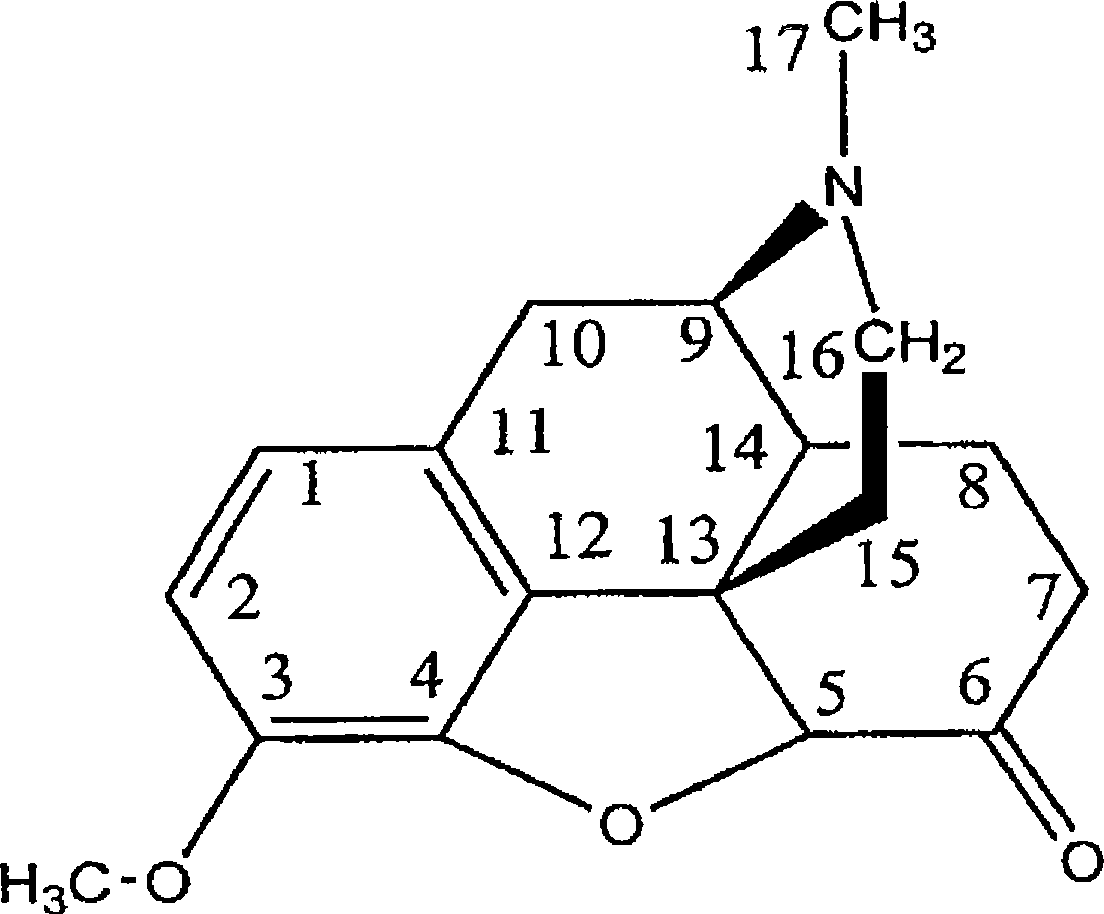
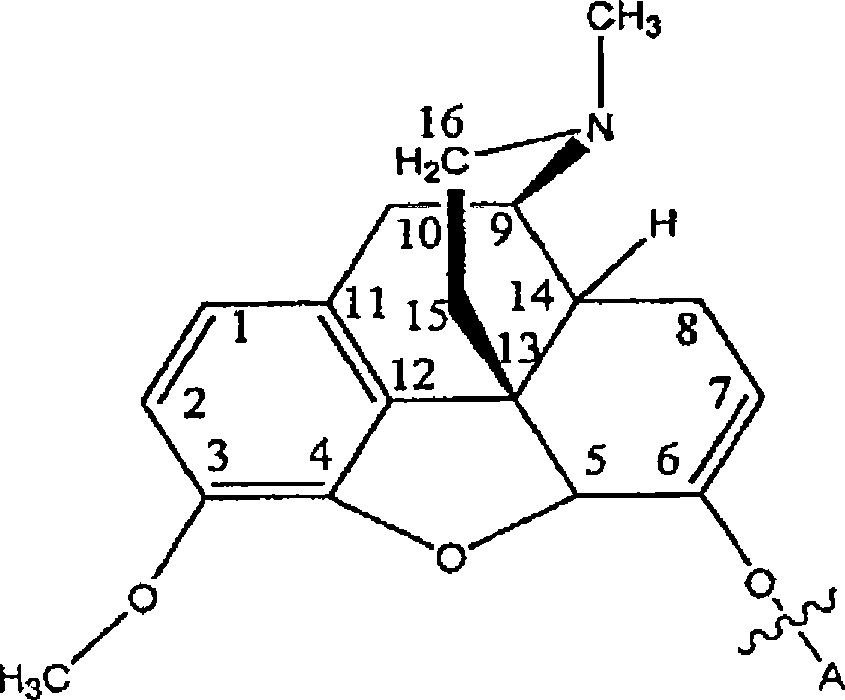
Compositions and methods for enhancing analgesic potency of covalently bound compounds, attenuating its adverse side effects, and preventing their abuse
A technology of covalent bonding and composition, applied in the field of compositions and methods for improving the analgesic effect of covalently bonded compounds, reducing their side effects and preventing their abuse
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0201] Example 1. Leu-hydrocodone
[0202] Reagent MW weight mmol Molar equivalent 1. Hydrocodone 299 1.00g 3.34 1.0 1. LiN(TMS) 2 , in THF 1M 10.5ml 10.5 3.15 1. THF - 25ml - - 2. Boc-Leu-OSu 328 3.28g 10.0 3.0
[0203] Addition of LiN(TMS) to hydrocodone in THF via syringe 2 of THF solution. The solution was stirred at room temperature for 5 minutes, then Boc-Leu-OSu was added. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 hours. The reaction was neutralized to pH 7 with 6M HCl. Solvent was removed. The crude product was dissolved in CHCl 3 (100ml), washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate (3 x 100ml), dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered and the solvent removed. Solid collected as yellow powder (1.98 g, 95% yield): 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 )δ 0.86(dd, 6H), 1.31(s, 9H), 1.46(s, 2H), 1.55(m, 2H), 1.69(m, 1H), 1.87(dt, 1H), 2.07(dt, 2H) , 2.29(s, 3H), 2.43(m, 2H), 2.93(d, 1H), 3.11(s, 1H), 3...
