Permanent magnet rotor with flux concentrating pole pieces
A technology of permanent magnets and rotors, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit rotating parts, magnetic circuits, magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, etc., can solve the problems of increasing rotor weight and inertia moment, etc., to improve performance, reduce costs, and reduce production cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
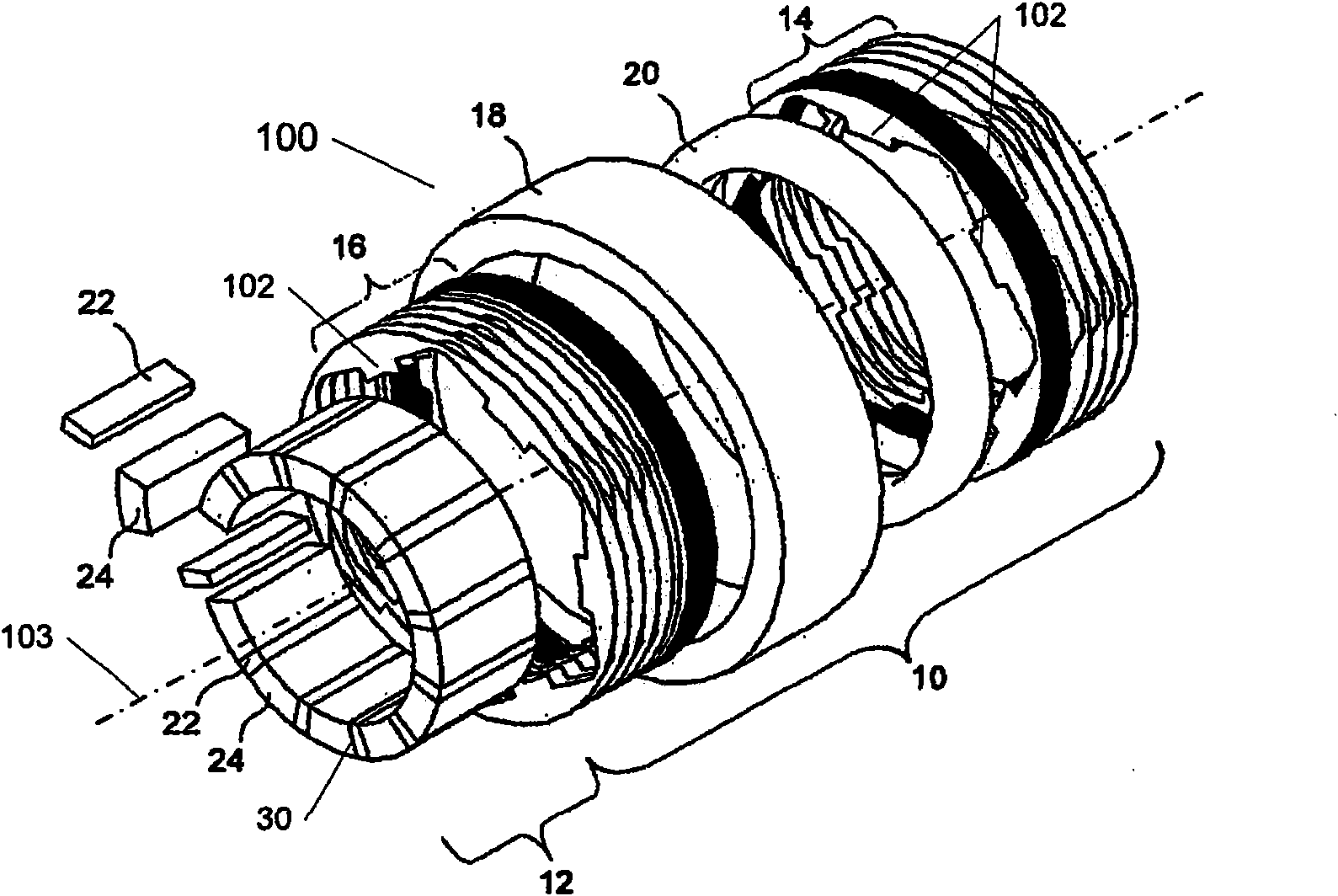
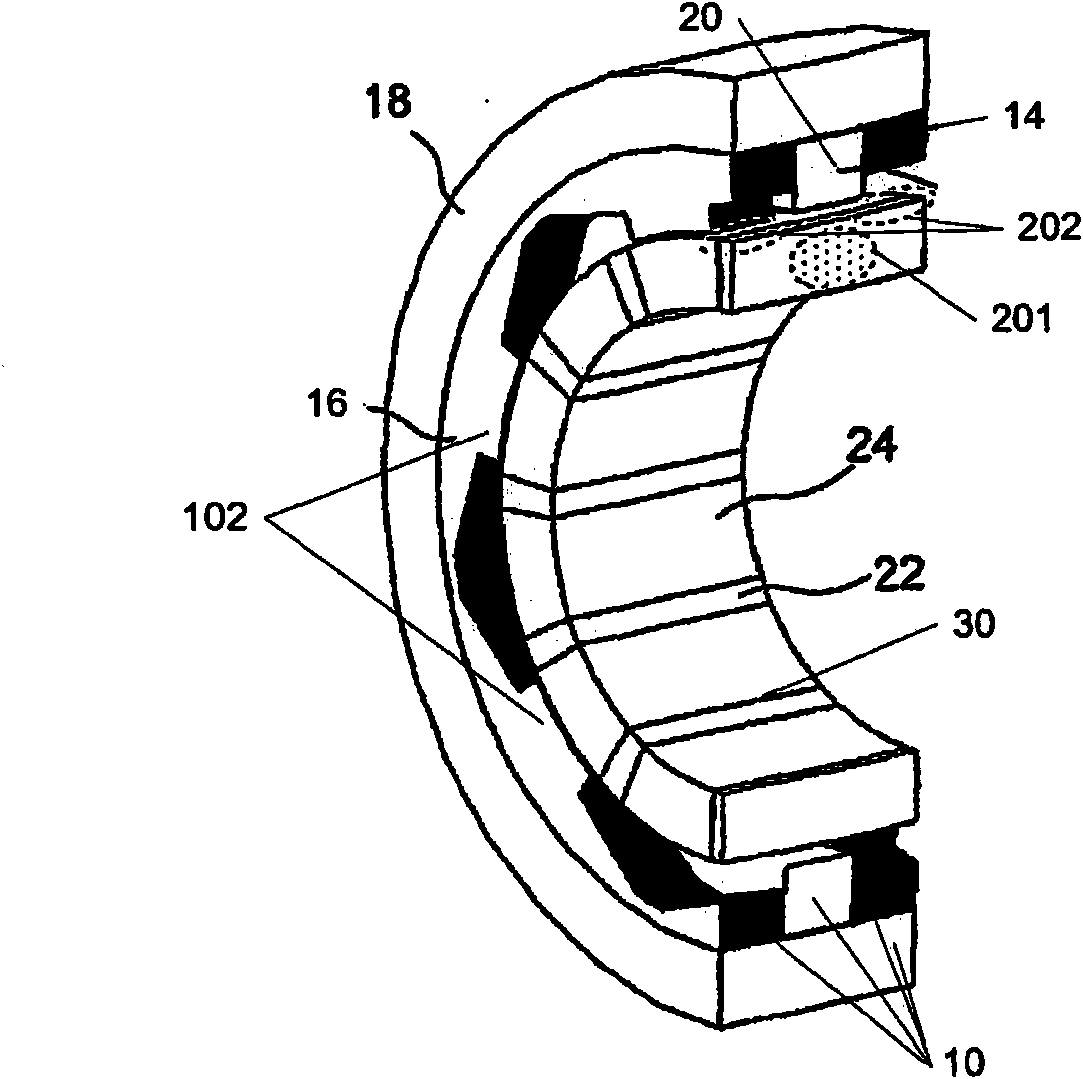
