Novel acetylsalicylic acid formulations
A technology of acetylsalicylic acid and gastric acid inhibitors, applied in the field of novel acetylsalicylic acid preparations, which can solve the problems of harmful long-term use, large and long-lasting gastric mucosal damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
other Embodiment approach
[0052] Other embodiments relate to methods for treating a disease or condition caused by chronic COX, reducing the risk of a thrombotic cardiovascular event in a human patient in need of such treatment and at risk of a thrombotic cardiovascular event, and / or treating a thrombotic disease . The method comprises administering an oral pharmaceutical formulation of the present specification to a patient. The method prevents and / or treats pathological conditions associated with excess thromboxane, in particular cardiovascular diseases and risks. The method consists of oral administration of the pharmaceutical formulation of the invention, preferably once or twice a day.
[0053] The inventors found that surprisingly, they could selectively inhibit COX-1 in the portal vein, allowing minimal aspirin to enter the systemic circulation. This significantly increases patient comfort and drug safety. Patients did not have to discontinue aspirin therapy or switch to another drug. This a...
Embodiment 1
[0112]Example 1: Preparation of aspirin-based microcapsules for controlled release
[0113] 66 g ethylcellulose (Ethocel 7 Premium / Dow), 7 g Plasdone K29 / 32(R) (Povidone / ISP), 8 g castor oil, 9 g magnesium stearate and 10 g tartaric acid were dispersed in 60% isopropanol and 40 % of the acetone composition of the 1200g mixture. This suspension was sprayed onto 900 g of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) crystals pre-screened to 200 to 500 μm.
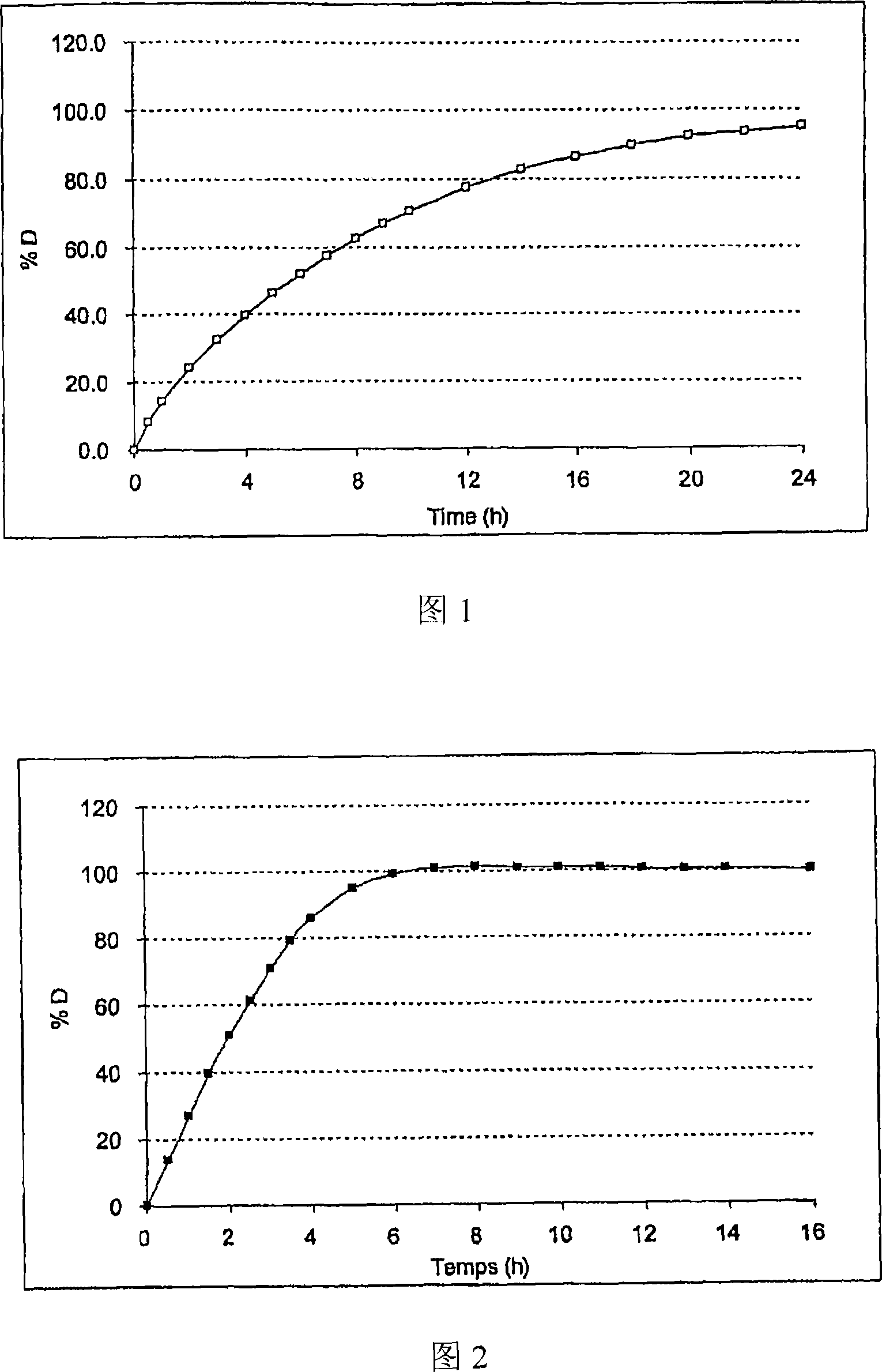
[0114] At pH6.8 (KH 2 PO 4 0.05M / NaOH), these microcapsules were tested under stirring with a stirring blade at a speed of 100 rpm (USP II equipment) in a dissolution medium maintained at 37°C (see Figure 1).
Embodiment 2
[0115] Example 2: Preparation of microcapsules based on omeprazole for controlled release
[0116] Step 1: Disperse 700 g of omeprazole and 100 g of Klucel EF(R) (Hydroxypropylcellulose / Aqualon) in 3000 g of isopropanol. The suspension was sprayed onto 200 g of neutral microspheres (Asahi-Kasei) in a spray coater Glatt GPCG 1 .
[0117] Step 2: 50 g ethylcellulose (Ethocel 20 Premium / Dow), 20 g Plasdone K29 / 32(R) (povidone / ISP), 20 g Lutrol F-68 (poloxamer 188 / BASF) and 10 g castor oil were dispersed in a in a mixture of 60% isopropanol and 40% acetone. This solution was sprayed onto 900 g of omeprazole granules (from step 1).
[0118] The microparticles obtained are filled into size 3 gelatin capsules. In this trial, the dose of omeprazole per capsule was 80 mg, ie 127 mg of microcapsules. At pH6.8 (KH 2 PO 4 0.05M / NaOH), these microcapsules were tested under stirring with a stirring blade at a speed of 100 rpm (USP II equipment) in a dissolution medium maintained at 3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com