Microfluidic control chip for cell immobilization and solution dilution
A technology of solution dilution and cell fixation, which is applied in the fields of bioengineering and analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of difficult design and not many uses, and achieve the effects of being conducive to popularization, low cost, and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
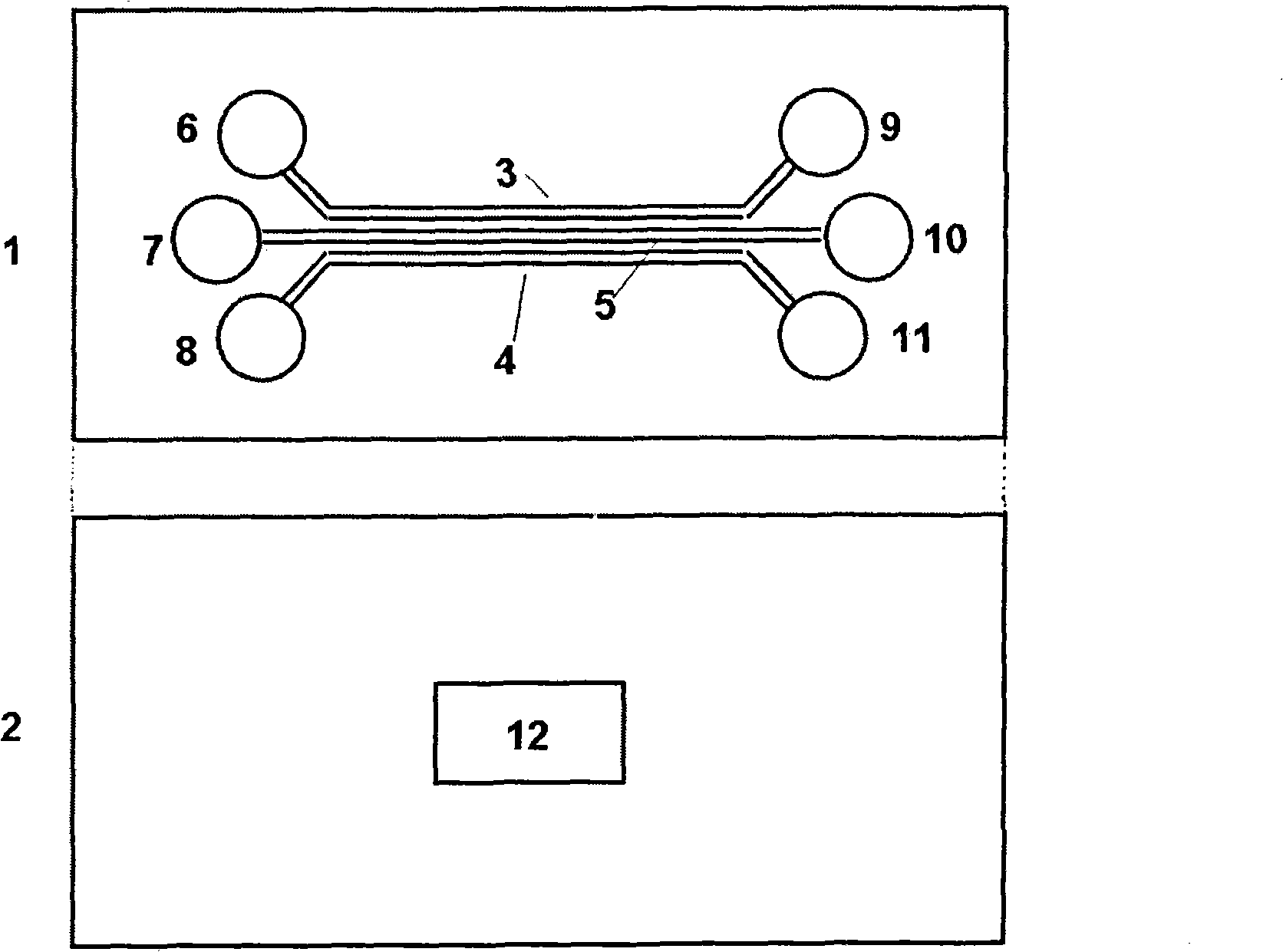
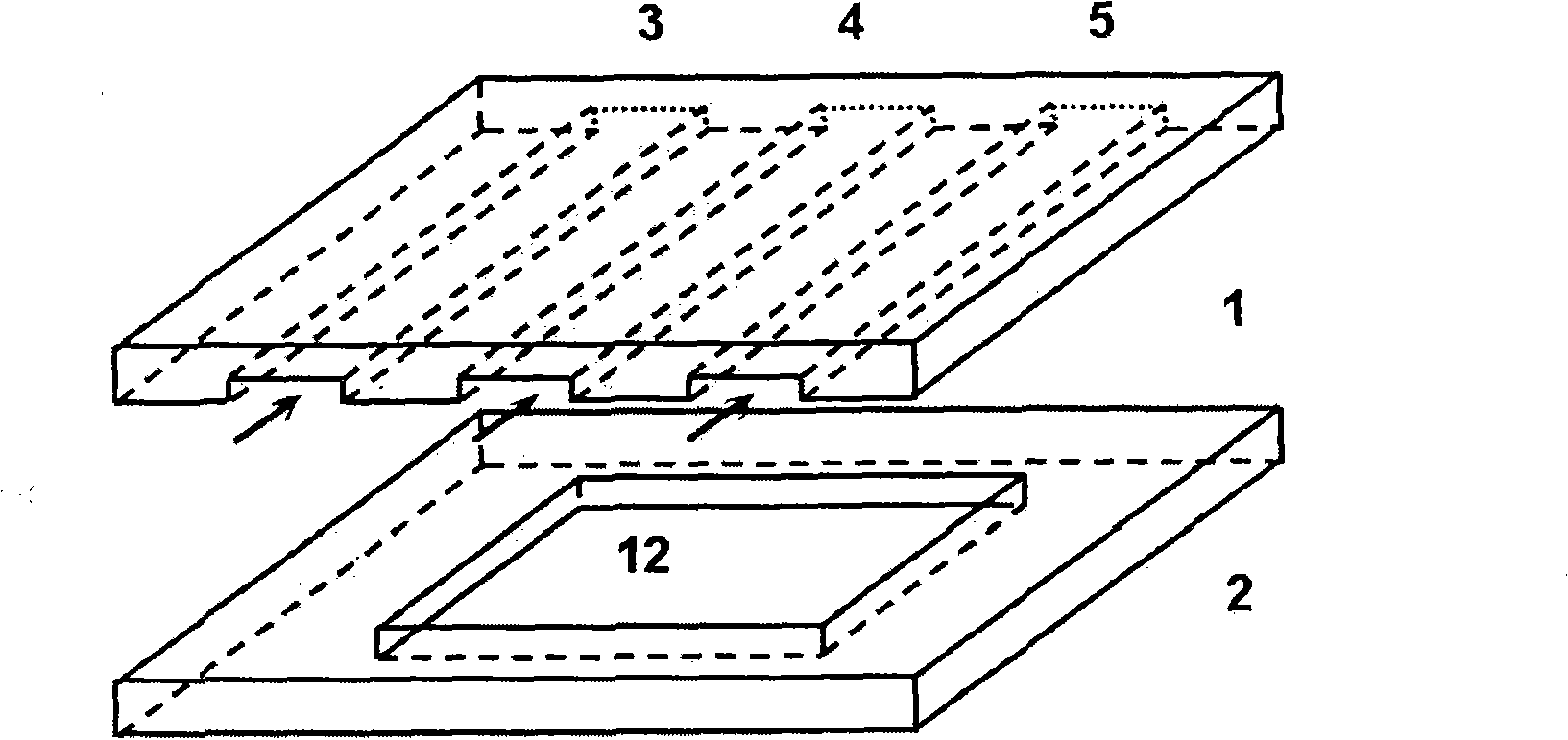
[0026] see figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 , The microfluidic chip is composed of two layers, the first layer is a transparent hard base layer 1 made of glass, and the second layer is a transparent elastic rubber layer 2 made of PDMS. One side of the transparent hard base layer 1 is processed with three parallel microchannels 3, 4, 5, and there are sample inlets 6, 7, 8 and sample outlets 9, 10, 11 at both ends of the microchannels. Driven by the micropump, the sample liquid can enter the microchannel from the sample inlet 6, 7, 8, and then flow out from the sample outlet 9, 10, 11. One side of the transparent elastic rubber layer 2 is processed with cuboid-shaped grooves to form a micro-water pool 12. The length and width of the micro-water pool 12 are different according to different application purposes. Before combining, treat the transparent elastic rubber layer 2 with oxygen plasma for 30 seconds, and then place it horizontally with the micro-water pool 12 facing up...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: Immobilizing cells using micro-pool chip structure
[0029] The human promyelocytic leukemia cell HL 60 suspension was respectively added from the injection ports 6, 7, and 8 of the chip described in Example 1, and a pressure of 40 Pa was applied to the injection ports by a micropump, and the outlet pressure was 0.
