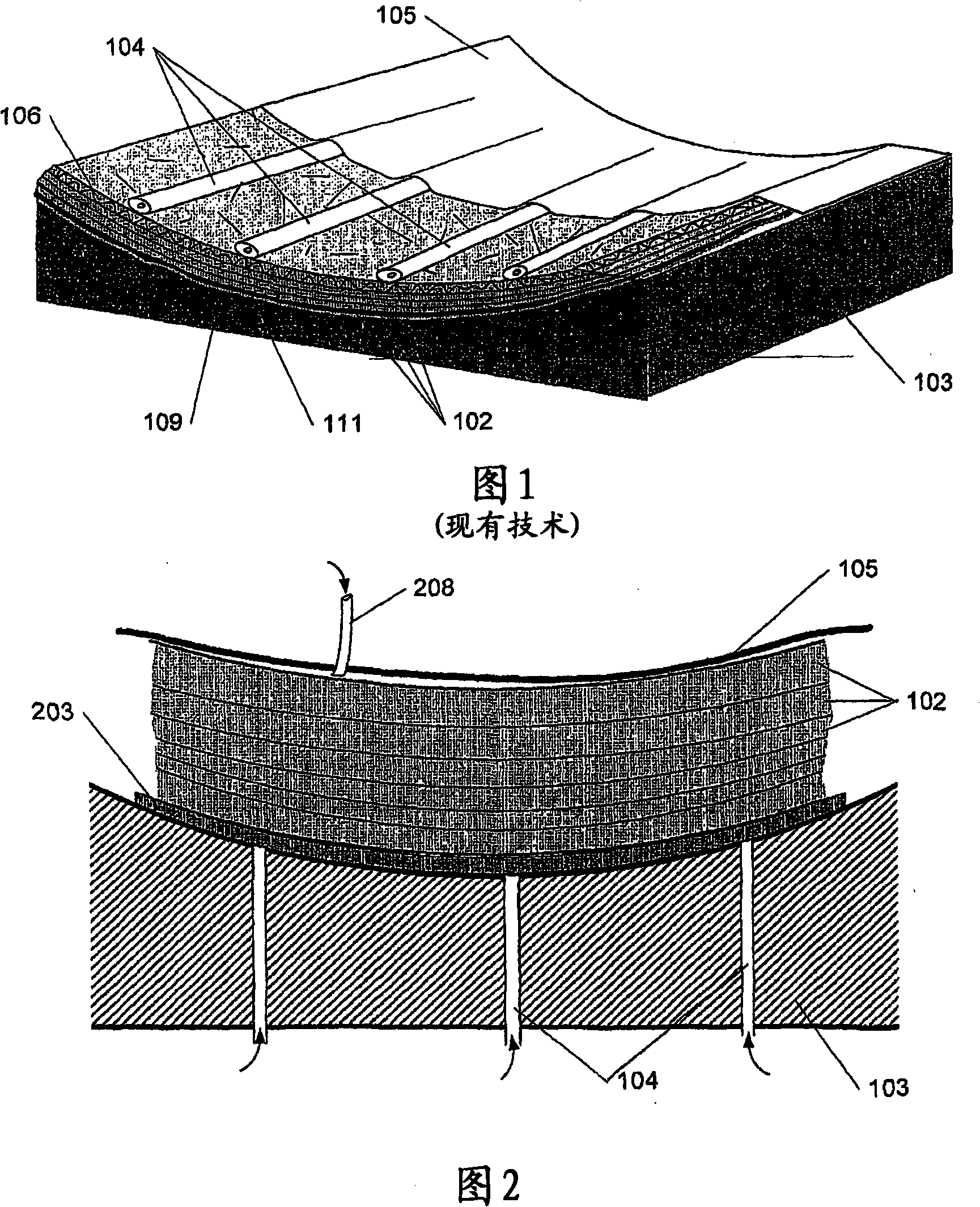
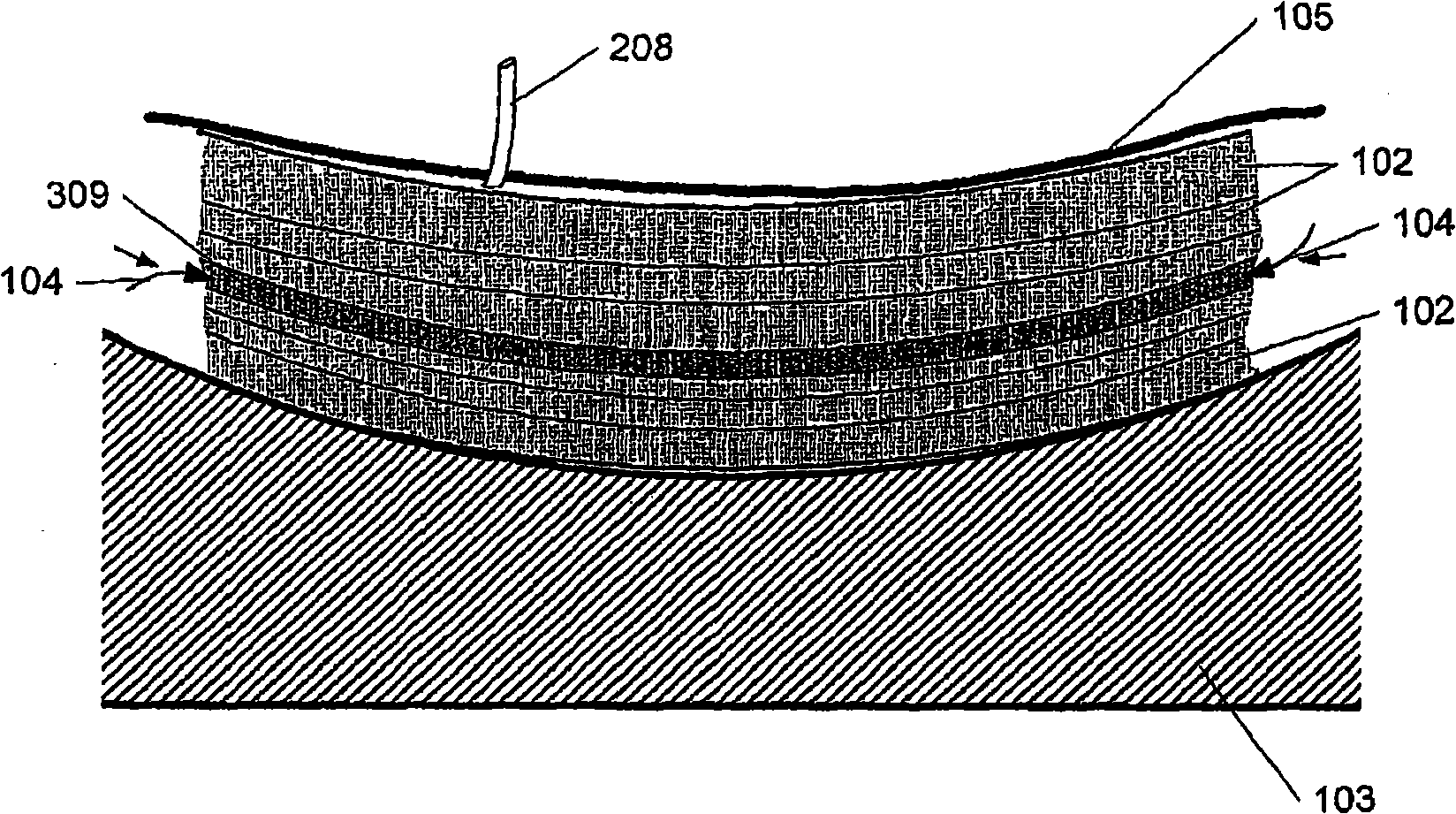
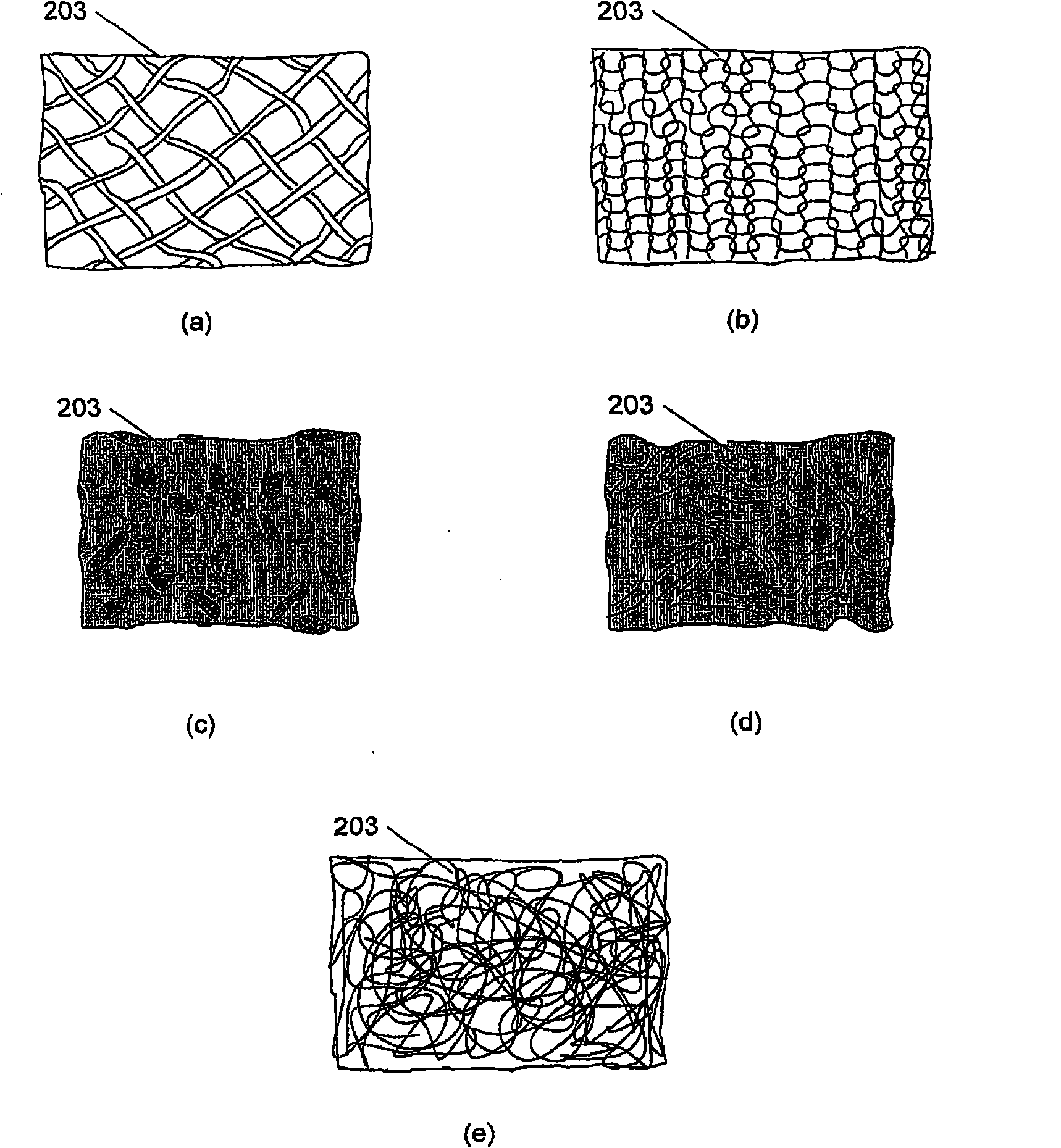
A method for producing a fibre-reinforced product
A technology for strengthening products and fibers, which is applied in the field of production of fiber reinforced products, and can solve problems such as prolonging production time, not being able to be reused, poisonous smoke, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0115] Dissolution of polymers in styrene
[0116] Selected polymers were placed in beakers containing styrene. The selected polymers were (a) polystyrene, (b) polyvinyl acetate and (c) polyurethane. The ability of styrene to dissolve the selected polymers was observed and recorded as a function of time elapsed.
example 2
[0118] Dissolution of polymers in styrene with external heating provided
[0119] The same polymers as in Example 1 were tested, along with (d) polyethylene copoly(styrene-alkylmaleimide), polyethylene glycol fumarate. Selected polymers were placed in beakers containing styrene. The beaker is placed on a heating source and external heating is provided. The temperature applied depends on the polymer selected. The ability of styrene to dissolve selected polymers was observed and recorded as a function of temperature and time used.
example 3
[0121] Dissolution of polymers in styrene and / or polyester / vinyl ester / epoxy resins, and formation of "gel" layers.
[0122] Beakers were lined up and samples of the polymer in Example 2 and resin with hardener were poured into the beakers. The resin was cured, and during the curing process, the state of selected polymers (eg, remained unchanged, dissolved, and partially dissolved) was observed and recorded as a function of the time elapsed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com