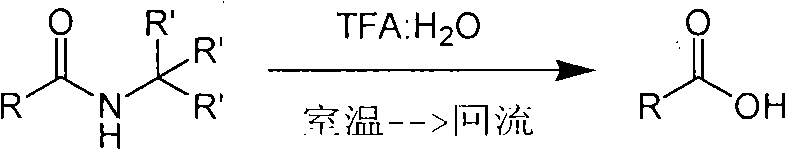
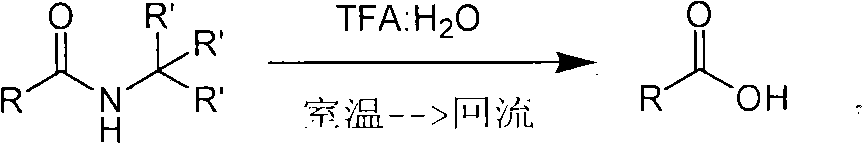Method of de-alkyl amine
A technology for removing tertiary alkylamines and tertiary alkylamides, which is applied in organic chemical methods, chemical instruments and methods, amide preparation, etc., can solve problems such as low yield and strong reaction conditions, and avoid hydrolysis conditions and reaction processes Choose a reasonable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020]
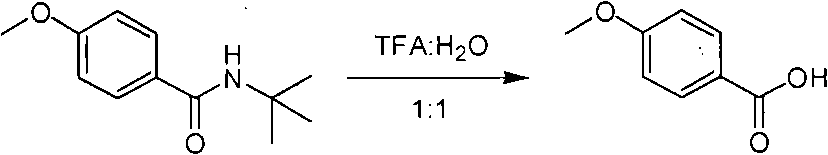
[0021] Add 50ml of water to a 250ml round bottom flask, slowly add 50ml of trifluoroacetic acid under ice cooling, keep the internal temperature below 25°C, then add (5g, 0.024mol) of N-tert-butyl in batches at the same temperature p-methoxybenzamide. After feeding, adjust the reaction temperature to 99°C until the reaction solution is clear, and then heat and reflux at a constant temperature for 24 hours. Sampling is detected by TLC plate, and the hydrolysis reaction is completed. The reaction solution was evaporated to dryness by a rotary evaporator under reduced pressure, and the residue was dissolved in 100 mL of ethyl acetate, washed once with 30 mL of saturated brine, twice with 50 mL of deionized water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, then filtered and concentrated by spinning under reduced pressure. The product was purified by column chromatography to obtain 2.55 g of p-methoxybenzoic acid (FW=152.15, 0.0168 mol), and the conversion rate was 70%. 1 H ...
Embodiment 2
[0023]
[0024] Add 66.6ml of water into a 250ml round-bottomed flask, slowly add 33.3ml of trifluoroacetic acid under cooling in an ice bath, keep the internal temperature below 25°C, then add (5g, 0.024mol) of N- tert-butyl-p-methoxybenzamide. After feeding, adjust the reaction temperature to 99°C until the reaction solution is clear, and then heat and reflux at a constant temperature for 24 hours. Sampling is detected by TLC plate, and the hydrolysis reaction is complete. The reaction solution was evaporated to dryness by a rotary evaporator under reduced pressure, and the residue was dissolved in 100 mL of ethyl acetate, washed once with 30 mL of saturated brine, twice with 50 mL of deionized water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, then filtered and concentrated by spinning under reduced pressure. The product was purified by column chromatography to obtain 2.88 g of the product p-methoxybenzoic acid (FW=152.15, 0.0191 mol), and the conversion rate was 79%.
[0025]...
Embodiment 3
[0027]
[0028] Add 75ml of water to a 250ml round bottom flask, slowly add 25ml of trifluoroacetic acid under ice-bath cooling, keep the internal temperature below 25°C, then add (5g, 0.024mol) of N-tert-butyl in batches at the same temperature p-methoxybenzamide. After the feeding is completed, adjust the reaction temperature to 98°C~99°C until the reaction solution is clear, and heat and reflux at a constant temperature for 36 hours. Sampling is detected by TLC plate, and the hydrolysis reaction is completed. The reaction solution was evaporated to dryness by a rotary evaporator under reduced pressure, and the residue was dissolved in 100 mL of ethyl acetate, washed once with 30 mL of saturated brine, twice with 50 mL of deionized water, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, then filtered and concentrated by spinning under reduced pressure. The product was purified by column chromatography to obtain 2.47 g of the product p-methoxybenzoic acid (FW=152.15, 0.0162 mol), with...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com