Mirror surface projection method for precisely determining orbit of geostationary orbit satellite
A geostationary orbit and precise orbit determination technology, applied in positioning, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult solution and separation of system errors, large investment, and difficult determination of orbit, so as to improve the accuracy of orbit determination and expand observation range, the effect of reducing the number of layouts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The specular projection method for precise orbit determination of geostationary satellites consists of the following steps:
[0024] 1. Calculate the projection surface required for the implementation of the mirror projection method
[0025] 1.a. Solve the orbital plane of the geostationary orbit satellite by geometric method or dynamic method, and use the orbital plane as the projection plane;
[0026] 2. Using mirror projection to form virtual observation stations and their corresponding virtual observation values
[0027] 2.a. Perform mirror projection on each observation station, that is, take the orbital plane as a symmetrical plane, and set up a virtual observation station at a place symmetrical to each observation station;
[0028] 2.b. The observation value of each virtual observation station adopts the observation value of its corresponding observation station.
[0029] 3. Combining the observation values of actual observation stations and virtual observati...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Utilize the standard orbit of the satellite, simulate 5 ground monitoring stations to the multi-day observation data of the geostationary orbit satellite, the observation noise obeys normal distribution N (0, 1), 10 meters of satellite clock difference, adopt the step of embodiment one to determine rail.
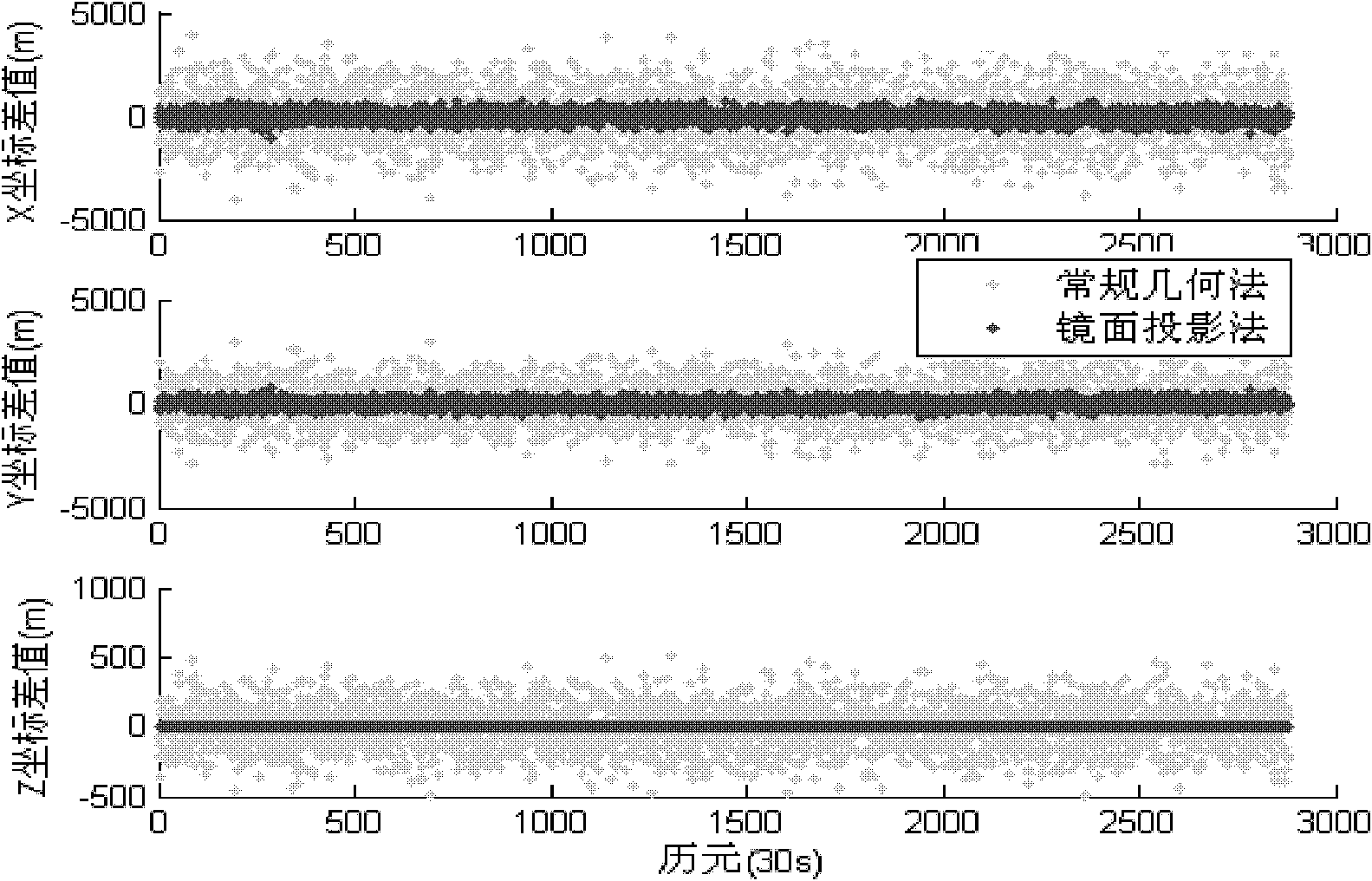
[0032] figure 1 It is the comparison of the difference between the orbital parameters of geostationary orbit satellites calculated by the geometric method without the specular projection method and the geometric method with the specular projection method and the true value. Among them, the horizontal axis is the number of epochs (30-second interval), and the three vertical axes are the difference between the calculated value and the true value in the X, Y, and Z directions respectively; the light-colored points in the figure are the calculated results without using the mirror projection method , and the dark points are the calculation results after using the mirror p...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Using the standard orbit of the satellite, the one-day observation data of the geostationary orbit satellite by five ground monitoring stations are simulated. For the convenience of dealing with the problem, the observation error term considers observation noise, troposphere, ionosphere and satellite clock error simulated by quadratic terms. The satellite's perturbation item considers multi-body perturbation, solar light pressure, and empirical force. The steps in Embodiment 1 are used for orbit determination.
[0035] When the mirror projection method is not used, the difference between the initial orbital elements calculated by the dynamic method and the true value is 0.5020 meters in the X direction, 0.4097 meters in the Y direction, and 1.6120 meters in the Z direction; The difference between the calculated initial orbit elements and the true value is 0.1402 meters in the X direction, 0.2335 meters in the Y direction, and 0.0262 meters in the Z direction; it can be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com