Simple method for removing trace bromate ion in water
A bromate and water removal technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as complex methods, unsatisfactory removal effects, and impact on effective applications.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] 1) Prepare the reaction solution:
[0019] The sulfuric acid and the aniline monomer are stirred so that the aniline monomer content is 0.1 mol / L, and the sulfuric acid concentration is 1.2 mol / L.
[0020] 2) Electrochemical polymerization:
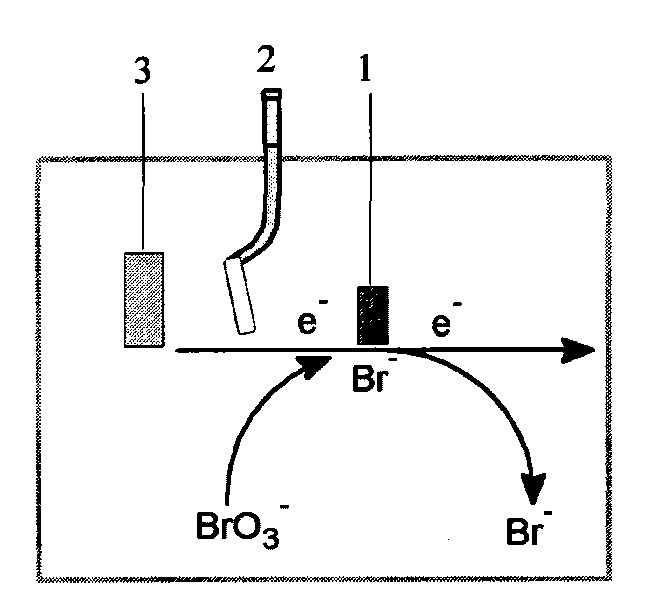
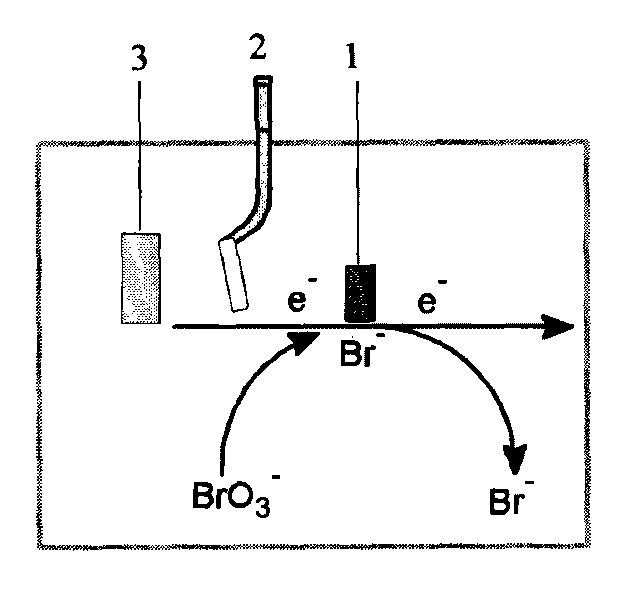
[0021] The three-electrode system ( figure 1 ) placed in a solution containing sulfuric acid and aniline monomer to react for 0.1 hour to carry out electrochemical polymerization. The three-electrode system includes a working electrode 1, a reference electrode 2 and a counter electrode 3. The working electrode 1 is a glassy carbon electrode, which is polished before use to achieve a potential range of -0.5~ in 0.5mol / L sulfuric acid. Maintain a stable cyclic voltammetry curve in the range of 1.0V, and then use deionized water to fully wash it, dry it and set it aside.
[0022] 3) Washing:
[0023] The obtained polyaniline film attached to the electrode is first immersed in 0.05mol / L sulfuric acid, then taken out and washed wit...
Embodiment 2
[0027] 1) Prepare the reaction solution:
[0028] Sulfuric acid and aniline monomer are stirred so that the content of aniline monomer therein is 0.5mol / L, and the concentration of sulfuric acid is 1.0mol / L;
[0029] 2) Electrochemical polymerization:
[0030] The three-electrode system ( figure 1 ) placed in a solution containing sulfuric acid and aniline monomers and reacted for 2 hours to carry out electrochemical polymerization;
[0031] 3) Washing:
[0032] The obtained polyaniline film attached to the electrode is first immersed in 0.05mol / L sulfuric acid, then taken out and washed with deionized water and dried for later use;
[0033] 4) Electrocatalytic reduction:
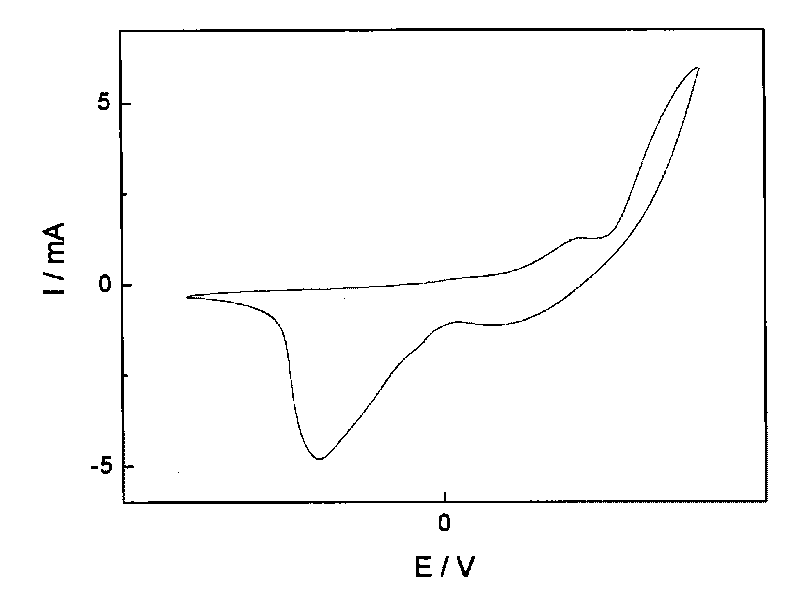
[0034] Immerse the obtained polyaniline membrane in a supporting electrolyte solution containing 50ppm bromate ions, and carry out cyclic voltammetry scanning in the potential range of -1.5~1.5V to achieve the purpose of reducing and removing bromate ions.
Embodiment 3
[0036] 1) Prepare the reaction solution:
[0037] Sulfuric acid and aniline monomer are stirred so that the content of aniline monomer therein is 0.8mol / L, and the concentration of sulfuric acid is 2.2mol / L;
[0038] 2) Electrochemical polymerization:
[0039] The three-electrode system ( figure 1 ) is placed in the solution containing sulfuric acid and aniline monomer and reacted for 1 hour to carry out electrochemical polymerization;
[0040] 3) Washing:
[0041] The obtained polyaniline film attached to the electrode is first immersed in 0.05mol / L sulfuric acid, then taken out and washed with deionized water and dried for later use;
[0042] 4) Electrocatalytic reduction:
[0043] Immerse the polyaniline membrane obtained in the above step 3) in a supporting electrolyte solution containing 100ppm bromate ions, and perform cyclic voltammetry scanning in the potential range of -1.5~1.5V to achieve the purpose of reducing and removing bromate ions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com