Stripping treatment method for dyed textiles
A treatment method and technology for textiles, applied in dyeing, textiles and papermaking, etc., to achieve the effects of convenient operation, wide range of adaptability to pH value, and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
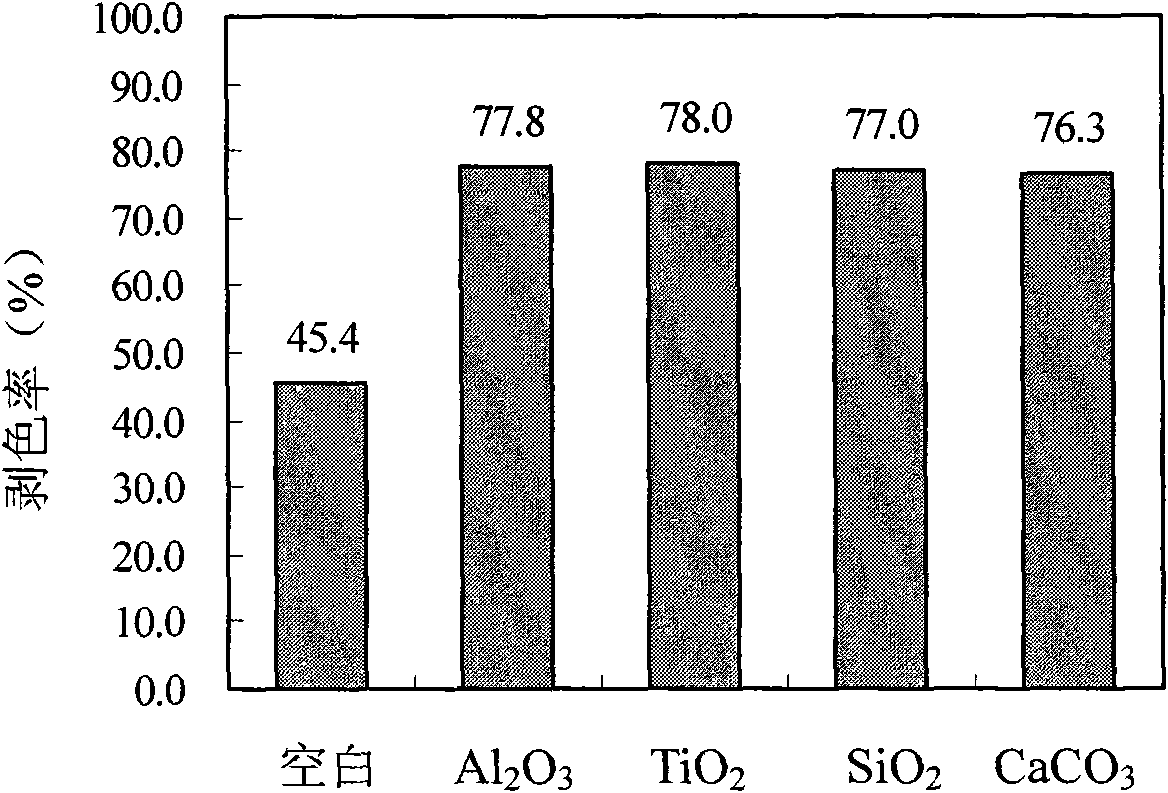
[0027] Nano material Al 2 o 3 The powder is a photocatalyst, and it is prepared to a mass concentration of 0.02g L -1 disperse aqueous solution, and adjust the pH of the solution to 6; then add it to the reaction device at a bath ratio of 1:50, as a stripping bath for nanomaterials. Similarly, the nanomaterials TiO 2 , SiO 2 and CaCO 3 The powder is a photocatalyst, and the stripping bath is prepared according to the above method.
