Miniature balanced antenna with differential feed
一种馈电、差分的技术,应用在天线、天线零部件、使天线同时工作在不同波段的装置等方向,能够解决平衡天线系统体积大、很难设计、平衡天线系统复杂阻抗匹配电路等问题,达到降低性能的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
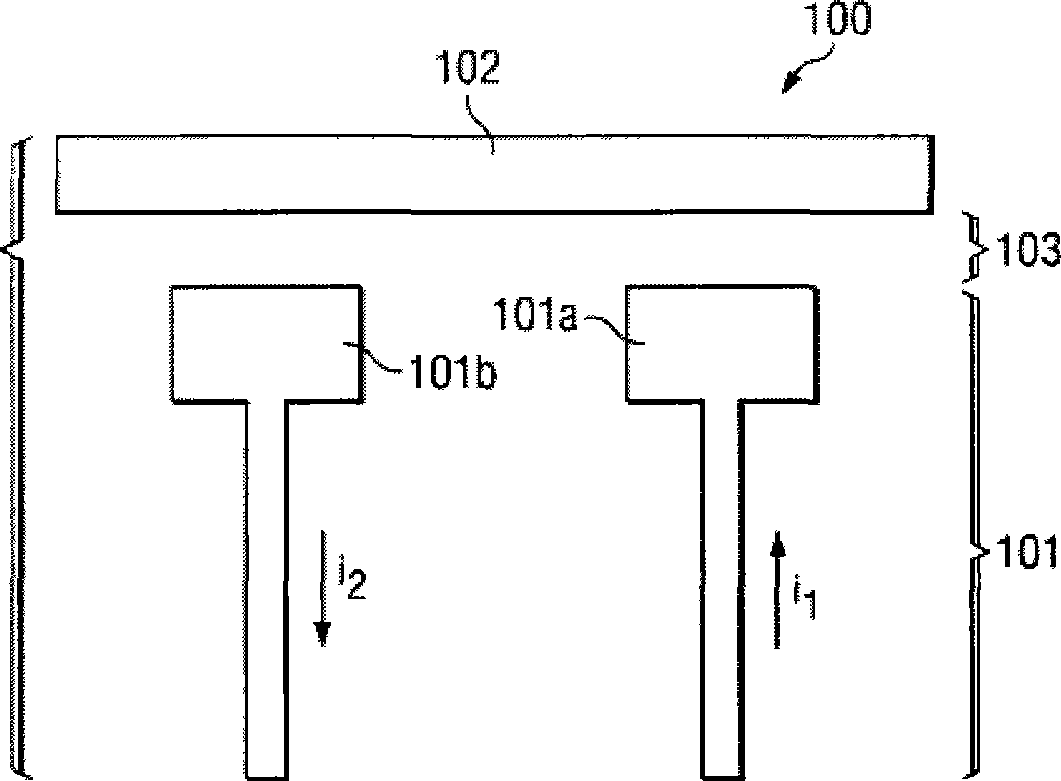
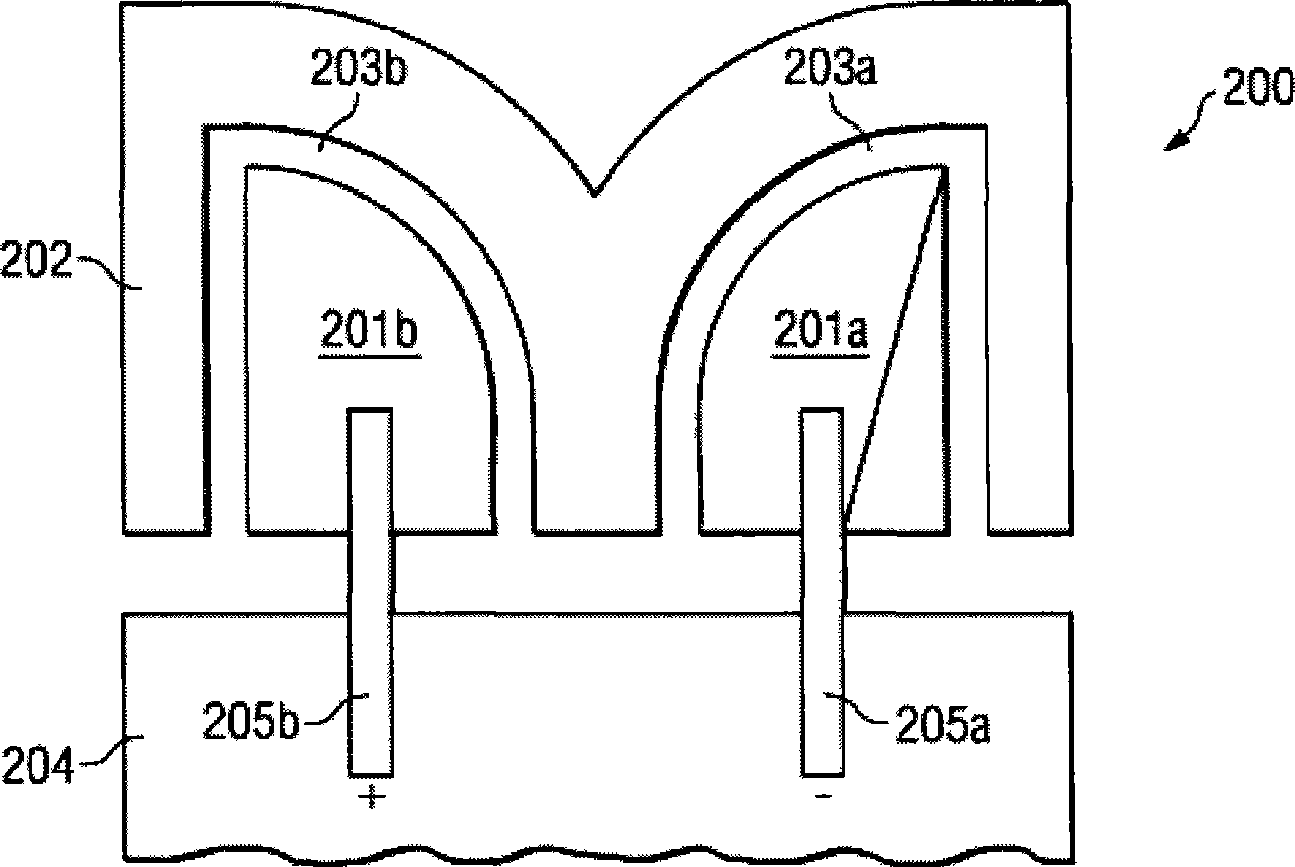
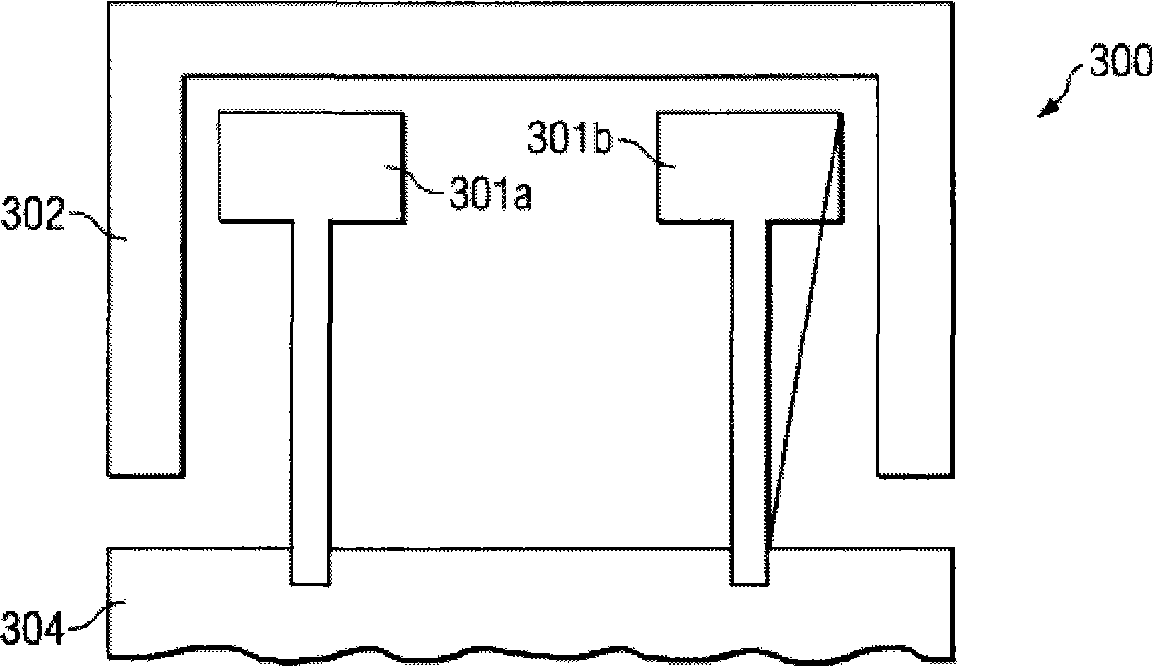
[0020] figure 1 A typical antenna system 100 for one embodiment of the invention is described. System 100 includes metal feed element 101 and metal parasitic element 102 . Individual feed elements 101a and 101b are "balanced" in that their currents (or potentials) are equal in magnitude and out of phase along their respective paths. Therefore, it is also a fact that the feeding element 101 is a differential structure with one side serving as the "+" side and the other side serving as the "" side. Gap 103 is a dielectric gap that may include air, plastic, fiberglass, or other dielectric material.
[0021] Metal element 102 is a parasitic element that is symmetrical with respect to the polarity of feed element 101 and separated by gap 103 . The parasitic element 102 has one or more resonance frequencies, and when an RF signal is supplied to the feeding element 101 at one resonance frequency, the parasitic element 102 resonates due to capacitive coupling. Feed element 101 als...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com