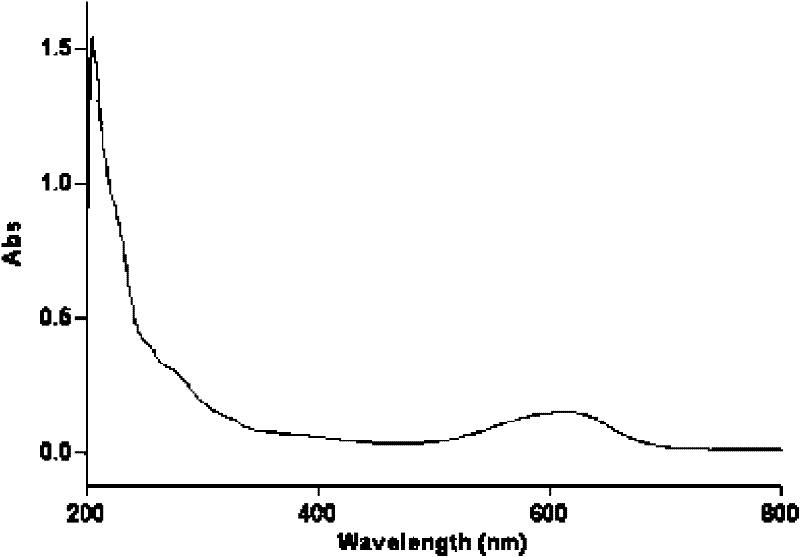
Extraction method of blue-green pigments of abalone shell
An extraction method and abalone shell technology are applied in the fields of natural pigment extraction and abalone shell waste utilization, can solve problems such as low utilization rate, medicinal use after grinding or direct disposal, etc., and achieve the effects of simple method, easy extraction and abundant resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Take 500 grams of abalone shells, add 3 L of 3% acetic acid aqueous solution at 50°C, soak for 4 hours, and filter off the residue. The residue was soaked and extracted with 3L of 3% acetic acid aqueous solution repeatedly according to the above conditions, and the supernatants were combined twice to remove impurities by suction filtration. Adjust the pH of the filtrate to 9.5 with NaOH, let it stand for 0.5h, and remove the supernatant by suction; add 5% acetic acid aqueous solution to the precipitate, stir until the precipitate is completely dissolved, add an equal volume of ethyl acetate to extract twice, and take the blue The ethyl acetate layer was evaporated to remove the solvent, and then dried at 60°C-80°C to solid particles to obtain 7.5 mg of blue-green pigment solid powder.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Take 500 grams of abalone shells, add 3 L of 5% acetic acid aqueous solution at 40°C, soak for 8 hours, and filter off the residue. The residue was soaked and extracted with 3L of 3% acetic acid aqueous solution repeatedly according to the above conditions, and the supernatants were combined twice to remove impurities by suction filtration. Adjust the pH of the filtrate to 10 with NaOH, let it stand for 0.5h, and remove the supernatant by suction; add 15% acetic acid aqueous solution to the precipitate, stir until the precipitate is completely dissolved, add an equal volume of ethyl acetate to extract twice, and take the blue The ethyl acetate layer was evaporated to remove the solvent, and then dried at 60°C-80°C to solid particles to obtain 6.0 mg of blue-green pigment solid powder.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Take 500 grams of abalone shells, add 3 L of 8% acetic acid aqueous solution at 35°C, soak for 12 hours, and filter off the residue. The residue was soaked and extracted with 3L of 3% acetic acid aqueous solution repeatedly according to the above conditions, and the supernatants were combined twice to remove impurities by suction filtration. Adjust the pH of the filtrate to 11 with NaOH, let it stand for 1 hour, and remove the supernatant by suction; add 20% acetic acid aqueous solution to the precipitate, stir until the precipitate is completely dissolved, add an equal volume of ethyl acetate to extract 3 times, and take the blue acetic acid The ethyl ester layer was evaporated to remove the solvent, and then dried at 60°C-80°C to solid particles to obtain 8.5 mg of blue-green pigment solid powder.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com