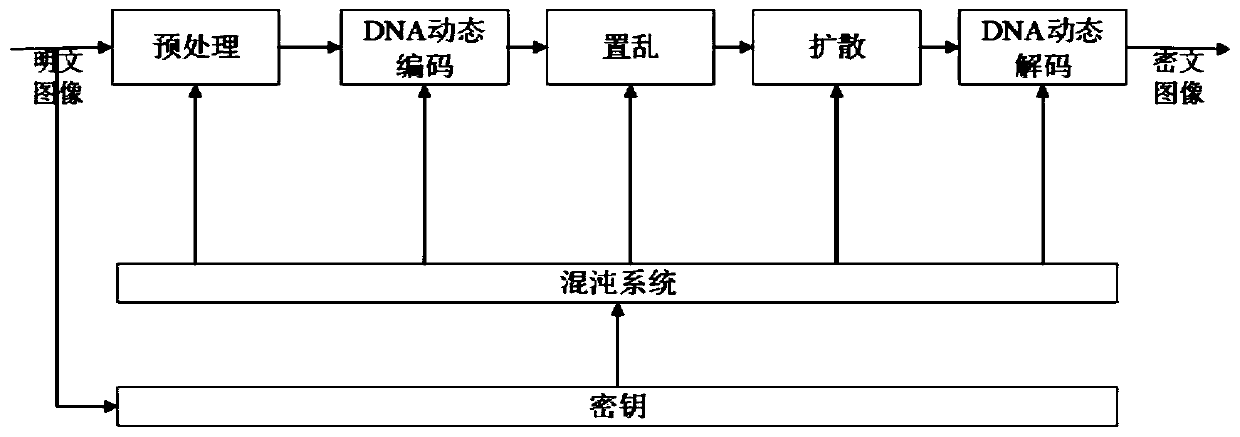
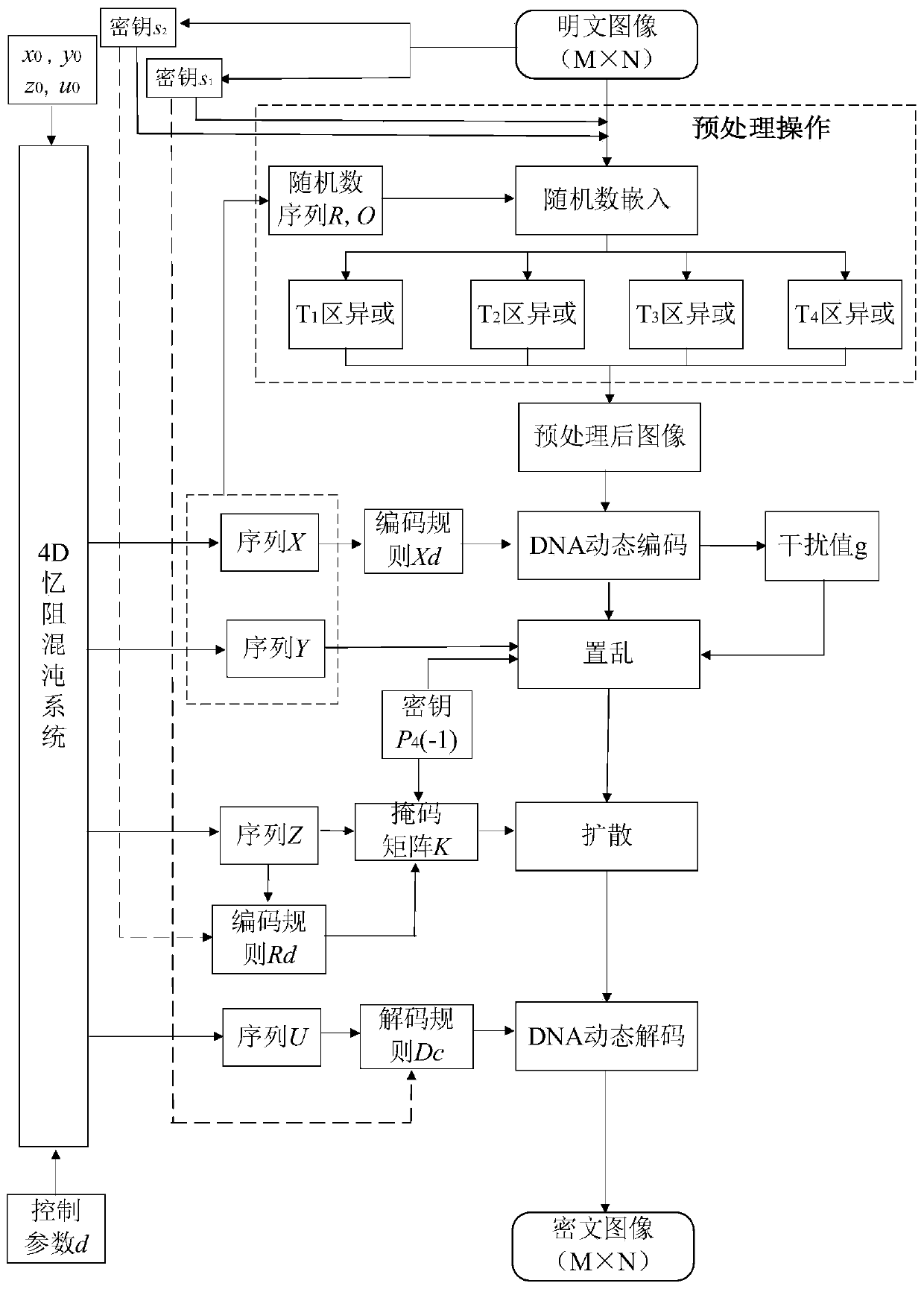
Image encryption method based on random number embedding and DNA dynamic coding
The invention provides an image encryption method based on random number embedding and DNA dynamic coding, and the method comprises the steps: firstly embedding a random number into a plaintext image,and carrying out the preprocessing operation; then, performing DNA dynamic coding on the preprocessed image, then, generating a scrambled position sequence by utilizing a chaotic sequence to completescrambling operation on a sequence after plaintext image DNA coding, and introducing plaintext-related DNA fixed feature information in a scrambling process to disturb generation of a scrambling sequence; and then performing exclusive OR operation on the scrambled DNA sequence of the plaintext image and the mask sequence generated by the chaotic system to complete diffusion; finally, carrying outDNA dynamic decoding on the diffusion DNA sequence to obtain a ciphertext image. According to the method, the problem that some image encryption algorithms are invalid for scrambling of special images (all-black and all-white images) is solved, meanwhile, the design of DNA coding rules is related to the pixel sum of plaintext images, and the sensitivity of the encryption algorithms to plaintext information is improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Method of reusing DNA-immobilization substrate
InactiveUS7078517B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsA-DNADna immobilization
It is intended to provide a method of reusing a DNA-immobilization substrate whereby the expensive DNA-immobilization substrate can be efficiently utilized and a reusable DNA-immobilization substrate having the same performance as a new product without any trouble in practical use can be provided. Namely, a method of reusing a DNA-immobilization substrate characterized in that, to remove DNA from a DNA-immobilization substrate carrying the DNA immobilized by an acid-amide bond via an oligonucleotide to thereby enable the immobilization of a fresh DNA, the acid-amide bond between the substrate and the DNA is hydrolyzed with an acid or an alkali.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD +2
Photoelectric sensor and application thereof, and preparation method of working electrode
ActiveCN105353006AHigh sensitivityAchieve ultra-sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesOrganic dyeCost (economic)
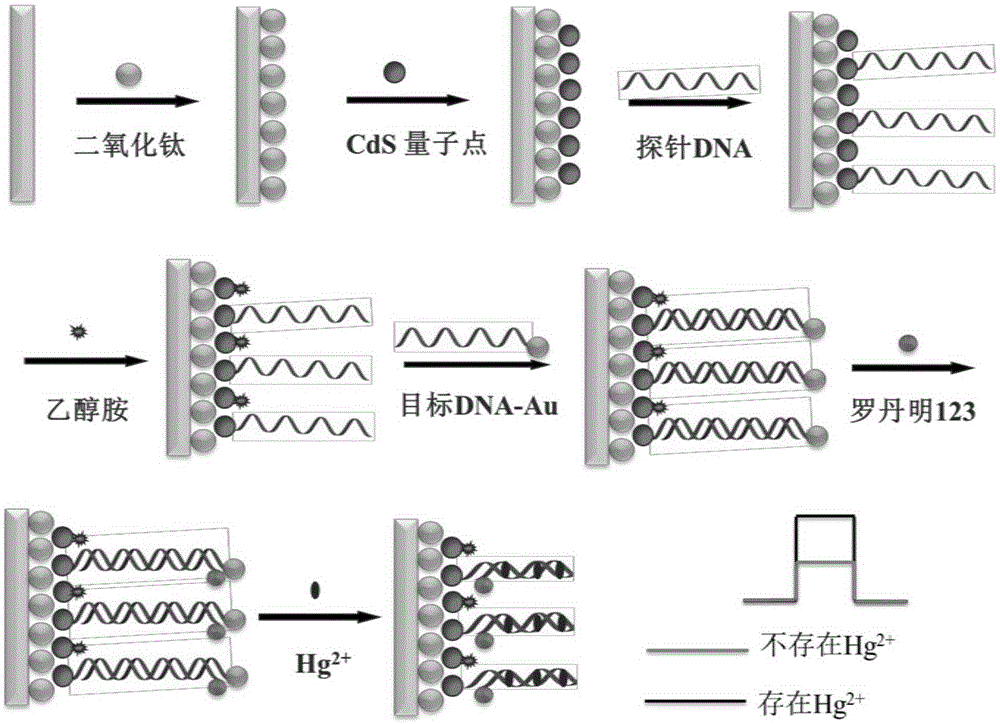
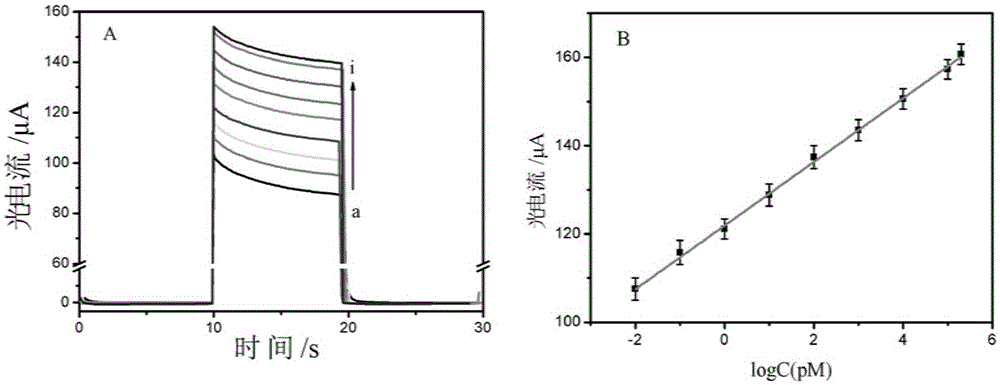
The invention discloses a preparation method of a working electrode of a photoelectric sensor. The preparation method includes the following steps: cleaning an ITO electrode, and then drying to obtain an electrode A; dropwise adding a titanium dioxide colloidal solution on the surface of the electrode A, drying, then calcining, and cooling to obtain an electrode B; placing the electrode B in a poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) aqueous solution, soaking, cleaning, next placing in a carboxylated quantum dot colloidal solution, soaking, and cleaning to obtain an electrode C; fixing a probe DNA on the electrode C to obtain an electrode D; dropwise adding a gold nanoparticle-labelled target DNA onto the electrode D, and making the gold nanoparticle-labelled target DNA hybridized with the probe DNA, to obtain an electrode E; and activating the electrode E, fixing an organic dye sensitizing agent on the surface of the electrode E, and cleaning to obtain the working electrode of the photoelectric sensor. The invention also discloses the photoelectric sensor. The photoelectric sensor has the characteristics of high sensitivity, good specificity, simple and convenient detection method, and economic cost.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Magnetic-bead-process-based kit for extracting free DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) and application method thereof
InactiveCN105695450AEfficient enrichmentGuaranteed not to degradeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSerum samplesMagnetic bead
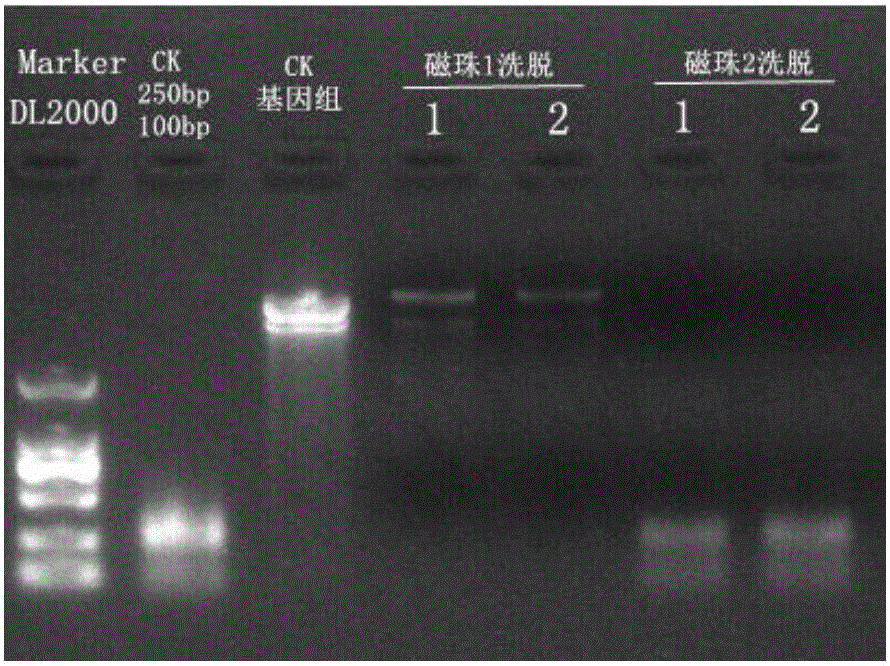
The invention relates to a magnetic-bead-process-based kit for extracting free DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) and an application method thereof. The kit comprises a DNA fixation combination solution, a first magnetic bead suspension, a cleaning solution, a genome DNA removal solution, a second magnetic bead suspension and an elution solution which are respectively packaged independently. The kit can be used for directly extracting free DNAs from the whole blood sample. The object for extracting and purifying free DNAs is widened from the serum or plasma to the whole blood sample, and the free DNA extraction step is extended forward to the blood preliminary treatment, thereby greatly reducing the original steps for extracting free DNAs from blood. Besides, the kit can also be used for extracting and purifying free DNAs from a plasma or serum sample. The kit can be used for removing genome DNA interference. The kit can be used for removing trace genome DNAs mixed in the whole blood, plasma or serum, thereby lowering the subsequent testing interference. Different reagents in the kit are compounded, so that the free DNA extraction efficiency and purity are maximally ensured.