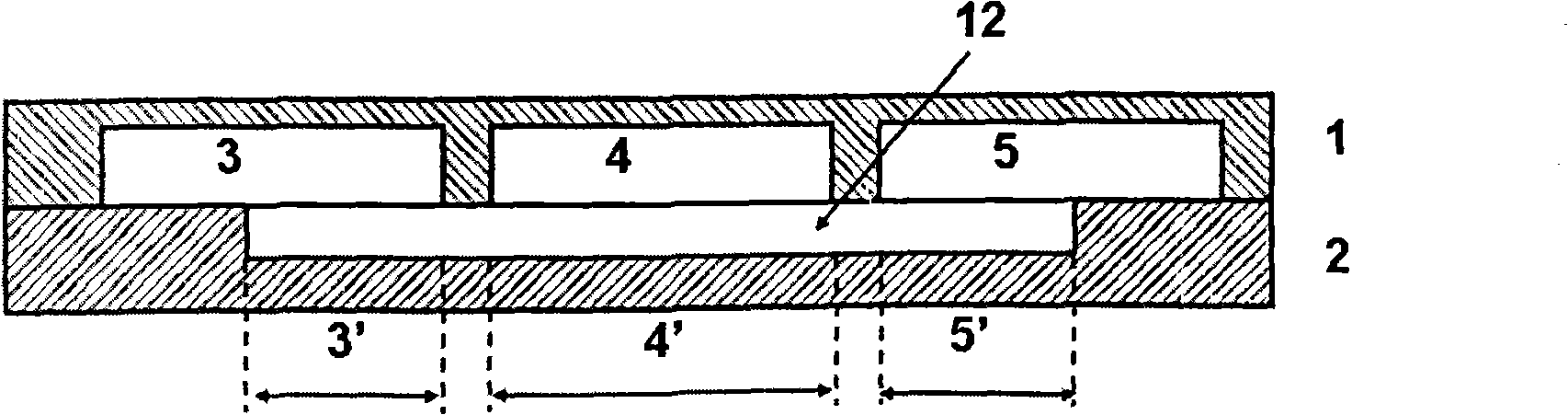
[0030] When the transparent elastic rubber layer 2 is combined with the transparent hard base layer 1, the symmetrical midline of the micro-water pool 12 coincides with the symmetrical midline of the middle microchannel 4. When the width of the micro-water pool 12 is greater than or equal to 340 μm (the width of 3 micro-channels adds the interval between them), after the liquid from the micro-channels 3, 4, 5 is full of the micro-water pool 12, there is no liquid to flow in or out. Micro-basin 12, therefore, there is also no lateral flow through micro-basin 12 and immobilization of cells, as shown in FIGS. 4A and 4B of FIG. 4 .
[0031]As shown ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: Utilize this chip to carry out solution mixing
[0034] In a microfluidic system, the flow of liquid is mainly laminar flow, and material diffusion is the main mixing mode. The degree of mixing is directly proportional to the diffusion coefficient and diffusion (residence) time of the substance, and inversely proportional to the diffusion distance, and the mixing speed is also inversely proportional to the diffusion distance.
[0035] In the solution dilution experiment, the fluorescent ethidium bromide solution is added from the chip inlet 4, and three-distilled water is added from the inlet 3 and 5. Under the pressure, different solutions flow from the inlet to the outlet. The flow and diffusion of ethidium bromide molecules in the microchannel can be obtained by laser confocal microscope detection.
[0036] Where the microchannels 3 , 4 , 5 contact the micro-water pool 12 , liquid can enter the micro-water pool 12 . Fluids from different microchannels...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com