Peptide slow-release formulations
A technology of pre-formulation and active agent, applied in the field of preparation precursors, can solve the problems of inability to filter sterilization, inability to heat sterilization, difficulty in preparing PLGA microbeads, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0191] Availability of Multiple Liquid Crystal Phases in Depot Formulations for Choice of Composition
[0192] Injectable formulations containing various ratios of phosphatidylcholine ("PC" - Epikuron 200) and glyceryl dioleate (GDO) and ethanol as solvent were prepared to illustrate the accessibility of the depot precursor formulation after equilibration with excess water Various liquid crystal phases.
[0193] Weigh an appropriate amount of PC and ethanol in a glass vial, and place the mixture on a shaker until the PC is completely dissolved to form a clear liquid solution. GDO is then added to form an injectable homogeneous solution.
[0194] Each formulation was injected into vials and equilibrated with excess water. Phase properties were evaluated visually and between cross-polarizations at 25 °C. The results are listed in Table 1.
[0195] Table 1
[0196]
[0197] L 2 = reverse micellar phase; I 2 = anti-cubic liquid crystal phase; H II = inverse hexagonal li...
Embodiment 2
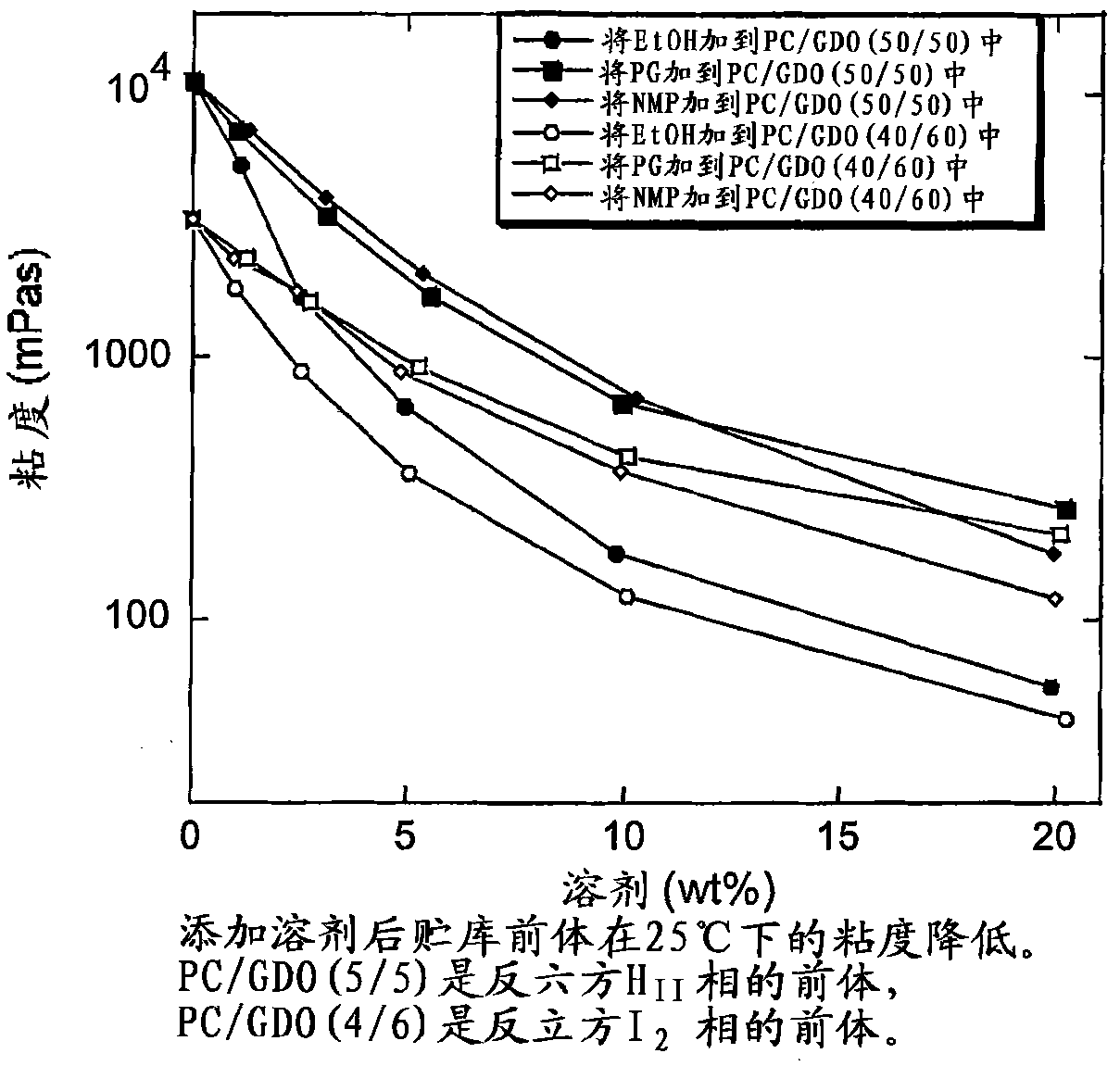
[0199] Viscosity in PC / GDO (5:5) or PC / GDO (4:6) with added solvents (ethanol, PG, and NMP)
[0200] A mixture of about 25% ethanol and PC / GDO / EtOH was prepared according to the method in Example 1. Use a rotary evaporator (vacuum, 1 hour at 40°C, then 2 hours at 50°C) to remove all or almost all of the ethanol in the mixture, weigh the resulting mixture in a glass vial, and then add 1, 3, 5, 10 Or 20% solvent (ethanol, propylene glycol (PG) or n-methylpyrrolidone (NMP)). The samples were allowed to equilibrate for several days, then the viscosity was measured with a CarriMed CSL 100 viscometer equipped with automatic notch setting.
