Composite material and preparation thereof
A technology of composite materials and manufacturing methods, applied in the field of high-corrosion-resistant chemical conversion coatings, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining and expanding uses, harm to the human body, use restrictions or prohibitions, etc., to achieve efficient manufacturing, high corrosion resistance and resistance to discoloration permanent, easy-to-manufacture effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
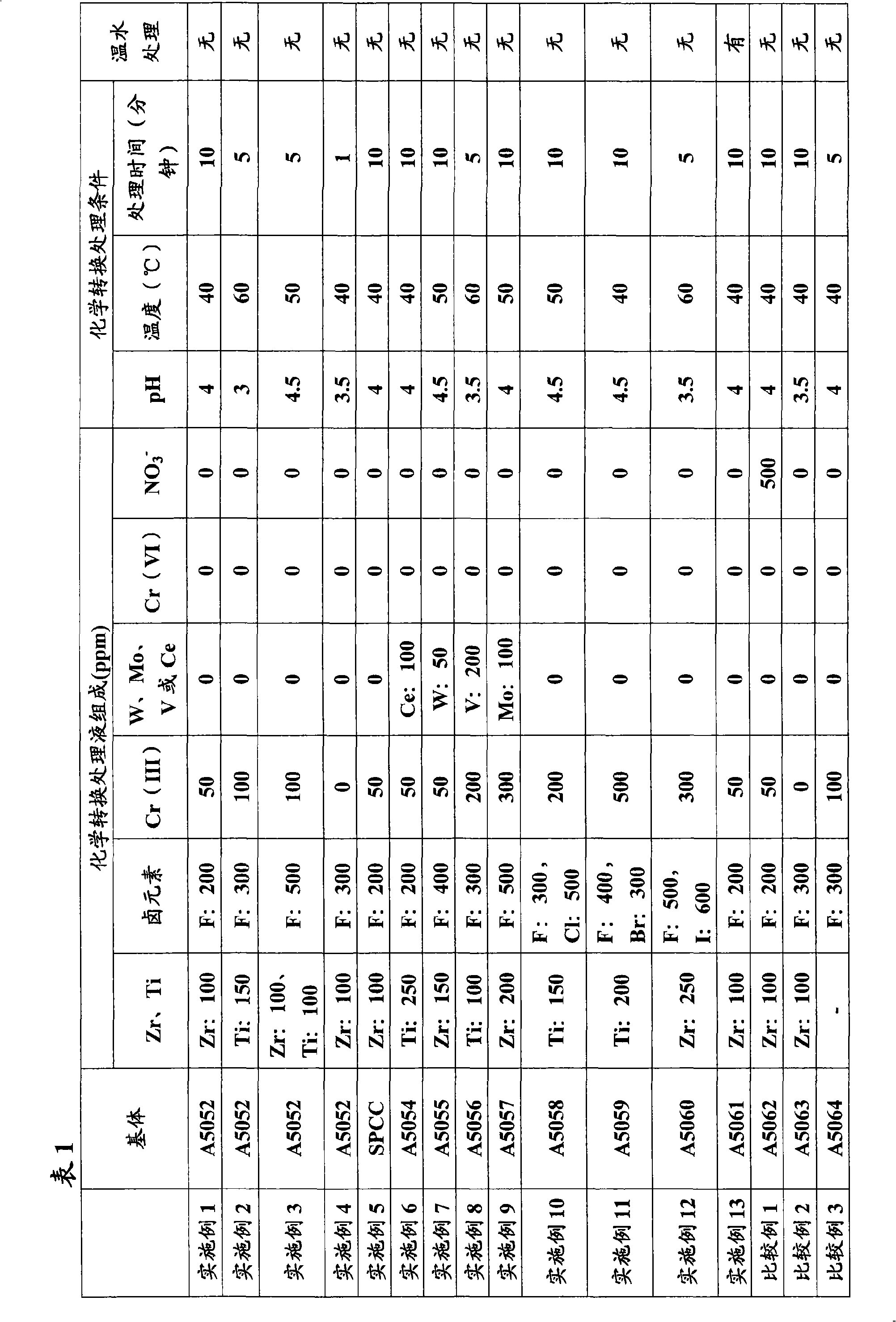
[0108] The above-mentioned nickel-phosphorus alloy plating A5052 material (thickness: 0.5 mm) was used as a base material. Prepared: containing fluozirconic acid as a component containing a main metal element, containing hydrofluoric acid as a component containing a halogen element, and containing chromium (III) fluoride as a component containing the first additional element, not containing nitrate ions, the pH Adjust to 4, adjust the temperature to 40° C., and have the chemical conversion treatment liquid having the composition shown in Table 1.
