Patents
Literature
43results about How to "Reduce radial thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
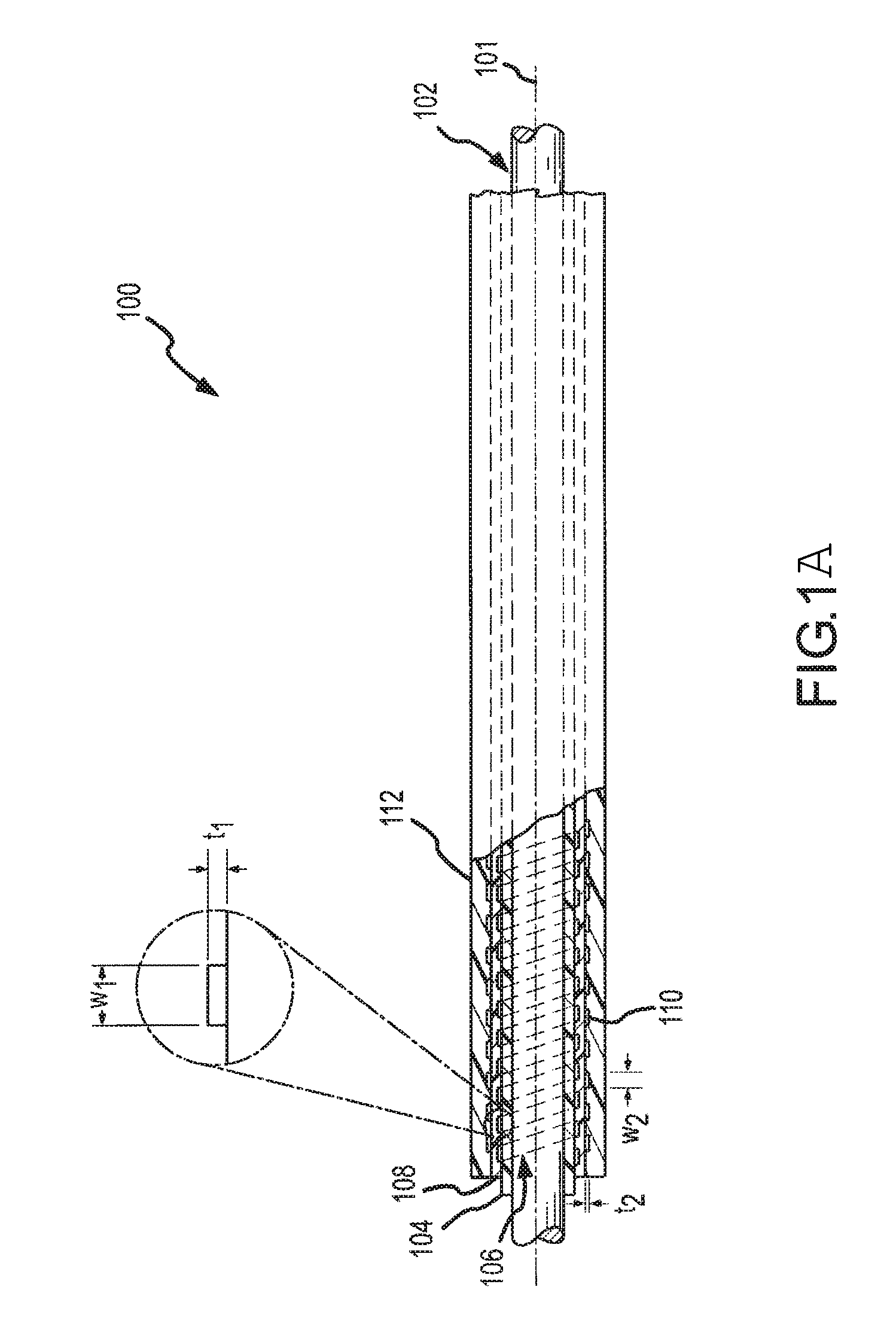
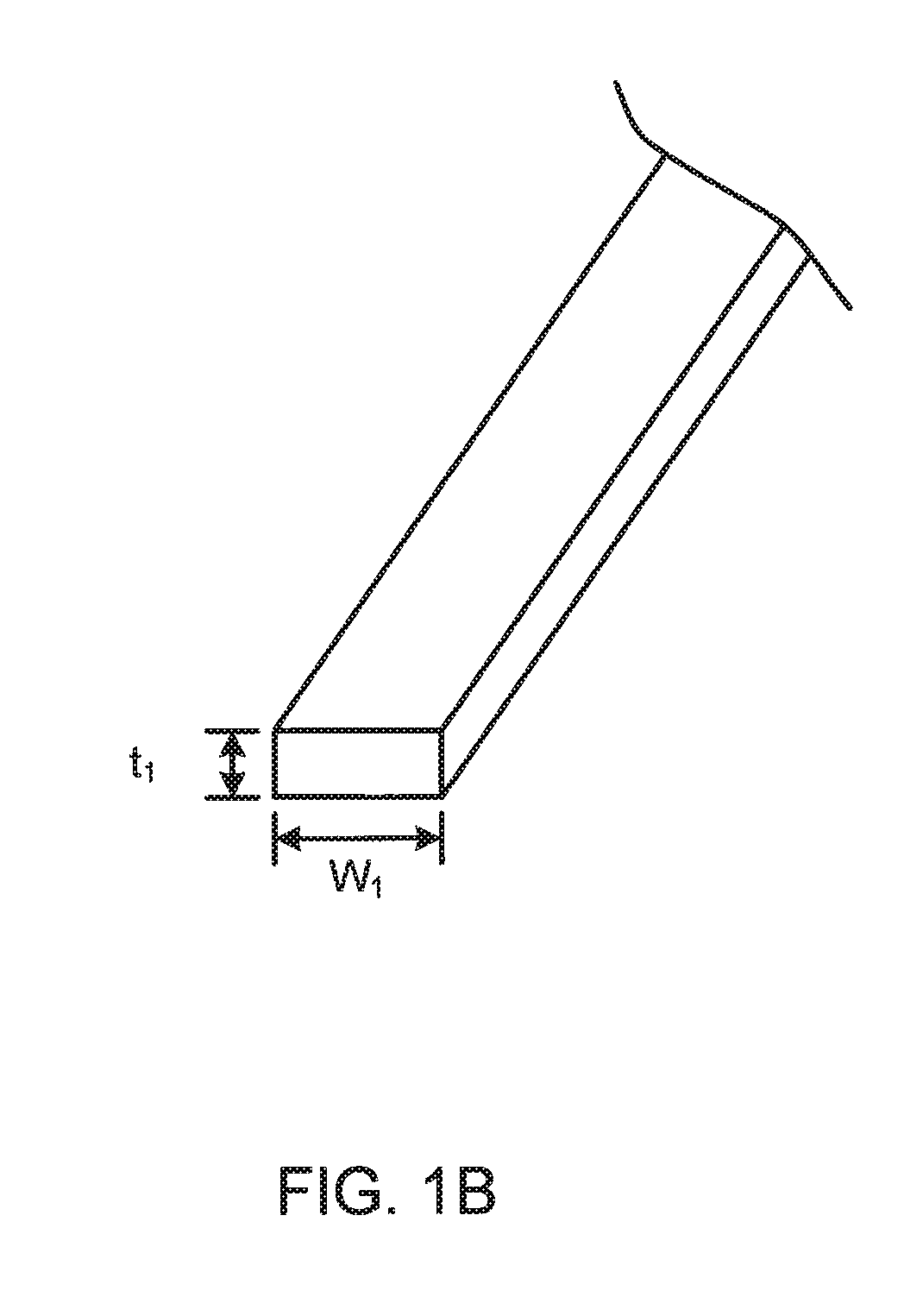
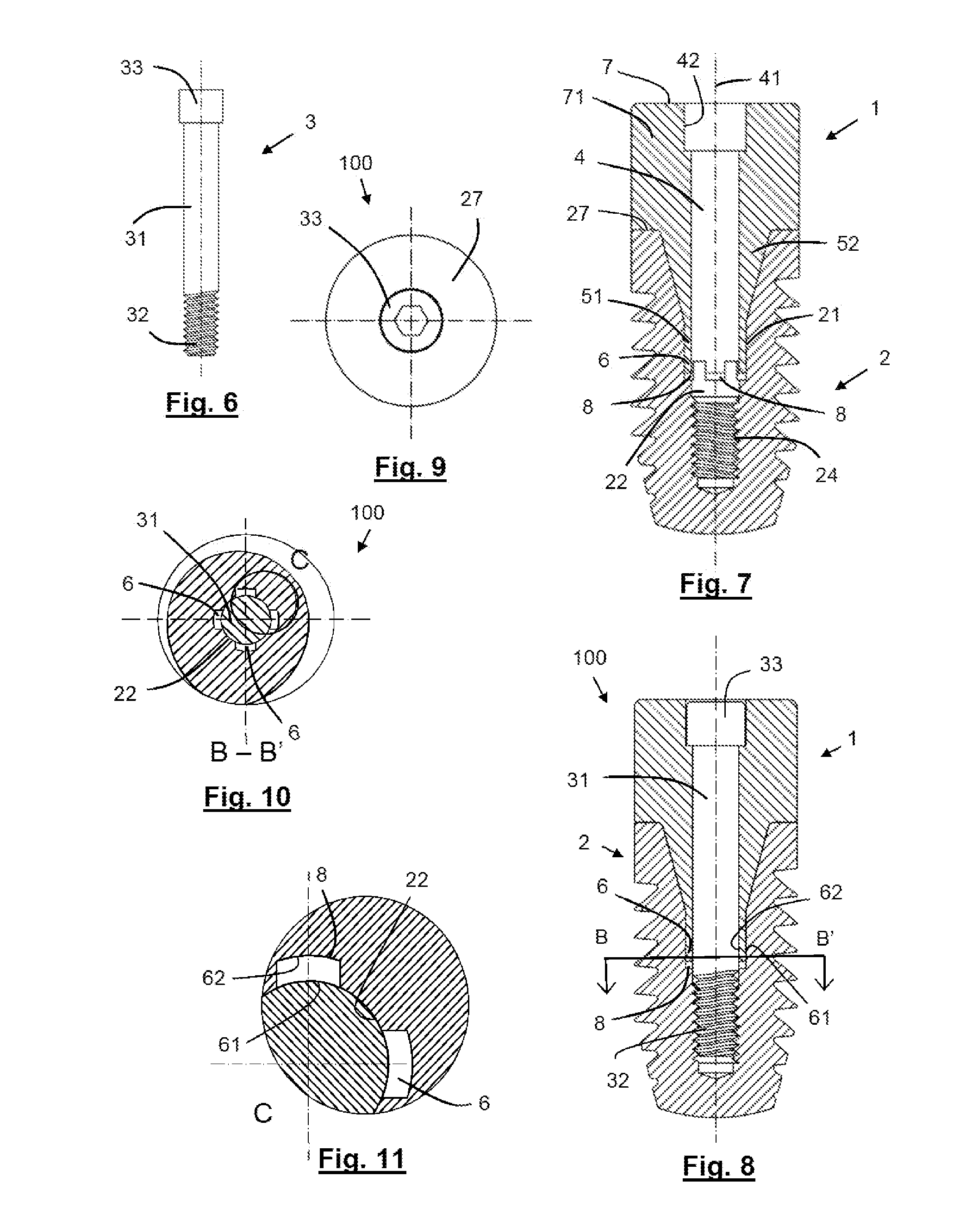
Dual braided shaft
ActiveUS20080161762A1Simple designReduce shaft diameterCatheterIntravenous devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
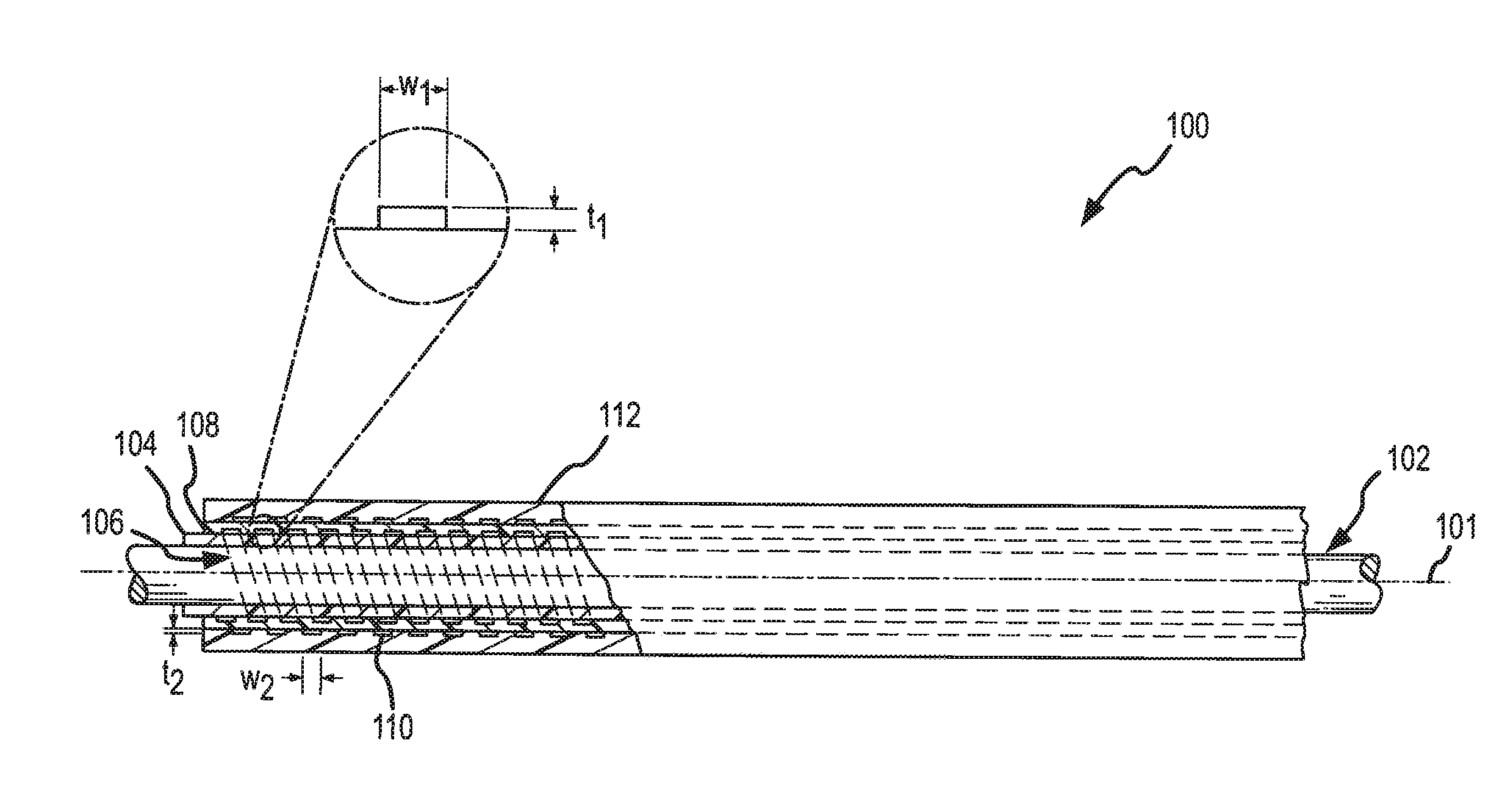
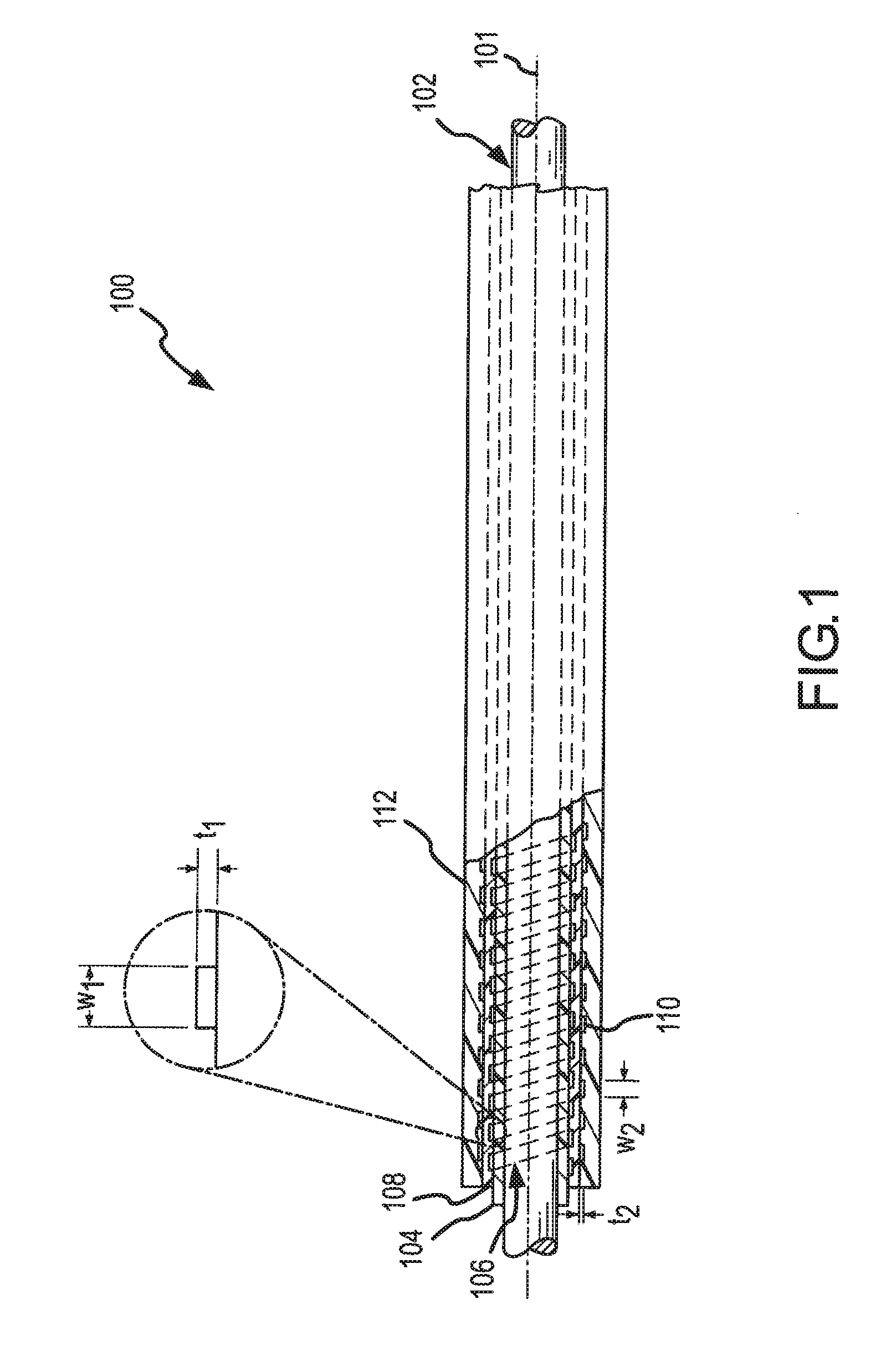
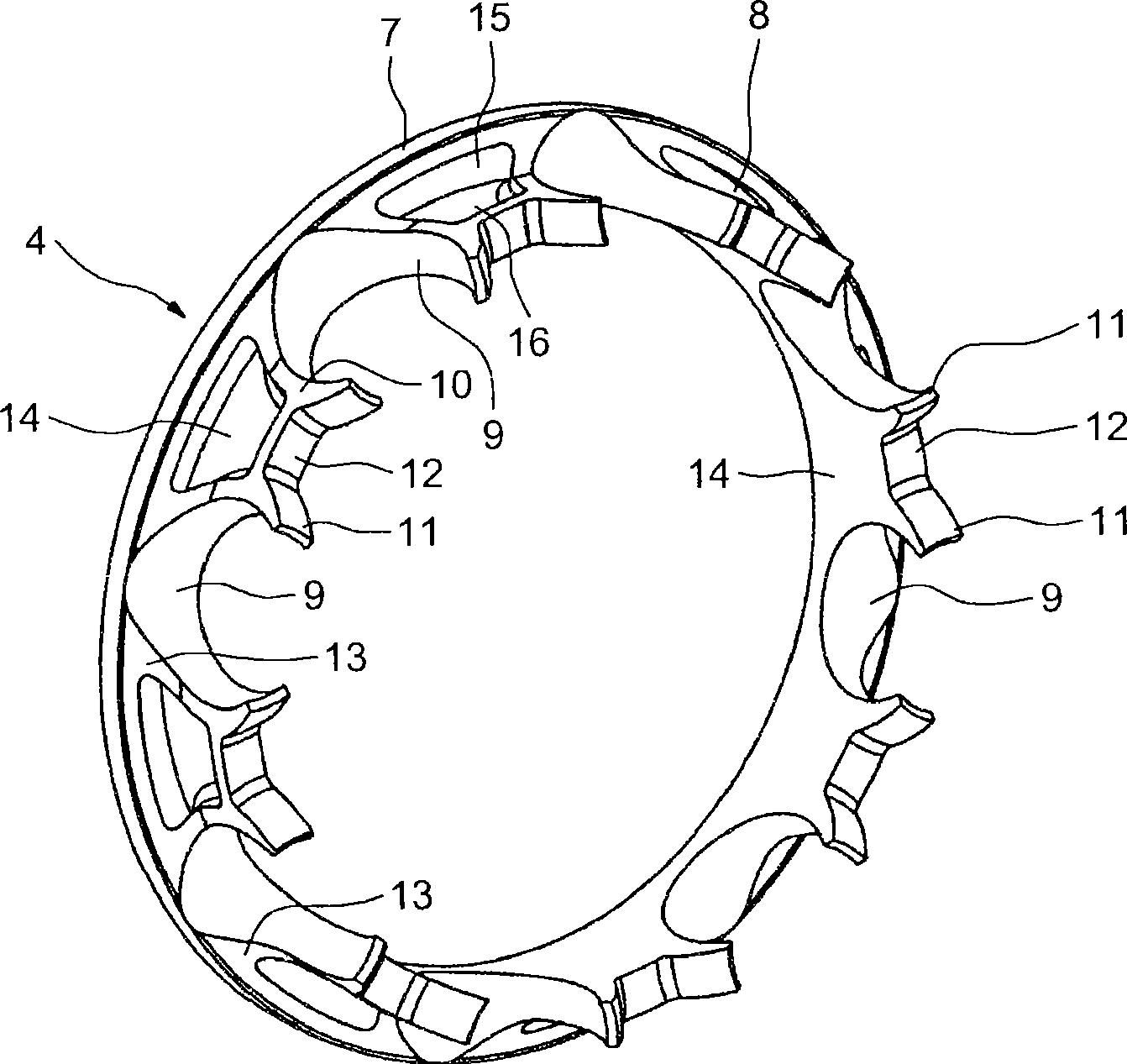
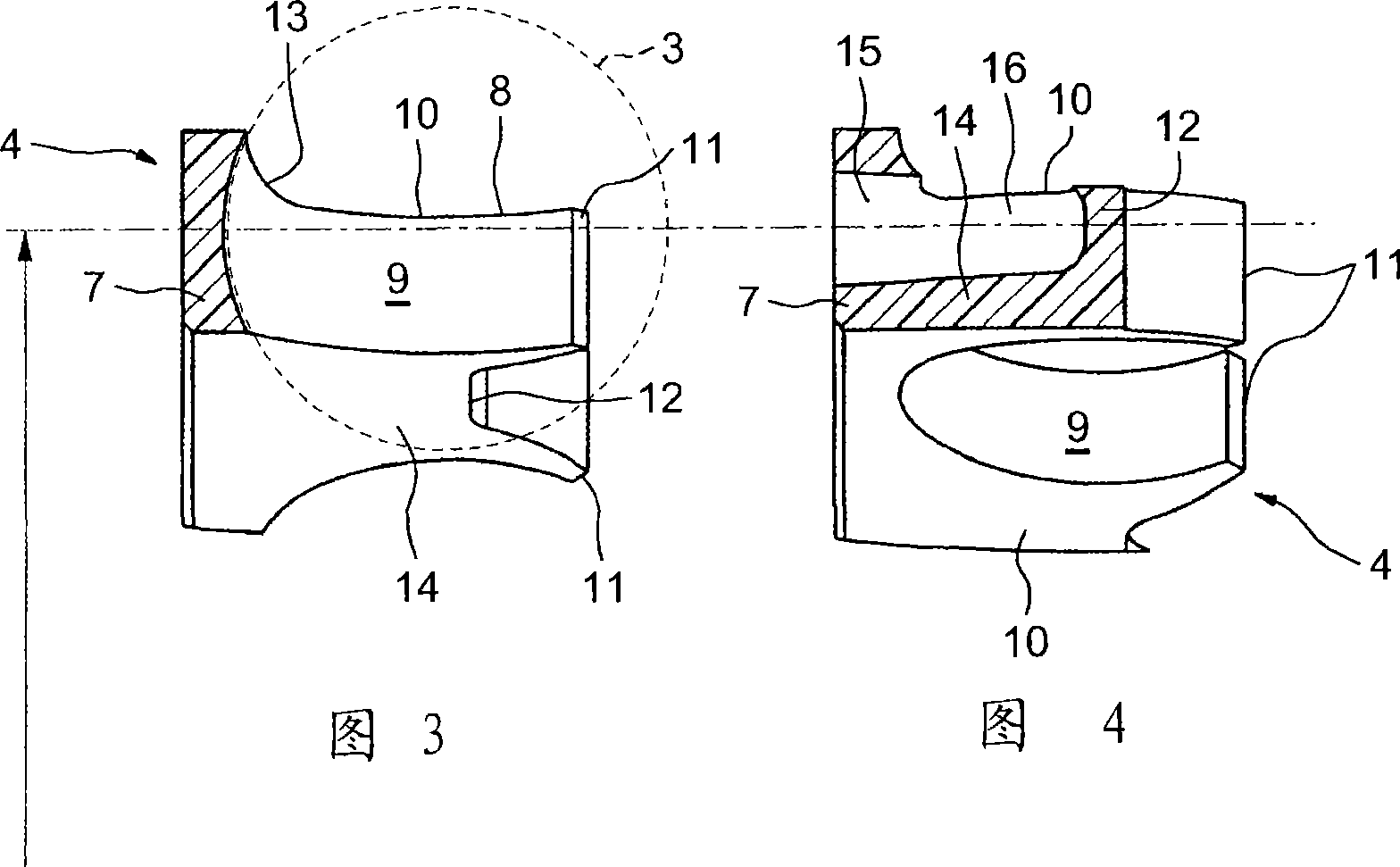
A dual braided catheter shaft includes a flat wire forming the inner braid, thereby potentially allowing for reduced radial thickness of the shaft. In one embodiment, the