Madder extract and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of extract and madder, applied in madder extract and its preparation and application fields, can solve problems such as no research report on pharmacological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] This example is the extraction method of madder extract-ethyl acetate part, which specifically includes the following steps: take dry madder, crush, extract with 95% alcohol by percolation at room temperature, recover the ethanol to obtain the extract; dissolve the extract In water, heat to completely dissolve; then extract with ethyl acetate and concentrate to obtain ethyl acetate extract.
Embodiment 2
[0024] This example is a separation method of the compound alizarin, the separated product of the ethyl acetate extract of Rubia sinensis, which includes the following steps: the ethyl acetate extract is subjected to 200-300 mesh silica gel column chromatography, and petroleum ether-acetone gradient elution (95 :5~9:1), 4 parts are obtained. The third part is eluted by silica gel H column chromatography, petroleum ether-acetone (15:1), detected by TLC, and combined by Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography, washed with acetone After removal, the compound alizarin is obtained.
Embodiment 3
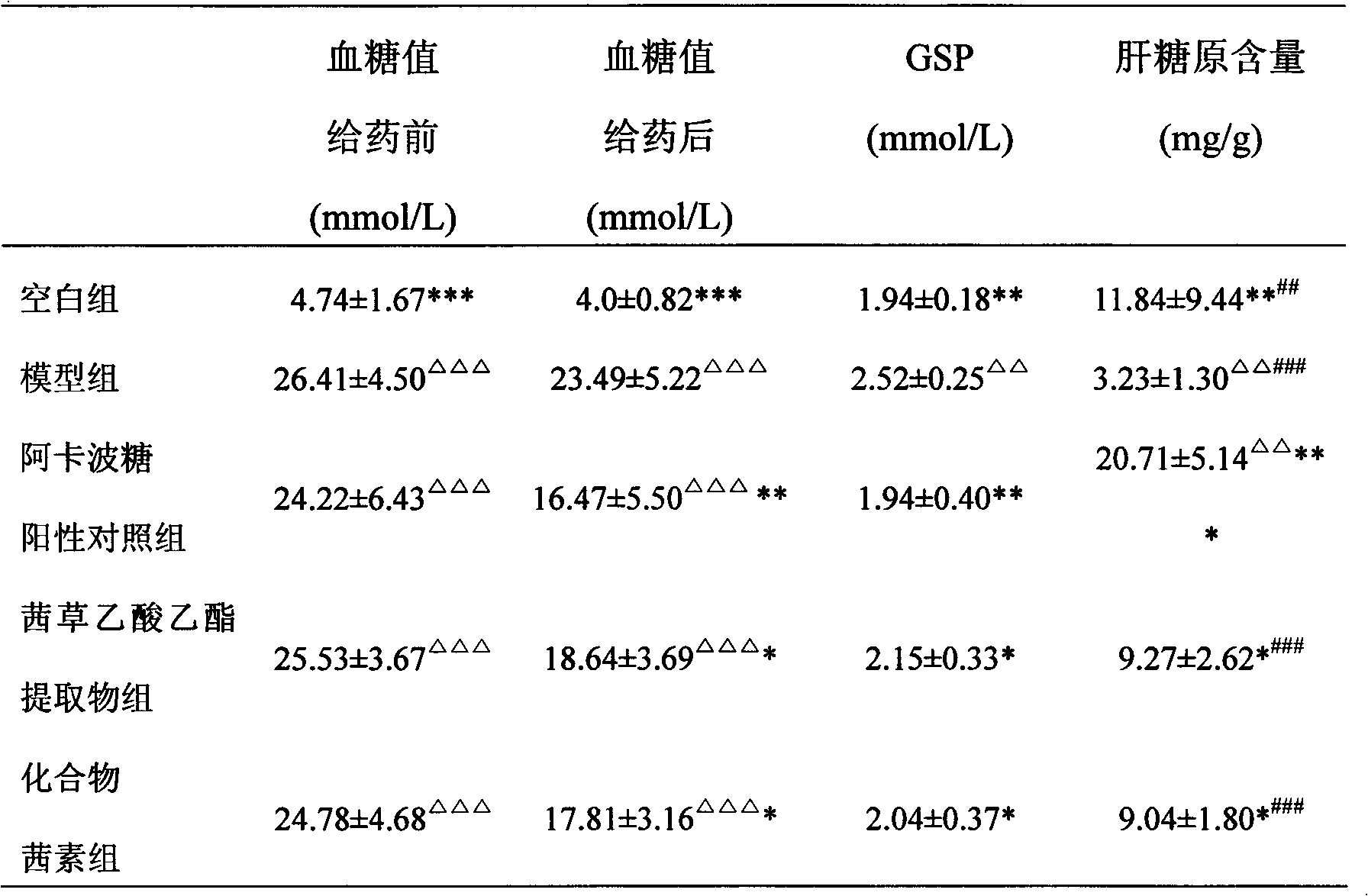
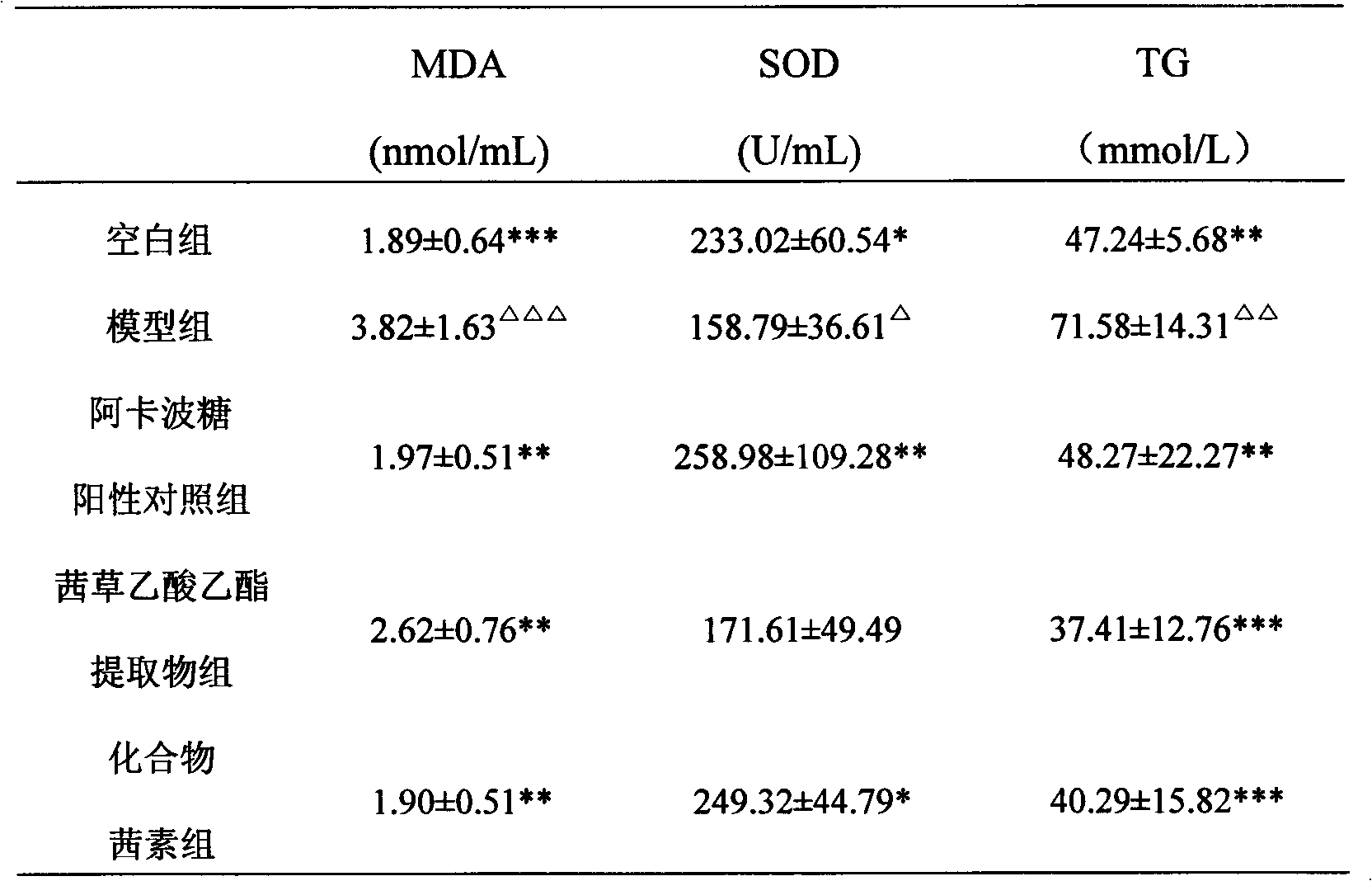
[0026] This example is an experiment on the treatment of diabetes with the ethyl acetate extract of rubia grass and the compound alizarin.
[0027] Method: Mouse Model of Alloxan Diabetes
[0028] Principle: Alloxan (Alloxan) is a pancreatic beta cell toxicant, which can selectively damage pancreatic beta cells in a variety of animals and cause diabetes. It is the most commonly used animal model of diabetes due to its simple and convenient method and high formation rate. For the stability study of the alloxan mouse diabetes model, the main method is to use the alloxan solution to induce diabetes after injection, and detect the blood glucose level in the mouse serum within a certain period of time. In diabetes, the level of GSP (glycated serum protein), which reflects the average blood glucose level in the past 1-2 weeks and the effect of drugs on non-enzymatic glycation in the body, will increase. At the same time, the activity of certain enzymes in the glycogen synthesis process ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com