[0201] This example clearly illustrates the need for solvents for some depot formulation precursors in order to obtain injectable formulations (see figure 1 ). The viscosity of solvent-free PC / GDO mixtures increases with increasing PC ratio. Systems with low PC / GDO ratios (more GDO) with low concentrations of solvent are injectable.
Embodiment 3
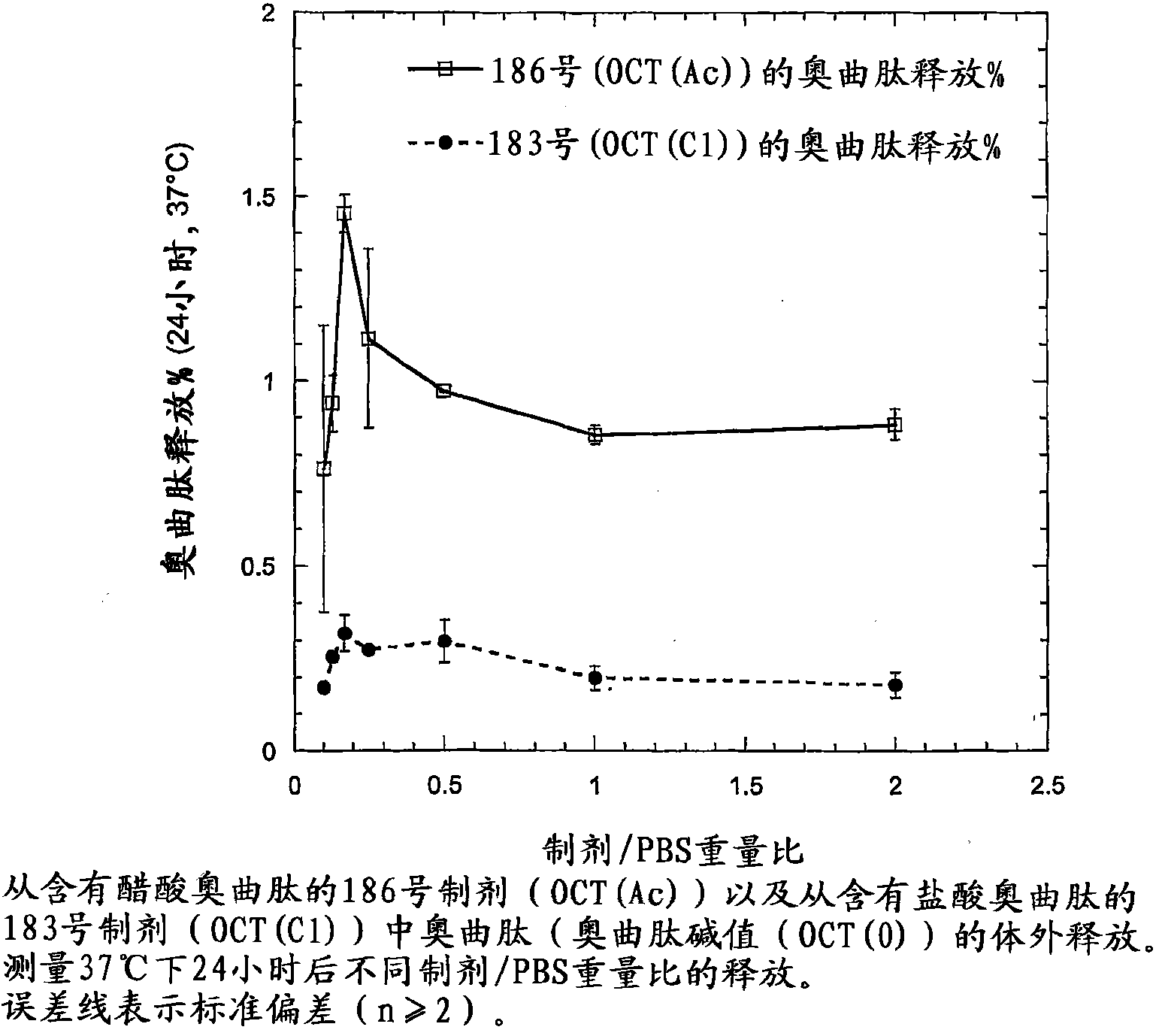
[0202] Example 3: Preparation of depot compositions containing the peptide octreotide
[0203] Octreotide acetate (24 mg or 60 mg) was dissolved in 0.1 g of ethanol. 0.36 g of PC and 0.54 g of GDO were sequentially dissolved in this solution to obtain a depot preparation precursor. The formulation precursor was injected into excess aqueous phase (syringe 23G, 0.6mm x 30mm) to obtain bulk liquid crystalline phase (I 2 structure). That is, octreotide (2.4% or 6.0%) did not change the overall composition and phase properties after exposure to an aqueous environment.