shaft (100) includes an inner polymer jacket (104), an inner braid (106) formed on the inner jacket (104), an intermediate jacket (108) formed over the inner braid (106), an outer braid (110) formed on the intermediate jacket (108) and an outer jacket (112) formed on the outer braid (110). A preferred construction process involves extruding polymer material directly onto each of the inner and outer braids (106 and 110) so that little or no air gaps remain between the polymer material and the braids (106 and 110). The braiding parameters of the inner and outer braids (106 and 110) can be varied along the length of the catheter to provide varying mechanical properties.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Slide-and-lock stent
InactiveUS20070032854A1Reduce recoilPrevent slidingStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusRecoilStent
The invention relates to an expandable stent comprising circumferentially adjacent modules. The modules comprise longitudinally adjacent slide-and-lock radial elements which permit one-way sliding of the radial elements from a collapsed diameter to an expanded / deployed diameter, but inhibit radial recoil from the expanded diameter.
Owner:REVA MEDICAL +1
Pusher sheath and deployment device
InactiveUS20080132906A1Increase flexibilityPromotes relative motionStentsEar treatmentStent graftingGuide tube
A stent or stent-graft deployment device and in particular a pusher member for such a device are disclosed. The pusher member ( 62 ) is provided with a reduced outer diameter section ( 64 ) and a pusher head ( 60 ). The reduced outer diameter section ( 64 ) reduces the thickness of the wall of the pusher member ( 62 ), with the result that the rigidity of the pusher member ( 62 ) is reduced at its distal end. This reduction in rigidity reduces the transition in flexibility between a guidewire catheter ( 24 ) extending through and beyond an inner channel of the pusher member ( 62 ) and the distal end of the pusher member ( 62 ). Thus, there is a gradual change in rigidities at the junction between these two components, which can reduce the possibility of kinking.
