Method for recognition of bump-scrape fault of rotor
A fault identification and rotor technology, applied in special data processing applications, complex mathematical operations, measurement devices, etc., can solve problems such as overlapping decomposition frequency bands, achieve improved accuracy, fast calculation speed, and solve the second generation wavelet decomposition frequency band Effects of overlapping problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
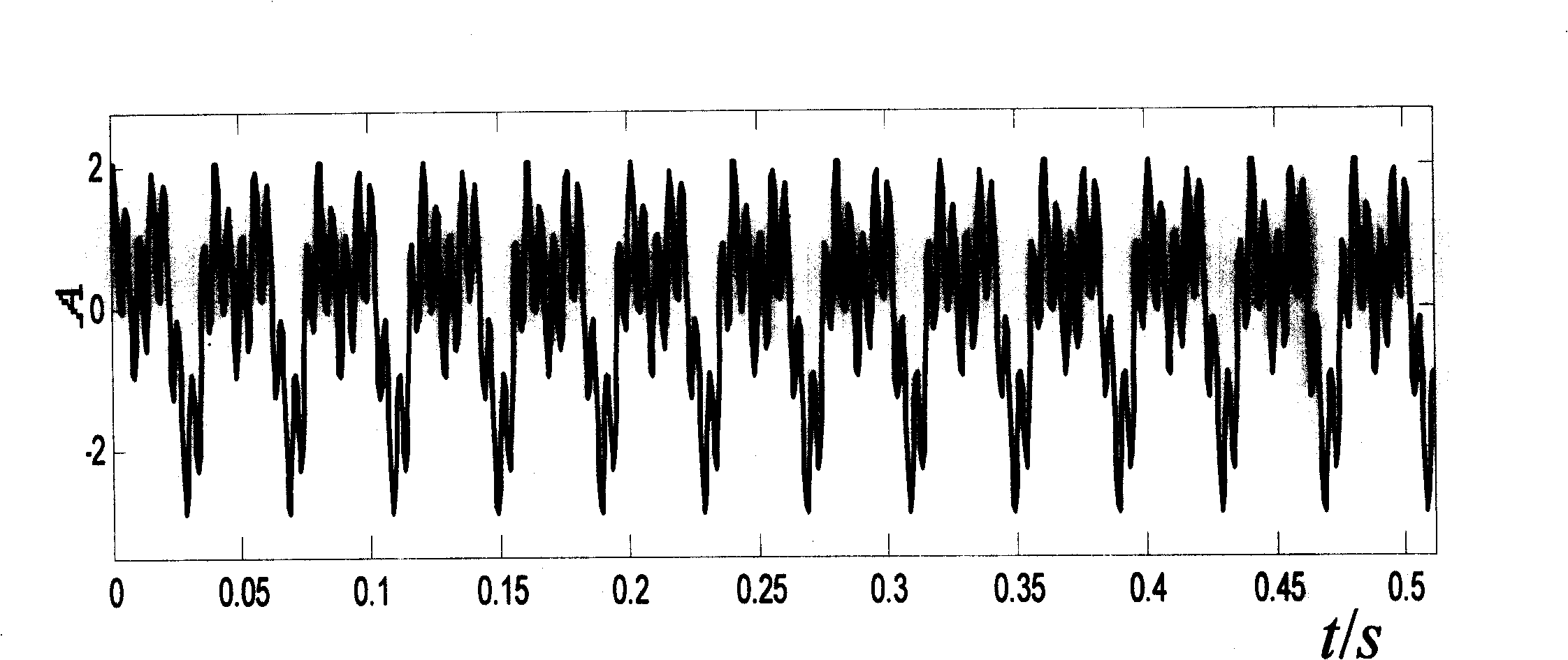
[0039] This embodiment mainly simulates and verifies the correctness of the method of the present invention to decompose the frequency band separation signal, and constructs a simulation signal x(t) composed of three harmonics to simulate the fundamental frequency and its multiple of the vibration signal when a rubbing fault occurs in the rotor system. Frequency components:
[0040] x(t)=sin(2πf 1 t)+sin(2πf 2 t+0.5π)+sin(2πf 3 t)
[0041] The frequencies of the harmonic signal components in x(t) are respectively f 1 = 25Hz, f 2 = 50Hz, f 3 = 200Hz. X(t) is discretized and sampled with a sampling frequency of 2000Hz, and the data length is 1024.
