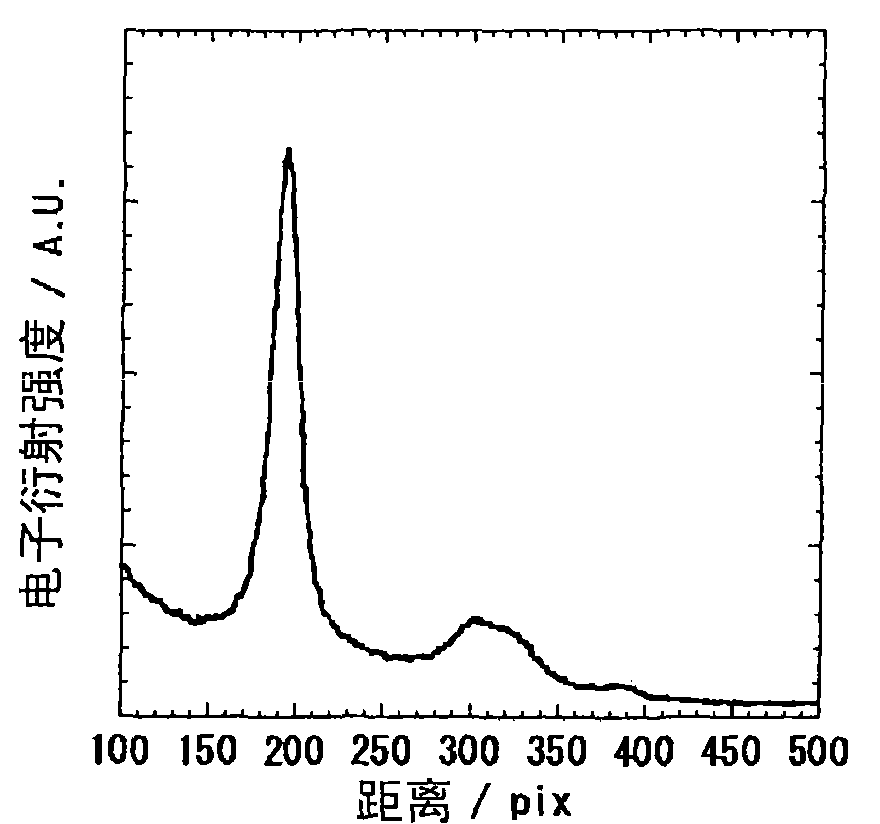
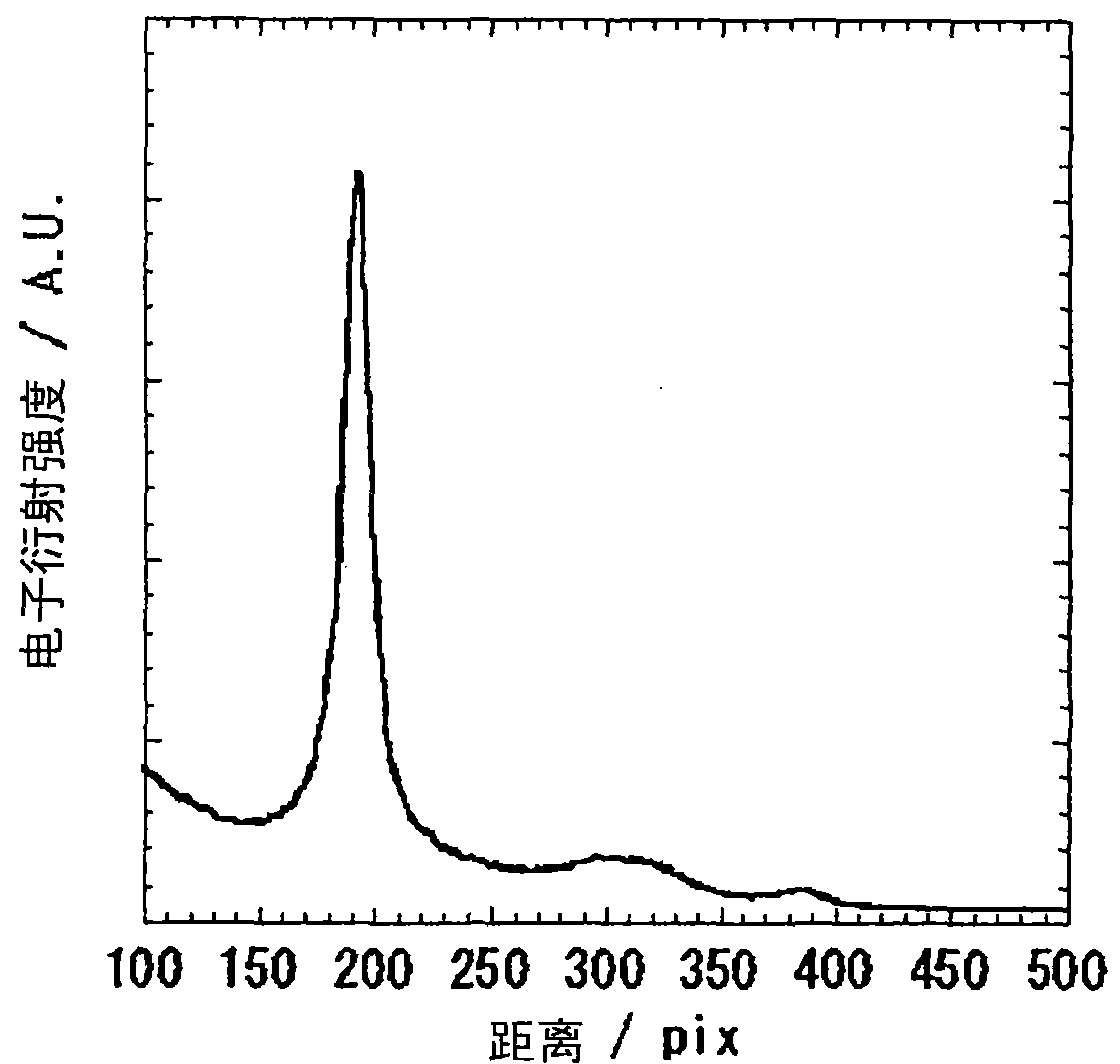
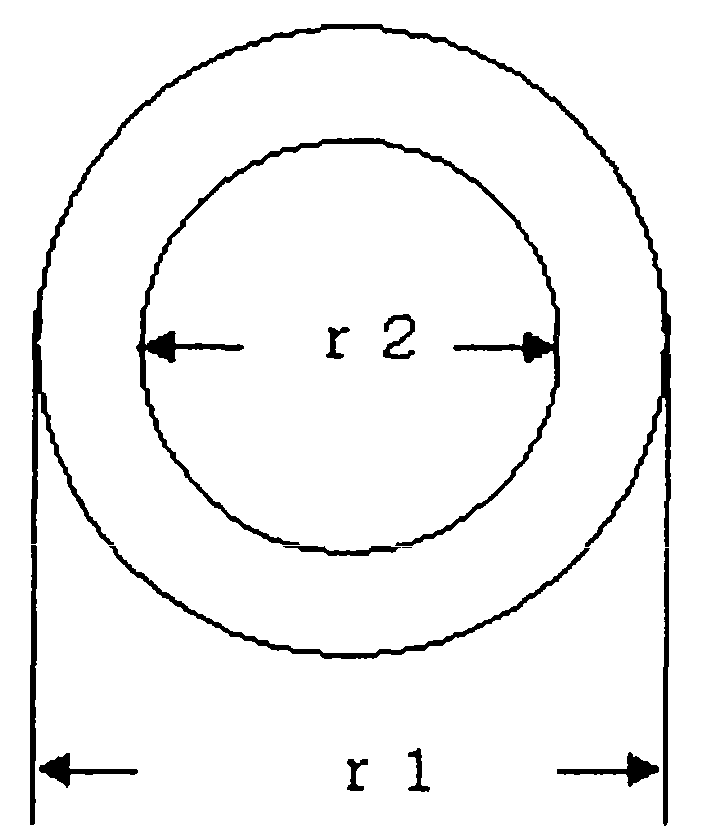
Polybenzazole fiber and pyridobisimidazole fiber
A polybenzazole-based, phenylene pyridine technology, applied in electrical components, electrical solid devices, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as wire breakage, changing spinning conditions, etc., and achieve fiber strength reduction, fibril suppression, post-processing properties improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~6、 comparative example 1~3
[0110] Using a spinning stock solution (14% by mass of PBO concentration) obtained by dissolving poly(p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) (hereinafter abbreviated as PBO) with an intrinsic viscosity [η] of 29 dl / g in polyphosphoric acid, Spinning was performed under conditions such that the diameter of the monofilament fiber was 11.5 μm and 1.65 dtex.
[0111] That is, at a spinning temperature of 175°C, the spinning dope is spun from a nozzle with a hole diameter of 0.20 mm and a number of holes of 166, and the spun dope fibers are passed through a quenching chamber (chamber) with a quenching temperature of 60°C , cooled, and after passing through the quenching chamber, they were immersed in the first coagulation and washing bath while being bundled into multifilaments to coagulate the fibers, and steam treatment was performed using the steam application conditions shown in Table 1 at the same time. Thereafter, the fibers were washed with water until the residual phosphorus concentr...