Owner:WILLIAM COOK EURO +1
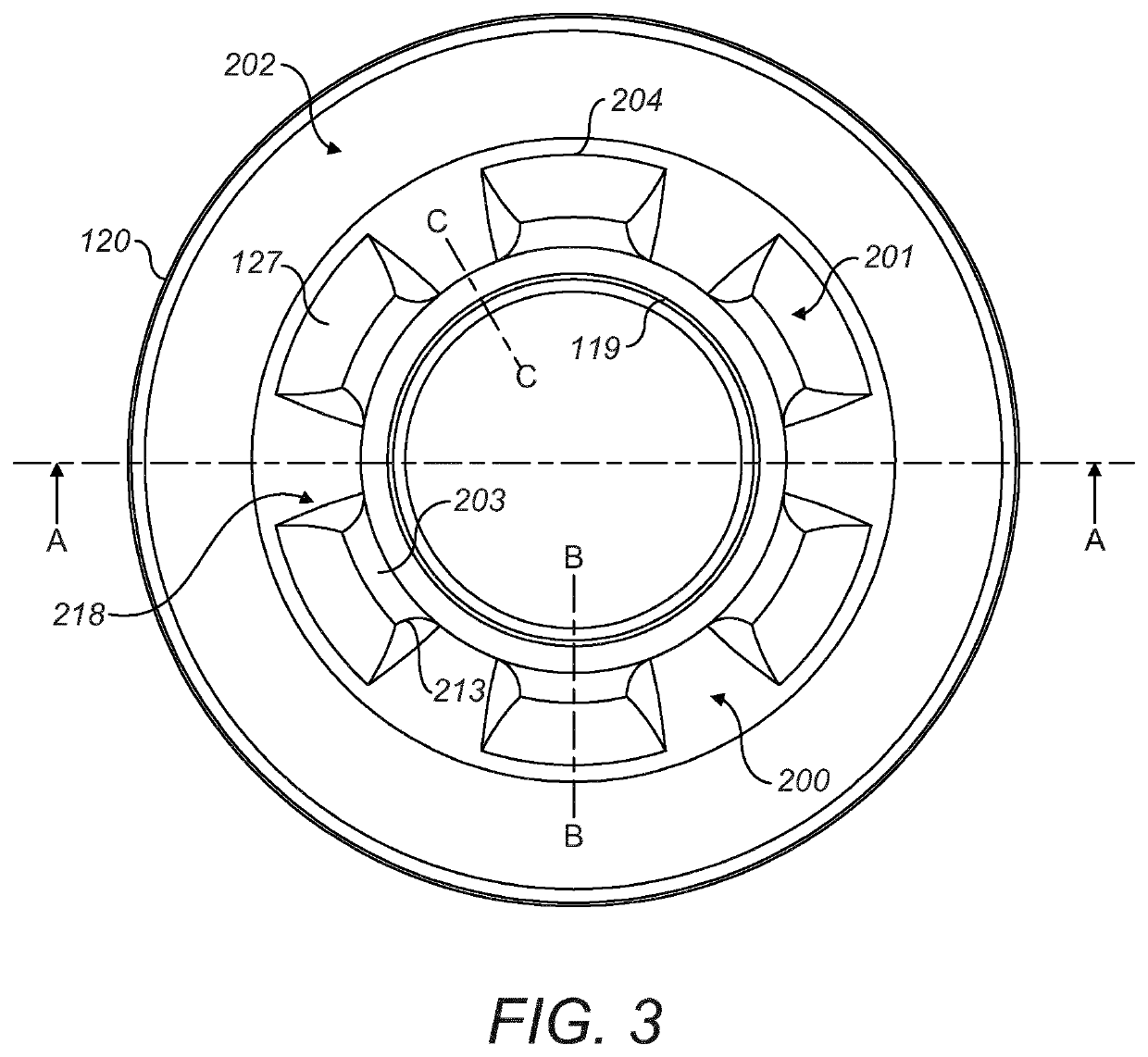
Gradient magnetic field coil unit, gantry for MRI apparatus, and MRI apparatus
InactiveUS20080169813A1Reduce radial thicknessElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceField coilMagnetic field
Provided is a gradient magnetic field coil unit includes a main coil layer that has a main coil for generating a gradient magnetic field and is formed in a substantially cylindrical shape, a shield coil layer that is attached to the outside of the main coil layer and has a shield coil for generating a magnetic field which shields a leakage magnetic field from the main coil, and a cooling layer that is attached between the main coil layer and the shield coil layer and has a plurality of flow paths for refrigerant, which are arranged in a substantially circumferential shape with the central axis of the main coil layer set to the center thereof, and a plurality of shim tray holding sections which hold a shim tray for a magnetic body.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Rotor of built-in permanent magnet motor and magnetic steel structural parameter determining method thereof
InactiveCN102157998AHigh mechanical strengthIncrease stiffnessMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
The invention relates to a rotor of a high-quality and high-speed built-in permanent magnet motor and a magnetic steel structural parameter determining method thereof. In the invention, the whole section magnetic steel of each electrode of the rotor of a conventional built-in permanent magnet motor is divided into