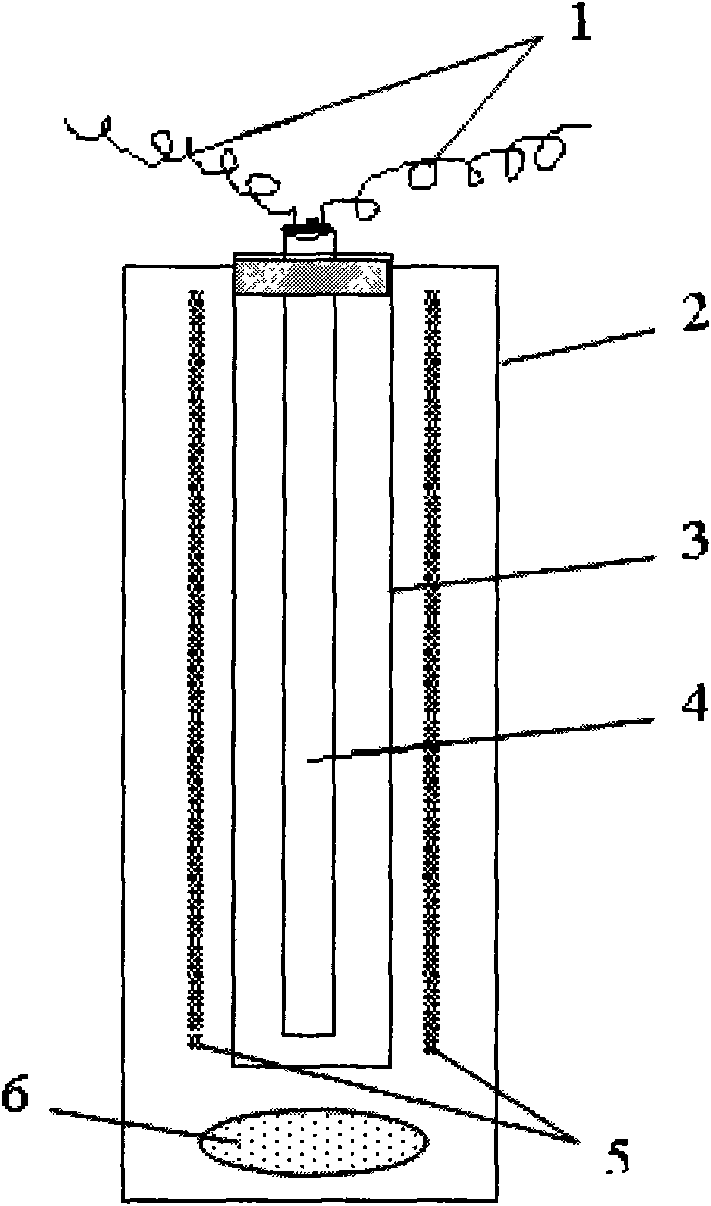
[0028] In this embodiment, a batch reaction device is used to perform nanomaterial photocatalytic stripping treatment on dyed textiles. See attached figure 1 , in the batch reactor 2, an oxygen increasing device 6 is installed, and an oxygen increasing pump is used to continuously feed air into the stripping bath; a quartz glass tube 3 and a low-pressure mercury lamp 4 are installed, and the present embodiment uses an 8W low-pressure mercury lamp It is an ultraviolet light source, and the power supply connection 1 (power supply is not shown)...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Select commercially available rare earth doped nano-semiconductor TiO 2 (Shandong Laiyangzi Xilai Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd.) is a photocatalyst and is prepared into a dispersed aqueous solution. Accelerator Al was added to a solution 3+ , the dosage is 2.0×10 -4 mol L -1 , adjust the pH of the solution to 4.5; add accelerator H to another solution 2 o 2 , the dosage is 6.0×10 -2 mol L -1 , adjust the pH of the solution to 10. The above two solutions were doped with nano-TiO 2 The final concentration is 0.04g L -1 , and then they are respectively added to two reaction devices at a bath ratio of 1:80, and according to the intermittent device and process provided in Example 1, the dyed cotton fabric in Example 1 is subjected to photocatalytic stripping under room temperature conditions. treatment, and with no accelerator (but containing equal amount of doped TiO 2 ) of the blank test is compared, and its specific steps and other conditions are...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Nano TiO 2 with SiO 2 After compounding at a mass ratio of 1:1, it becomes a photocatalyst, and the dosage is 0.04g L -1 Prepared as a water dispersion solution, and the accelerator Al 3+ The concentration is 2.0×10 -4 mol L -1 , the solution pH is 4.5. Then join in the batch reaction device by the bath ratio of: 40, press the method for embodiment 1, carry out photocatalytic decolorization treatment 52min at room temperature to the cotton fabric dyed with anthraquinone reactive dye, its specific steps and other conditions As described in Example 1.
[0054] In the present embodiment, the anthraquinone reactive dye dyed textile is a semi-finished pure cotton woven fabric (140g m -2 ) was dyed by the conventional dyeing process of Everzol Blue R (ECI) reactive dyes, and the technological conditions were: 3% (o.m.f.) Everzol Blue R (ECI) reactive dyes, dyeing at 30°C, adding salt to promote dyeing after 10 minutes, and then dyeing at 1°C min -1 After heating up to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com