Method of discriminating cancer and atypical cells and cell analyzer
An atypical cell and analyzer technology, applied in individual particle analysis, particle and sedimentation analysis, biochemical equipment and methods, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
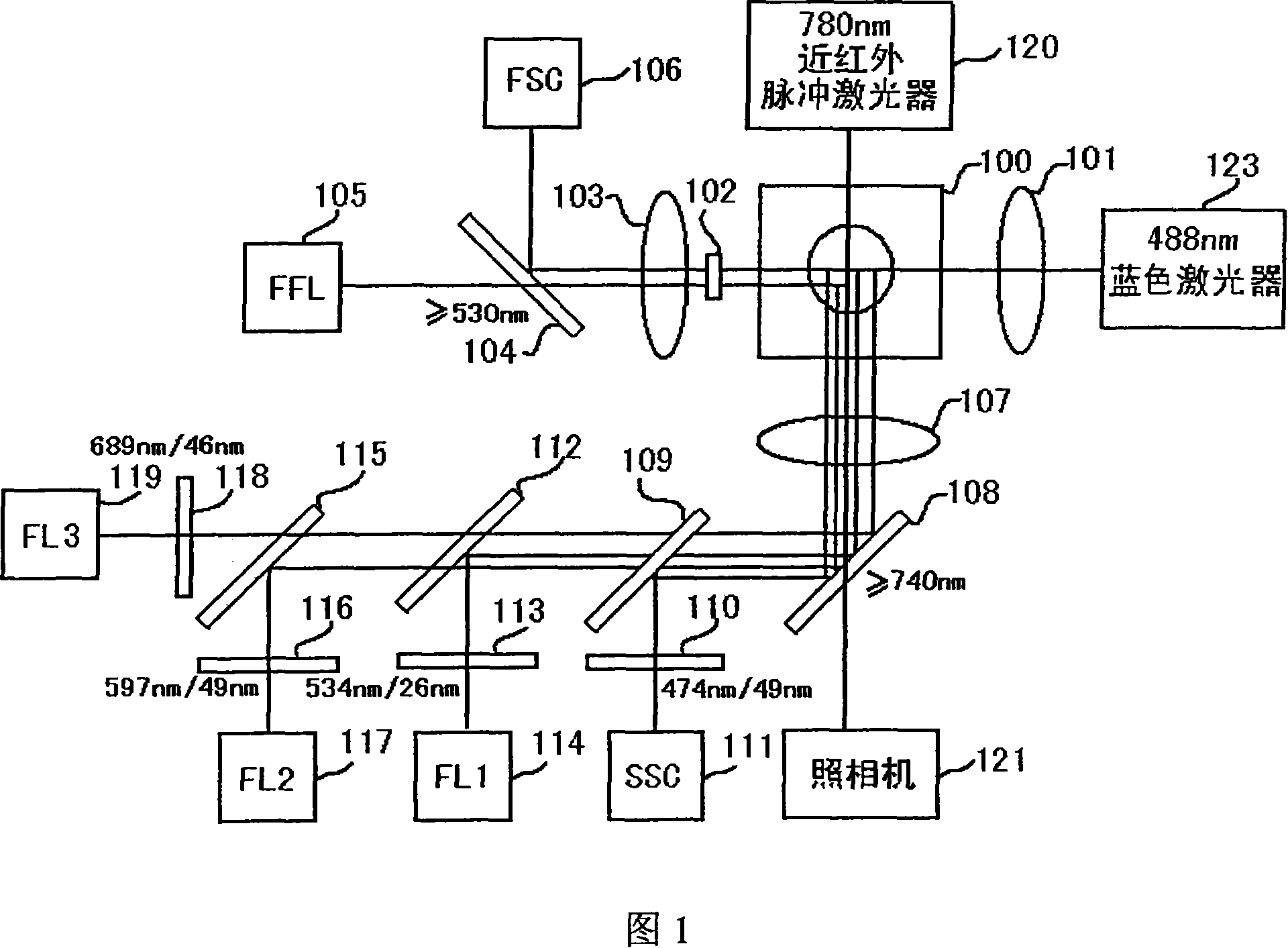
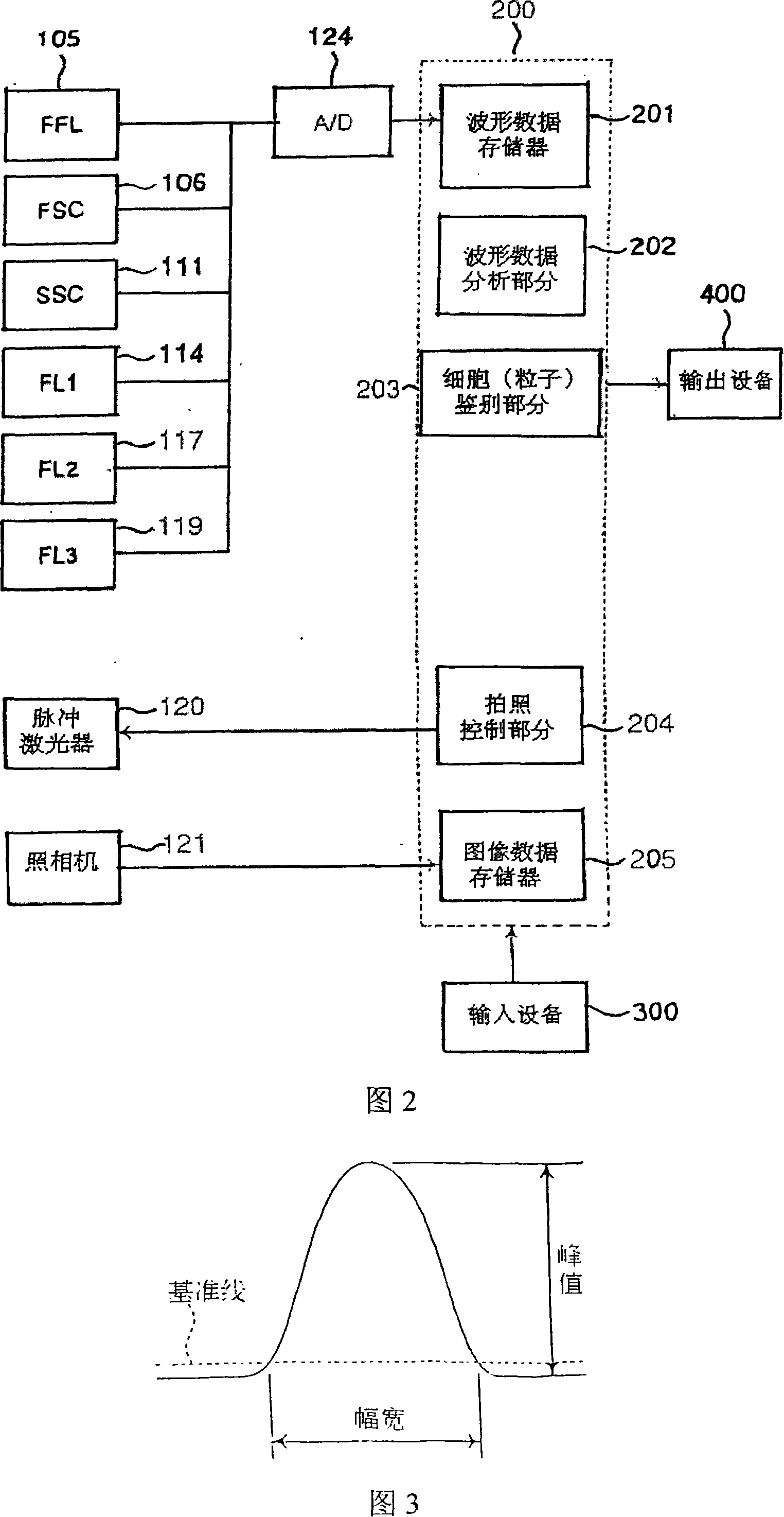
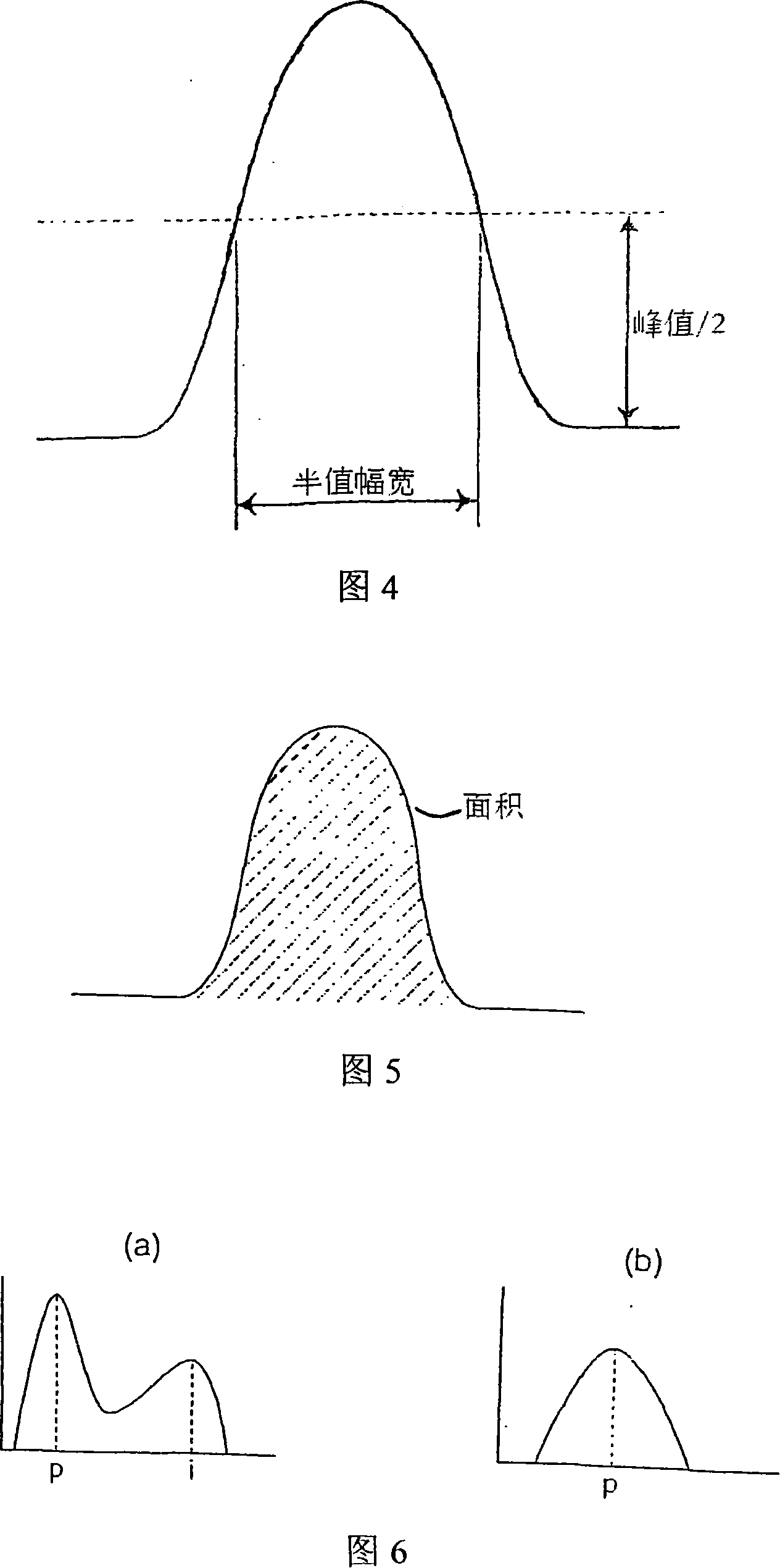
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0151] Cancer / abnormal cells are mixed with white blood cell mass, normal squamous epithelial cell mass, and normal squamous epithelial cell mass. Therefore, identifying single cells from cell mass is a prerequisite for distinguishing cancer / abnormal cells from other cells.
[0152] In order to measure the discrimination rate of the present invention in a simulated way, artificial particles, ie microbeads, were used to replace cells.
[0153] According to the procedure shown in Fig. 11, first about 12,000 single microbeads (latex particles) with a particle diameter of 9 μm were suspended in the reticulocyte sheath fluid (manufactured by Sysmex Co., Ltd.) to prepare a measurement sample (1). Next, about 12,000 single