Owner:SUZHOU ENRICHING BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for detecting potassium ion by preparing biosensor based on G-quadruplex and gold nanoparticle
InactiveCN102866185AHigh sensitivityGood linear relationshipMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorA-DNA
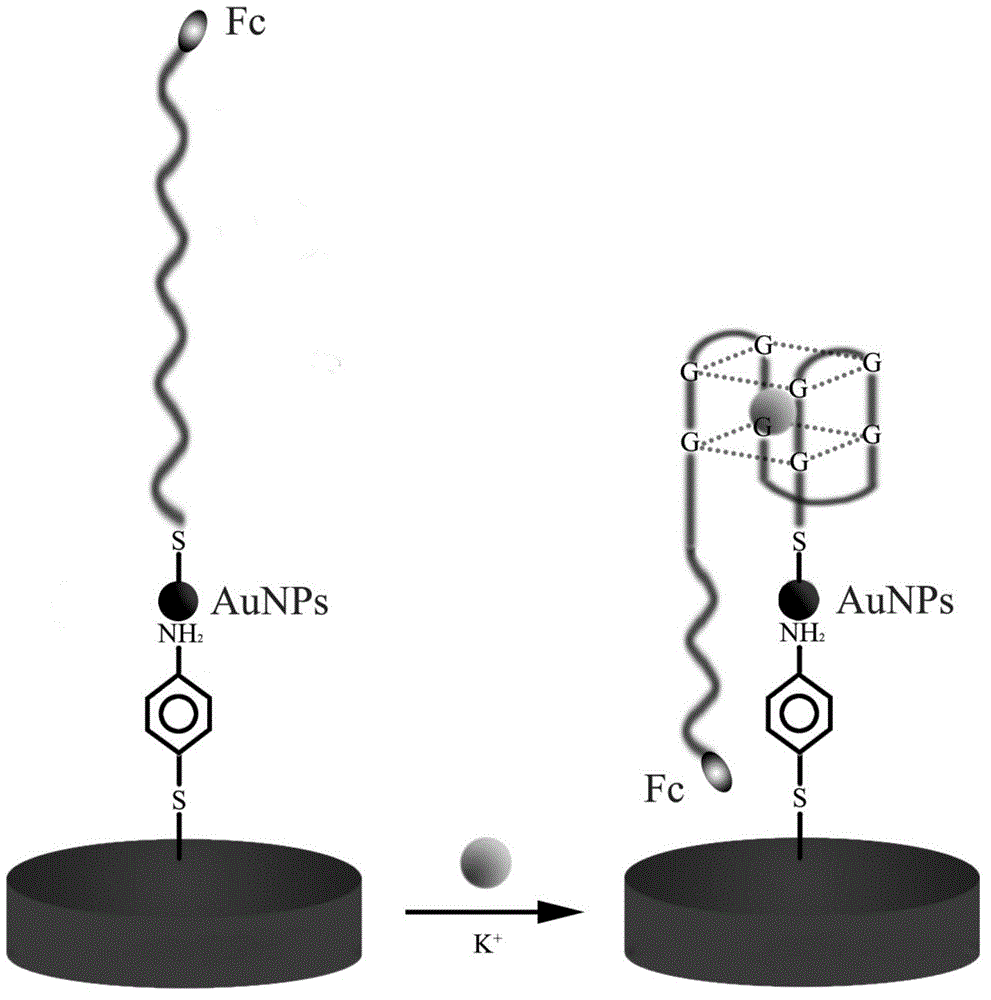
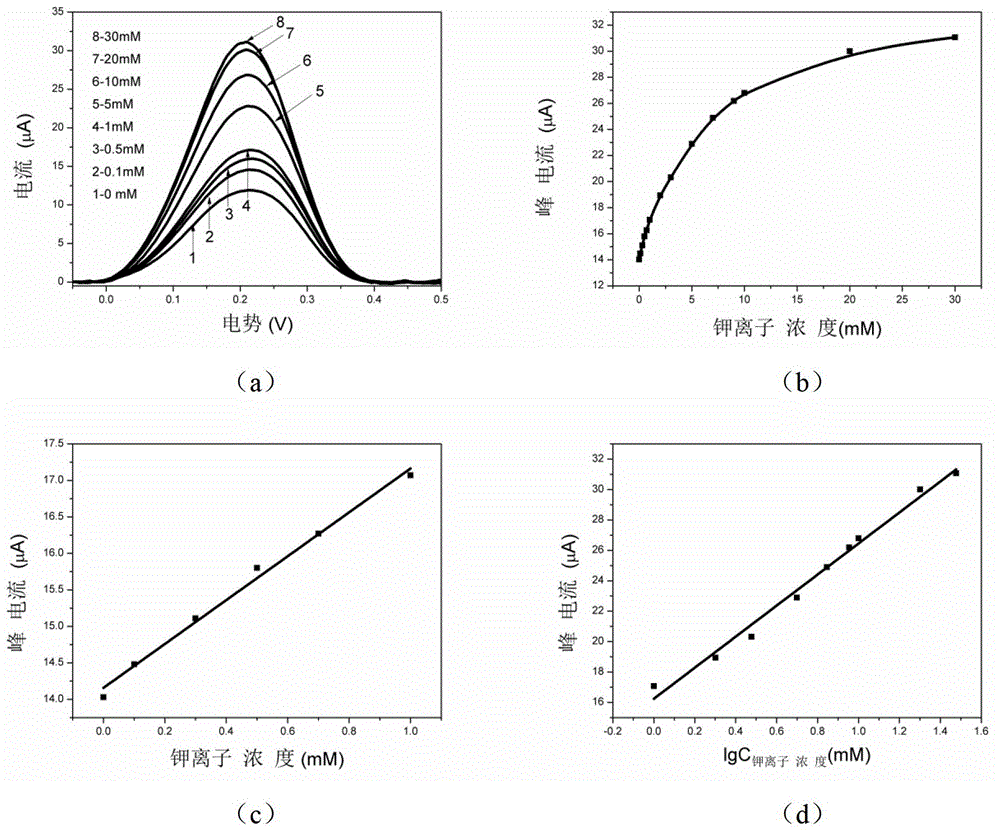
The invention discloses a method for detecting a potassium ion by preparing a biosensor based on a G-quadruplex and a gold nanoparticle, and belongs to the field of the biosensor. A detection method comprises the following steps of: modifying the gold nanoparticle on the surface of a gold electrode by taking para-aminothiophenol (p-ATP) as a medium, fixing a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) marked by ferrocene (Fc) and capable of forming a G-quadruplex structure onto the surface of the gold nanoparticle by a sulfydryl self-assembly action, and taking the DNA as an aptamer to prepare an electrochemistry biosensor to detect the potassium ion. The method for detecting the potassium ion by preparing the biosensor based on the G-quadruplex and the gold nanoparticle has the advantages that the detection is simple and quick, the sensitivity is high, the real-time detection can be carried out on the potassium ion, the minimum detection concentration to the potassium ion reaches 0.1 mM, and the linear range of the detection is large. In a concentration range of 0.1-1 mM, a square wave volt-ampere peak current is in a well linear relation with the concentration of the potassium ion; and in a concentration range of 1-30 mM, the square wave volt-ampere peak current is in a well linear relation with the logarithm of the concentration of the potassium ion.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere and preparation and application of DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere and nucleic acid aptamer compound
ActiveCN109745567AHas a specific targeting functionEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumor targetAptamer
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical and biochemical medicines, particularly relates to a DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere, a preparation method of the DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere and a nucleic acid aptamer compound and an application of the DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere as a tumor targeting preparation. The preparation method is simple, only a segment of single-stranded DNA is synthesized at one end of the nucleic acid aptamer as a connecting arm when the nucleic acid aptamer is synthesized, and the sequence of the DNA connecting arm and the DNA sequence on the surface of the nano material of the nano hydrogel microsphere can be complemented and paired. One or a plurality of nucleic acid can be matched and connected on the surface of the nano materialat one time by co-incubation in aqueous solution so as to obtain the drug delivery carrier with the specific targeting function. According to the method, one or more nucleic acid aptamers can be connected on the surface of the drug delivery carrier at one time in a base complementary pairing mode; the base complementary pairing can be carried out in aqueous solution; reaction conditions are mild and easy to control; and the preparation process is very simple.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
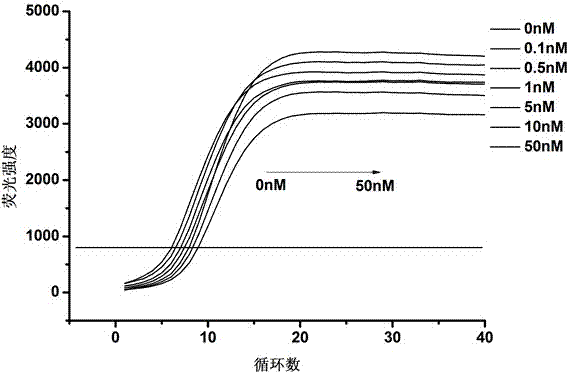
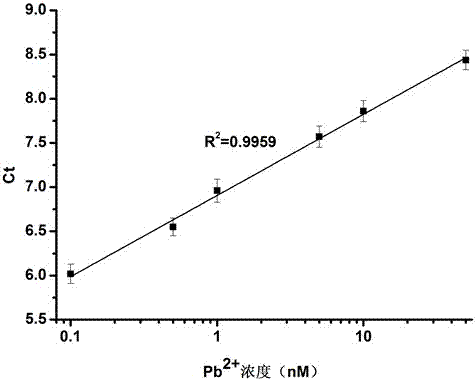
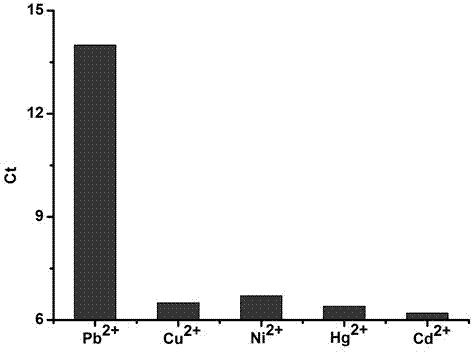
Method for detecting lead ions based on combination of fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and nuclease GR-5
InactiveCN103695540AImprove detection limitHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceBiology
The invention provides a method for detecting lead ions based on combination of fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and nuclease GR-5. The method comprises steps of (1) immobilizing nuclease GR-5 and complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) onto the inner surface of a PCR reaction vessel; (2) adding a sample to be tested into the PCR reaction vessel obtained in step (1), wherein when lead ions exist, in the presence of the nuclease GR-5, the complementary DNA breaks at the ribonucleotide so as to generate a short nucleic acid chain; (3) washing the PCR reaction vessel with citrate buffer solution so as to remove the nucleic acid molecules which are not immobilized; (4) adding an amplification primer into the PCR reaction vessel so as to carry out real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR on the immobilized complementary DNA; (5) confirming the concentration of the lead ions in the sample based on the Ct value of the real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. According to the method, a brand-new biosensor with high selectivity and high sensitivity is provided and can be used for simply and rapidly detecting the concentration of lead ions in the sample.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
