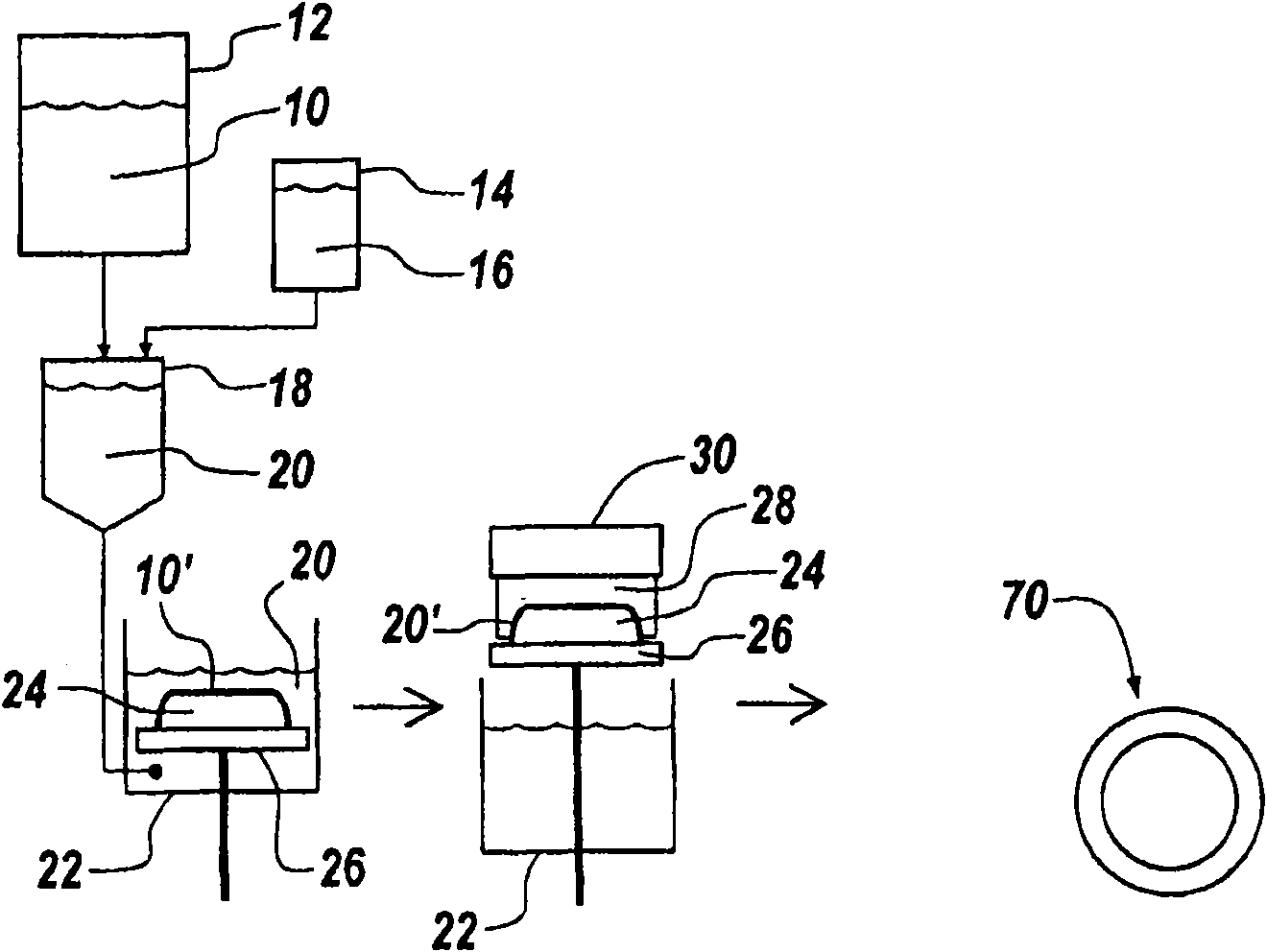
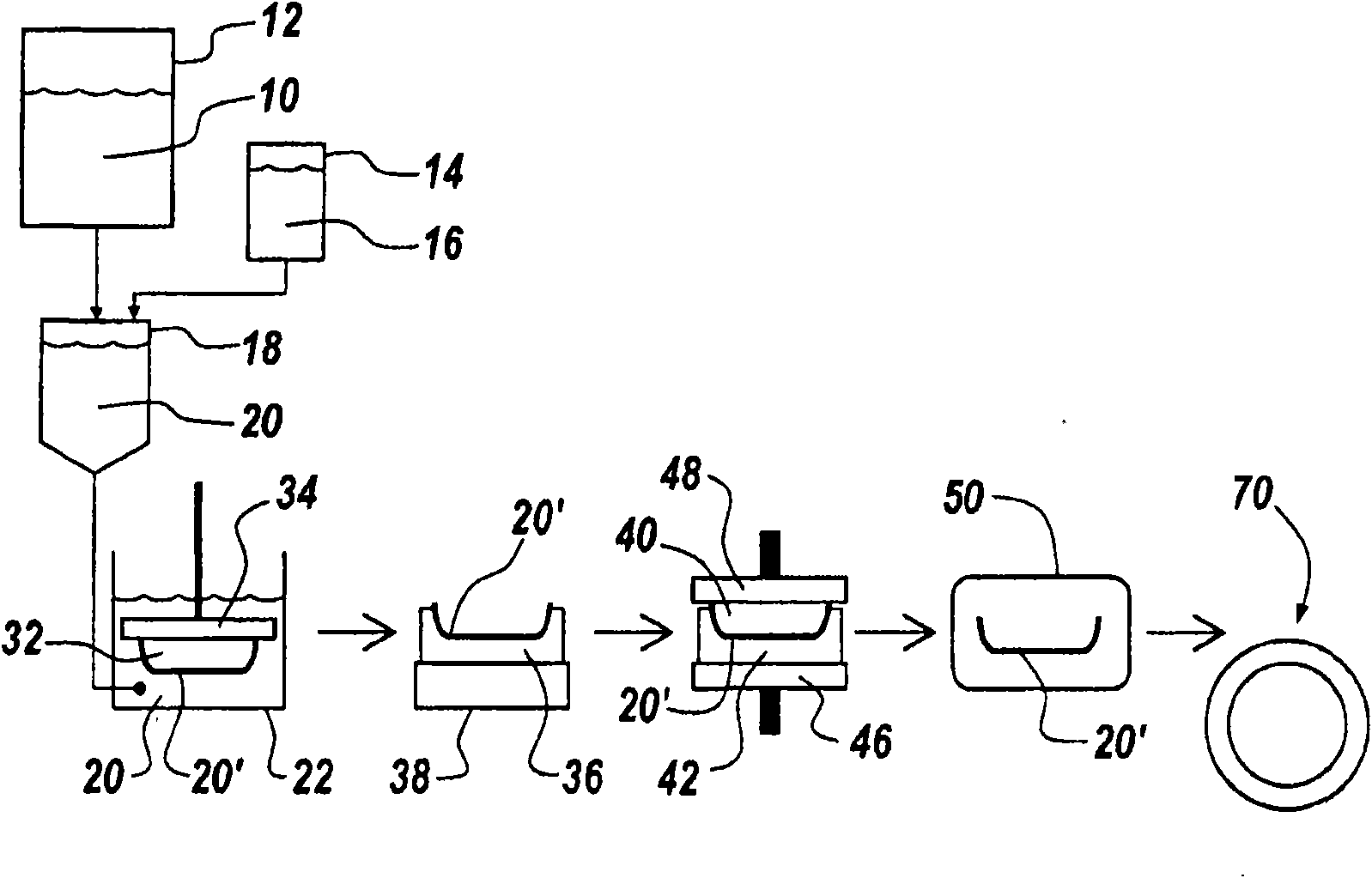
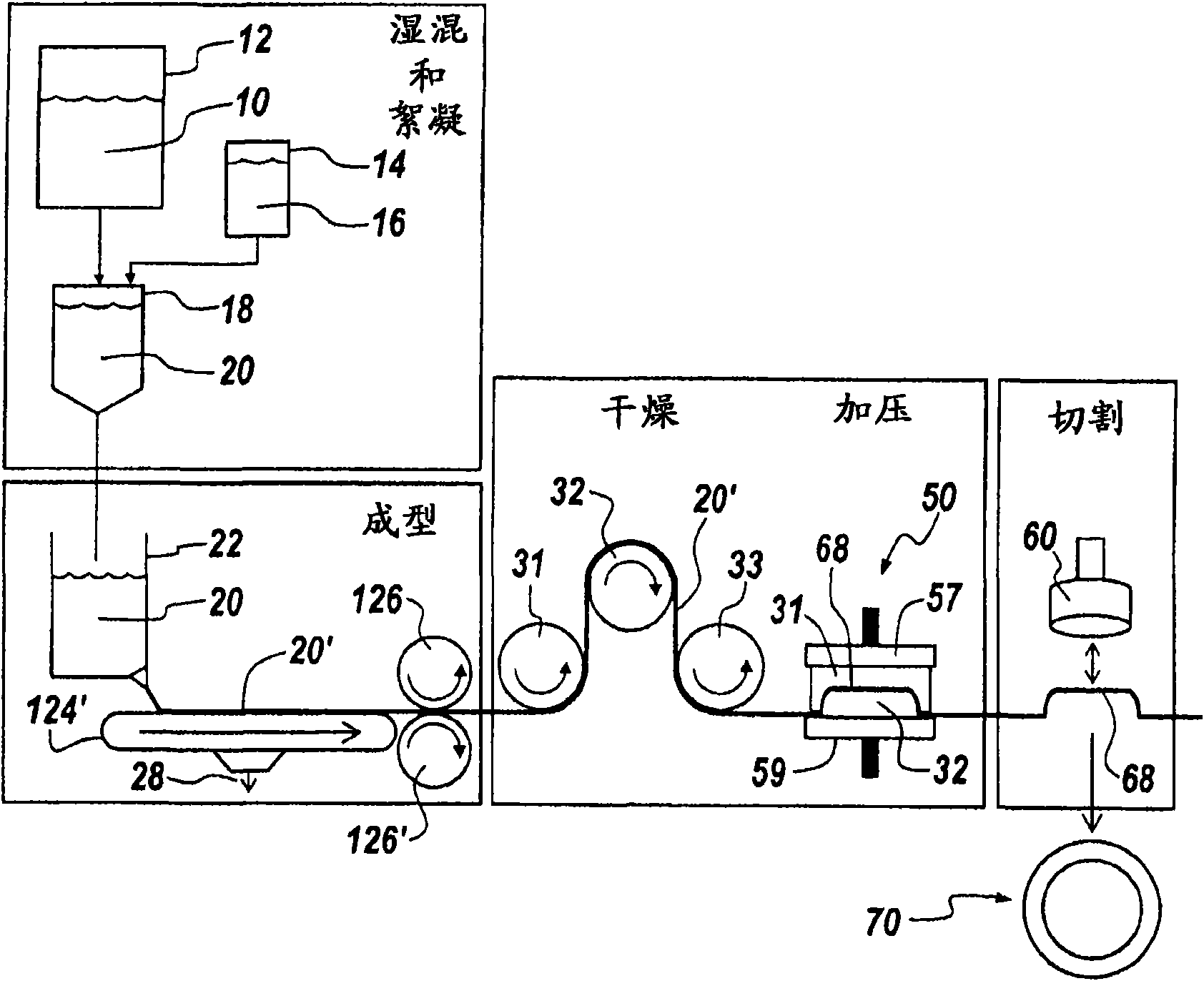
Engineered wood product
A wood product and engineering technology, applied in the field of engineered wood products, can solve problems such as cracking and warping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-5
[0179] Examples 1-5: Preparation of Representative Engineered Wood Products
[0180] A series of five formulations of the engineered wood products described herein were prepared and tested using the following general procedure.
[0181] Measure out water in an appropriately sized beaker to process the remainder of the recipe ingredients with agitation. Add all fibers and fillers (fibers and fillers can be premixed) to the water under agitation with a good vortex.
[0182] The desired amount of wet strength resin, such as Kymene 736 (Hercules), is measured out and added to the fiber stock. After 1 minute, latex, antioxidant and hydrophobic agent such as wax are added (these components can optionally be premixed). After 1 minute, a polyamine such as Alcofix 159 (Ciba) is added. After 