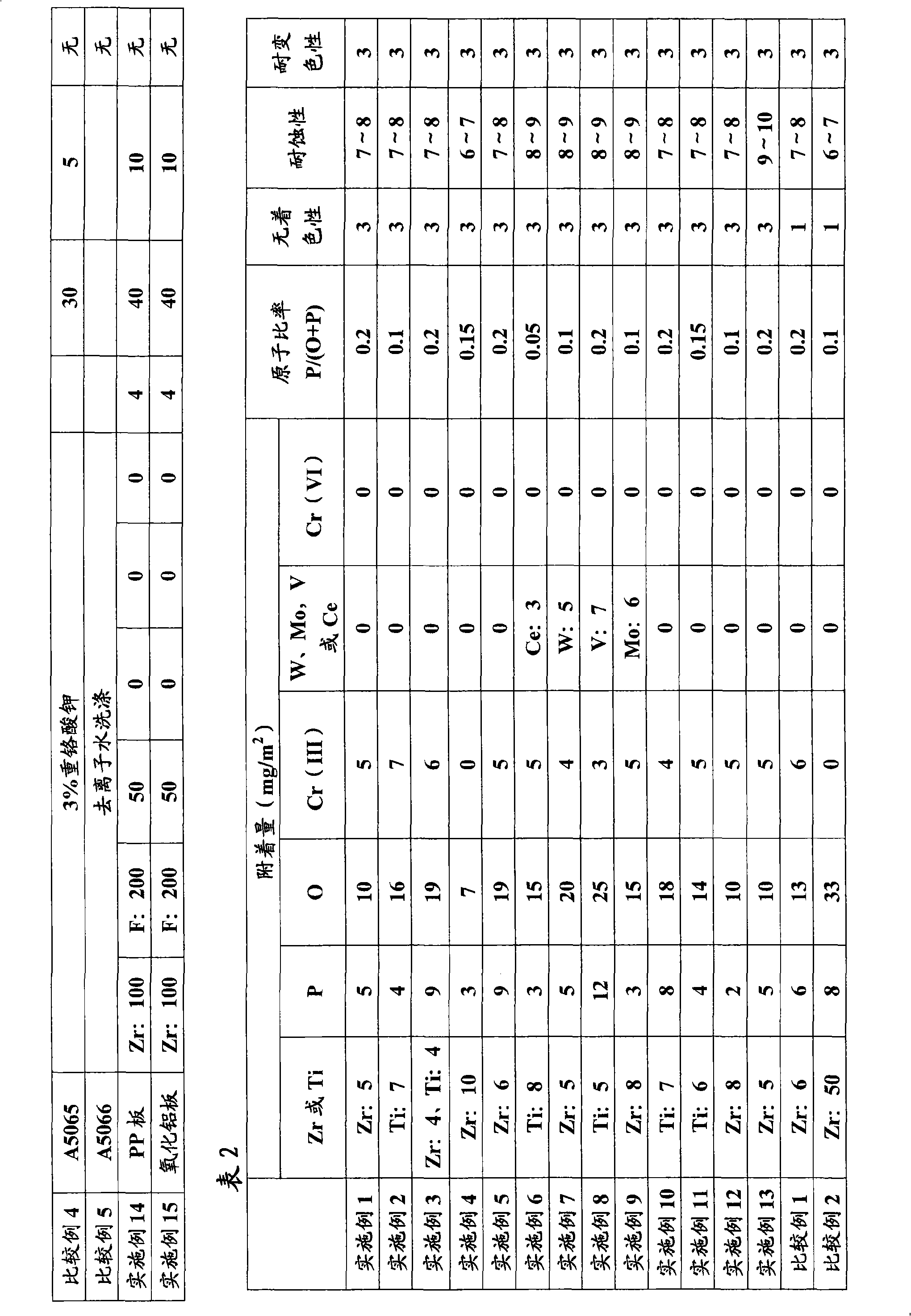
[0109] Immerse the above-mentioned base material in the above-mentioned chemical conversion treatment solution for 10 minutes, then take out the obtained composite metal material after chemical conversion treatment, wash with deionized water, and dry at a temperature of 120°C for 10 minutes . No warm water treatment. The analysis and evaluation results are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 2
[0111] In the same manner as in Example 1, a composite material was manufactured, analyzed and evaluated. However, as shown in Table 1, the chemical conversion treatment liquid and treatment conditions were changed.