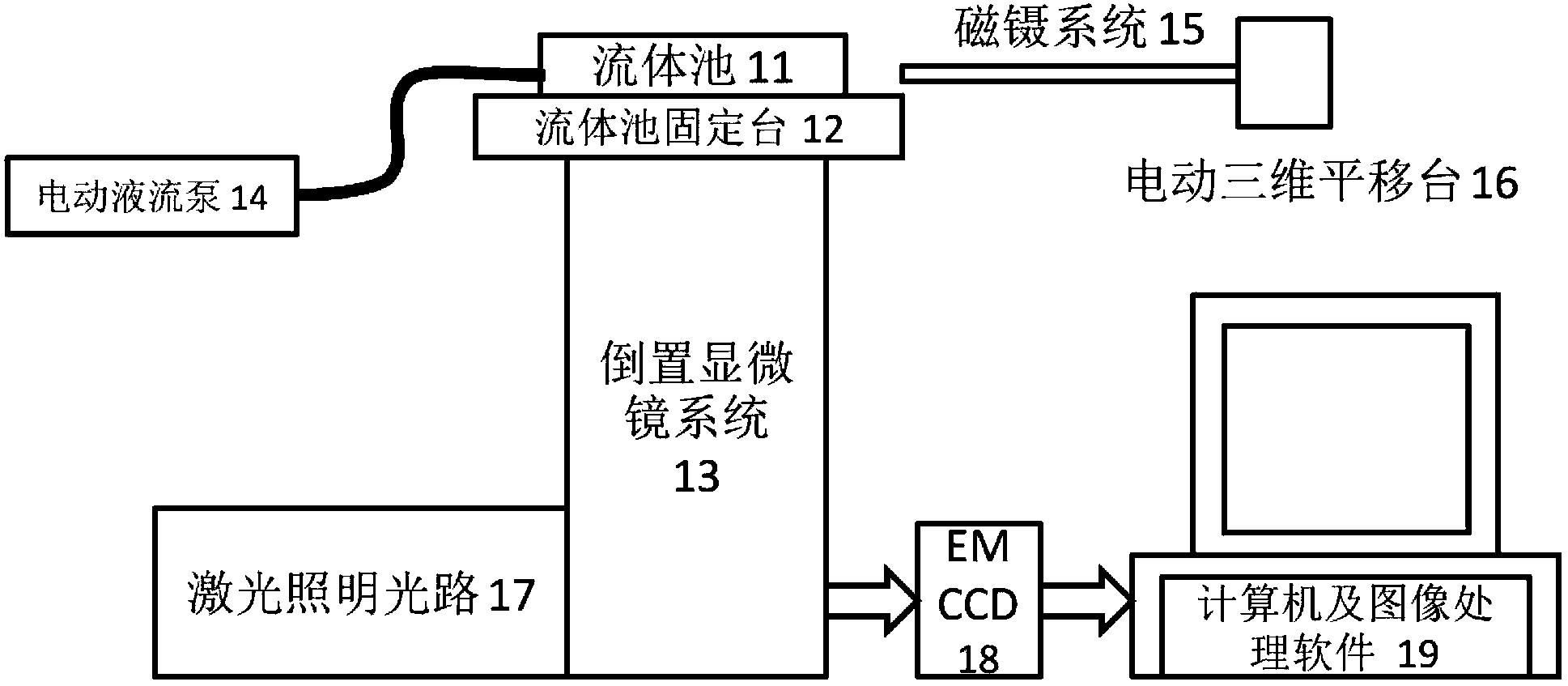
Single molecule fluorescence apparatus and application method thereof
InactiveCN103424386AAchieve Controlled StretchHigh precision observationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescence microscopeHandling system
The invention discloses a single molecule fluorescence apparatus and an application method thereof. The single molecule fluorescence apparatus comprises a lens-type full internal reference fluorescence microscope system, an image acquisition and processing system, a controllable magnetic tweezer system and a fluid pool system. The fluid pool system comprises a fluid pool fixed station, a fluid pool and an electric liquid flow pump; one side of the fluid pool fixed station is fixed on a sample stage of an inverted microscope of the full internal reference fluorescence microscope system, and the other side of the fluid pool fixed station is fixed with the fluid pool. The electric liquid flow pump and the fluid pool are connected; and the bottom of the fluid pool is equipped with more than one column of DNA fixed points. Columns of DNA fixed points are arranged in the fluid pool, so controllable fixing of a large amount of DNA can be realized. Through the transverse magnetic tweezer system, controllable drawing on a large amount of DNA molecules can be realized; and high precision observation on protein fluorescence signals can be realized without dyeing on DNA molecules.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cell DNA staining kit and its prepn process
InactiveCN101046434AEasy to manufactureEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationBiological cellHuman medicine
The present invention is cell DNA staining kit for use in life science and medicine, especially the sole staining of cell nucleus, and its preparation process. The kit includes DNA staining solution, DNA fixing solution and DNA rinsing liquid in the volume ratio of 1.05 to 2 to 1. It is prepared through the following steps: preparing DNA staining solution, preparing DNA fixing solution, preparing DNA rinsing liquid, preparing cell preserving solution, and setting slide glass, the DNA staining solution, the DNA fixing solution, the DNA rinsing liquid and the cell preserving solution into a box to constitute the cell DNA staining kit. The present invention facilitates cell DNA staining and raises the accuracy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Substrates for immobilizing and amplifying DNA and DNA-immobilized chips
InactiveUS7022473B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAmplification dnaPcr method
Substrates for producing a DNA library are produced by immobilizing DNA onto a suitable substrate having excellent thermal conductivity. A surface of the substrate is chemically modified with a radical having a terminal polar radical. DNA can be amplified by the PCR method in a short period of time using substrates of the present invention onto which DNA is immobilized.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
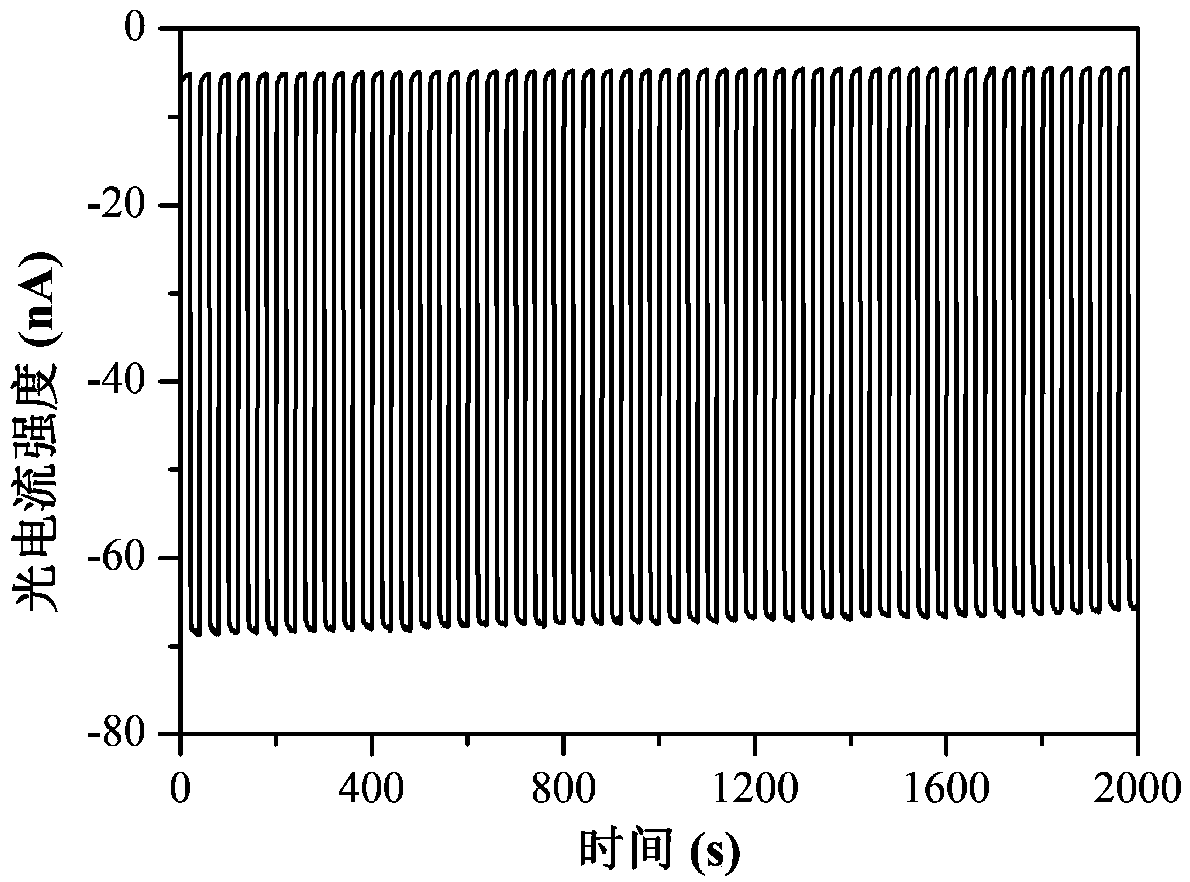
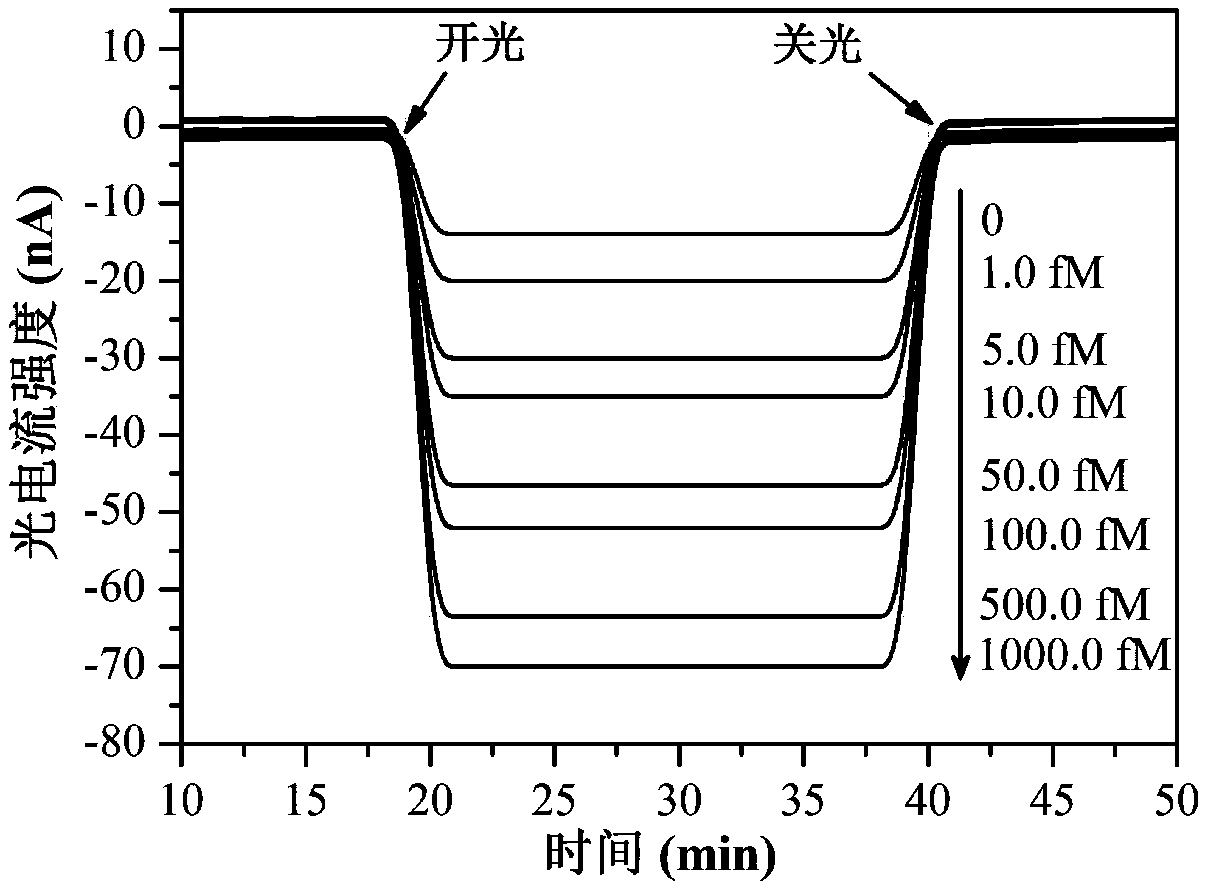
Preparation method and application of photoelectrochemical biosensor based on iridium complex
ActiveCN107589162AHighly Specific Analytical DetectionHighly sensitive and specific analytical detectionGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIridiumPhotocurrent
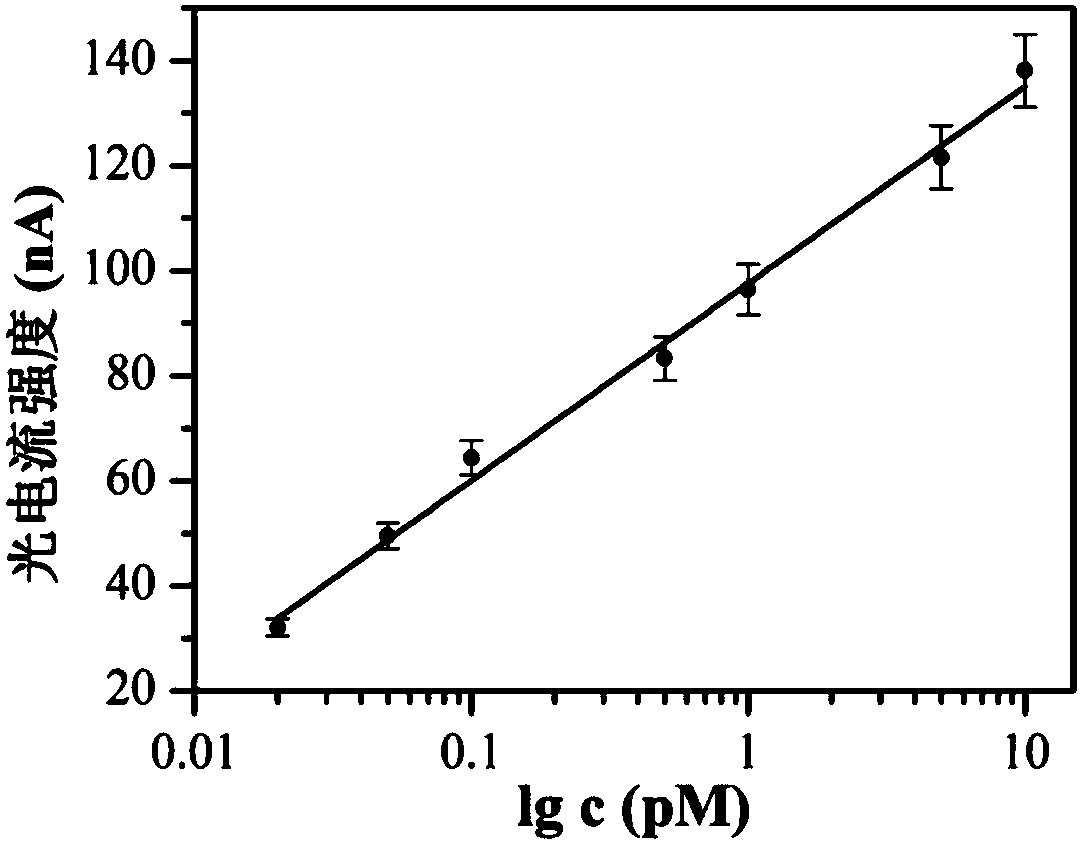
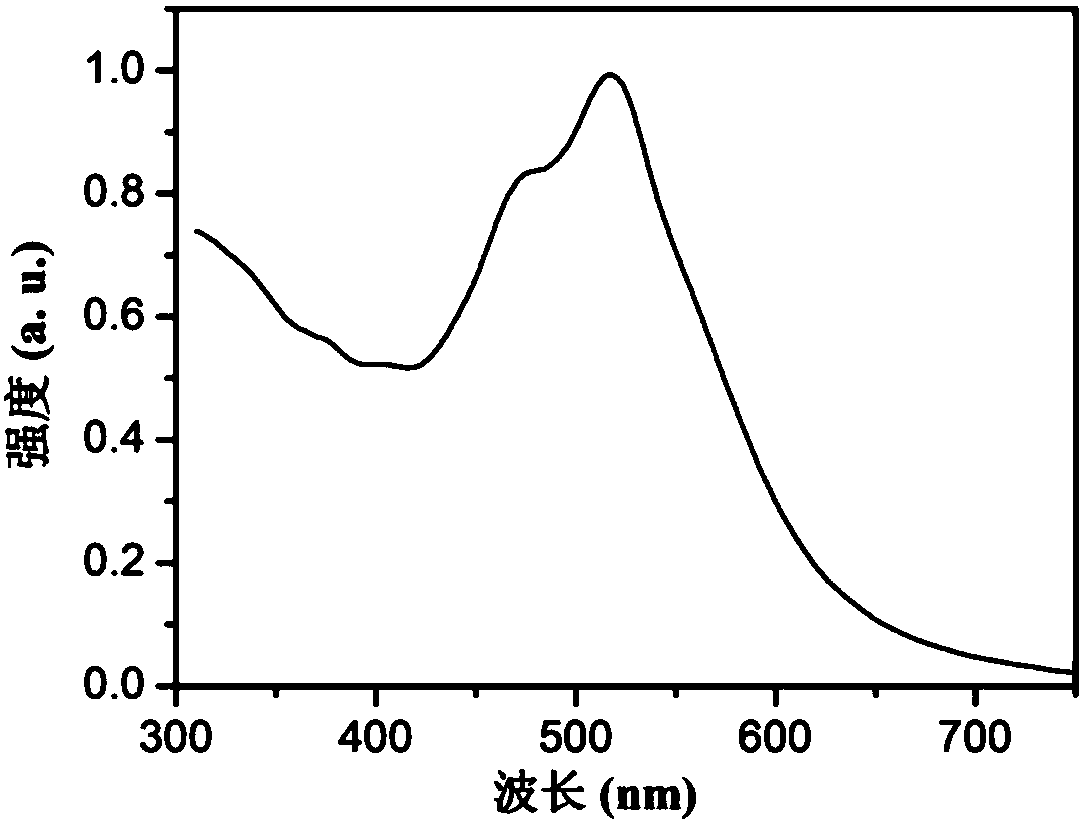
The invention discloses a preparation method of a photoelectrochemical biosensor based on a cyclometalated iridium complex and application of the photoelectrochemical biosensor to thrombin detection.The biosensor uses the visible light-excited iridium complex as a photoelectrically active material, and the iridium complex is located on colloidal gold to prepare a gold nanometer signal probe. Capturing hairpin DNAs are immobilized on a modified ITO electrode to prepare a working electrode of the biosensor. A thrombin recognition system includes a specific recognition hairpin HP1 and an adjuvant hairpin HP2; in the presence of thrombin, a large number of secondary targets T-DNAs are released under the action of the excision enzyme ExoIII and hybridize with the capturing hairpin DNAs on theworking electrode so as to capture the gold nanometer signal probe, thereby realizing response to photocurrent signals; thrombin with different concentrations allows the amount of the signal probe connected to the working electrode to be different, so photocurrent intensities are different, and thus, quantitative detection of thrombin is realized. The method has the advantages of high sensitivityand good selectivity.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System for analysis of gene sequence