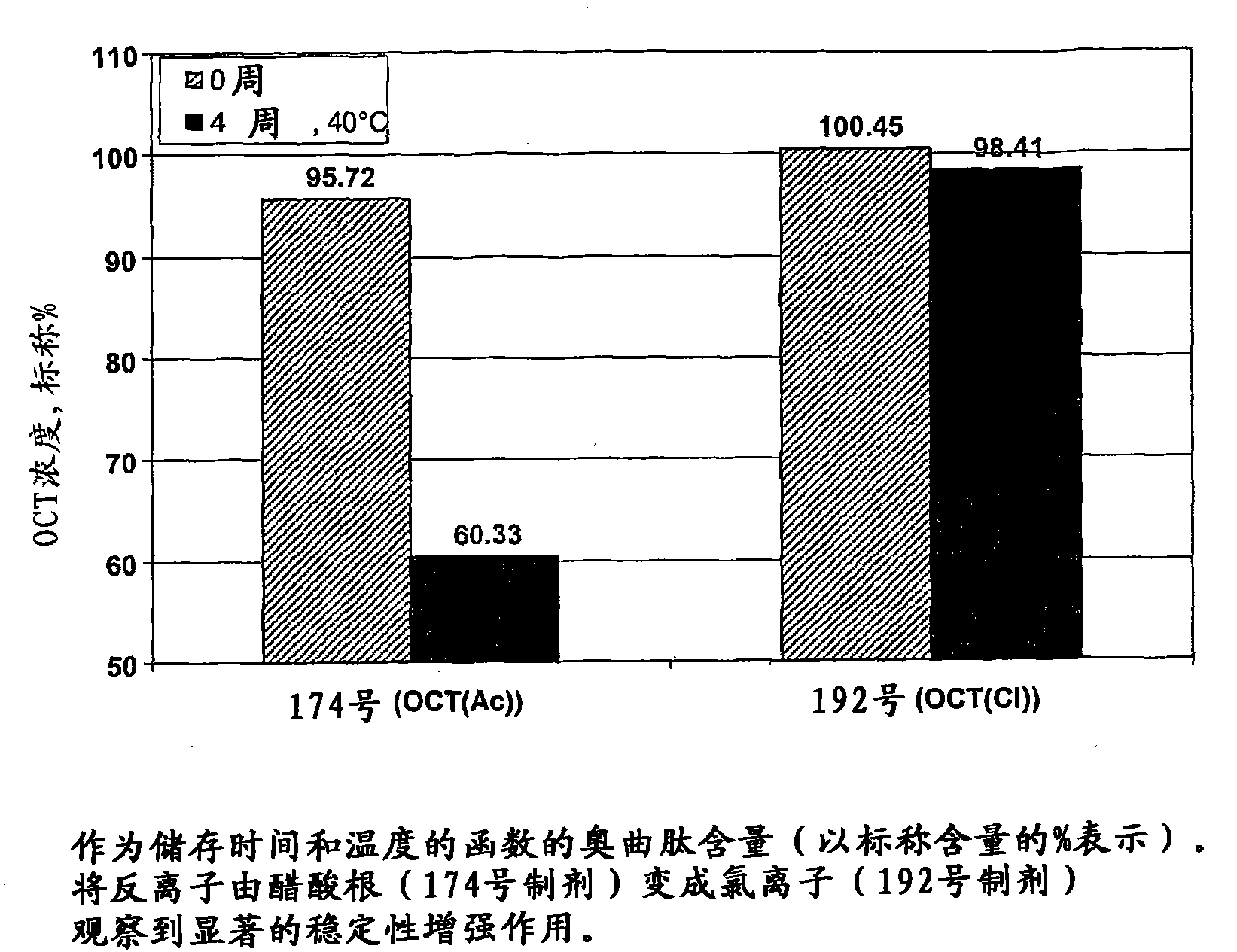
[0204] The octreotide depot precursor formulation in this example was tested for stability to crystallization during storage. Each formulation was stable for at least two weeks at 4-8°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com