Preparation method of macropore activated carbon fiber with intensity more than 0.3GPa
A technology of activated carbon fiber and carbon fiber, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as low strength, affecting the range of use and service life of ACF, and achieve high product strength, The effect of high strength and simple activation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Step 1. Mix the phosphoric acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 10wt% and the aqueous sodium chloride solution with a concentration of 0.5mol / L at a volume ratio of 1:1, and then impregnate the viscose-based carbon fiber with a strength of 0.7GPa for 24 hours. Dry at 100°C;
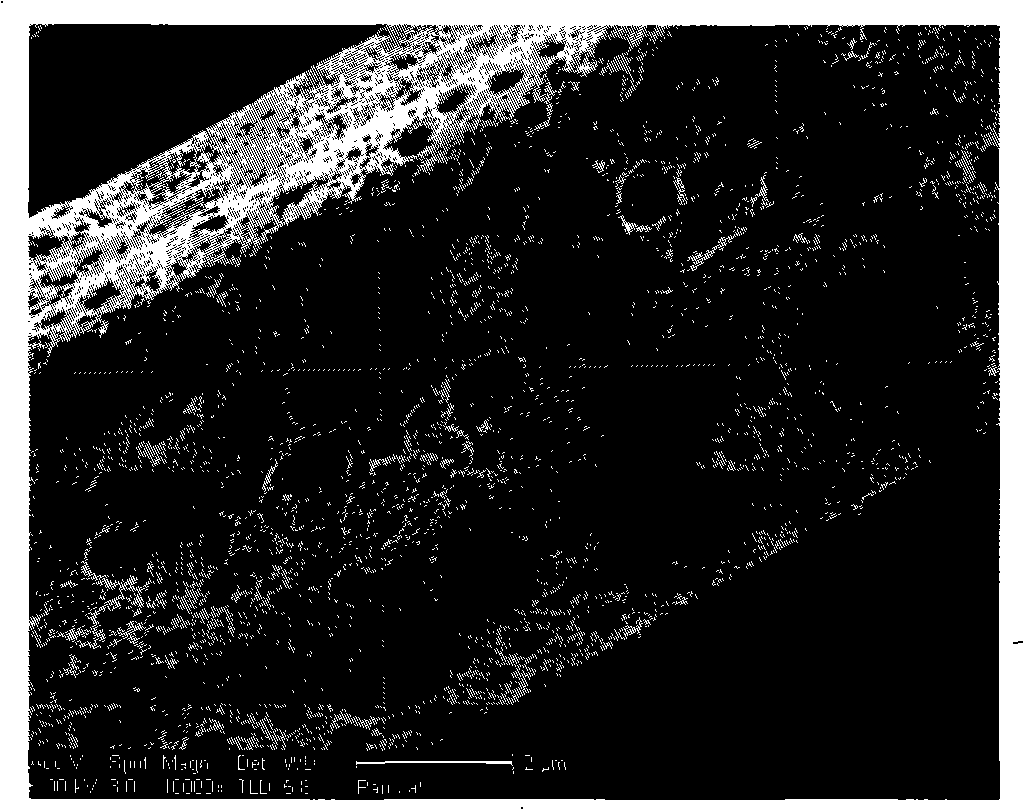
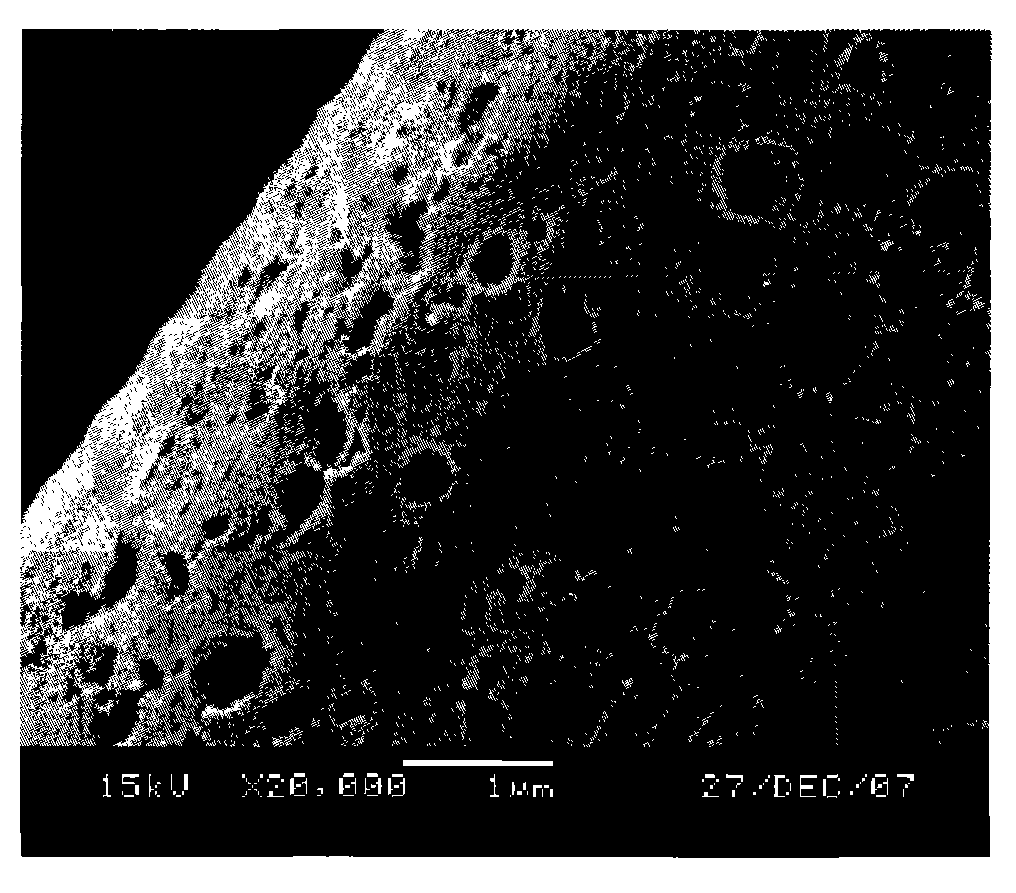
[0023] Step 2. Put it into an activation furnace, heat it to 1000°C at a rate of 20°C / min under the protection of nitrogen, keep the temperature at a constant temperature for 0.5 hours, and cool to room temperature to obtain macroporous activated carbon fibers with a strength greater than 0.3GPa. Among them, heat to 600 After the temperature is lowered to 200°C, water vapor is introduced, and during the cooling process, when the temperature