Embodiment 2
[0206] Example 2. Example of a conjugate containing two different amino acids: Ala-Pro-Hydrocodone
[0207] Reagent MW weight mmol Molar equivalent Pro-Hydrocodone 468 0.25g 0.53 1.0 Boc-Leu-OSu 286 0.33g 1.2 2.26 NMM 101 0.50ml 5.38 10.2 DMF - 10ml - -
[0208] To a solution of Pro-hydrocodone in DMF was added NMM followed by Boc-Ala-OSu. The solution was stirred at room temperature for 18 hours. Solvent was removed. The crude product was purified by preparative HPLC (Phenomenex Luna C18, 30×250 mm, 5 μM, 100 ; gradient elution: 100 water / 00.1% TFA-MeCN → 0 / 100; 30ml / min.). Solid collected as light yellow powder (0.307 g, 85% yield): 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 )δ 1.16(d, 3H), 1.35(s, 9H), 1.51(m, 2H), 1.86-2.10(m, 6H), 2.50(m, 1H), 2.54(m, 1H), 2.69(m, 1H), 2.88(s, 3H), 3.02(dd, 1H), 3.26(d, 1H), 3.55(m, 1H), 3.67(m, 1H), 3.72(s, 3H), 3.80(s, 1H ), 4.25(m, 1H), 4.43(d, 1H), 5.01(s, 1H), 5.59(d, 1H), 6.75(d, 1H), 6.88(d,...
Embodiment 3
[0210] Example 3. Example of a conjugate containing two identical amino acids: Glu-Glu-Hydrocodone
[0211] Glu-Glu-hydrocodone was prepared according to the similar method of Example 2, but the amino acid raw material was Boc-Glu(OtBu)-OSu, and the conjugate raw material was Glu-hydrocodone.
[0212] tripeptide hydrocodone conjugate
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com