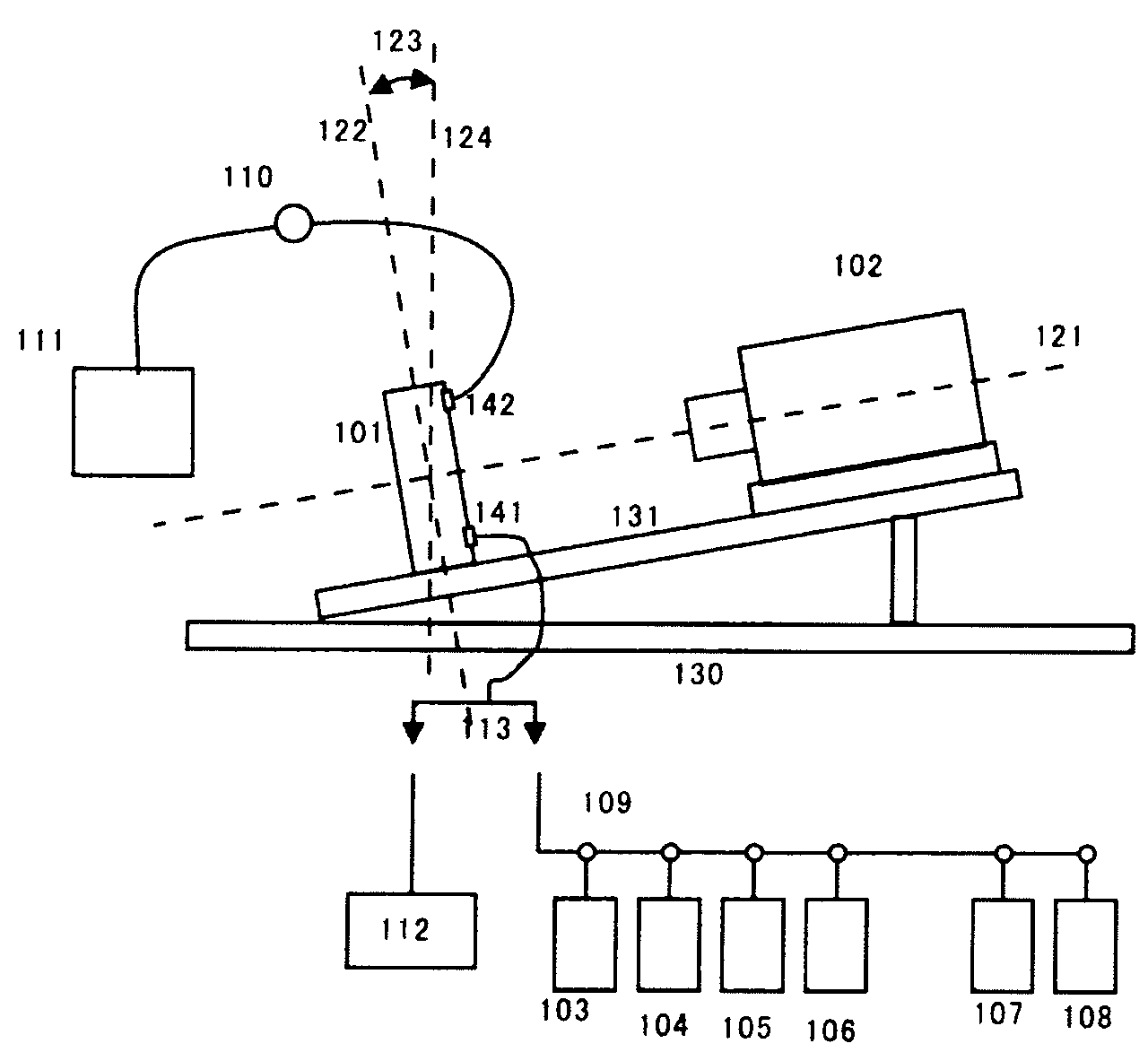
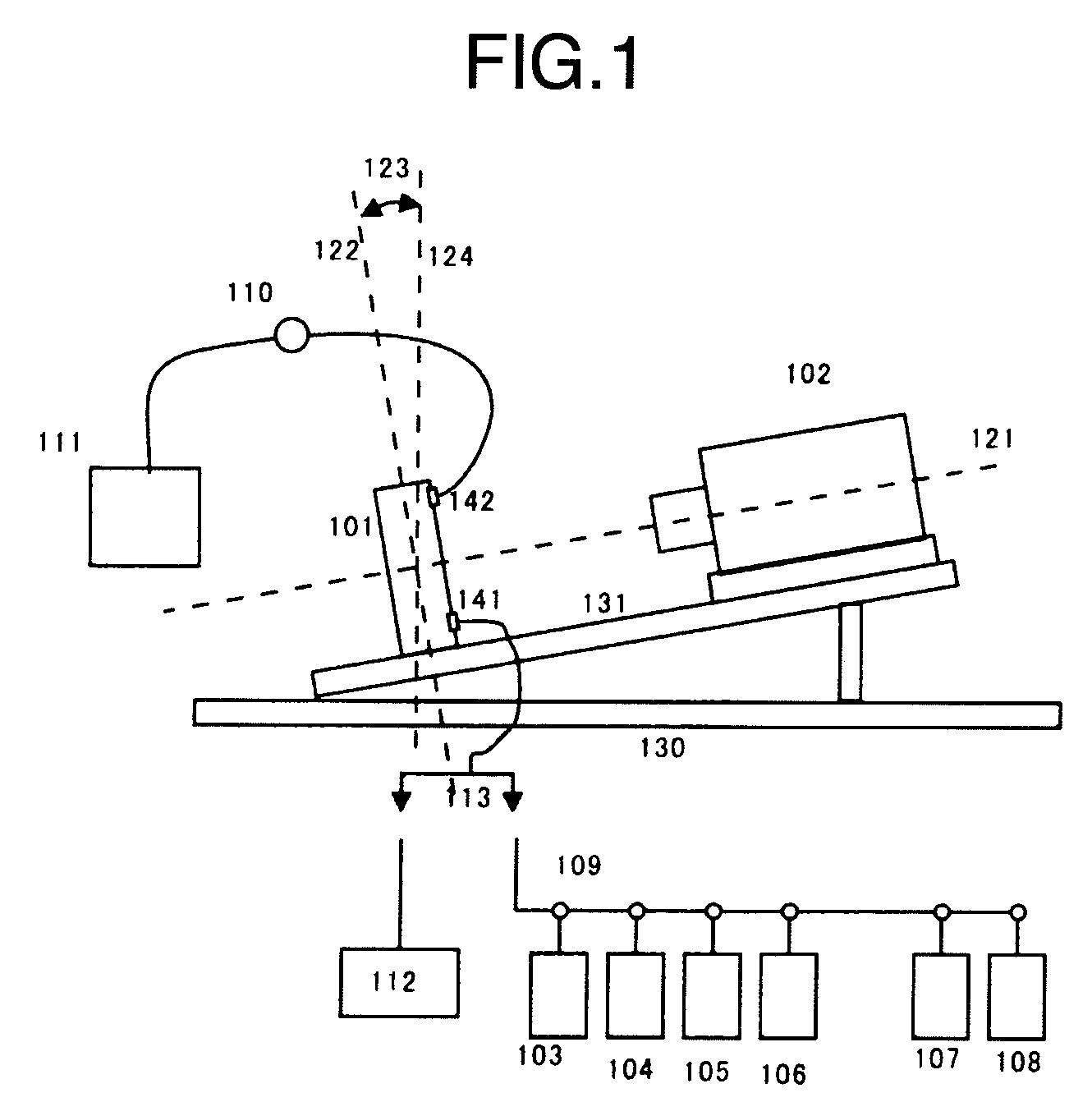
InactiveUS20080102469A1Improve throughputAvoid error introductionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFlow cellOptical axis
A conventional large-scale parallel pyrosequencing apparatus has the disadvantage that throughput decreases because much time and a large number of procedures are required for introduction of measurement beads, and analysis accuracy is deteriorated due to a reduction in accuracy of reagent replacement. There is provided an apparatus, wherein the apparatus includes a flow cell having a plurality of microfabricated reactors, and a camera opposed thereto, and DNA to be measured is fixed on the surfaces of beads having a specific gravity of 4 or greater, preferably zirconia beads. The flow cell is made horizontal when introducing the beads into the flow cell, and opposed to an optical axis of the camera when measuring an elongation reaction, the optical axis of the camera having a gradient with respect to the horizontal direction.
Owner:KAJIYAMA TOMOHARU +2
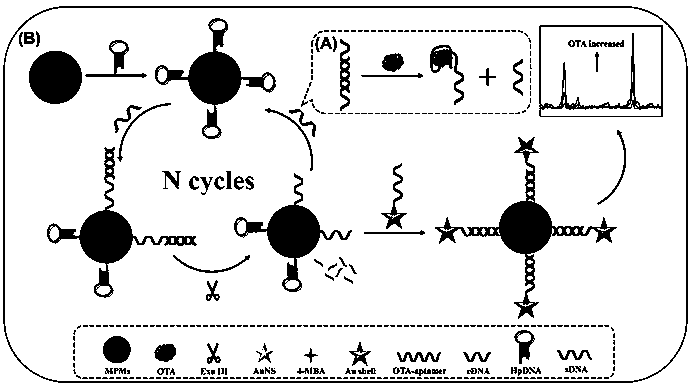
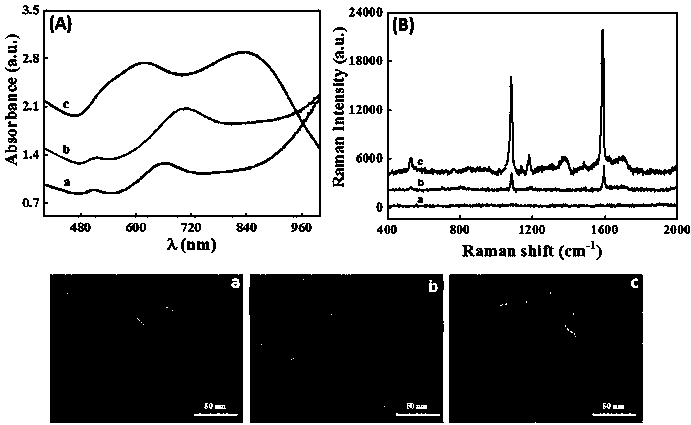
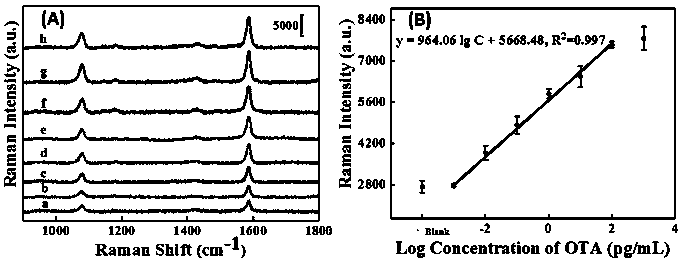
Method for detecting ochratoxin A based on SERS
InactiveCN110592181AIncrease surface areaHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRaman scatteringNanoparticleMagnetic bead
The present invention discloses a method for detecting ochratoxin A based on SERS. The method comprises the following steps: fixing sDNA on surfaces of AuNanostatr @ 4-MBA @ Au core-shell starlike gold nanoparticles as an SERS capture probe and also fixing hairpin DNA on surfaces of magnetic beads. By utilizing high affinity of OTA and OTA aptamers and an Exo III cyclic amplification effect, a large amount of the AuNanostatr @ 4-MBA @ Au core-shell starlike gold nanoparticle SERS capture probes are connected to the surfaces of the magnetic beads. Therefore, intensity of the SERS obtained by detection has a close relation with concentration of the OTA, namely, an open mode of a SERS adapter sensor is developed for ultra-sensitive OTA detection. The provided detection method has characteristics of low cost, enhancement, high detection sensitivity, low detection line and good anti-interference performance for detecting the ochratoxin.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
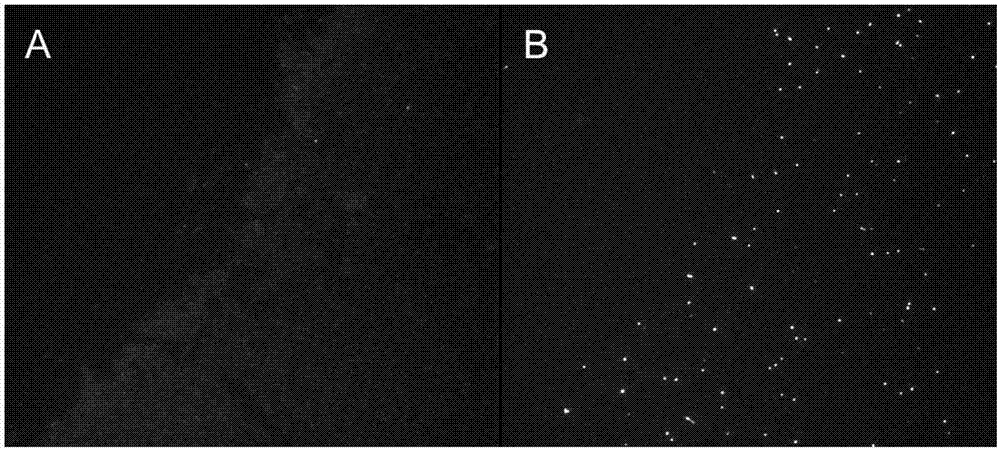
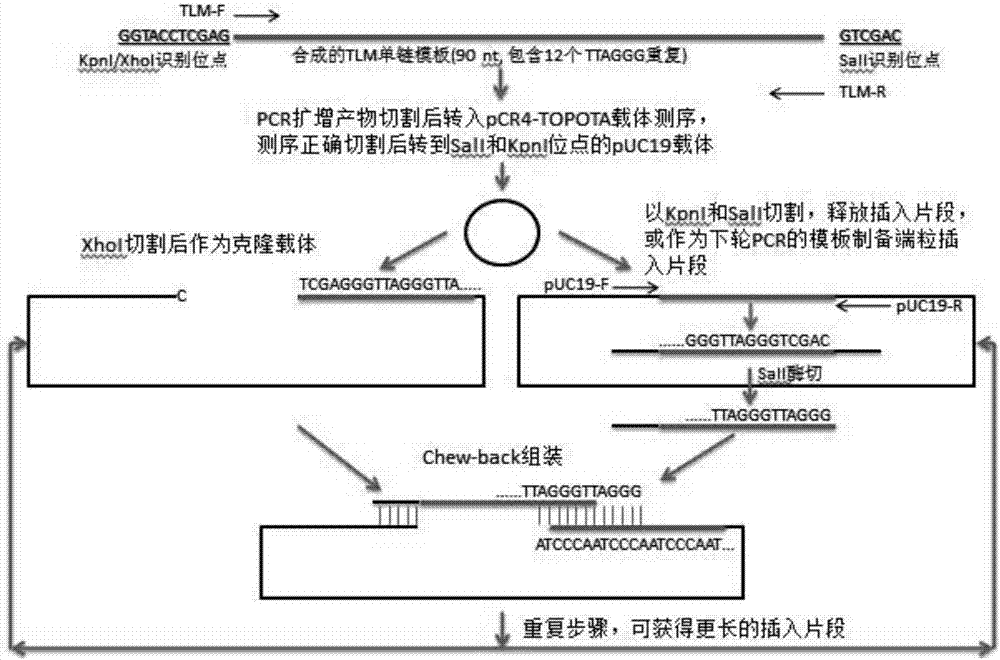
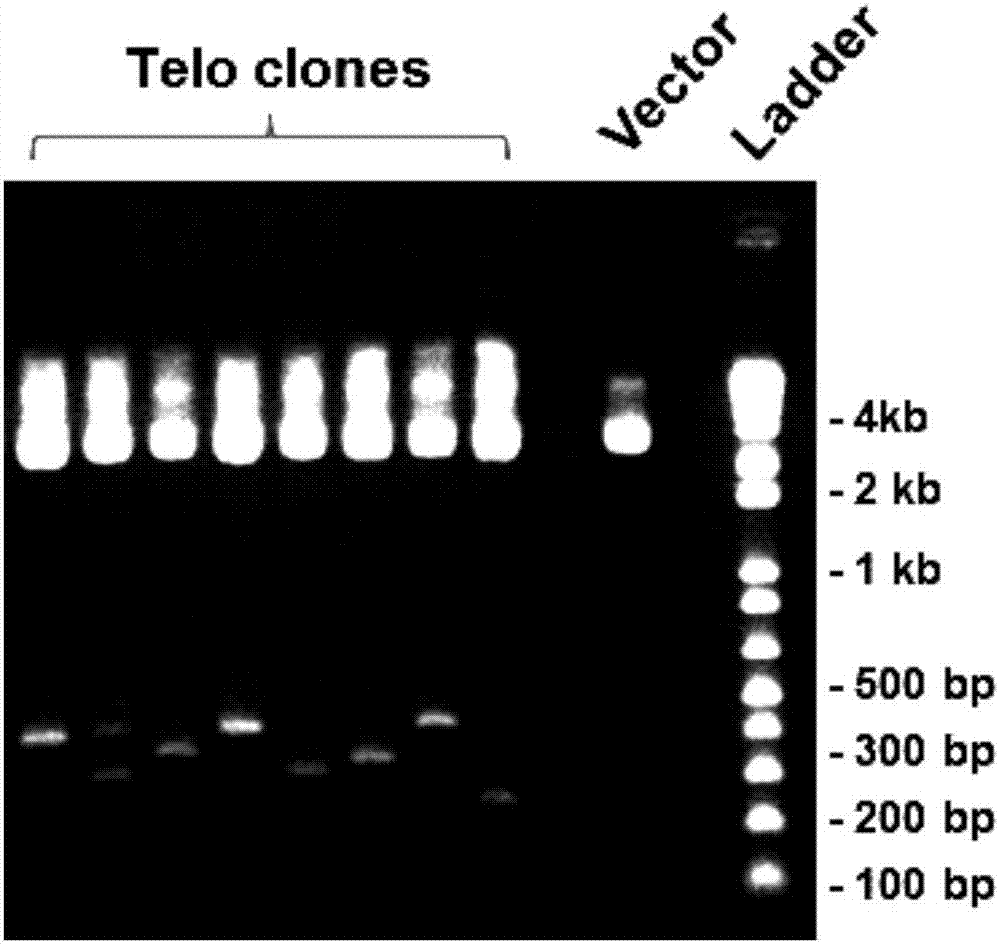
Fluorescence quantitative in-situ hybridization (Q-FISH) method for determination of telomere length by using genomic DNA
ActiveCN108004299AImprove accuracyReduce dosageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIn situ hybridisationLength variation
The invention provides a fluorescence quantitative in-situ hybridization (Q-FISH) method for determination of telomere length by using genomic DNA, wherein the method comprises the steps: the genomicDNA is fixed on a glass slide and then is hybridized with a telomere-specific PNA probe, and fluorescence data are collected; the method is also suitable for determination of the telomere lengths of split active and senescent cells; a plurality of telomere length parameters comprising the average telomere length, the telomere length variation and the frequency of abnormal-length telomeres can be obtained, and the defect that the telomere function is evaluated by single dependency of the average telomere length to obtain information is eliminated. The invention also provides a stronger-specificity telomere-specificity PNA probe, TTAGGG is shortened to 2 repetitions, the amount of the probe is reduced by half and a fluorescence signal is doubled. The invention also provides a telomere lengthstandard and a preparation method thereof, wherein the telomere length standard can be used for measuring the base length of each telomere and also can be used as calibration standard for different tests. If the automatic detection method is adopted, a large number of samples can be processed, and the method saves manpower compared with other methods.