microbeads (latex particles) with a particle size of 5 μm that were naturally aggregated into agglomerates were suspended in reticulocyte sheath fluid (manufactured by Sysmex Co., Ltd.) to prepare measurement samples (2 ) (step S1). Each measurement sample is meas...
Embodiment 2
[0161] The following describes the case where cervical bit cells are used as clinical specimens for measurement.
[0162] First, as shown in step S1 of FIG. 11, a measurement sample is prepared in the following manner.
[0163] Clinical specimens (approximately 2×10 5 Cells / tube) were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 1 minute, 10% N-acetyl-L-cysteine PBS solution was added to the obtained particles, and then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 1 minute to obtain particles from which mucus was removed.
[0164] Add Zamboni fixative solution (0.2% 2,4,6-trinitrophenol, 2% paraformaldehyde) to this granule, after reacting for 10 minutes, centrifuge with 10000rpm speed for 1 minute, remove supernatant, add enzyme reaction solution ( PBS containing 0.2% type I collagenase, 0.2% type II collagenase, and 0.1% protease (manufactured by Sigma) was reacted at 37°C for 2 minutes and 30 seconds. After the reaction, an ice-cold 1% protease inhibitor (manufactured by Sigma) in PBS was added, cen...
Embodiment 3
[0177] The above-mentioned 10 kinds of characteristic parameters are calculated according to the signal waveform of the forward scattered light obtained during the test of the second embodiment, and the identification rate of these characteristic parameters in the following three aspects is investigated:
[0178] (1) Atypical cells and white blood cell clusters
[0179] (2) Atypical cells and squamous epithelial cells
[0180] (3) Atypical cells and squamous epithelial cell clusters. The discrimination threshold is set to an optimal value.
[0181] As a result, characteristic parameters with relatively high resolution obtained from the survival rate of each cell are shown in FIGS. 18 , 19 , and 20 , respectively.
[0182] That is, as shown in Figure 18 as the single characteristic parameter suitable for the discrimination of above-mentioned (1), it is B (difference integral value ÷ peak value), M (standard second-order moment) or J (waveform undulation); (2) The single char...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com