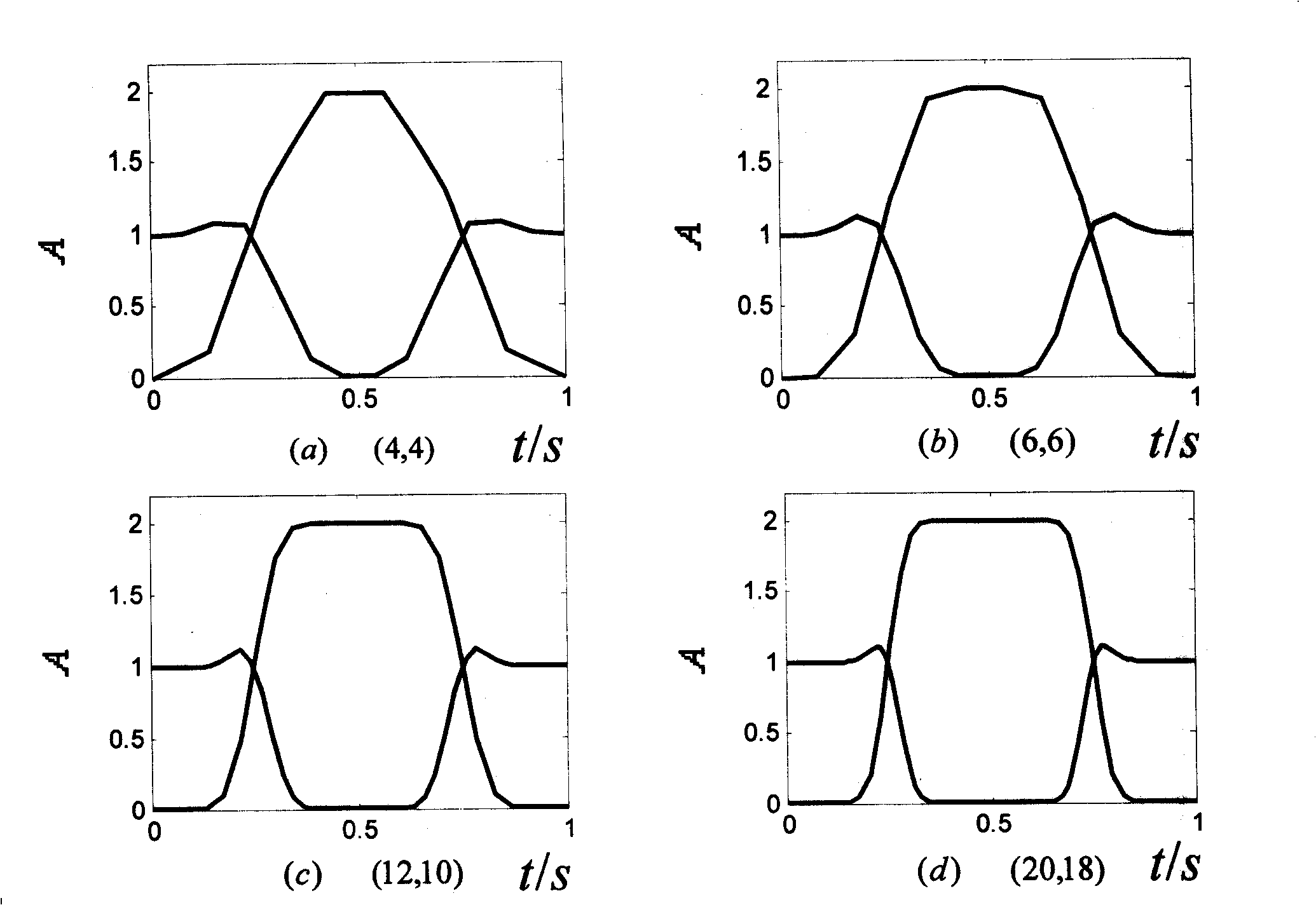
[0042] Step 1: Calculate the second-generation wavelet predictor and updater
[0043] The second generation wavelet predictor P=[p(1), p(2), p(3), ..., p(N)] and updater U = [ u ( 1 ) , u ( ...