Owner:济南海湾生物工程有限公司
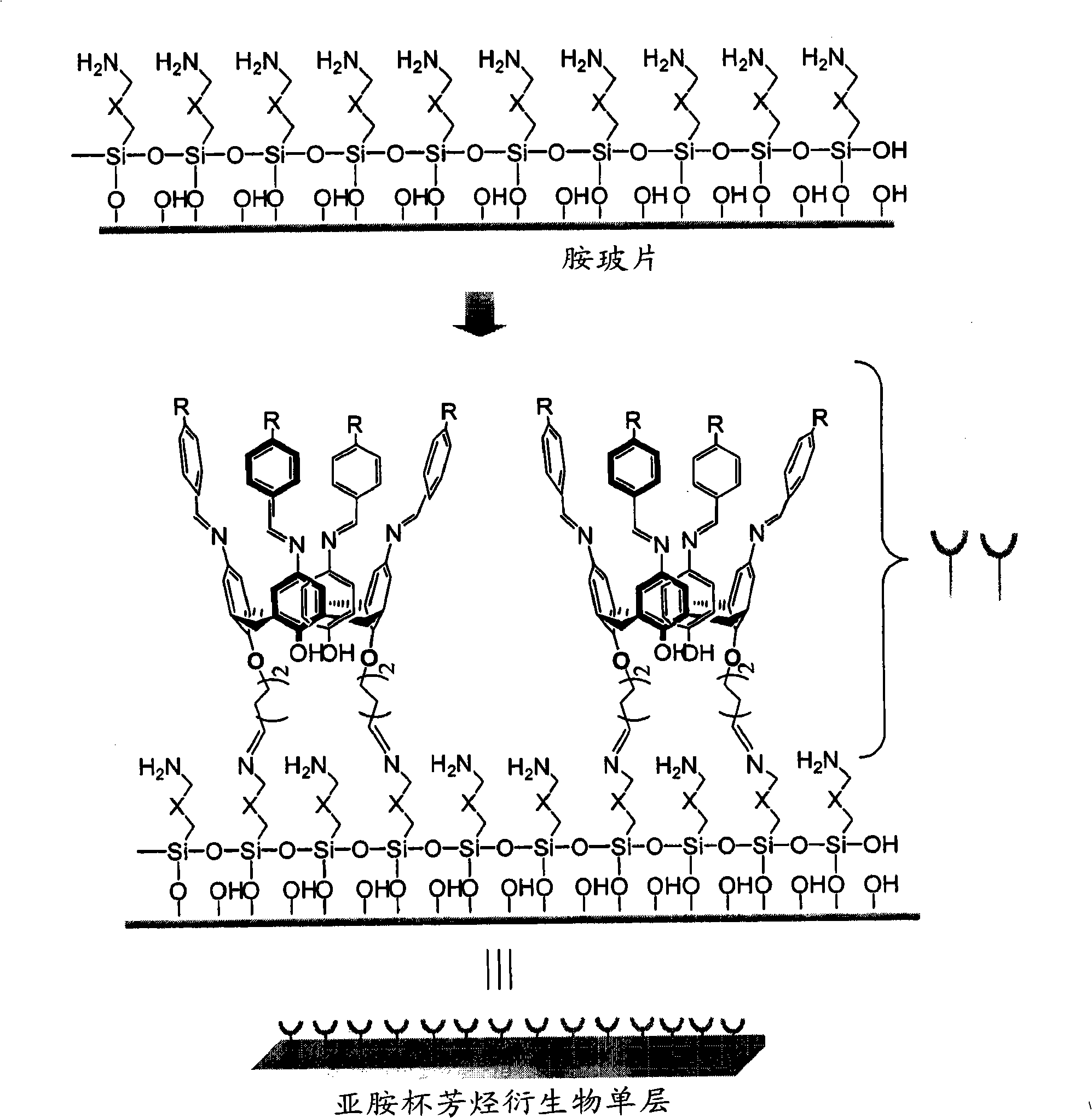
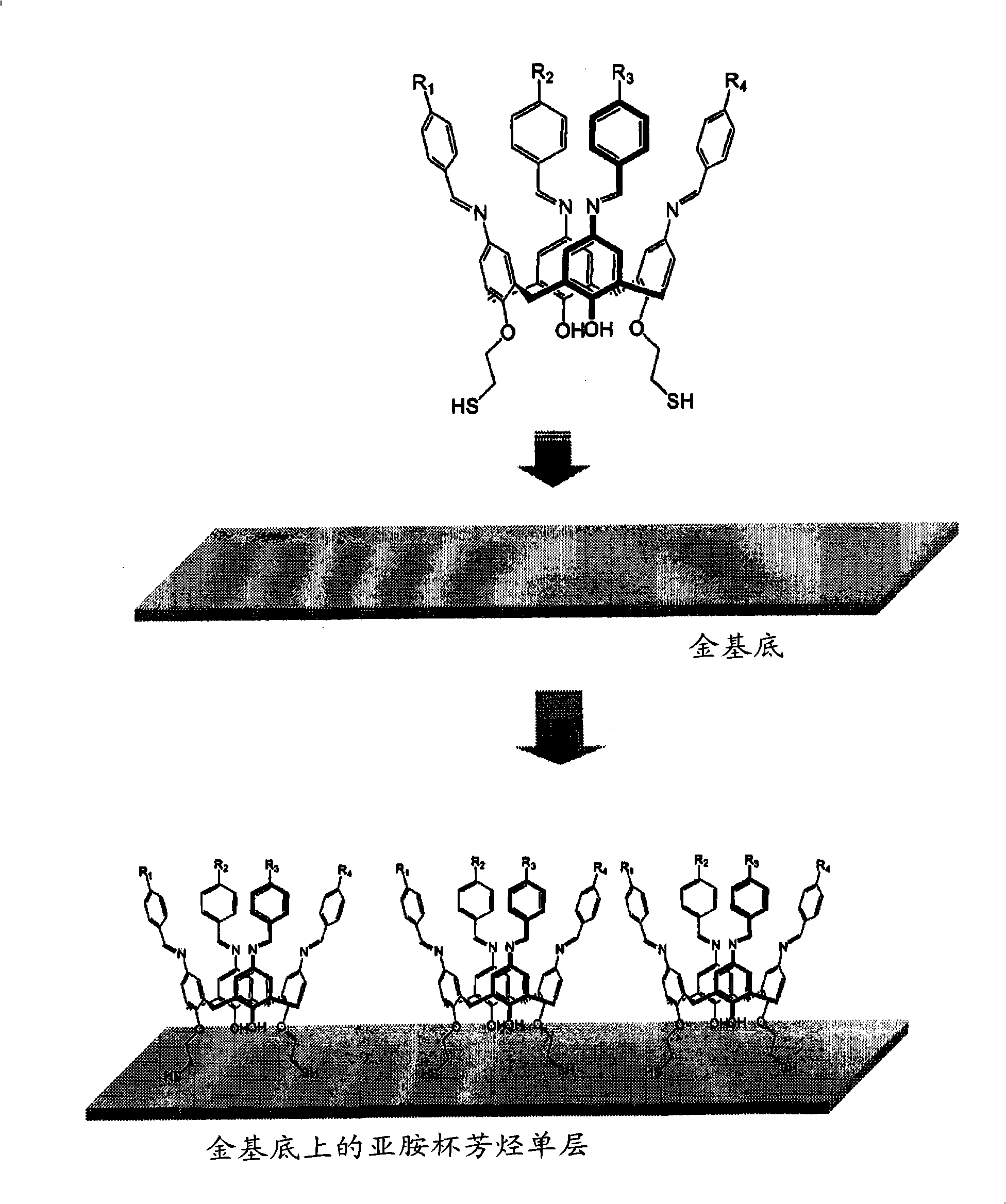
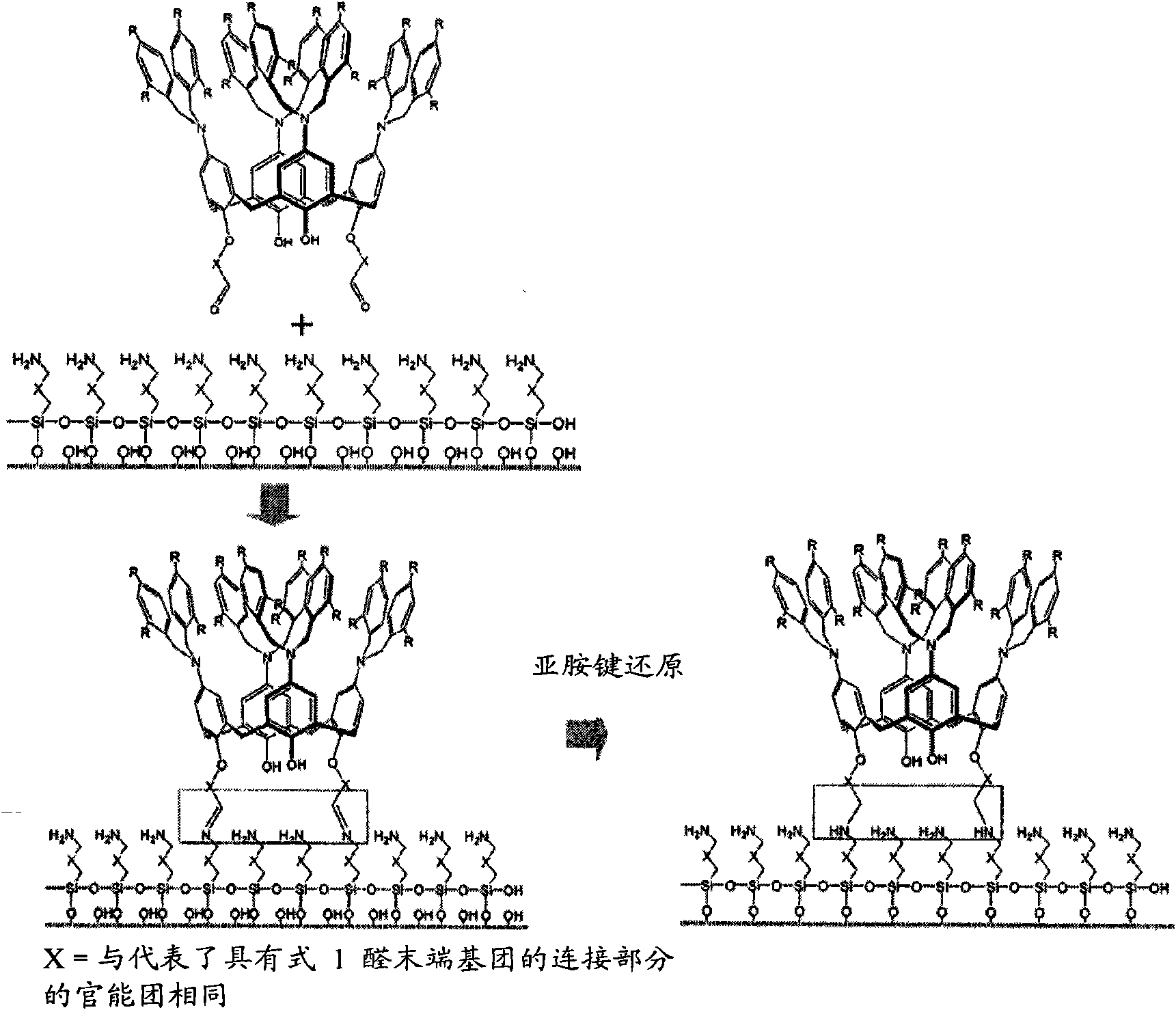
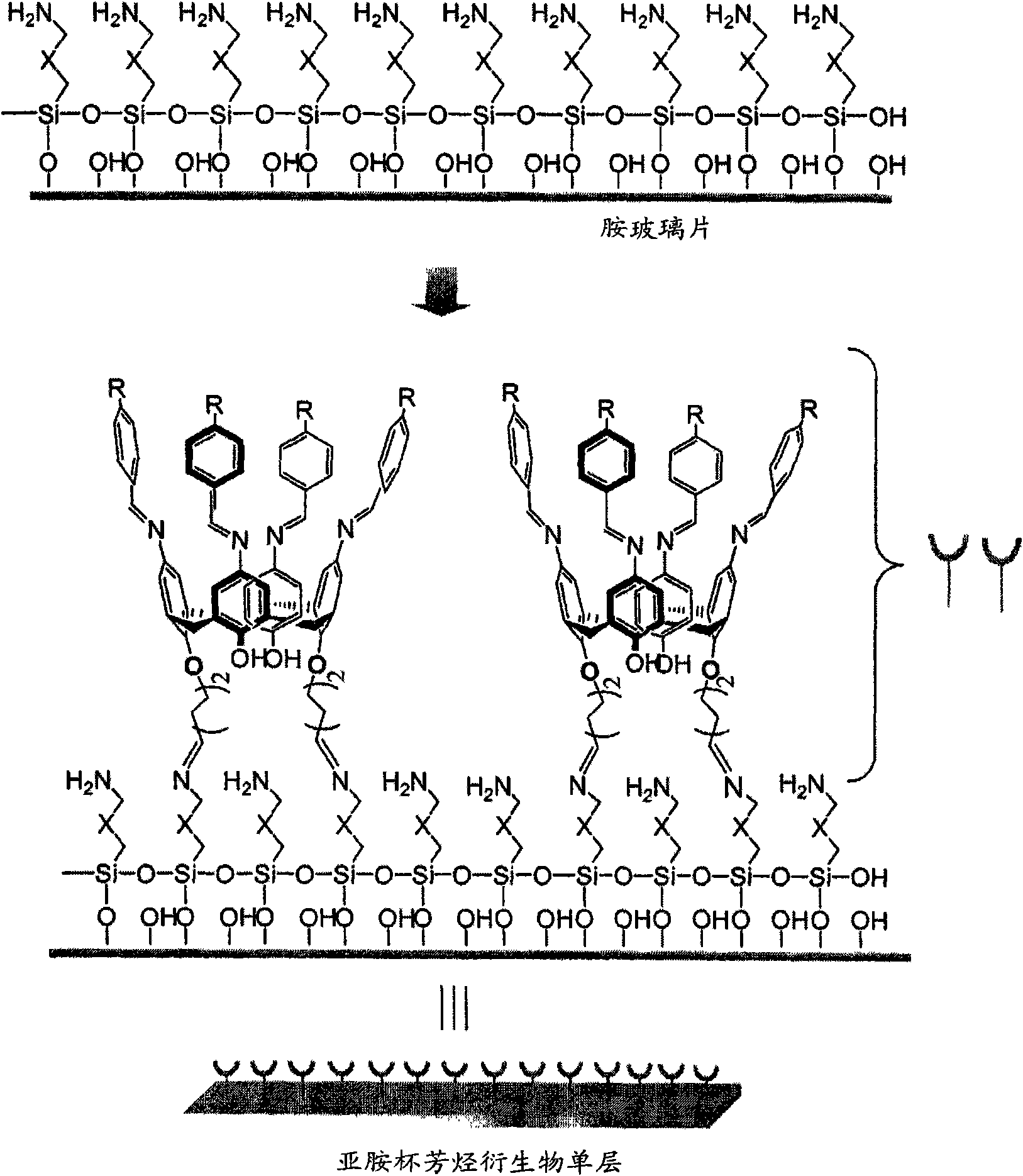
Novel iminecalixarene derivatives and aminocalixarene derivatives, method of preparation thereof, and self-assembled monolayer prepared by the method, fixing method of oligo-dna by using the self-asse
ActiveCN101309896ASolve the real problemResolve connectionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSelf-assembled monolayerDna immobilization
The invention provides novel iminecalixarene derivatives, a method for preparation thereof, and a self-assembled monolayer prepared by the method, a method for fixing oligo-DNA by using the self-assembled monolayer, and an oligo-DNA chip prepared by the method. Additionally, the invention provieds novel aminocalixarene derivatives, a method for preparation thereof, and a self-assembled monolayer prepared by the method, method for fixing oligo-DNA in which the oligo-DNA is voluntarily fixed by molecular recognition on said self-assembled monolayer in a liquid phase, and an oligo-DNA chip prepared by the method.
