Regulated expression of transgenes in the central nervous system of mammals
A technology of transgene and transcription factor, applied in the field of gene regulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
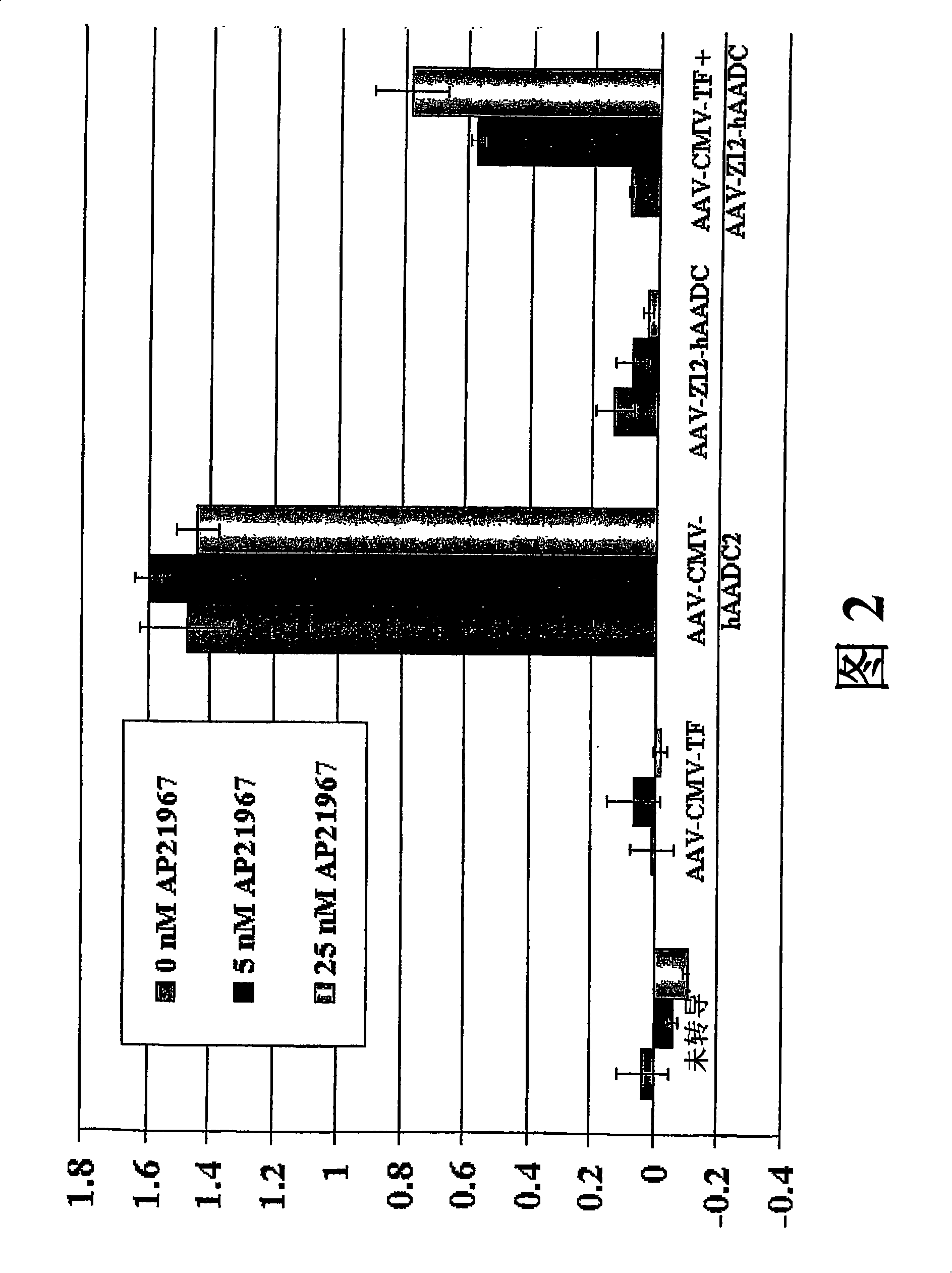
[0131] Regulatable expression of AADC in vitro
[0132] In vitro regulation of the AADC transgene was obtained as follows:
[0133] AAV vector
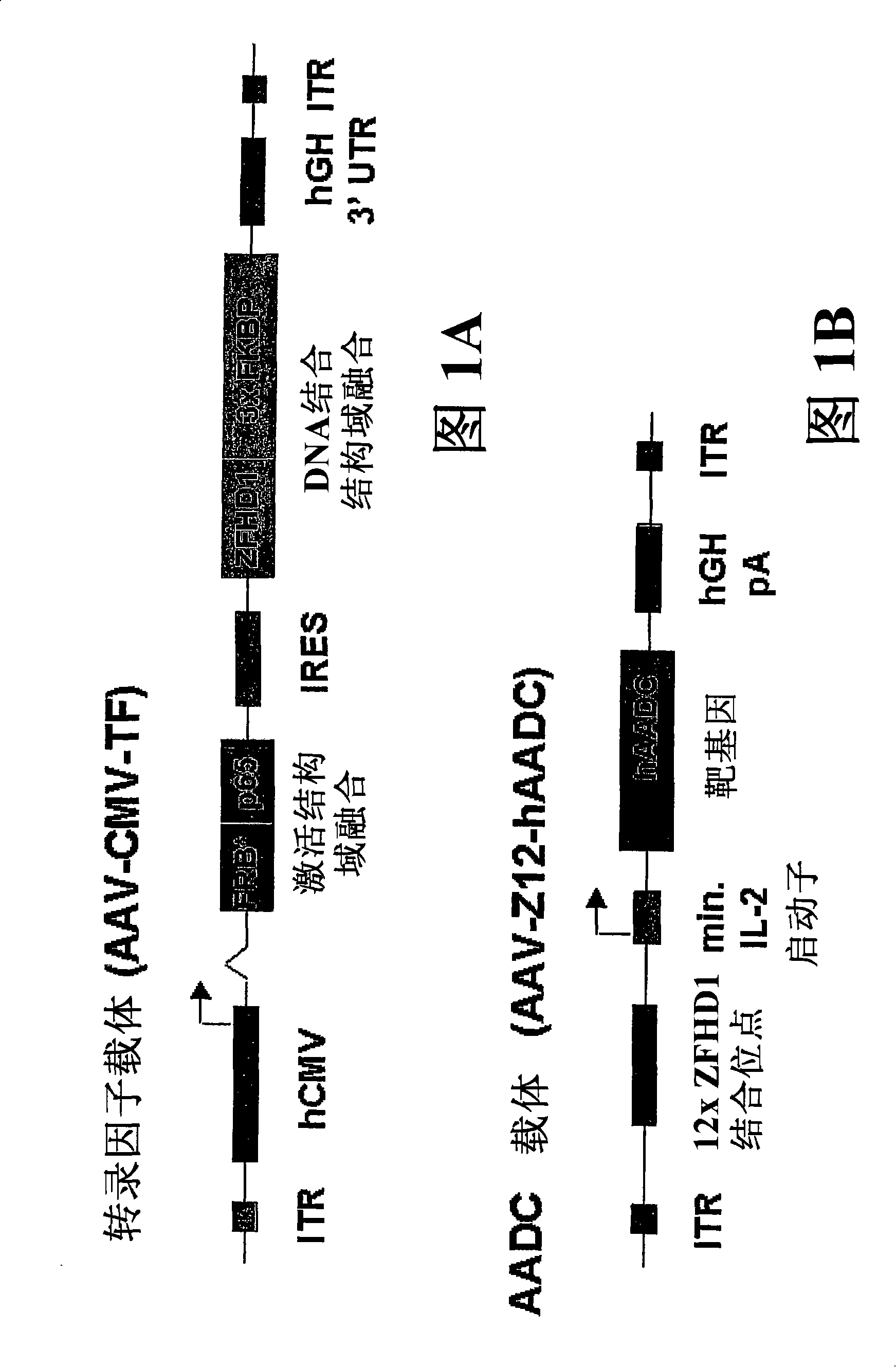
[0134] To obtain dimer-dependent expression of hAADC: AAV-CMV-TF and AAV-Z12-hAADC, two vectors were constructed. Figure 1A is a map of AAV-CMV-TF in which a cytomegalovirus (CMV) enhancer / promoter drives expression of a bicistronic message encoding an activation domain and DNA binding domain fusion protein. The activation domain fusion protein contains the human FRAP rapamycin binding domain (FRB * ), which is fused to the (p65) transcriptional activation domain derived from NFκB. The particular FRB domain used in this embodiment (FRB T2098L ) and the specific FRB domain (FRB * ) carries a T to L mutation at position 2098. Pollock et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 97:13221-26. FRB T2098L AP21967 or rapamycin can be used to dimerize to DNA-binding domain fusions.
[0135] The internal ribosome entry sequence (IRES) is d...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Tunable expression of AADC in vivo
[0148] In vivo assays were also used in the 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) rat model of Parkinson's disease to demonstrate AAV-mediated transduction of dimer-regulated hAADCs in vitro (Example 1, Figures 1A and 1B) The same vector, as follows. In Example 2, rapamycin was used instead of AP21667 as the dimer because of its higher potency and known pharmacokinetics. In the body, rapamycin has a half-life of approximately 10 hours and is rapidly cleared. Gallant-Haidner et al. (2000) Ther. Drug Monit. 22:31-5.