[0112] That is, in the chemical conversion treatment liquid, fluotitanic acid was used as the main metal element-containing component, the Ti concentration was changed to 150 ppm, the amount of hydrofluoric acid used was changed so that the F concentration was 300 ppm, and the concentration of chromium (III) fluoride was changed. The amount used was such that the Cr(III) concentration was 100 ppm, the pH of the chemical conversion treatment solution was changed to 3, the treatment temperature was changed to 60° C., and the treatment time was changed to 5 minutes.
[0113] The analysis and evaluation results are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0115] Composite materials were produced in the same manner as in Example 1, and analyzed and evaluated. However, as described in Table 1, the composition and treatment conditions of the chemical conversion treatment liquid were changed.
[0116] That is, using fluozirconic acid as the main metal element-containing component, changing its usage amount so that the Zr concentration is 100ppm, and adding fluotitanic acid and adjusting the usage amount so that the Ti concentration is 100ppm, using hydrofluoric acid as the halogen-containing The composition of the elements was changed so that the concentration of F was 500ppm. Chromium (III) fluoride was used as a component containing the first additional element, and the quantity was changed so that the concentration of Cr(III) was 100ppm. The pH was changed to 4.5, the treatment temperature was changed to 50° C., and the treatment time was changed to 5 minutes.
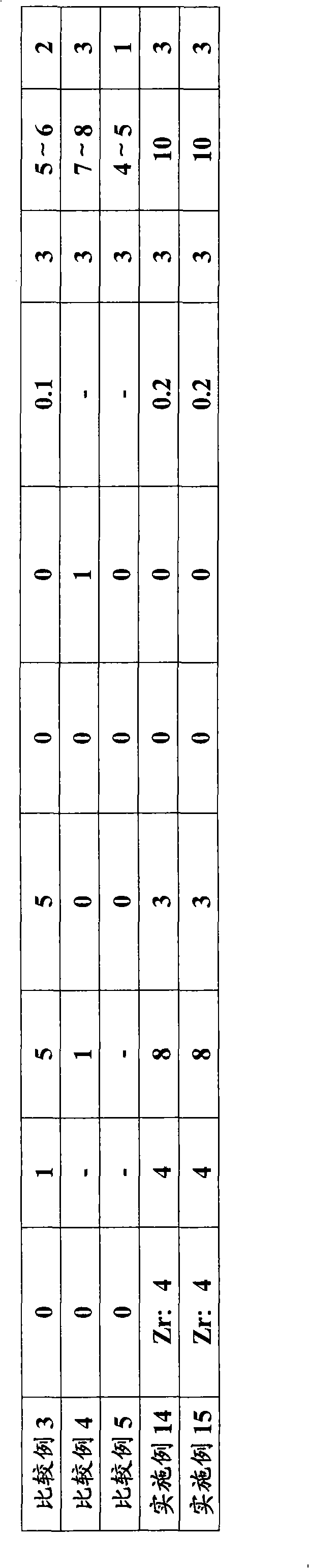
[0117] The analysis and evaluation results are shown in Table 2. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com