Fluorescence quantitative in-situ hybridization (Q-FISH) method for determination of telomere length by using genomic DNA
A technology for telomere length and fluorescence quantification, which can be used in recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, and microorganism determination/inspection. , the effect of improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1 Preparation and effects of telomere-specific PNA probes.
[0067] 1.1 Preparation of telomere length standard
[0068] The base sequence of the telomere-specific PNA probe is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, the N-terminal is modified with a fluorescent group Cy3, and an O-linker is added between the fluorescent group and the N-terminal base, and its sequence is: Cy3- O-TT A GGG TTAGGG, bases underlined are modified miniPEGs, synthesized by PNA Bio (Thousands Oaks, CA).
[0069] 1.2 Fluorescent detection of telomere-specific PNA probes binding to telomeres
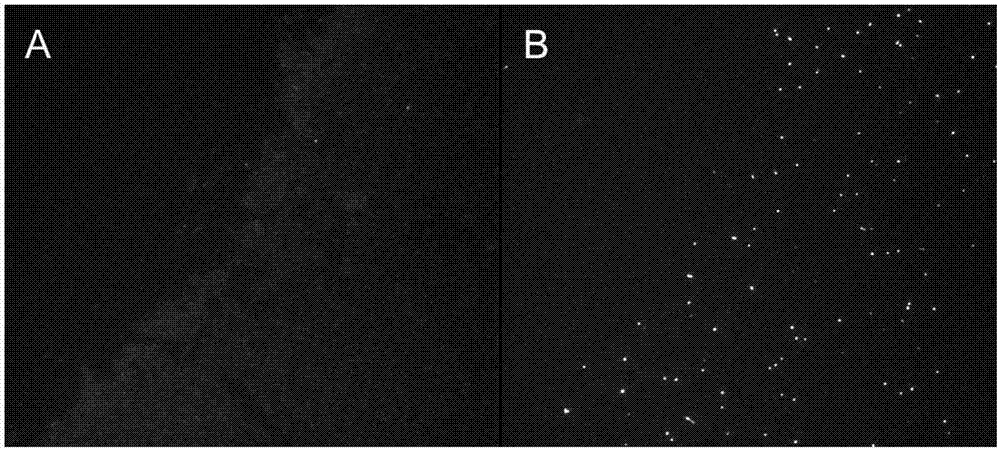
[0070] Two slides loaded with the same DNA samples extracted from blood leukocytes were treated with 0.3 M YoYo-1 dye and telomere-specific PNA probes, and fluorescent images were taken under a 100X oil microscope (Leica DM400B Fluorescence microscope connected to Hamamatsu ORCA-flash 2.8 digital camera, exposure 250 ms, Metamorph image acquisition software), picture as figure 1 Shown: figure 1 A is an image ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2 Preparation of Telomere Length Standards.
[0072] 2.1 Preparation of telomere length standard
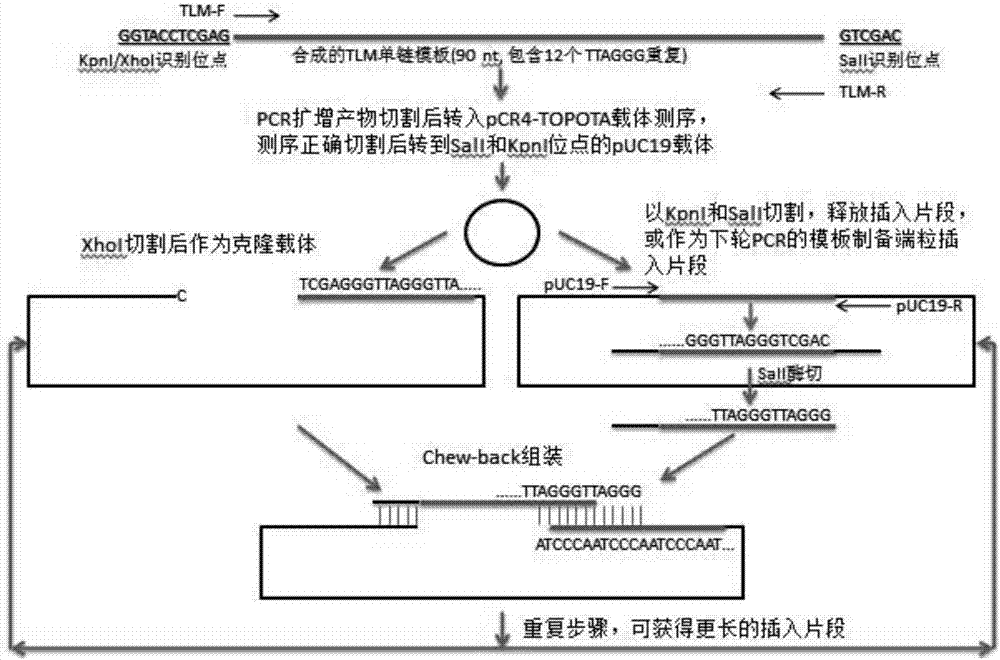
[0073] The preparation process of telomere length standard is as follows: figure 2 , the specific process is as follows:
[0074] (1) Synthesize single-stranded telomeric repeat fragments, which contain 12 telomeric repeat sequences, and the 5' end contains KpnI and wxya site, the 3' end contains SalI site, its sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc;
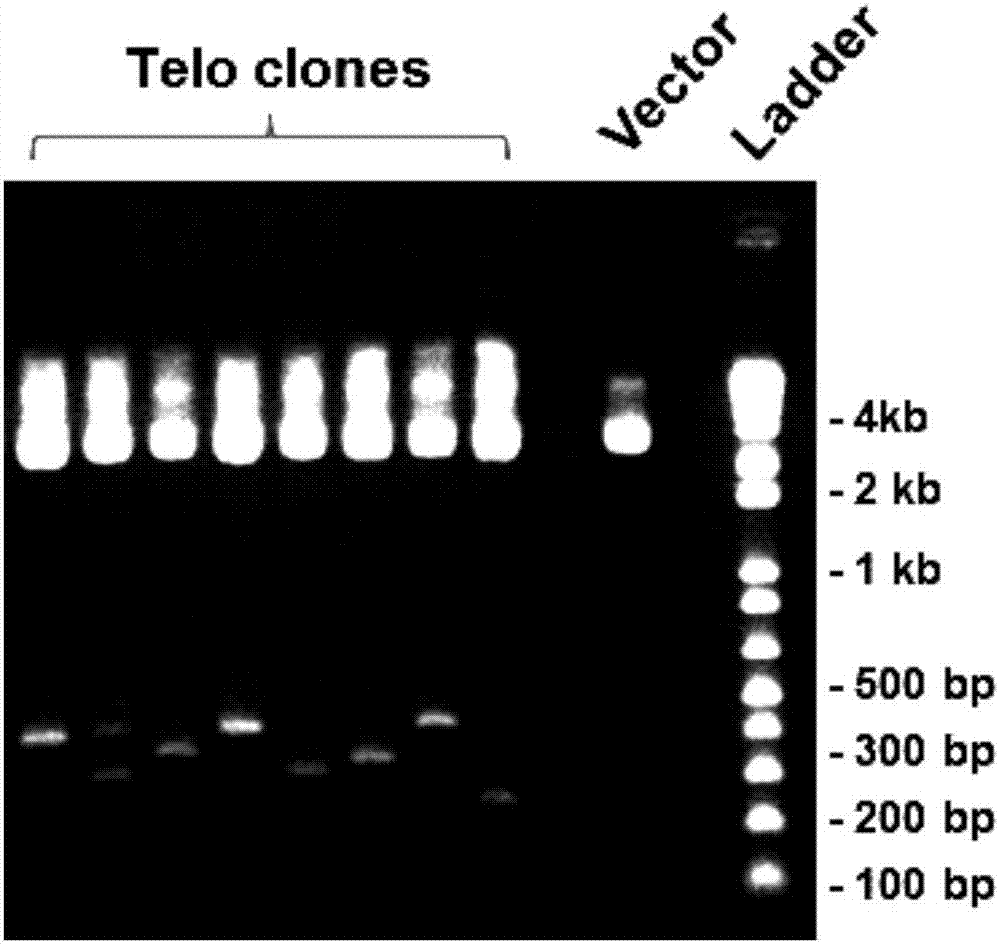
[0075] (2) Perform PCR using the above telomeric repeat fragment as a template. The sequence of the forward primer (TLM-F) of PCR is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, and the sequence of the reverse primer (TLM-R) is shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 Annealed at 55 degrees, amplified for 30 cycles to obtain PCR products; the PCR products were cloned into pCR4-TOPO TA vector (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY), and verified by Sanger DNA sequencing (Genwiz, Germantown, MD) sequence is c...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Example 3 Determination of telomere length using the Q-FISH method of genomic DNA.
[0086] 3.1 Determination of Telomere Length Using Genomic DNA Q-FISH
[0087] (1) Genomic DNA was extracted from primary human embryonic lung fibroblasts (WI38) and human breast cancer cells (MCF-7).
[0088] (2) 100 ng of genomic DNA extracted from the two cell lines and telomere length standards of different lengths (100 bp, 200 bp, 400 bp, 600 bp, 900 bp, 1.2 kb, 2.4 kb, 3.6 kb) were coated separately Heating at 75°C for 1 hour on a slide area with a diameter of 0.5 cm, then fixing in cold methanol at 0-4°C, and drying the slide to obtain a slide covered with DNA.
[0089] The telomere-specific PNA probe was then dissolved in hybridization buffer at a concentration of 0.3 μg / mL, coated on the above-mentioned DNA-coated slide, denatured at 75°C for 5 min, and incubated at 30°C for 3 h to complete After hybridization, wash three times with different concentrations of SSC at 42°C (1×S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com