Owner:BIOMETRIX TECH
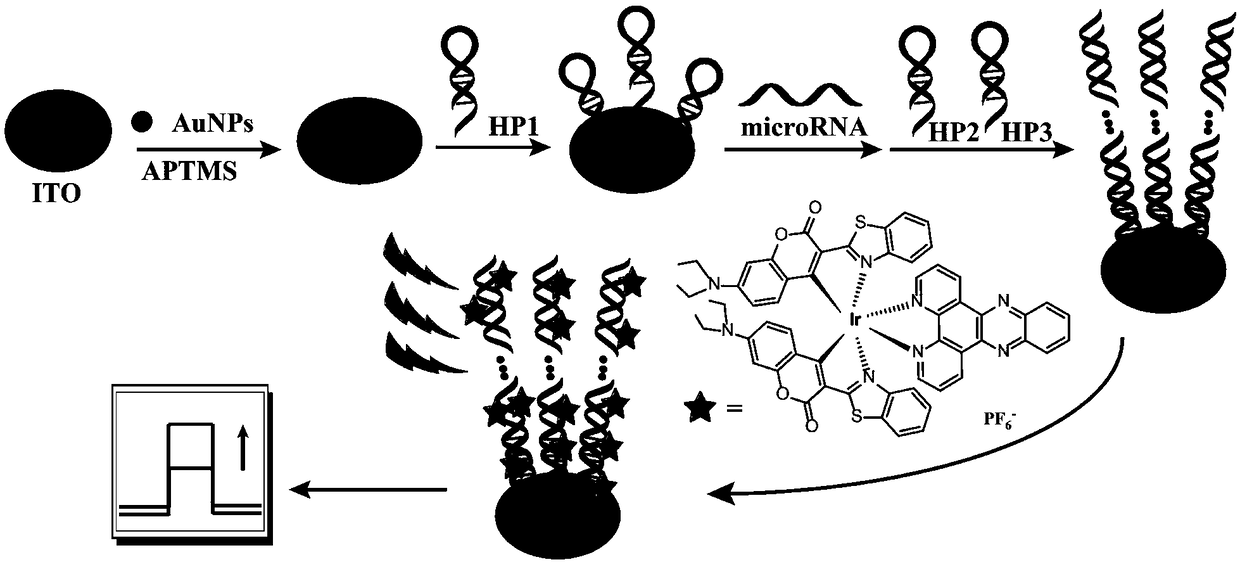
Preparation method of photoelectric chemical biosensor for microRNA detection
ActiveCN109142486AImprove stabilityImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyMaterial electrochemical variablesIridiumMicroRNA
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cyclometalated iridium complex biosensor for microRNA detection. The preparation method includes: designing and synthesizing a cyclometalated iridiumcomplex insertable into DNA dual strands as a photoelectric material; fixing capture hairpin DNA to a modified ITO electrode to obtain a working electrode of the biosensor herein; if target microRNA exists, hybridizing with the capture hairpin DNA fixed on the working electrode to release its neck portion, and allowing the released neck portion to hybridize with another two hairpin DNAs to triggerhybridization chain reaction, so that a long DNA dual-strand polymer is formed on the surface of the working electrode. Massive cyclometalated iridium complexes can be inserted into the polymer herein so as to amplify signals, and therefore, high-sensitivity detection of microRNA is achieved. The preparation method has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, good stability and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
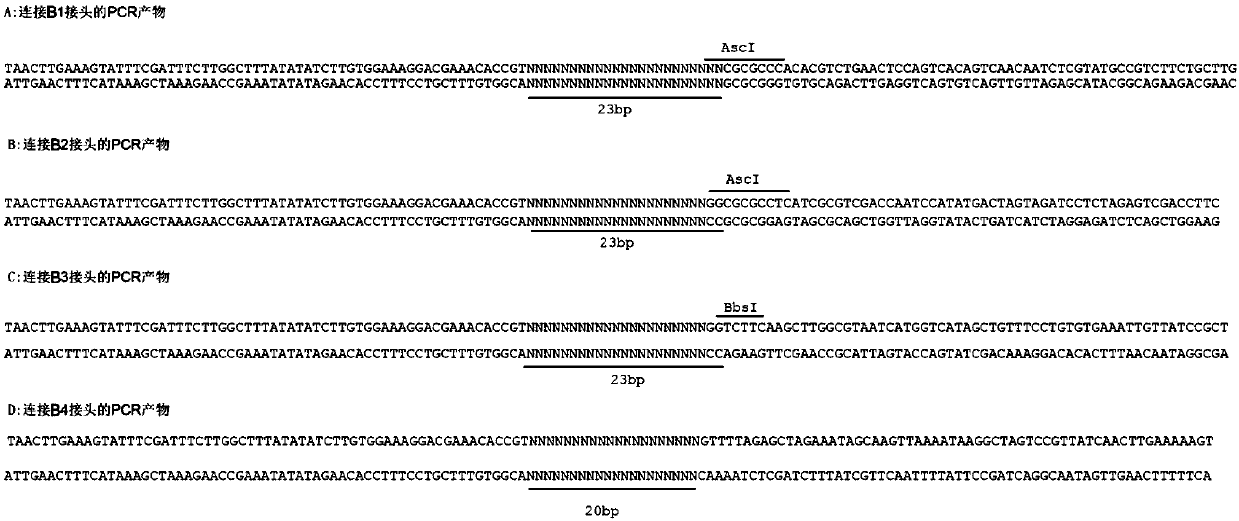
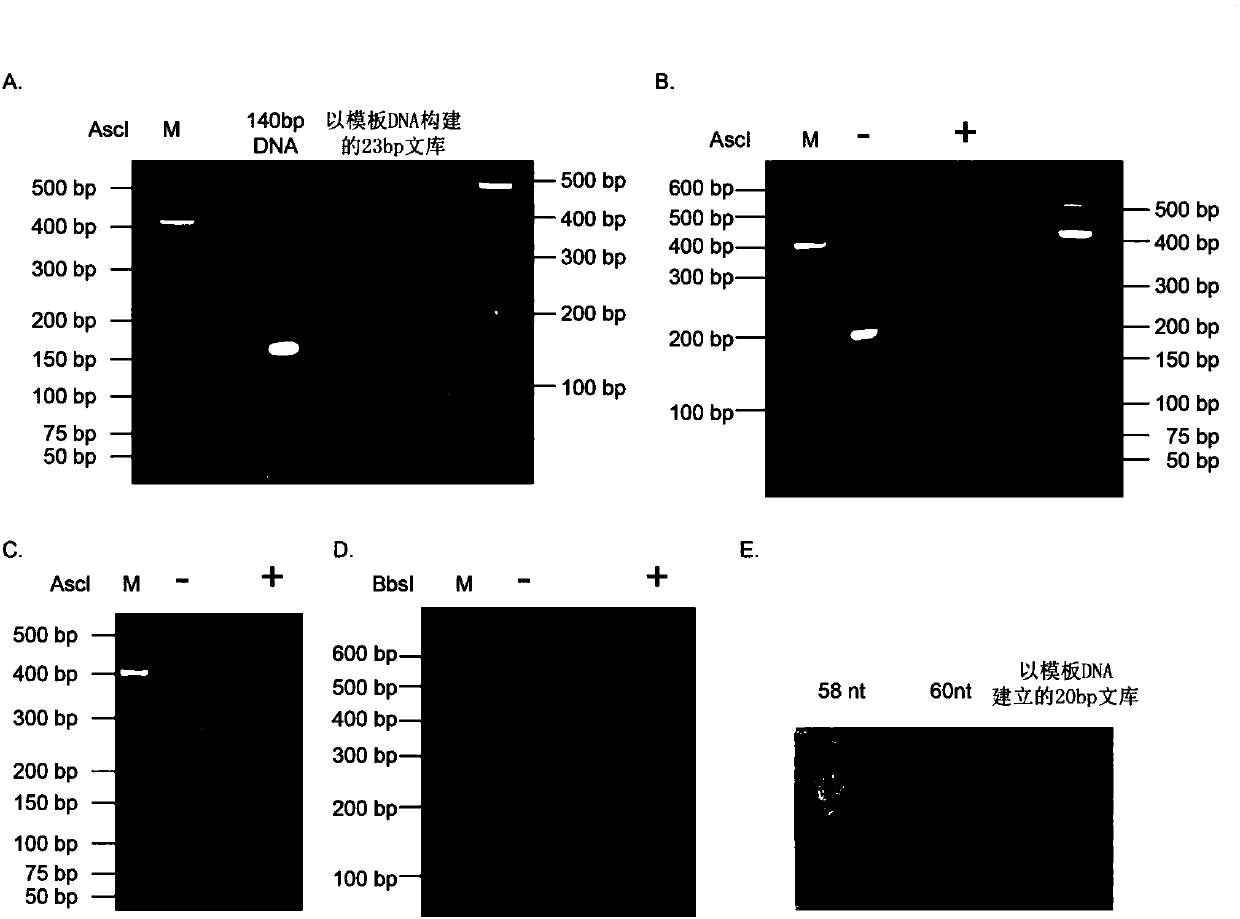
Method used for synthesis of DNA library with fixed length and specific terminal sequence based on template material
ActiveCN110158157ANo design inaccuraciesLower build costsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCDNA libraryA-DNA
The invention belongs to the field of biological field, and more specifically relates to a method used for synthesis of a DNA library with a fixed length and a specific terminal sequence based on a template material. The method comprises following steps: fragmentation double chain DNA obtaining; DNA terminal restoration and 3' terminal tailing; 3'Biotin modified A1 joint connection; connection product purification; fixing of DNA onto a streptavidin containing solid phase; denaturation of double chain DNA into single chain DNA; primer 1 hybridization; reversible chemical modification of dNTPs extension basic group with deoxyribosyl 3' terminal hydroxyl; pentose 3' terminal hydroxyl restoration; extension of DNA of fixed length; 5' terminal trimming; tail end sequence selection; tail end sequence removing; and connection of joint used for molecular cloning. The method is capable of realizing construction of the library with region fixed length, specific terminal sequence, and high sequence variability, without reference genome, and library construction cost is reduced greatly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
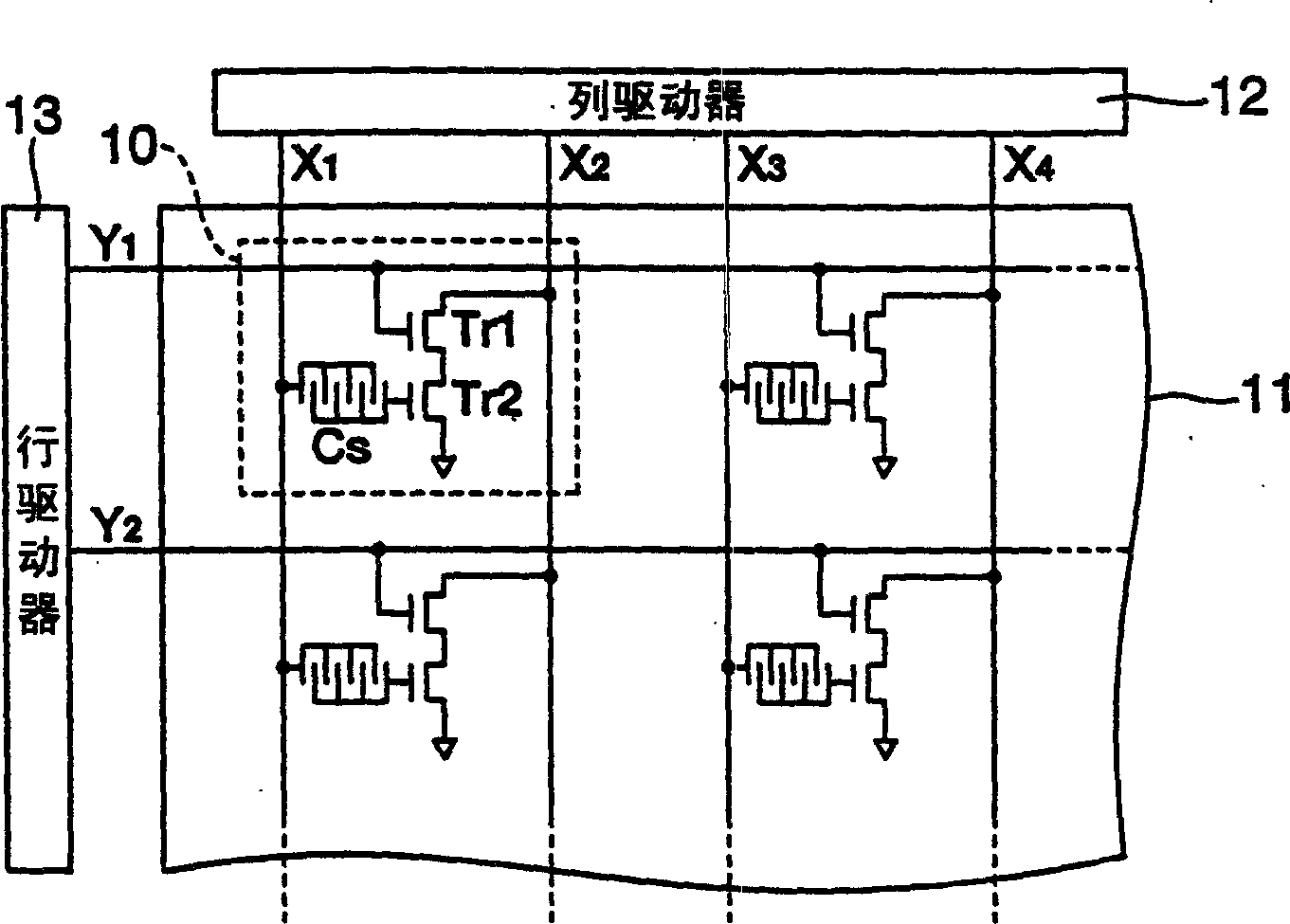
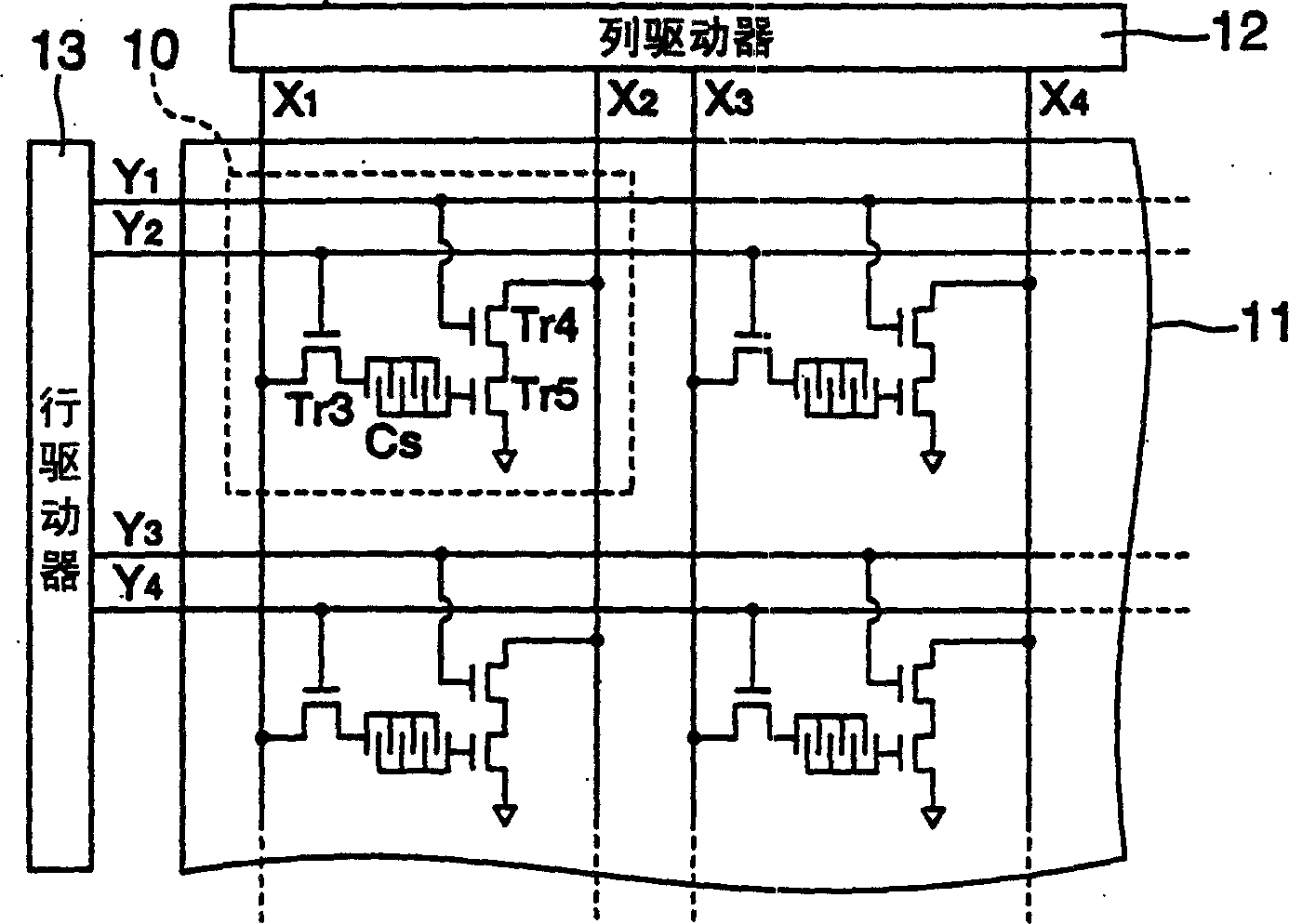
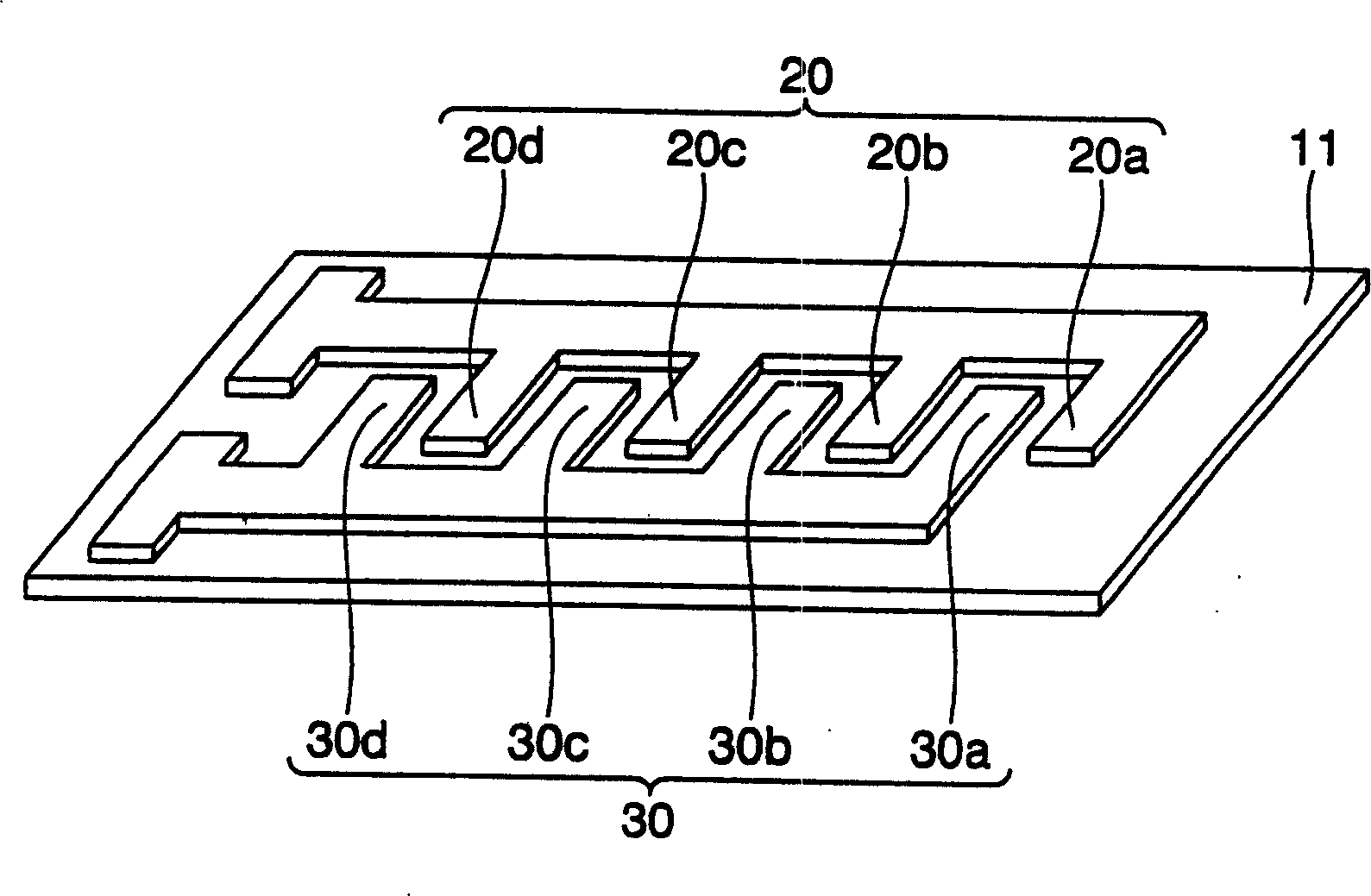
Sensor cell, biosensor, capacitive device manufacturing method, biological reaction detection method, and gene analyzing method
The present invention provides a biosensor which comprises: a sensor matrix where sensor cells are arrayed in a matrix, a row driver for supplying a predetermined voltage signal to sensor cells arrayed in the row direction of the matrix, and a column driver for supplying a predetermined voltage signal to sensor cells arrayed in the column direction of the matrix. Each of the sensor cells has: a capacitive element (Cs) composed of a pair of opposed electrodes on which a probe DNA immobilized on the electrode surface selectively reacts with the target DNA; a transistor (Tr2) for varying the value of the current outputted from a drain terminal in response to the variation of the capacitance of the capacitive element (Cs) caused by DNA hybridization, and a switching element (Tr1) for supplying a voltage signal supplied from the column driver to the current input terminal of the transistor (Tr2).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
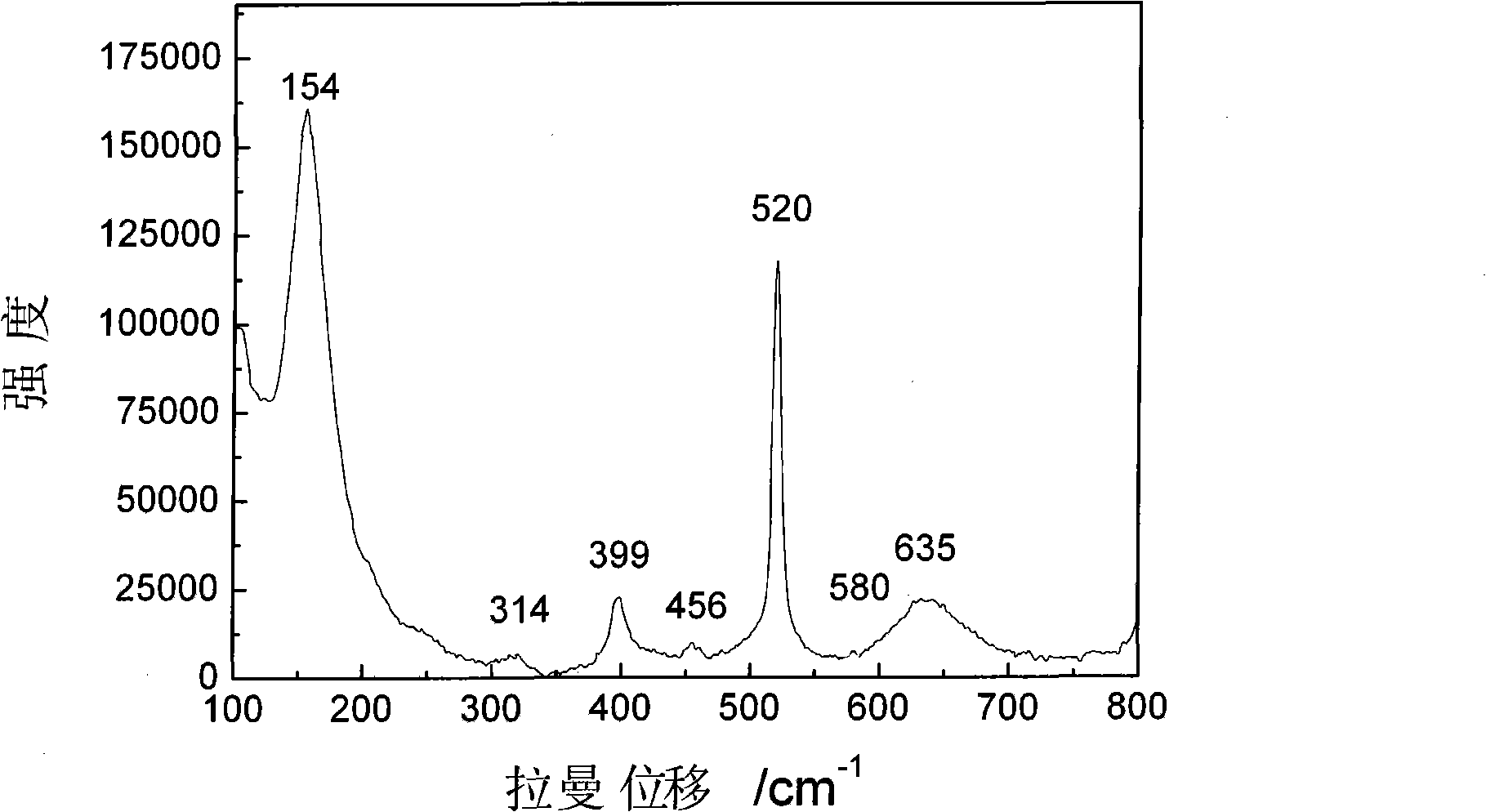
Method for preparing immobilized DNA guiding substrate surface nano-titanium dioxide film growth
InactiveCN101314525ANo pollution in the processRealize immobilizationCoatingsSolar batteryCalcination
