Embedded system real time task scheduling method
An embedded system and real-time task technology, applied in the direction of multi-programming devices, sustainable buildings, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems that cannot be clarified, and there is no combination of system real-time performance, so as to reduce demand and improve flexibility The effect of stability and delay stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
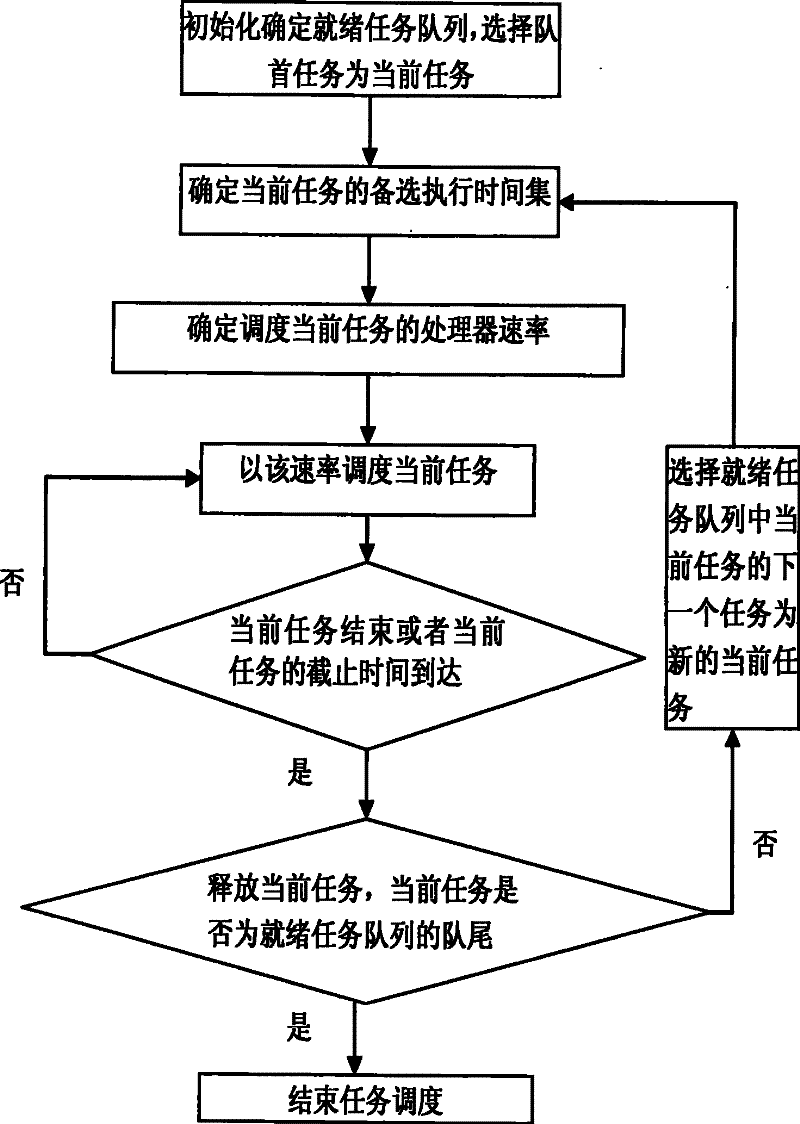
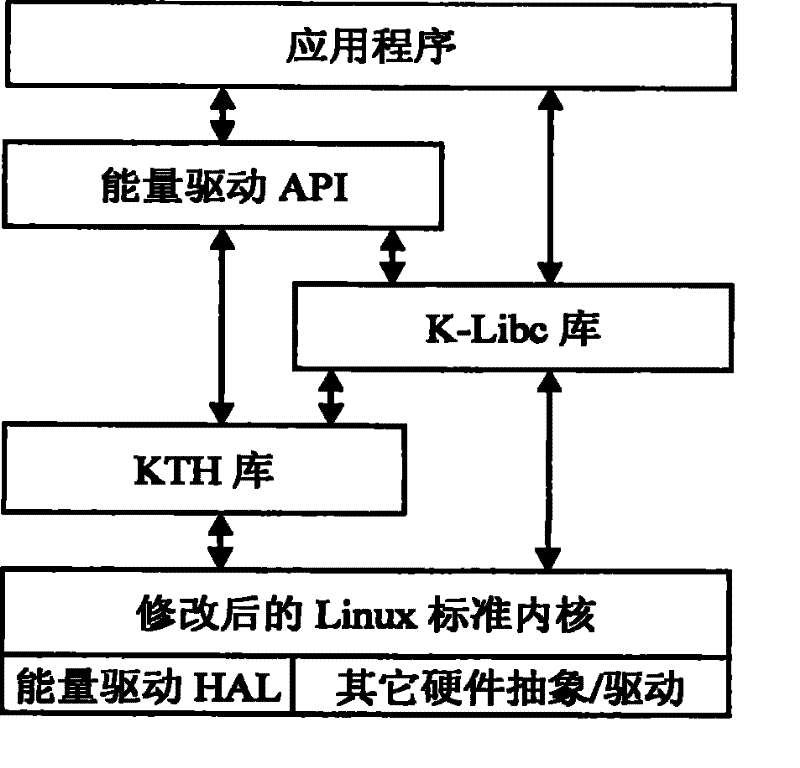
[0027] The method proposed by the present invention is a part of the embedded real-time operating system kernel. Below, the embedded real-time operating system Embsys KLinux based on the hardware platform environment of the AMD Athlon4 processor is an example to illustrate the implementation of the task scheduling method of the present invention.
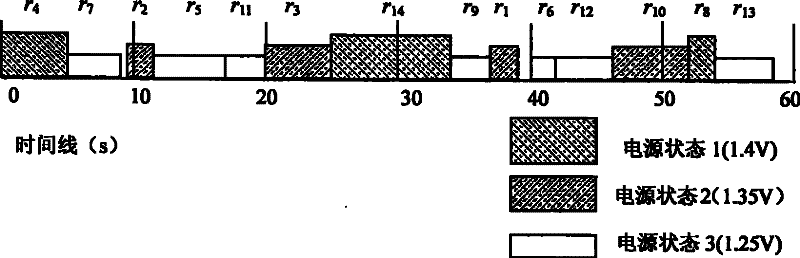
[0028] AMD's PowerNow! The technology uses segmented low frequency and low voltage, which can provide variable processor operating speed and greatly improve the efficiency of energy utilization. The hardware platform adopts the 1.1GHz AMD mobile Athlon4 processor, and its core voltage can be continuously changed in increments of 0.05V within the range of 1.2V to 1.4V. There is a predetermined maximum clock frequency for each core voltage, although lower clock frequencies can be used. Table 1 shows the setting of the power state of the Athlon4 processor. In this embodiment, the power state and voltage settings shown in Table 1 are ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com