Plants having improved characteristics and a method for making the same
A plant and plant seed technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems not mentioned
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 40
[0802] The table of Example 40 gives examples of orthologs and paralogues of the SYB1 protein represented by SEQ ID NO:286. Using the BLAST process described above, other orthologs and paralogs can be easily identified.
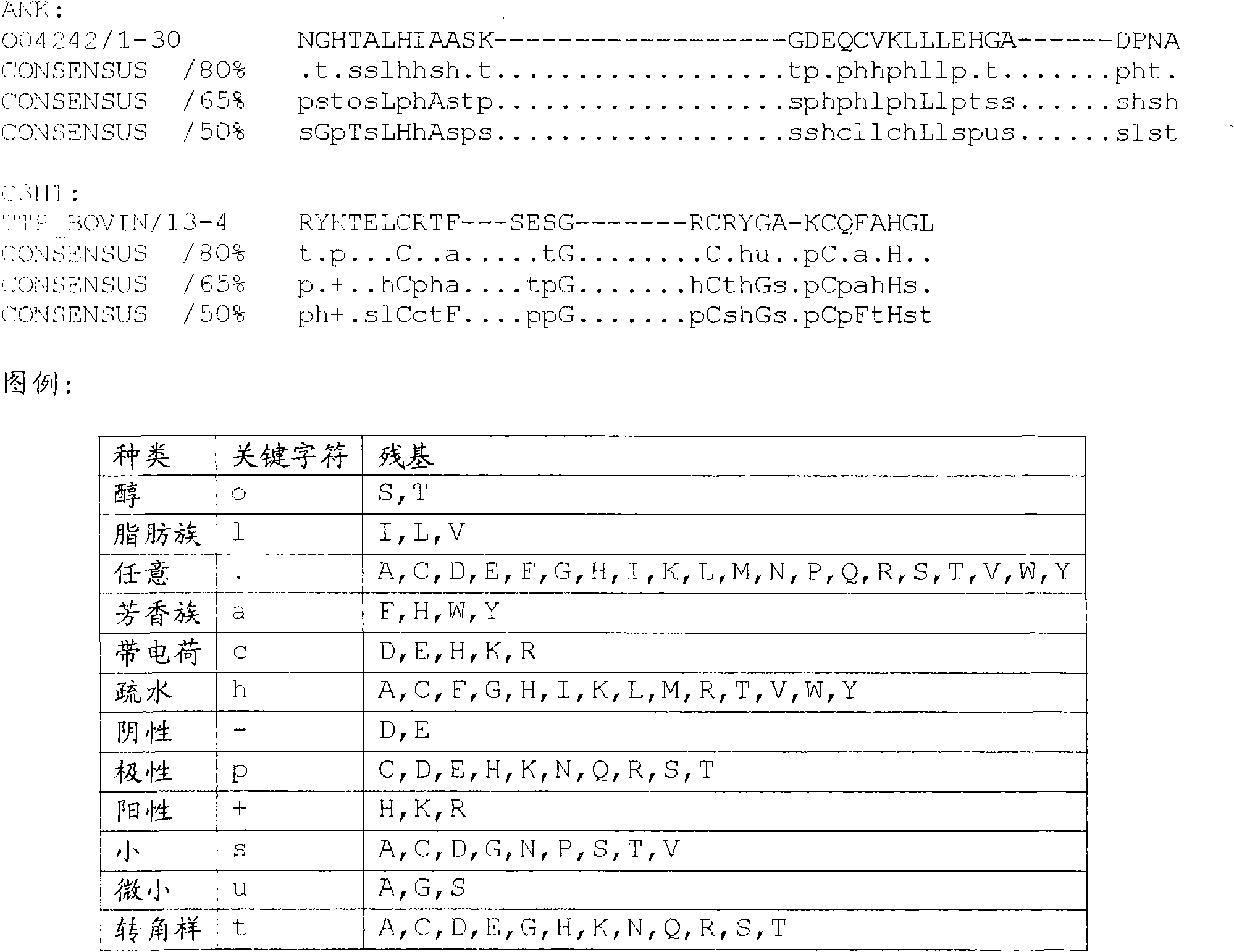
[0803] Through three conserved ZnF_RBZ type zinc finger domain domains ( Figure 22 The appearance of (shown) can identify the protein of the present invention. The terms "domain" and "motif" or "tag" are defined in the "definitions" section. There are also specialized databases for identifying structural domains, such as SMART (Schultz et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S. 95, 5857-5864; Letunic et al. (2002) Nucleic Acids Res 30, 242-244), InterPro ( Mulder et al. (2003) Nucl. Acids. Res. 31, 315-318), Prosite (Bucher and Bairoch (1994), generalized map syntax for biomolecular sequence motifs and its function in automated sequence interpretation, ( In) ISMB-94; Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. ...
Embodiment 1
[0906] Example 1: Identification of sequences related to the nucleic acid sequence used in the method of the present invention
[0907] Use database sequence search tools, such as the Basic Local Alignment Tool (BLAST) (Altschul et al. (1990) J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403-410; and Altschul et al. (1997) Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 3389-3402) in Among those sequences maintained in the Entrez nucleotide database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), sequences (full-length cDNA, EST or genome) related to the nucleic acid sequence used in the method of the present invention were identified. This program is used to find regions of local similarity between sequences by comparing nucleic acid sequences or polypeptide sequences with sequence databases and calculating the statistical significance of matches. For example, the TBLASTN algorithm is used for the polypeptide encoded by the nucleic acid used in the present invention, and default settings and filtering are used to igno...
Embodiment 2
[0913] Example 2: Gene cloning AZ
[0914] The Arabidopsis AZ encoding gene (CDS3104) was amplified by PCR using an Arabidopsis seedling cDNA library (Invitrogen, Paisley, UK) as a template. After reverse transcription of RNA extracted from seedlings, cDNA was cloned into pCMV Sport 6.0. The average size of the inserts in the library is 1.5 kb and the initial number of clones is 1.59×10 7 cfu. In 6×10 11 After the first round of amplification of cfu / ml, the original titer was determined to be 9.6×10 5 cfu / ml. After plasmid extraction, 200 ng template was used in 50 μl PCR mix. The primer prm06717 (sense, the AttB1 site is in italics, and the start codon is in bold: 5’- tqctqtqqatcaqacc-3') (SEQID NO 7) and prm06718 (antisense, complementary: the position is in italics: 5'- ggttag gtctctca attctgc·-3') (SEQ ID NO 8) is used for PCR amplification, wherein the primer includes an AttB site for Gateway recombination. PCR was performed using Hifi Taq DNA polymerase under standard cond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com