The invention discloses a preparation method for leading the growth of a nanometer titanium dioxide film on the surface of a substrate by DNA immobilization. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) the substrate is cleaned and dried; (2) DNA molecules on the surface of the substrate are immobilized; and (3) the substrate treated by the step (2) is immersed into a 2 to 20 mM of TiCl4 aqueous solution containing hydrochloric acid and subject to the sedimentation of the nanometer titanium dioxide film. The method has no environmental pollution, realizes the immobilization and the ordered assembly of DNA and leads the assembly and growth of the nanometer titanium dioxide film at a low temperature with the substrate as a template. The nanometer titanium dioxide film prepared on the substrate surface by the method needs no high-temperature calcination, has a certain crystal structure, even film surface and strong adhesive force with the substrate surface and can be used for preparing a transparent conductive film and a self-cleaning surface of a solar battery and other functional devices.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Substrate activation kit and method of detecting DNA or the like by using the same
InactiveCN1606693AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPhosphateBiological activation
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a convenient and fast method for immobilizing DNA on a substrate and a method for accurately detecting DNA, and the density of DNA immobilized by the method is as high as that of the traditional method. A substrate activation kit is provided, which includes phosphate buffered saline at pH 6, solution A (aqueous) of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]3-ethylcarbodi Solution B of imine (dioxane solution); a method for detecting DNA is provided, which is characterized in that the DNA is spotted onto the substrate activated with the above-mentioned activation kit, and then hybridized with fluorescently labeled DNA with the spotted DNA.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
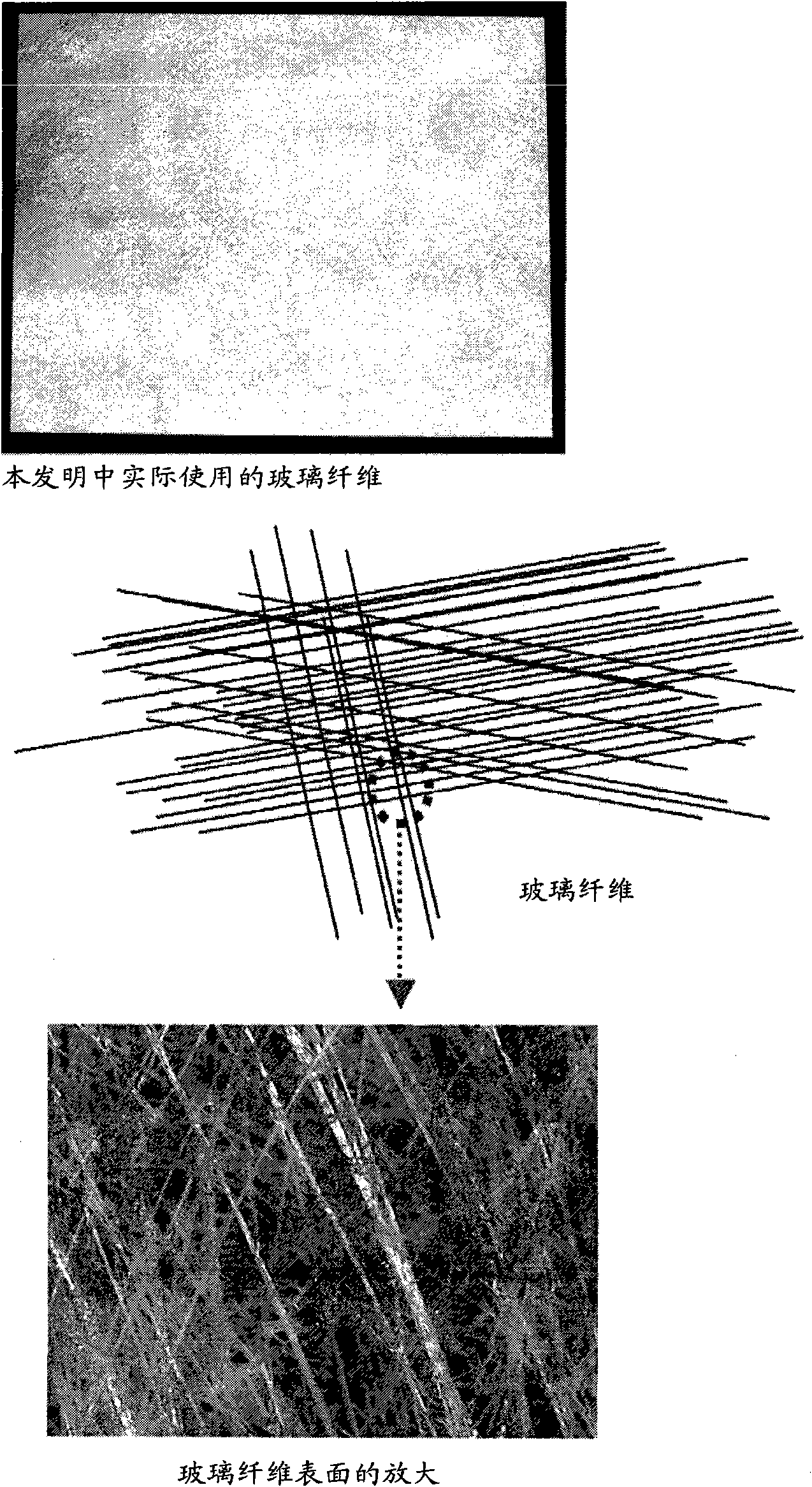
Modified glass fibers with monolayers of aminocalixarene derivatives and iminecalixarene derivatives, and oligo-dna modified glass fibers by fixing oligo-dna's to the monolayers, and the preparation m
ActiveCN101568645AGood reproducibilitySolve operational problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisGlass fiberDna immobilization
The present invention relates to a method of preparing a surface-modified glass fiber by bonding an aminocalixarene derivative or an iminecalixarene derivative on the surface of a glass fiber to form a monolayer, a method of preparing a glass fiber where oligo-DNAs are immobilized by immobilizing oligo- DNAs having consecutive guanine bases on the glass fiber prepared according to said method, and a method of preparing a rapid genotyping kit using the glass fiber where various oligo-DNAs are immobilized according to said method, thereby allowing genotyping of various genes.
Owner:BIOMETRIX TECH
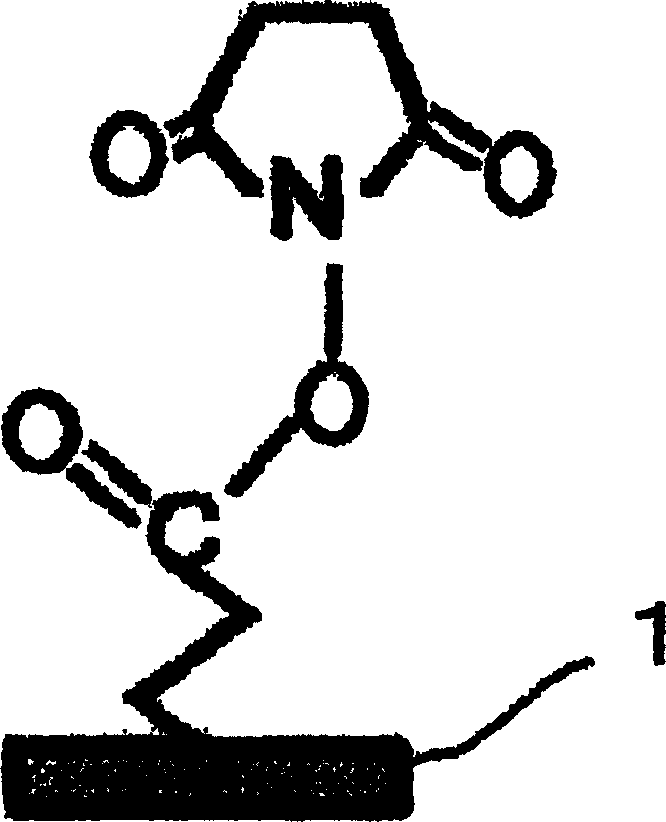
DNA immobilization method based on nucleic acid immobilization by gel and use thereof
InactiveCN101481733AImprove carrying capacityImprove fixation efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementEthylenediamineA-DNA
The invention relates to a method of immobilizing DNA on gel, in particular to a DNA immobilization method based on immobilization of nucleic acid on the gel and the application thereof. The immobilization method of a DNA sample comprises three steps of raw material selection, mixing and polyreaction. In the step of raw material selection, the selected raw materials and dosage are as follows: 10 percent of 10*TBE(pH13), 10-70 percent of 40 percent methacrylamide storage liquid, 1muL-5ml diluted degeneration amino terminal modified nucleic acid, 1-10 percent of N, N, N, N-tetramethyl ethylenediamine, 1-10 percent of 10 percent ammonium persulfate, and water. In the step of mixing, configured gel raw material is added with amino terminal modified nucleic acid to be mixed. The nucleic acid amount in the mixture is 10-1,000ng / 3muL. In the step of polyreaction, 5muL mixture is put in a PCR reaction tube at 37 DEG C for 30min. After the polyreaction is finished, the mixture is molded into gel shape, and the amino terminal modified nucleic acid is immobilized by the polyreaction in the gel. The method has the advantages of high bearing capacity, immobilization of the terminal modified nucleic acid molecule by stable covalent bond formed between the molecule and a solid phase carrier and capacity of enduring dramatic conditions of the PCR reaction, etc.
