Minimum mean square error beam forming-based information transmission method in two-way channel
A minimum mean square error, beamforming technology, applied in baseband system components, error prevention/detection through diversity reception, space transmit diversity, etc., can solve problems such as poor bit error rate performance, high complexity, and errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
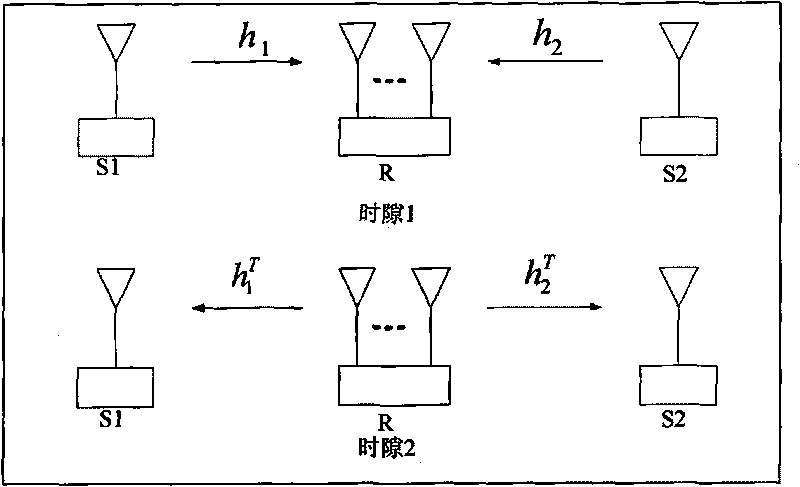
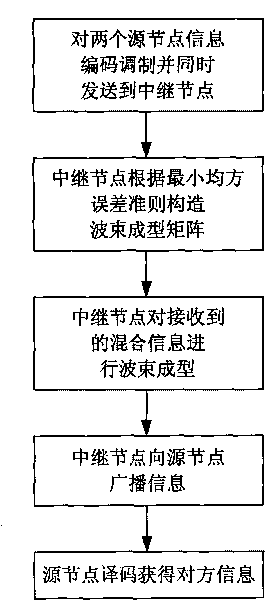
[0030] refer to figure 2 , an information transmission method based on minimum mean square error beamforming in a two-way channel, comprising the following steps:
[0031] Step 1, two source nodes send information at the same time
[0032] refer to figure 1 , use Turbo code to compare the data information d of two source nodes 1 , d 2 Encode separately to obtain the encoding sequence x 1 , x 2 , modulate the encoded sequence, and the modulated signal s 1 (n) and s 2 (n) with power p 1 and p 2 At the same time, it is sent to the relay node.
[0033] Step 2, the relay node constructs the beamforming matrix
[0034] The relay node constructs the beamforming matrix according to the minimum mean square error criterion:
[0035] (2.1) Let the uplink channel H UL =[h 1 , h 2 ], downlink channel H DL =[h 2 , h 1 ] T , h 1 and h 2 are the channels from the source node to the relay node, and for the uplink channel H UL Perform singular value decomposition H UL =U∑...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com