drops to 200°C, the nitrogen and water vapor are turned off. It can be seen that the surface of the obtained macroporous activated carbon fiber is covered with macropores (100nm<aperture<600nm) through electron micrographs (Fig. 1), and the strength mea...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Step 1. Mix the mixed aqueous solution of nitric acid and sulfuric acid with a concentration of 15wt% and the aqueous mixture of disodium hydrogen phosphate and sodium nitrate with a saturated concentration of 1:1 by volume, and then impregnate the viscose-based carbon fiber with a strength of 0.5GPa Among them, 12 hours, after taking it out, dry it at 100°C;
[0026] Step 2. Put it in an activation furnace, heat it to 900°C at a rate of 10°C / min under the protection of helium, keep the temperature at a constant temperature for 0.5 hours, and cool to room temperature to obtain macroporous activated carbon fibers with a strength greater than 0.3GPa. Activated carbon fibers are heated to Water vapor is introduced after 600°C, and during the cooling process, when the temperature drops to 200°C, helium and water vapor are turned off. It can be seen that the surface of the obtained macroporous activated carbon fiber is covered with macropores (200nm<aperture<600nm) through e...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Step 1. Mix hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 20wt% and 2mol / L sodium dihydrogen phosphate aqueous solution at a volume ratio of 1:1, and then impregnate the viscose-based carbon fiber with a strength of 0.6GPa for 12 hours, take it out and place it at 100°C drying;
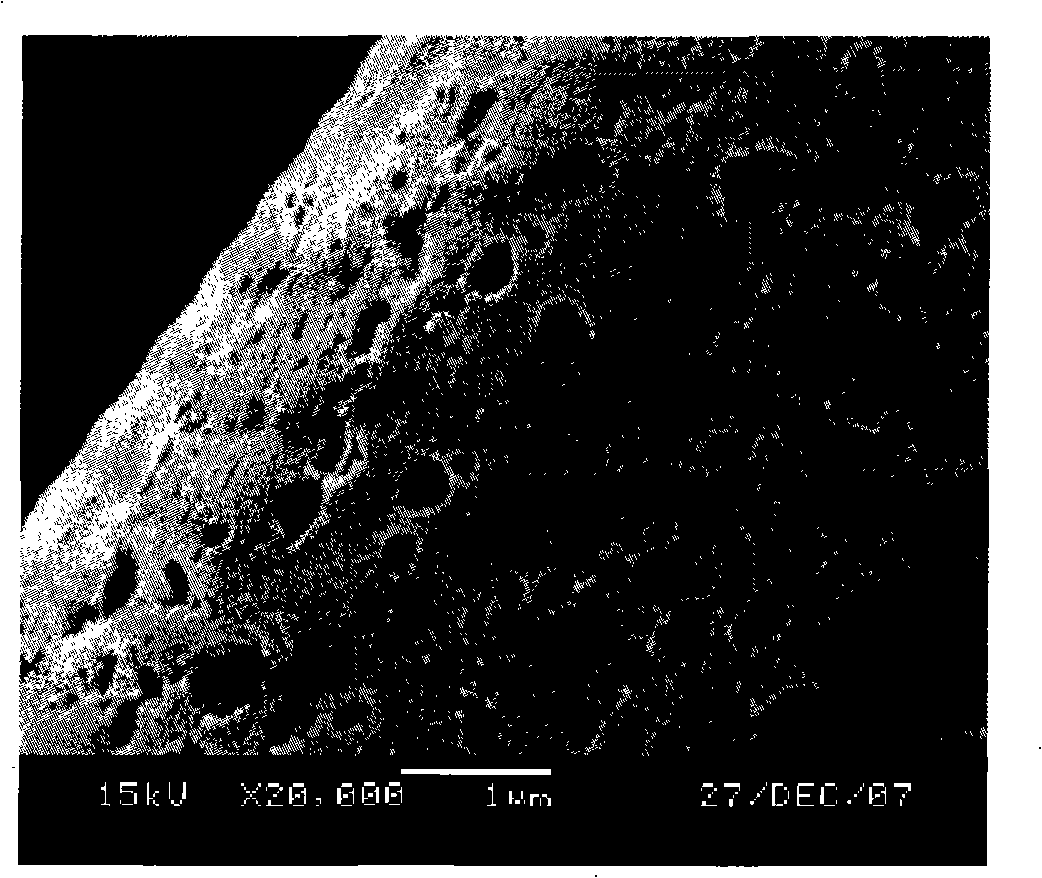
[0029] Step 2. Put it into an activation furnace, heat it to 900°C at a rate of 15°C / min under the protection of argon, keep the temperature constant for 1 hour, and cool to room temperature to obtain a macroporous activated carbon fiber with a strength greater than 0.3GPa Activated carbon fiber, wherein, heated to Water vapor was introduced after 600°C, and during the cooling process, when the temperature dropped to 200°C, the argon and water vapor were turned off. It can be seen from the electron micrograph (Fig. 3) that the surface of the obtained macroporous activated carbon fiber is covered with macropores (50nm<aperture<100nm), and the strength measured by the conventional carbon fiber streng...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com