Method of producing fermented milk using novel lactic acid bacterium
A technology of fermented milk and lactic acid bacteria, applied to bacteria, lactobacillus, streptococcus/lactococcus used in food preparation, etc., can solve the problems of damaged flavor, high price, difficult to preserve bifidobacteria, etc., and achieve intestinal effects high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
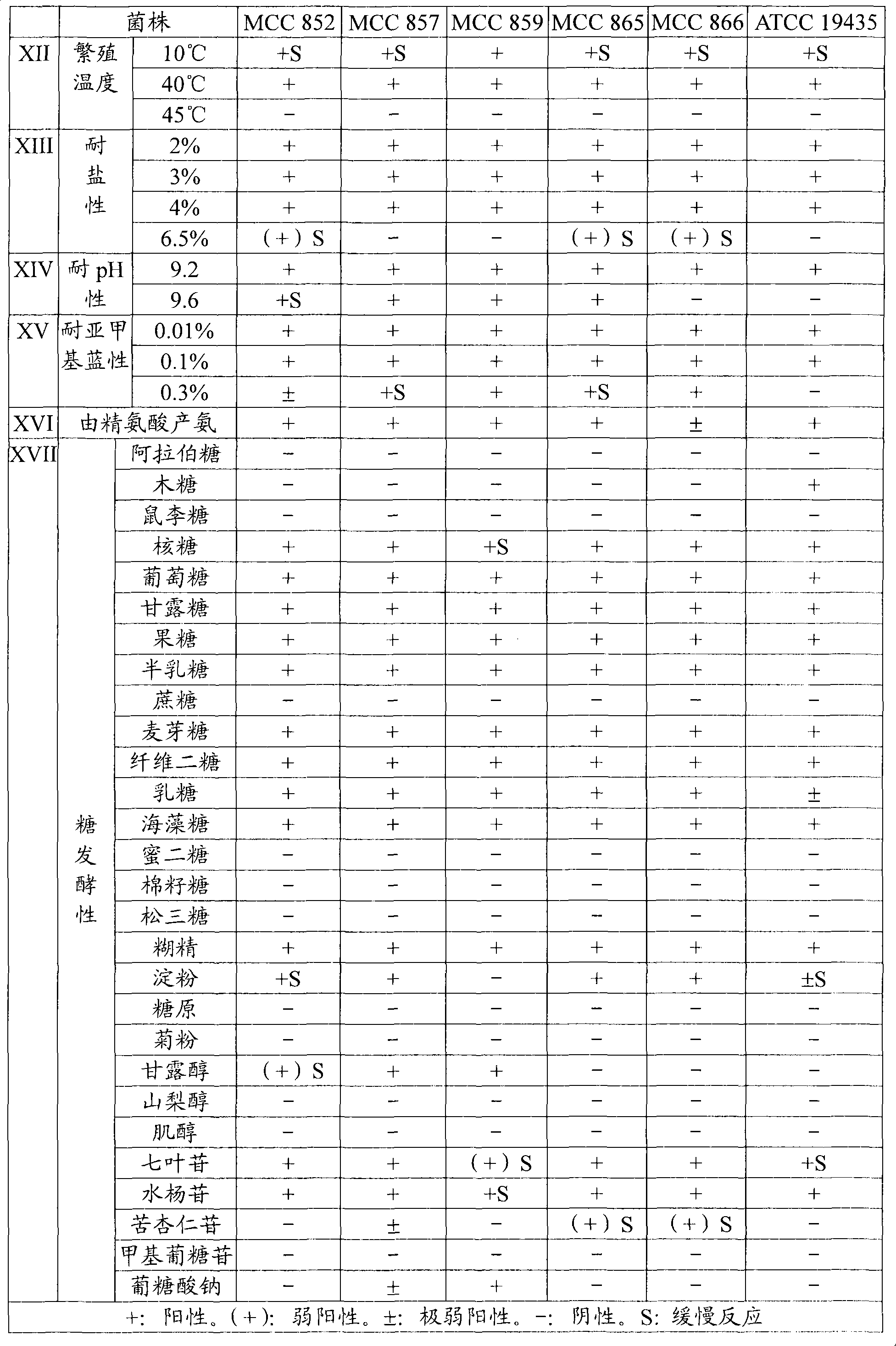
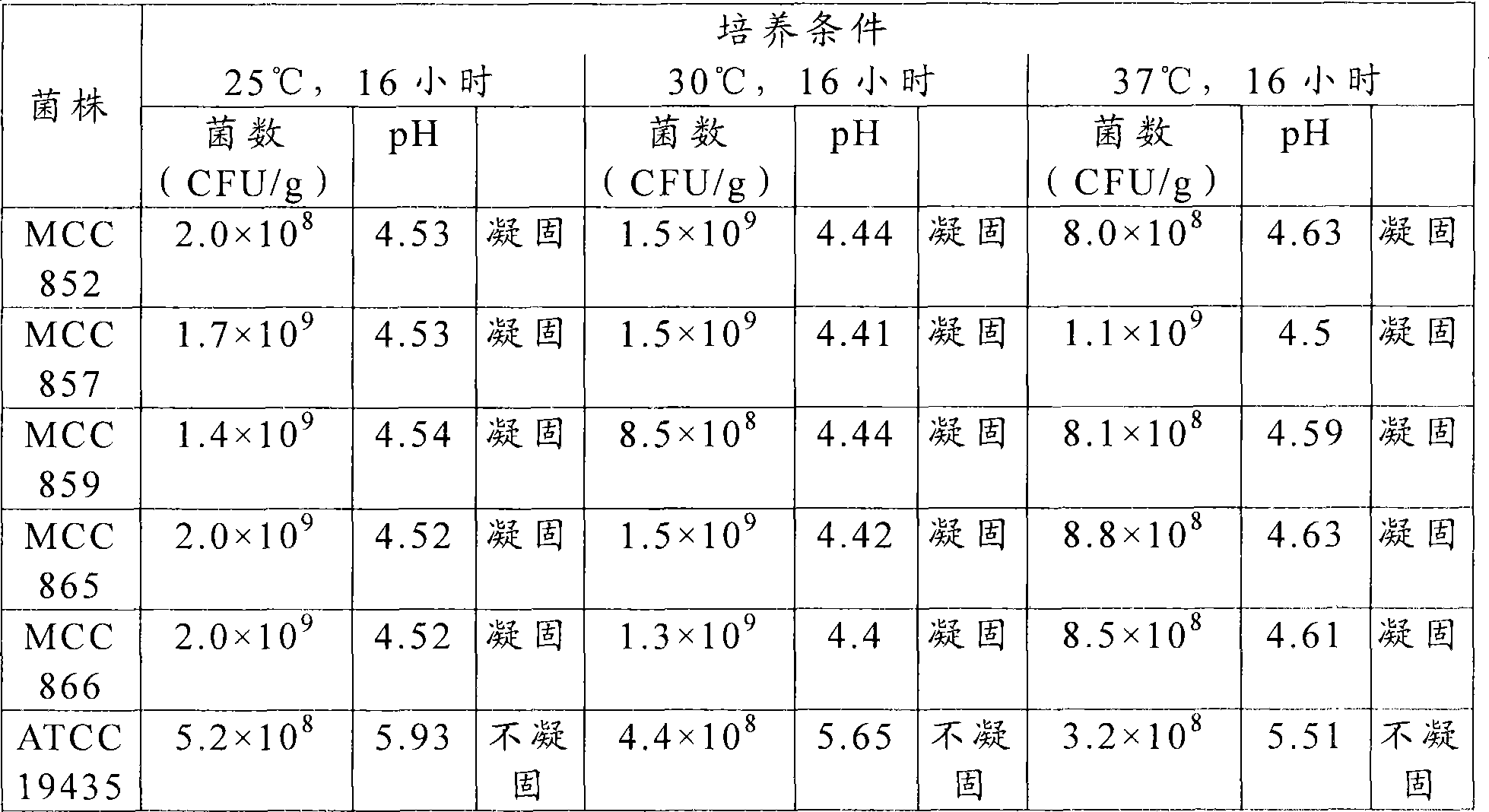
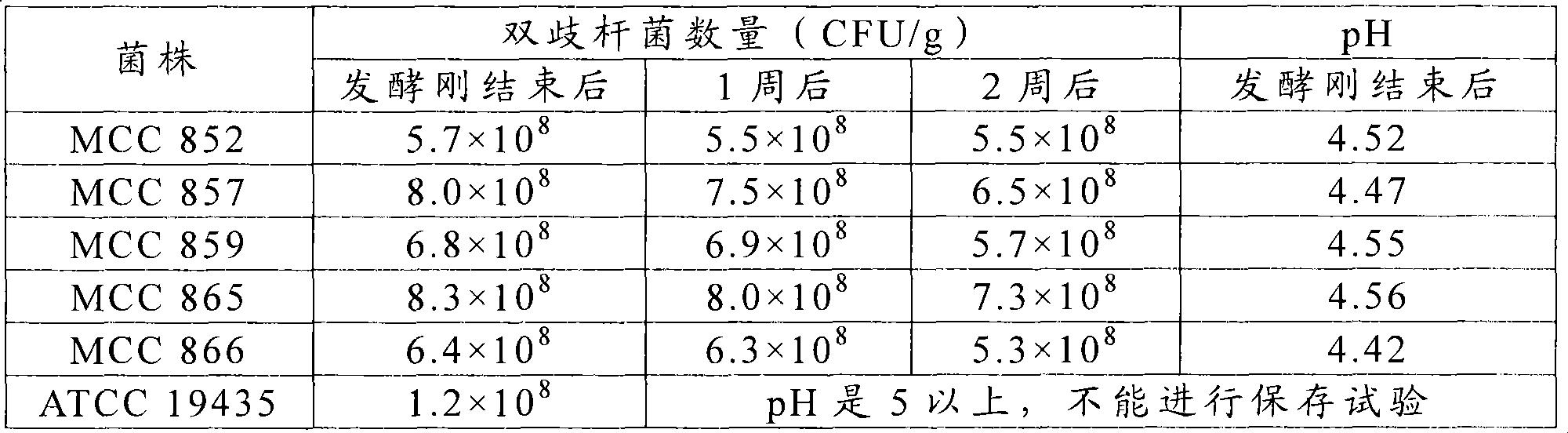
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0104] 10% (W / W) reconstituted skim milk powder (manufactured by Morinaga Dairy Co., Ltd.) was dissolved in water to obtain 1000 mL of 10% (W / W) reconstituted skim milk medium, which was sterilized at 90° C. for 30 minutes, and then Inoculate 30 mL of a seed culture of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MCC857 strain, and culture at 25° C. for 16 hours. On the other hand, 1000 mL of 11% (W / W) skim milk medium containing 0.2% (W / W) yeast extract was sterilized at 90°C for 30 minutes, and inoculated with 100 mL of Bifidobacterium longum FERM BP-7787 strain Seed cultures were incubated at 37°C for 6 hours.