Owner:HANGZHOU ENSHI GENE TECH DEV
DNA carrier, method of producing the same and collection system using the same
InactiveCN1984965AReduced elutionEasy to manufactureSugar derivativesOther chemical processesSilane compoundsCollection system
Provided are a DNA carrier where DNA is firmly held in a substrate, which can reduce the elution of DNA into water and can take full advantage of the capability of DNA to selectively and specifically collect a substance; and a method of producing the DNA carrier. Also provided is a collection system using DNA, which can be used in the high-accuracy detection of a particular substance and in an environmental cleanup capable of efficiently removing a substance, in which the DNA carrier is used to collect the substance contained in air or water by taking full advantage of the capability of DNA to selectively and specifically collect the substance. The DNA carrier is one where DNA is held in a porous matrix containing polyorganosiloxane with a basic functional group and particles. Preferably, the polyorganosiloxane with a basic functional group contains a hydrolysis condensate of one or more of particular silane compounds with an amino group.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Globular cellulose DNA immunoadsorbent
InactiveCN1111430CImprove adsorption capacityGood clinical effectPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsImmunological disordersCelluloseChlorobenzene
The present invention is one medical adsorbent material. Short cotton velvet as material is processed successively through bleaching with sodium hypochlorite, treatment with sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide to obtain cellulose xanthate derivative, which is heated and solidified at 85-95 deg.c for 1-3 hr through suspension process utilizing chlorobenzene and carbon tetrachloride as dispersing medium to obtain globular cellulose. The globular cellulose is then activated with epoxychloroproane in alkali condition and reacted with DNA solution to result in globular cellulose DNA immunoadsorbent with DNA content of 0.5-3.0 mg each milliliter resin. The said immunoadsorbent is superior to carbonized resin DNA immunoadsorbent in DNA fixing amount and adsorptivity and is one new product for treating systematic lupus erythematosus.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
DNA analysis apparatus
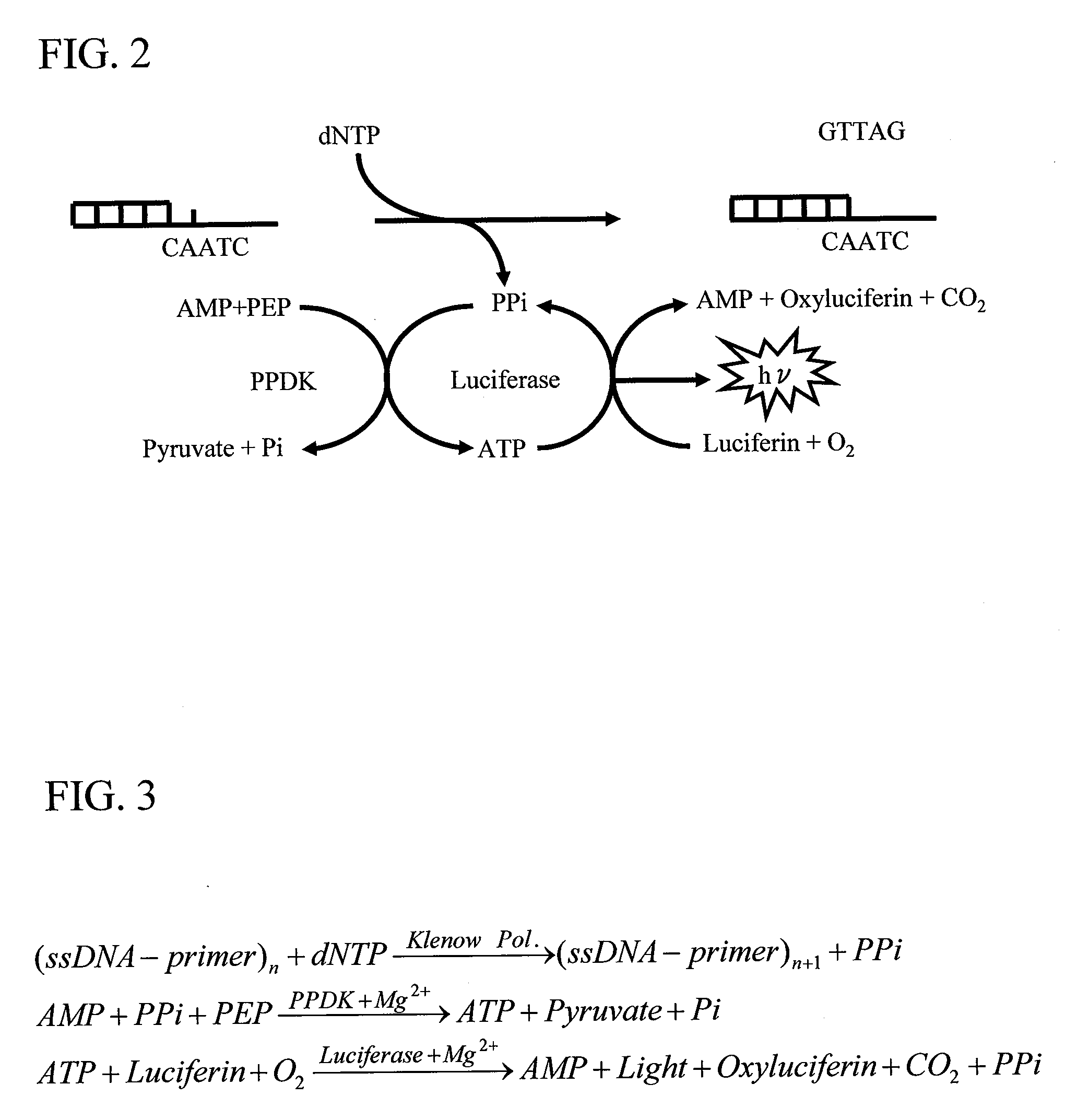
InactiveUS20090253194A1Highly sensitive and accurate sequencingShort timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusA-DNADna immobilization
Accurate and sensitive sequencing in pyrosequencing is achieved by allowing complementary strand synthesis reaction to proceed homogeneously and completely in a short time while performing luminescence reaction for a sufficiently long time. DNA as a sequencing target is immobilized on the surface of a solid supporter. Nucleic acid substrates are injected from a dispenser to the supporter site where complementary strand synthesis is in turn performed rapidly and completely in a short time under a small reaction volume. Next, the supporter together with the product thereon is moved into a luminescence reaction solution where luminescence reaction is in turn performed. Thus, a DNA complementary strand synthesis reaction site and a luminescence reaction site are completely separated. The-supporter surface is also washed by dipping the supporter in the luminescence reaction solution that contains a luminescence reagent and an enzyme that degrades redundant nucleic acid substrates.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com