Embodiment 2
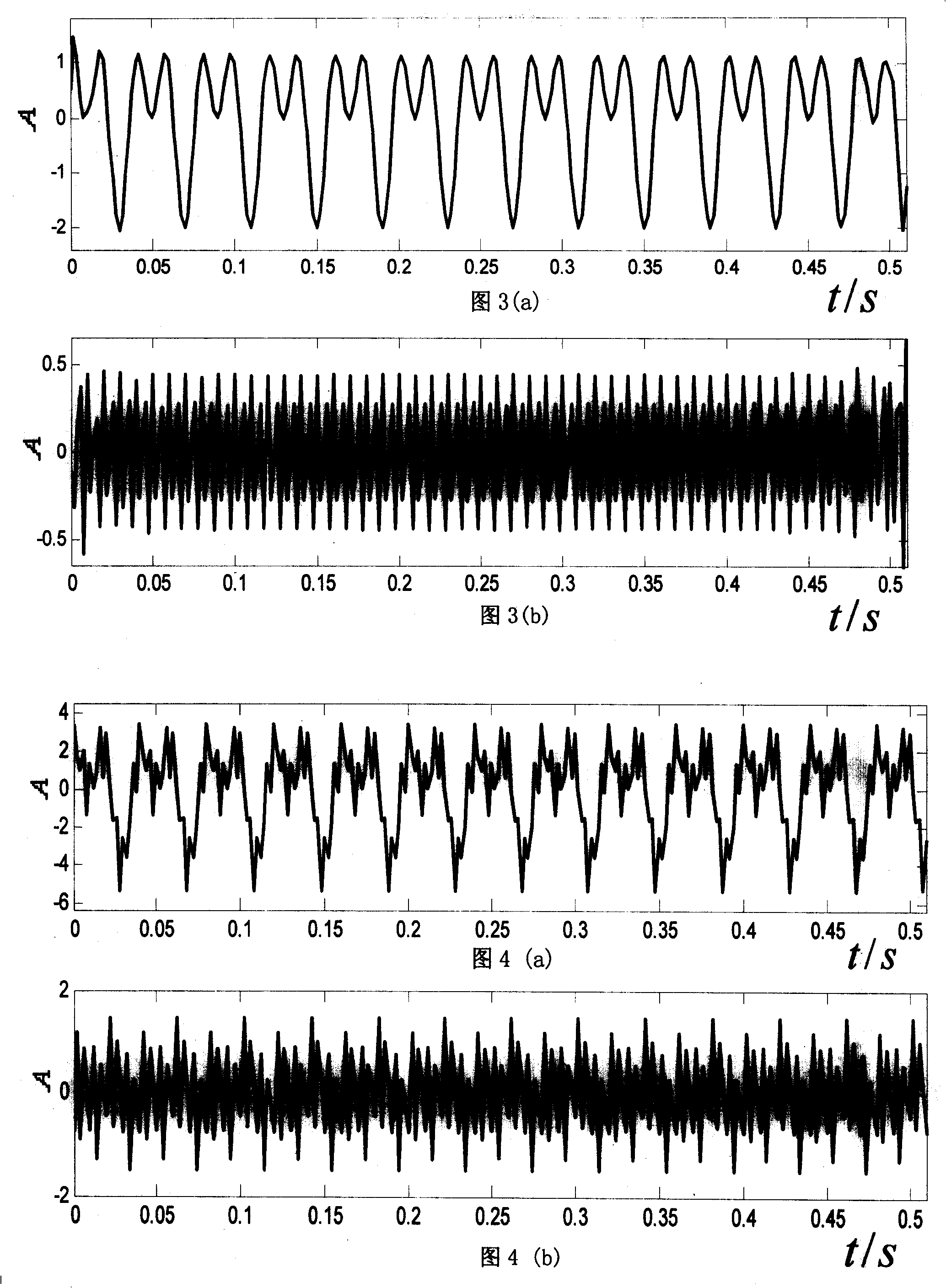
[0081] This embodiment mainly verifies the correctness of engineering fault diagnosis of the method of the present invention. A 50MW turbogenerator set in a thermal power plant consists of a high-pressure cylinder, a low-pressure cylinder, a generator and an exciter. The rated speed of the unit is 3046.8r / min, that is, the power frequency is 50.78Hz. After the unit was overhauled once, it was found that the bearing bush of the high-pressure cylinder vibrated a lot when it was put into operation. In order to find out the cause of the failure, the vibration signal is collected at a sampling frequency of 2000Hz in the vertical direction of the bearing bush of the high-pressure cylinder 2#, and the data length is 1024.
[0082] Step 1: Calculate the second-generation wavelet predictor and updater
[0083] The second generation wavelet predictor P=[p(1), p(2), p(3), ..., p(N)] and updater U = [ u ( 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com