1 minute, polyacrylamide (Nalco 61067) was added. After 1 minute, if necessary, improve the mixture with variable amounts of silica gel such as Eka NP 780 (Eka Chemicals) until clear water is ob...
Embodiment 6
[0194] Example 6: Additional Formulation Examples
[0195] Two additional formulations (Examples 7 and 8) were prepared following the order of addition shown in Table 4. Example 8 used recycled denim and recycled carpet fibers instead of wood fibers. The use of formulations of such materials can lead to improvements in different properties such as sound insulation or cushioning or strength properties.
[0196]Samples were prepared by layering different combinations of these materials. It is desirable to make samples 1 / 2 inch thick to 1 inch thick. In order to improve the bonding of the layers in the middle of the laminate, it was decided to compress in stages. For example, a 3 / 4" thick sample was made by combining a total of 12 sheets of the formulation of Example 7. The process was started with 4 stacks of 3 sheets / stack and heated in a hot press at 500 gauge pressure. All 4 individual stacks were compressed simultaneously on the board. After 1 minute, the 4 laminated sam...
Embodiment 7
[0206] Example 7: Additional formulation examples
[0207] The following examples show the effect of latex level on the hydrophobicity of engineered wood products. Formulations 1-4 were made following the order of addition shown.
[0208] Unlike the previous examples, it should be noted that in this example no additional hydrophobic agents were added to any of the formulations shown. The amount of latex added to each formulation was reduced by 5%, with formulation 1 containing 15% latex and formulation 4 containing no latex. The removal of latex was offset by a corresponding increase in recycled carpet fiber, as this fiber was felt to have minimal impact on the water management performance of the resulting wood samples.
[0209] Local adjustments were made to the flocculant packs in formulations 3 and 4 to obtain proper flocculant formation. The data (shown in Table 5) show that the addition of latex helped reduce the level of water intrusion into the samples and retarded d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com