[0105]In addition to this, 50 L of 0.5% (W / W) milk fat, 8.0% (W / W) non-fat milk obtained by mixing and dissolving raw materials including skimmed milk powder, whole milk powder, pectin, and sucrose A minimal medium of solid components, 5.0% (W / W) sucrose and 0.2% (W / W) pectin was sterilized at 90°C for 10 minutes and cooled to 40°C. In this sterilized minimal medium, 50 mL of...
Embodiment 2
[0107] 1000 mL of 10% (W / W) reconstituted skim milk medium was sterilized at 90° C. for 30 minutes, and then 30 mL of a seed culture of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MCC866 strain was inoculated, followed by cultivation at 25° C. for 16 hours. On the other hand, 1000 mL of 11% (W / W) skim milk medium containing 0.2% (W / W) yeast extract was sterilized at 90°C for 30 minutes, and inoculated with 100 mL of Bifidobacterium longum FERM BP-7787 strain Seed cultures were incubated at 37°C for 6 hours. Separately, 1500 mL of 10% (W / W) reconstituted skim milk medium was sterilized at 90°C for 30 minutes, and 50 mL of a mixed culture of Streptococcus thermophilus (manufactured by HAN SEN) and Lactobacillus bulgaricus (manufactured by HANSEN) was inoculated , and then incubated at 37°C for 5 hours.