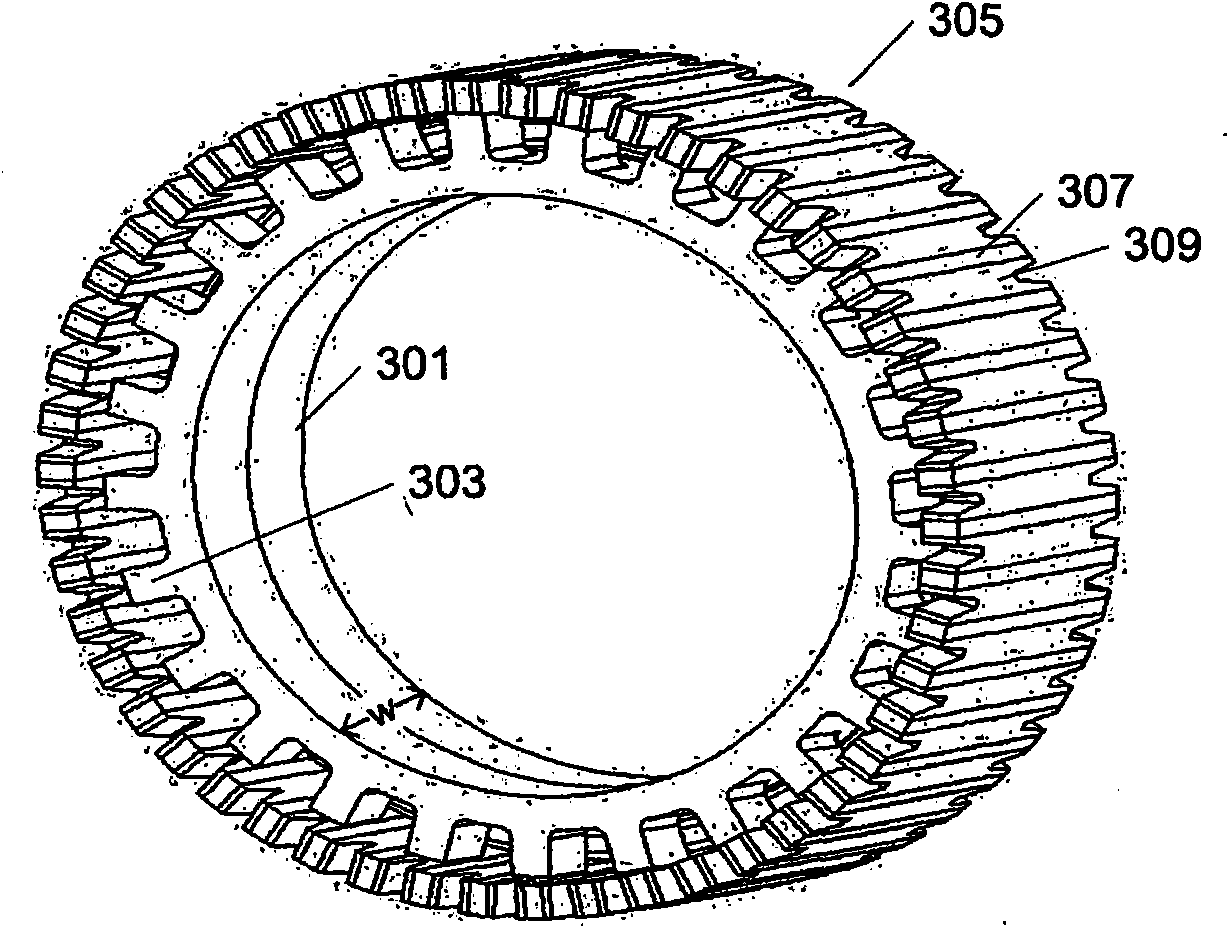
[0031] The present invention is in the field of permanent magnet electric machines 100 , an example of which is shown in the exploded perspective schematic diagram of FIG. 1 . A fundamental feature of the permanent magnet motor stator 10 is the use of a magnetic coil, eg, a central single winding 20, which provides magnetism to a plurality of teeth 102 formed from a soft magnetic core structure. The stator core is then formed around the windings 20, although in other common electric machine constructions the windings are formed around the individual tooth core segments. Examples of modulated pole machine layouts are sometimes considered to include, for example, claw pole, hook foot, Rendell or TFM machines. More specifically, a permanent magnet electric machine 100 is shown comprising: two stator core sections 14 and 16 each comprising a plurality of teeth 102 and having a substantially annular shape; disposed between first and second annular stator core sections a coil 20; a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com