Anti-cd16 binding molecules
A technology of binding molecules and binding fragments, which is applied in the direction of antibodies, anti-inflammatory agents, antibacterial drugs, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0129] Example 1: Transient expression and purification of human CD16A-Fc fusion protein
[0130] HEK-293 cells were transiently transfected with the plasmid pCDM-CD16-Fc encoding human CD16A and human IgG1 Fc fragment recombinant protein to secrete soluble CD16A-Fc fusion protein (Mandelboim et al., 1999, supra).
[0131] Use full DMEM medium (with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS), 2mM L-glutamine, 100 U / mL penicillin G sodium and 100 μg / mL streptomycin sulfate; all purchased from Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany), at 37°C, certain humidity and 5% CO 2 Under the conditions of HEK-293 cells (ATCC deposit number CRL-1573) were cultured. Calcium phosphate-mediated transfection efficiencies for these cells are described below.
[0132] One day before transfection, 1.5×10 6 HEK-293 cells were inoculated in a 10 cm diameter cell culture dish with 10 mL of full DMEM medium. Take 10 μg of plasmid DNA with 500 μL of 250 mM CaCl 2 Mix well, then drop into 500μL 2x HEBS bu...
Embodiment 2
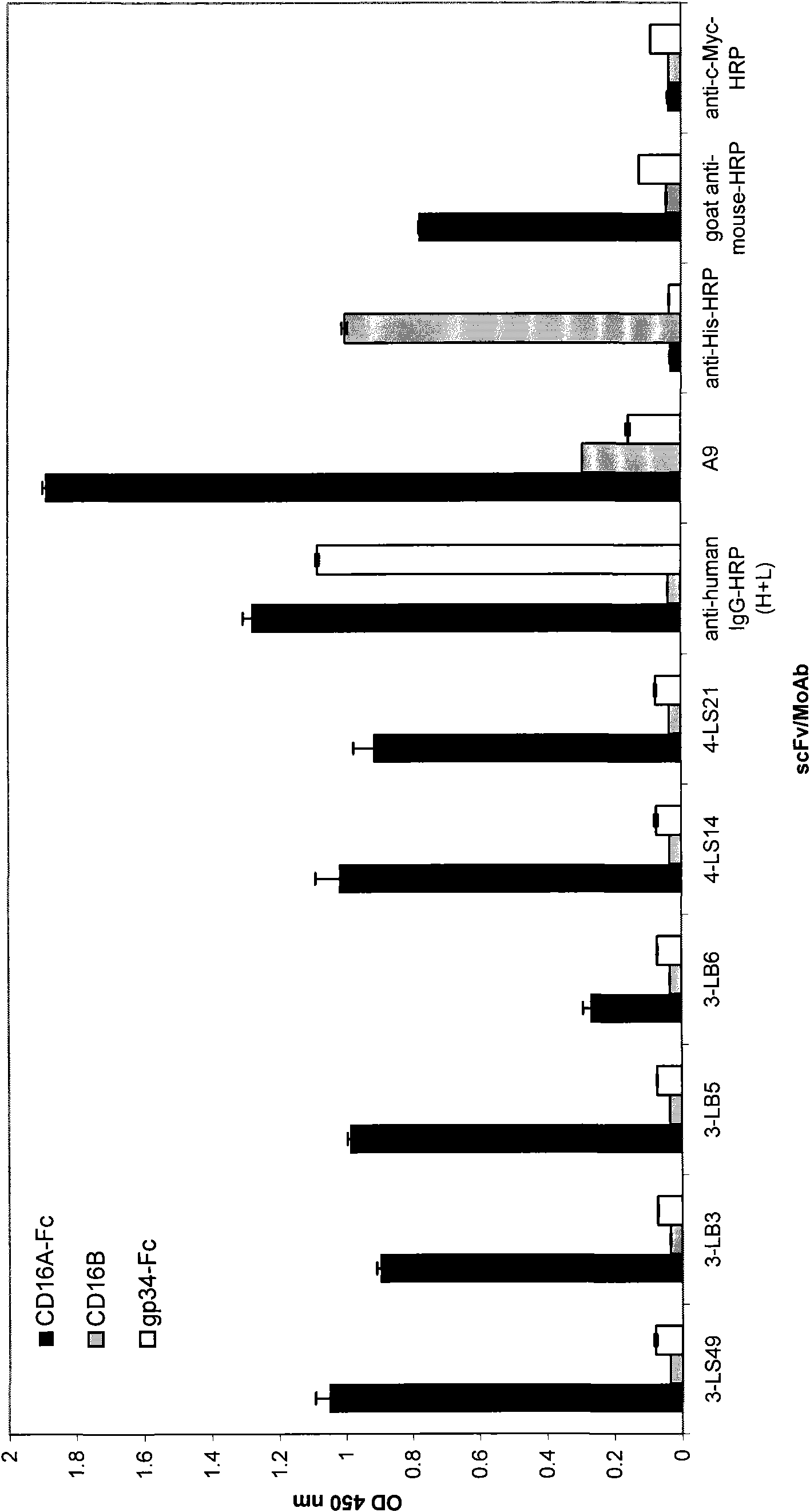
[0135] Example 2: Identification and isolation of CD16-A specific antibody
[0136] The CD16A-Fc fusion protein that obtains with above-mentioned similar method, is used for screening IgM derived scFv phage display library (D rsam etc., 1997FEBS Letts 414:7-13, Little etc., 1999J.Immunol.Methods 231:3-9 , Schwarz et al., FASEB J. 18:1704-6). Clones of this library contained the sequence between the scFv coding sequence and the phage M13pIII gene encoding a hexa-histidine tag, an amber stop codon and a c-myc epitope.
