Neodymium iron boron permanent magnetic material using zirconium to substitute niobium
A permanent magnet material, neodymium iron boron technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the cost of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
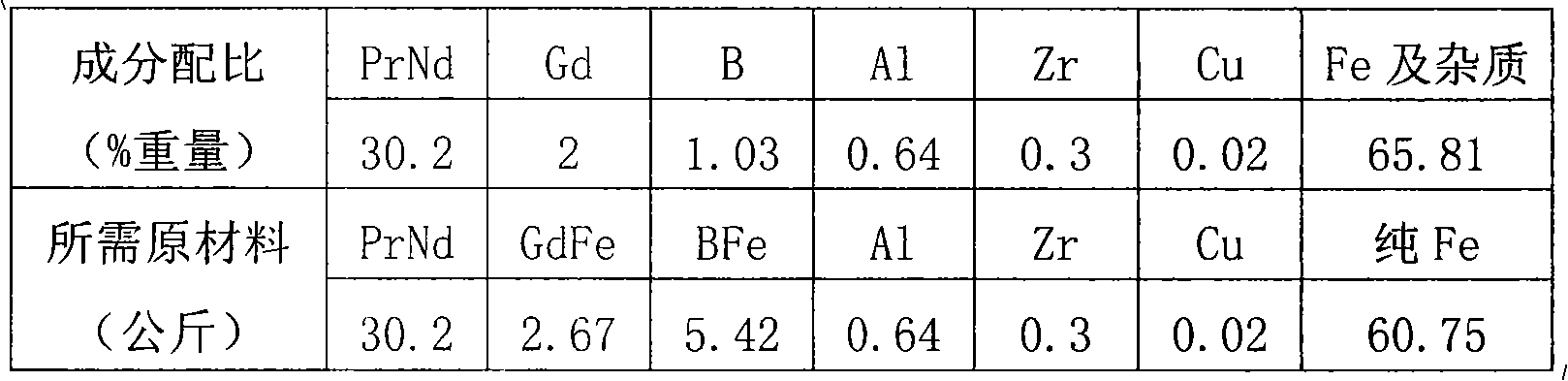
[0008] Ingredients: according to the following composition ratio weight ingredients, praseodymium neodymium alloy 30.2% by weight, gadolinium 2.0% by weight, boron element 1.03% by weight, aluminum 0.64% by weight, zirconium 0.3% by weight, copper 0.02% by weight, the balance is iron and other impurities , wherein in the praseodymium neodymium alloy, praseodymium accounts for 25% by weight, neodymium accounts for 75% by weight, boron element is added in the state of BFe alloy, the boron content is 19%, and the iron content is 81%; Gadolinium element is added in the state of GdFe alloy, and the content of gadolinium is 75%, iron content is 25%;
[0009] Take smelting 100 kg NdFeB alloy as an example:
[0010]
[0011] The metal raw materials described in the above table are loaded into the vacuum induction furnace.
[0012] Melting and casting: After loading into the vacuum induction furnace, evacuate the air in the vacuum induction furnace to less than 1Pa, start heating a...
Embodiment 2
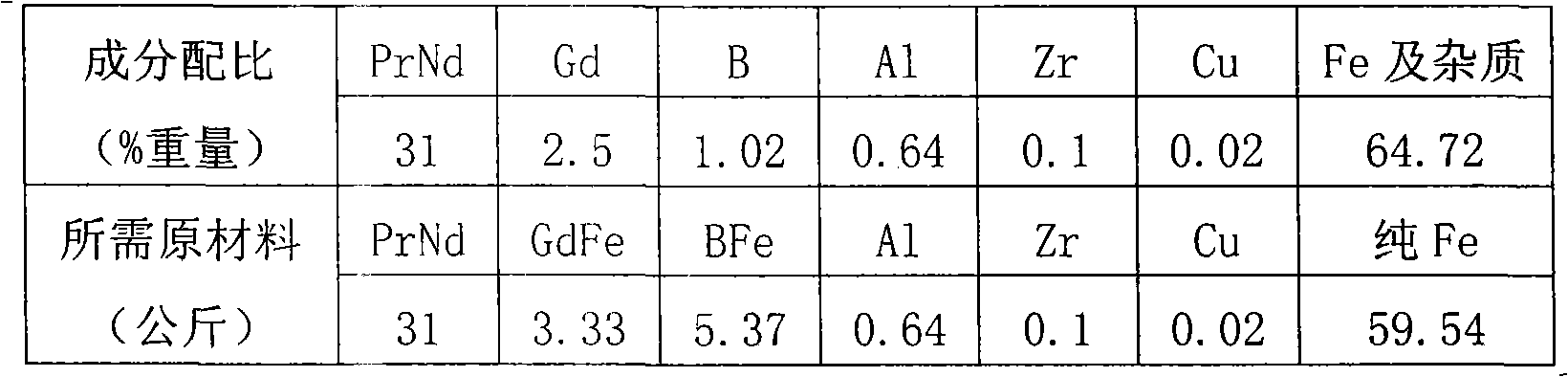
[0028] Ingredients: according to the following weight ratio ingredients, praseodymium neodymium alloy 31% by weight, gadolinium 2.5% by weight, boron 1.02% by weight, aluminum 0.64% by weight, zirconium 0.1% by weight, copper 0.02% by weight, and the balance is iron and other impurities , wherein in the praseodymium-neodymium alloy, praseodymium is 25% by weight, and neodymium is 75% by weight; boron element is added in the state of BFe alloy, and the boron content is 19%, and the iron content is 81%; gadolinium element is added in the state of GdFe alloy, and the content of gadolinium is 75%, iron content is 25%;