[0149] All rats used in this example had unilateral 6-OHDA lesions on the left side. There were three test groups: vehicle-infused control group (vehicle-infused (+) rapamycin-treated), vehicle-infused (-) rapamycin-treated control group and vehicle-infused (+) rapamycin-treated group . The vector infused (-) rapamycin group serves to control hAADC gene expression in the absence of rapamycin, ie, to determine if the system is l...
Embodiment 3
[0187] In vitro regulated expression of GDNF
[0188] Mammalian cells were transduced with dimer-regulatable GDNF transgene constructs, as follows.
[0189] AAV-GDNF vector
[0190] Figures 8A and 8B are diagrams of recombinant AAV vector plasmid constructs for delivery of the human GDNF (hGDNF) transgene. A control vector for delivery of constitutively expressed hGDNF (pAAV-CMV-hGDNF) is shown in Figure 8C middle.
[0191] Regulatable constructs (Figures 8A and 8B) consisted of a single rAAV vector carrying the activation domain fusion protein and DNA binding domain fusion protein components encoding the hGDNF gene and transcription factors. In both constructs, expression of hGDNF was driven by a minimal IL-2 promoter adjacent to the binding site for eight transcription factors for dimerization, described in more detail below.
[0192] In the construct (pPAAV-TF-Z8-hGDNF) illustrated in Figure 8A, the CMV enhancer / promoter drives the expression of a single transcript enc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com