[0108] Besides, 50 L of raw material milk containing 3.0% (W / W) milk fat and 9.0% (W / W) non-fat milk solids content was heated to 70C. °C, homogenize under a pressure of 15 MPa, then, st...
Embodiment 3
[0110] 1000 mL of 10% (W / W) reconstituted skim milk medium was sterilized at 90° C. for 30 minutes, then inoculated with 30 mL of seed culture of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MCC865 strain, and cultivated at 25° C. for 16 hours. On the other hand, 1000 mL of 11% (W / W) skim milk medium containing 0.2% (W / W) yeast extract was sterilized at 90°C for 30 minutes, and inoculated with 100 mL of Bifidobacterium longum FERM BP-7787 strain Seed cultures were incubated at 37°C for 6 hours. In addition, 1500 mL of 10% (W / W) reconstituted skim milk medium was sterilized at 90°C for 30 minutes, and 50 mL of a mixed culture of Streptococcus thermophilus (manufactured by HANSEN) and Lactobacillus bulgaricus (manufactured by HANSEN) was inoculated, and then in Incubate at 42°C for 5 hours.
[0111] In addition to this, 500 L of raw milk containing 3.4% (W / W) milk fat and 12.2% (W / W) non-fat milk solid content was heated to 70°C, homogenized under a pressure of 15 MPa, and then , steriliz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com