[0029] Take smelting 100 kg NdFeB alloy as an example:
[0030]
[0031] Put the metal raw materials described in the above table into the vacuum induction furnace;
[0032] Melting and casting: After loading into the vacuum induction furnace, evacuate the air in the vacuum induction furnace to less than 1Pa, start heating and melting, when the ingredients in t...
Embodiment 3
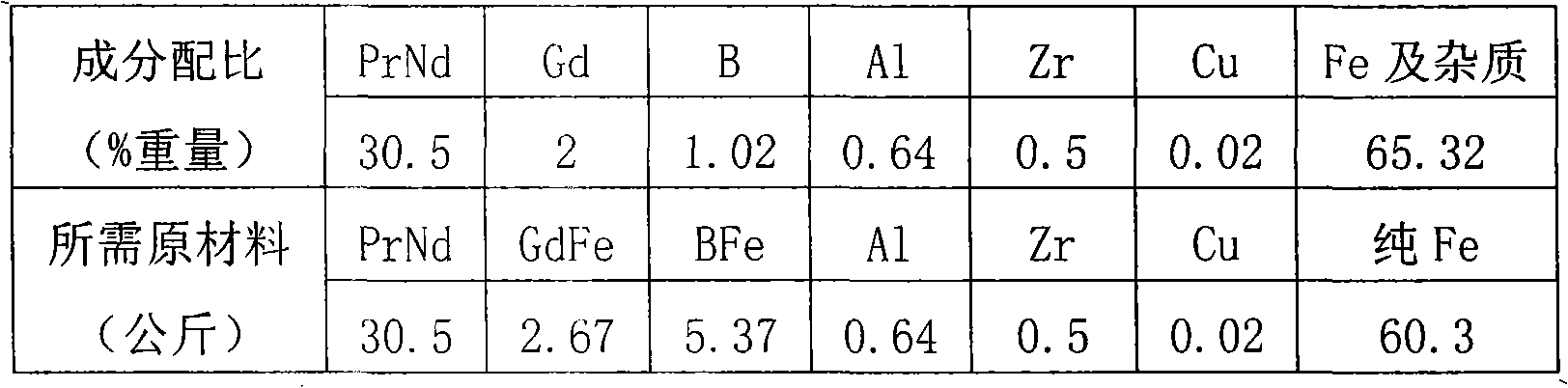
[0048] Ingredients: according to the following composition ratio weight ingredients, praseodymium neodymium alloy 30.5% by weight, gadolinium 2% by weight, boron element 1.02% by weight, aluminum 0.64% by weight, zirconium 0.5% by weight, copper 0.02% by weight, the balance is iron and other impurities , wherein in the praseodymium neodymium alloy, praseodymium is 25% by weight, neodymium is 75% by weight, boron element is added in BFe alloy state, boron content is 19%, iron content is 81%; Gadolinium element is added in GdFe alloy state, gadolinium content is 75% with 25% iron content;
[0049] Take the smelting of 100 kg NdFeB alloy as an example:
[0050]
[0051] Put the metal raw materials described in the above table into the vacuum induction furnace;
[0052] Melting and casting: After loading into the vacuum induction furnace, evacuate the air in the vacuum induction furnace to less than 1Pa, start heating and melting, when the ingredients in the furnace turn red, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic coercive force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic induction coercive force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic energy product | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com