Embodiment 7~12、 comparative example 3~6
[0119] A spinning stock solution (benzene, phenylene) obtained by dissolving phenylenepyrididimidazole-2,6-diyl (2,5-dihydroxy-p-phenylene) with an intrinsic viscosity [η] of 22 dl / g in polyphosphoric acid was used. Pyridinediimidazole-2,6-diyl (2,5-dihydroxy-p-phenylene) concentration: 14% by mass), spinning under conditions such that the single filament fiber diameter becomes 11.5 μm and 1.65 dtex .
[0120] That is, at a spinning temperature of 175°C, the spinning dope is spun from a nozzle with a hole diameter of 0.20 mm and a number of holes of 166, and the spun dope fibers are passed through a quenching chamber with a quenching temperature of 60°C, cooled, and after passing through the quenching chamber, while While bundled into multifibers, the fibers were immersed in a first coagulation / washing bath to coagulate the fibers, and steam treatment was performed under the steam application conditions shown in Table 1. Thereafter, the fibers were washed with water until the...
Embodiment 13
[0128] The fibers prepared in Example 1 were heat-treated for 2.4 seconds under a tension of 5.0 g / d and a temperature of 600°C. The results are shown in Table 5 and Table 6.
[0129]
[0130] As can be seen from the results in Table 5, the fibers of the present invention maintain excellent heat resistance and flame retardancy.
[0131] [Table 6]
[0132]
[0133] From Table 6, it can be confirmed that the fiber of the present invention maintains a good state of process passability even when heat-treated.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com