[0137] 500 μg of CD16A Fc fusion protein was biotinylated using the ECL protein biotinylation module (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala Sweden) and then used for three rounds of screening against a phage display library. Prior to screening of the library, sequential preabsorption using streptavidin-coated polystyrene and human IgG (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) was performed in order to eliminate other potential molecules for these proteins. combinatio...
Embodiment 3
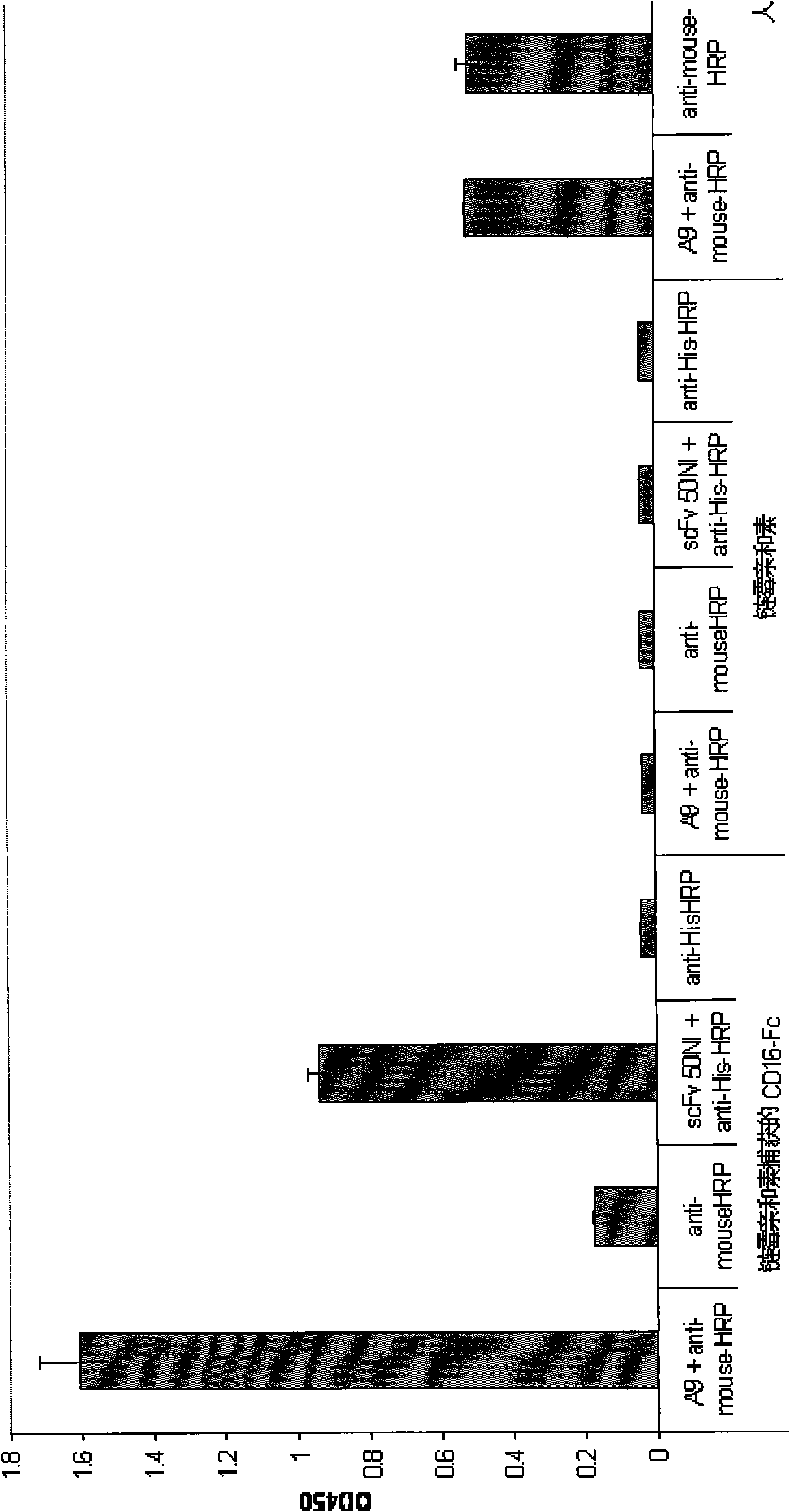
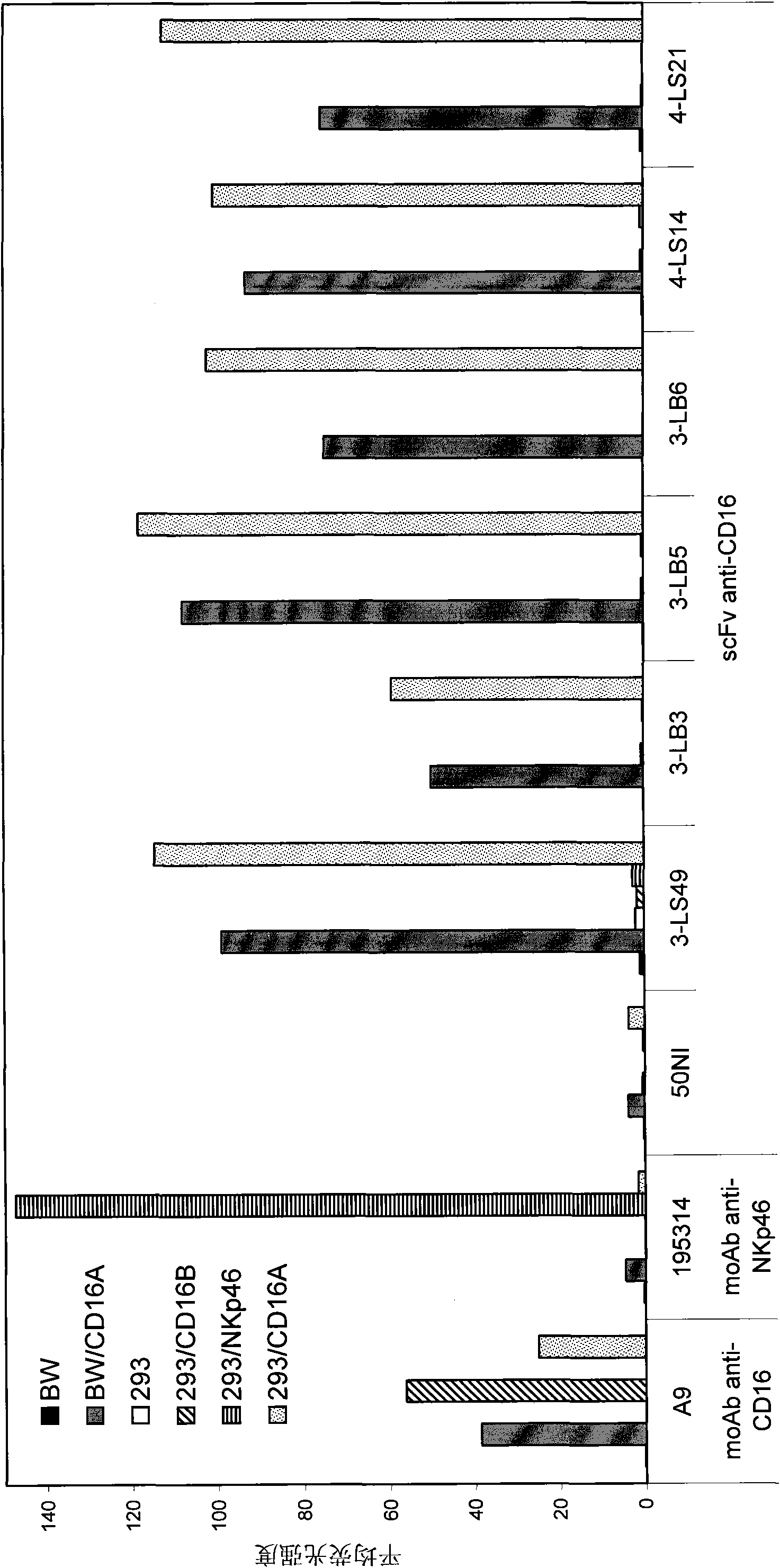
[0143] Example 3: Detection of scFv 50NI in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and granulocytes stably transfected with CD16 subtype
[0144] To test whether 50NI scFv binds to native CD16A protein on the cell surface, we used flow cytometry to detect scFvs expressing either CD16A or CD16B in the cytoplasmic extracts of two different cell lines. The cell lines used for the test are: cell line BW / CD16A expressing CD16A (Mandelboim et al., 2001, Nature 409: 1055-1060); cell line 293-CD16 (stabilized with a plasmid encoding the NA-2 allele of the human CD16B subtype transfected HEK-293 cell line).
[0145] In order to verify whether 50NI scFv has the ability to bind CD16A expressed on the surface of natural killer cells (NK) and / or CD16B expressed on the surface of neutrophils (van de Winkeland Capel, 1993, supra; van Spriel et al., 2000, Immunol. Today 21 (8):391-397), which we detected by flow cytometry compared with freshly isolated pleomorphic cells containing 10-20% N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com