multiple sections of magnetic steel which have the same polarity and different widths; the multiple sections of the magnetic steel are respectively arranged in a rotor core; and reinforcing ribs with the function of magnetic isolation are arranged among the multiple sections of the magnetic steel. By reasonably modulating and determining the width and distribution of each section of the magnetic steel, the air gap magnetic density waveform approaches sine distribution; harmonic components are reduced to the greatest extent; the eddy current loss of the magnetic steel and the torque pulsation of the motor are simultaneously reduced; and the electromagnetic performance of the motor is enhanced. Furthermore, the multiple sections of the magnetic steel are arranged in the circumference along the rotor; the highest rotating speed of the safe operation of the rotor is greatly enhanced on machinery; the radial thickness which is needed by the magnetic circuit of the rotor is obviously reduced on the structure; the rotational inertia and weight of the rotor are reduced; the dynamic response of the motor is improved; and the requirements of a high-speed driving system on the performance of the motor are met.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Dual braided catheter shaft
A dual braided catheter shaft includes a flat wire forming the inner braid, thereby potentially allowing for reduced radial thickness of the shaft. In one embodiment, the shaft (100) includes an inner polymer jacket (104), an inner braid (106) formed on the inner jacket (104), an intermediate jacket (108) formed over the inner braid (106), an outer braid (110) formed on the intermediate jacket (108) and an outer jacket (112) formed on the outer braid (110). A preferred construction process involves extruding polymer material directly onto each of the inner and outer braids (106 and 110) so that little or no air gaps remain between the polymer material and the braids (106 and 110). The braiding parameters of the inner and outer braids (106 and 110) can be varied along the length of the catheter to provide varying mechanical properties.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
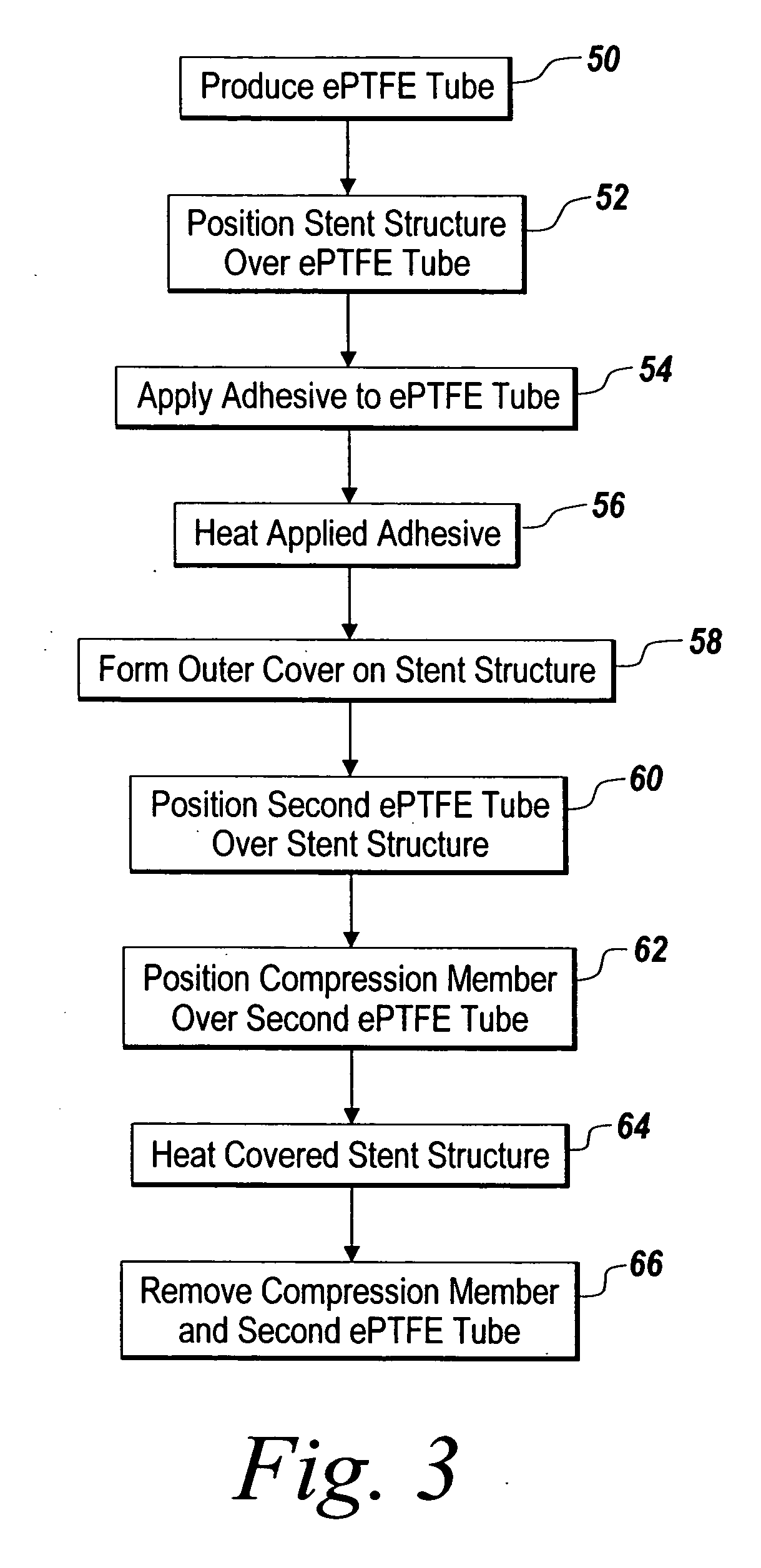
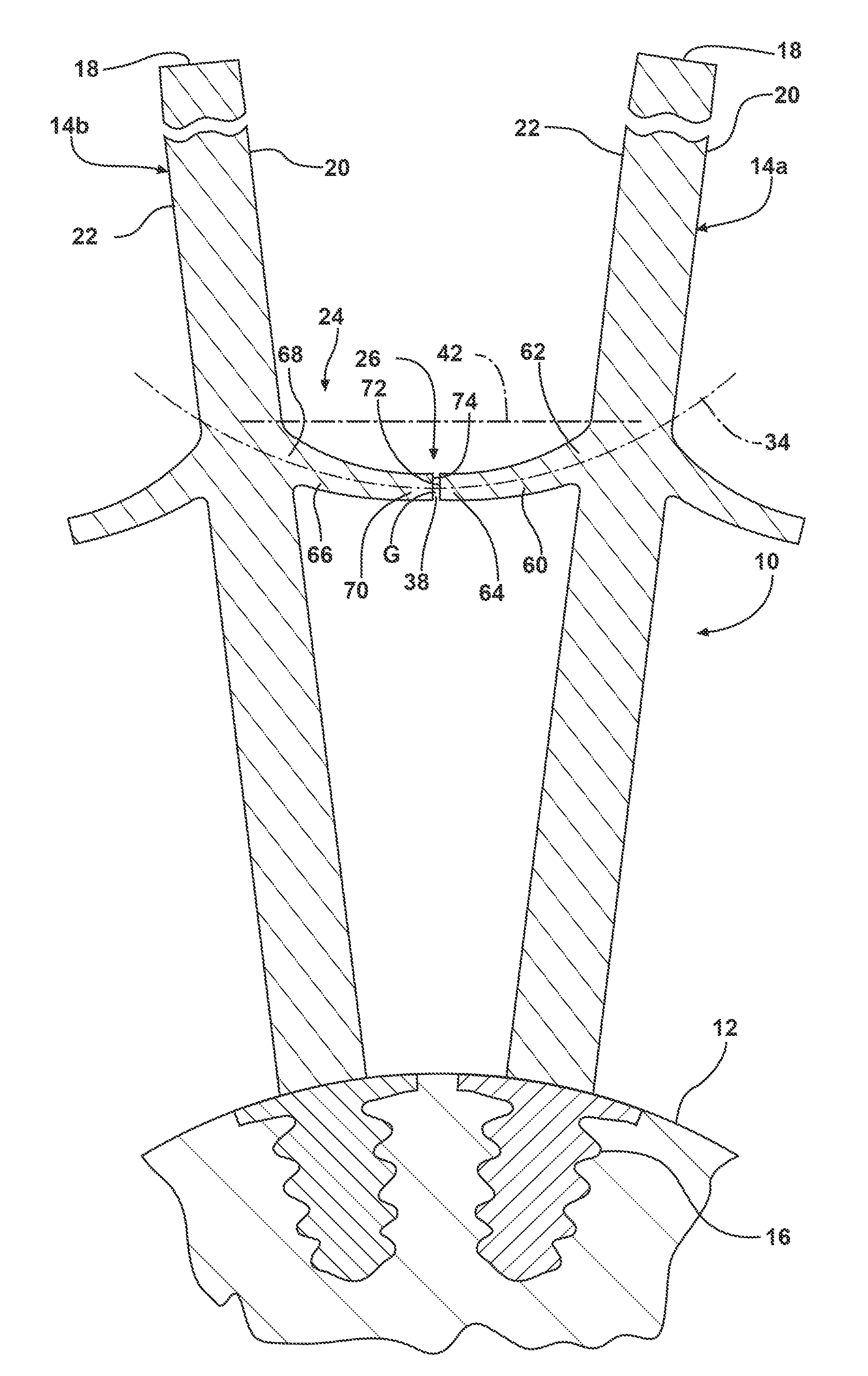
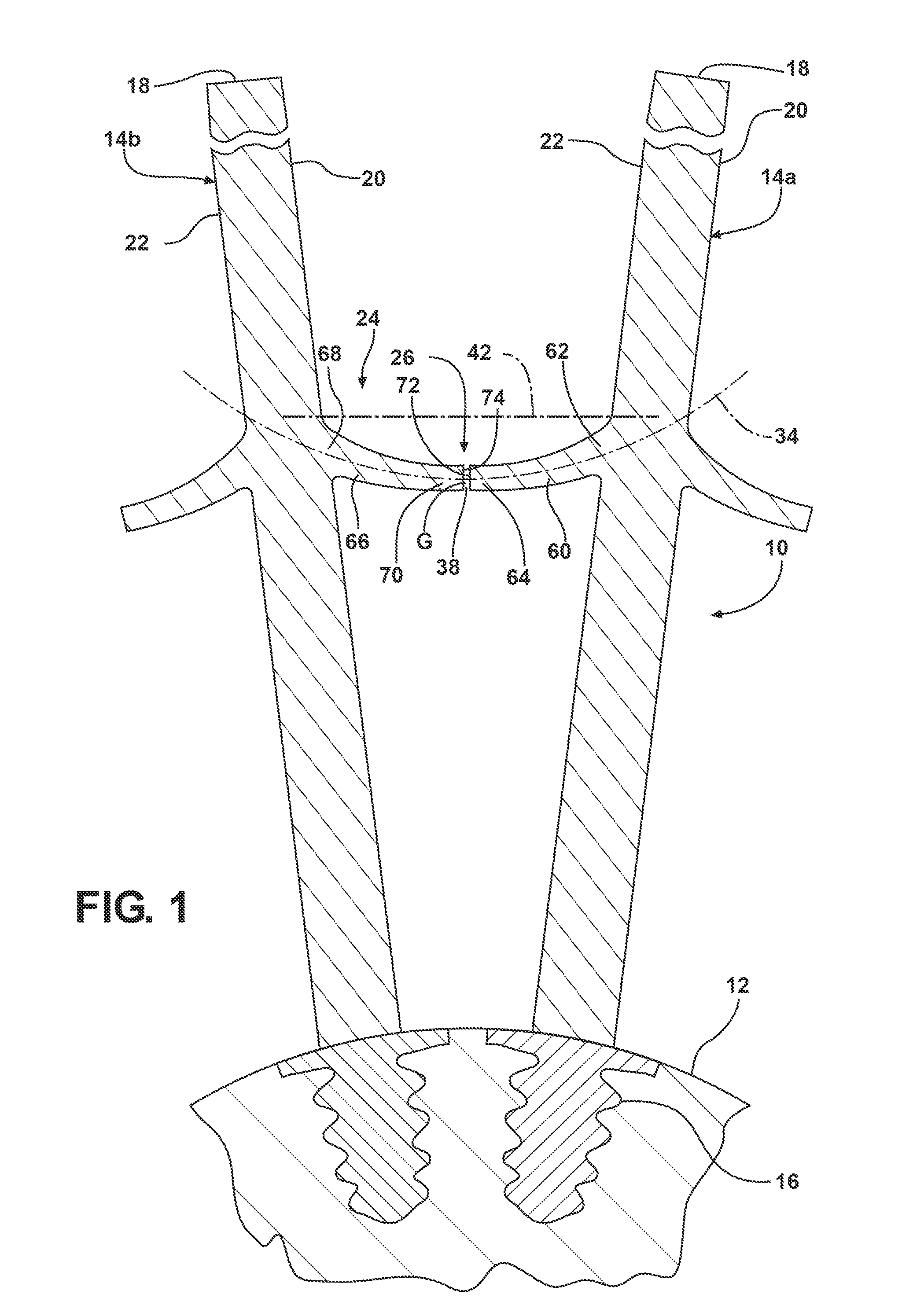
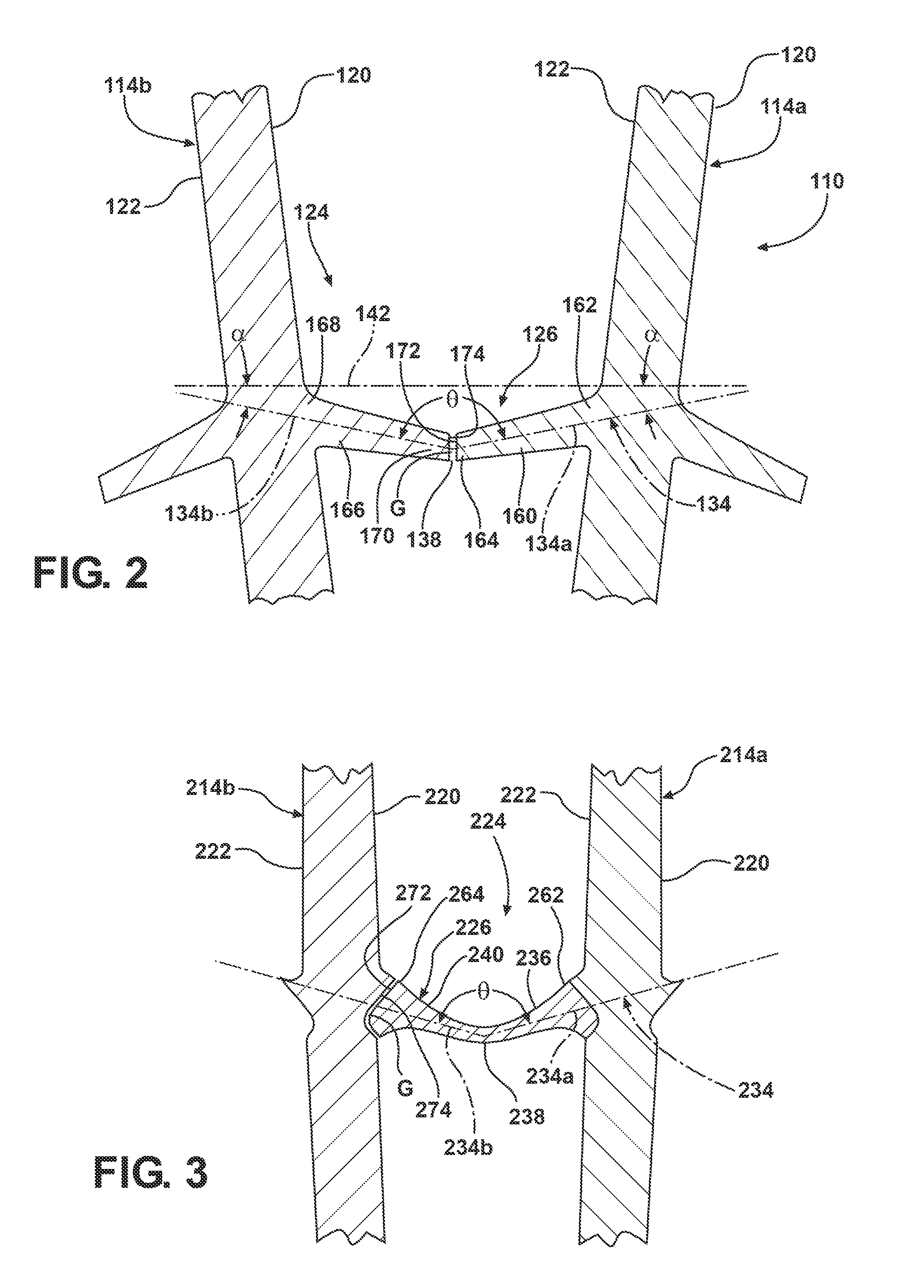
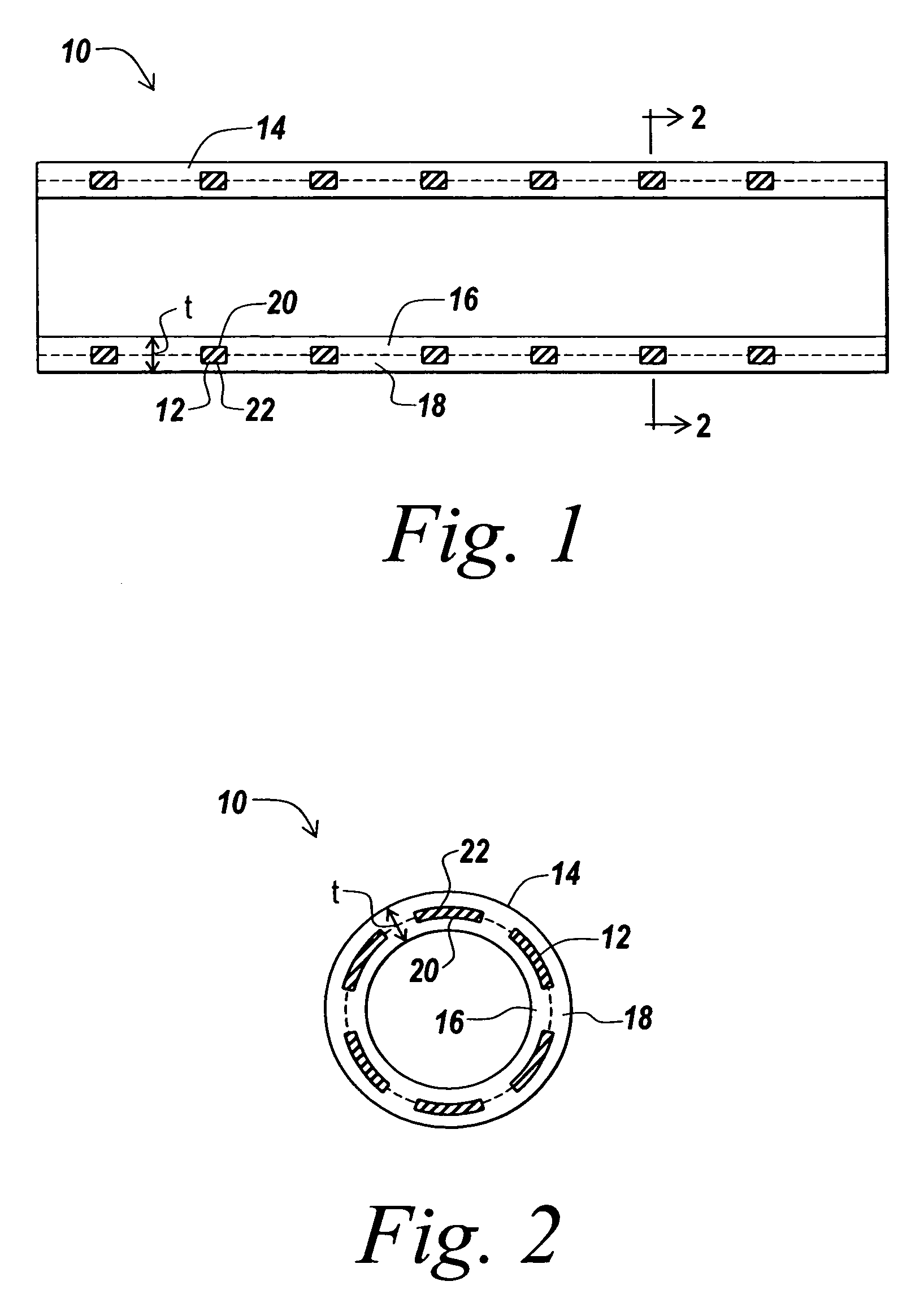
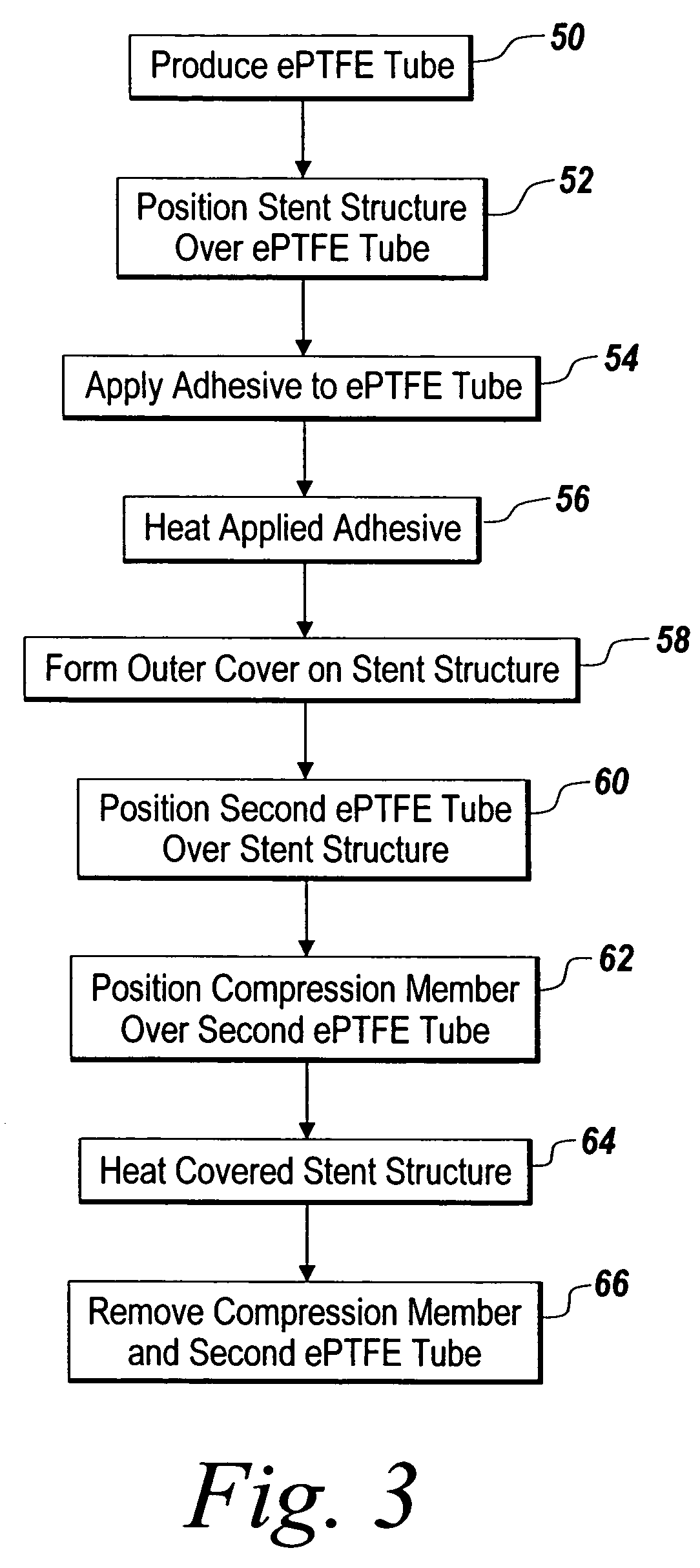
Covered stent and method of covering a stent
A radially deployable covered stent that predictably and dependably expands to an increased diameter state at relatively low deployment pressures while concomitantly minimizing the risk of tearing of the stent covering during expansion. The stent covering includes an inner cover and an outer cover that are bonded together through and around the stent structure to cover the stent. The stent cover is constructed from expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) having a structure of nodes interconnected by fibrils. The stent covering has a radial thickness of at least about 0.008″ and an average internodal distance (IND) of at least about 100 microns when the stent is in the reduced diameter, unexpanded state. The covered stent deploys at an average deployment pressure of less than or equal to about 10 atm. A method for covering a stent structure according to the present invention includes placing a compression member in the form of a tubular sleeve over the outer cover and heating the compressed covered stent to bond the inner cover to the outer cover. An adhesive in the form of an aqueous dispersion of PTFE can be applied to either the inner cover or the outer cover to facilitate bonding of the inner cover to the outer cover.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
Turbine Blade Damping Device with Controlled Loading
A damping structure for a turbomachine rotor. The damping structure includes an elongated snubber element including a first snubber end rigidly attached to a first blade and extending toward an adjacent second blade, and an opposite second snubber end defining a first engagement surface positioned adjacent to a second engagement surface associated with the second blade. The snubber element has a centerline extending radially inwardly in a direction from the first blade toward the second blade along at least a portion of the snubber element between the first and second snubber ends. Rotational movement of the rotor effects relative movement between the first engagement surface and the second engagement surface to position the first engagement surface in frictional engagement with the second engagement surface with a predetermined damping force determined by a centrifugal force on the snubber element.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
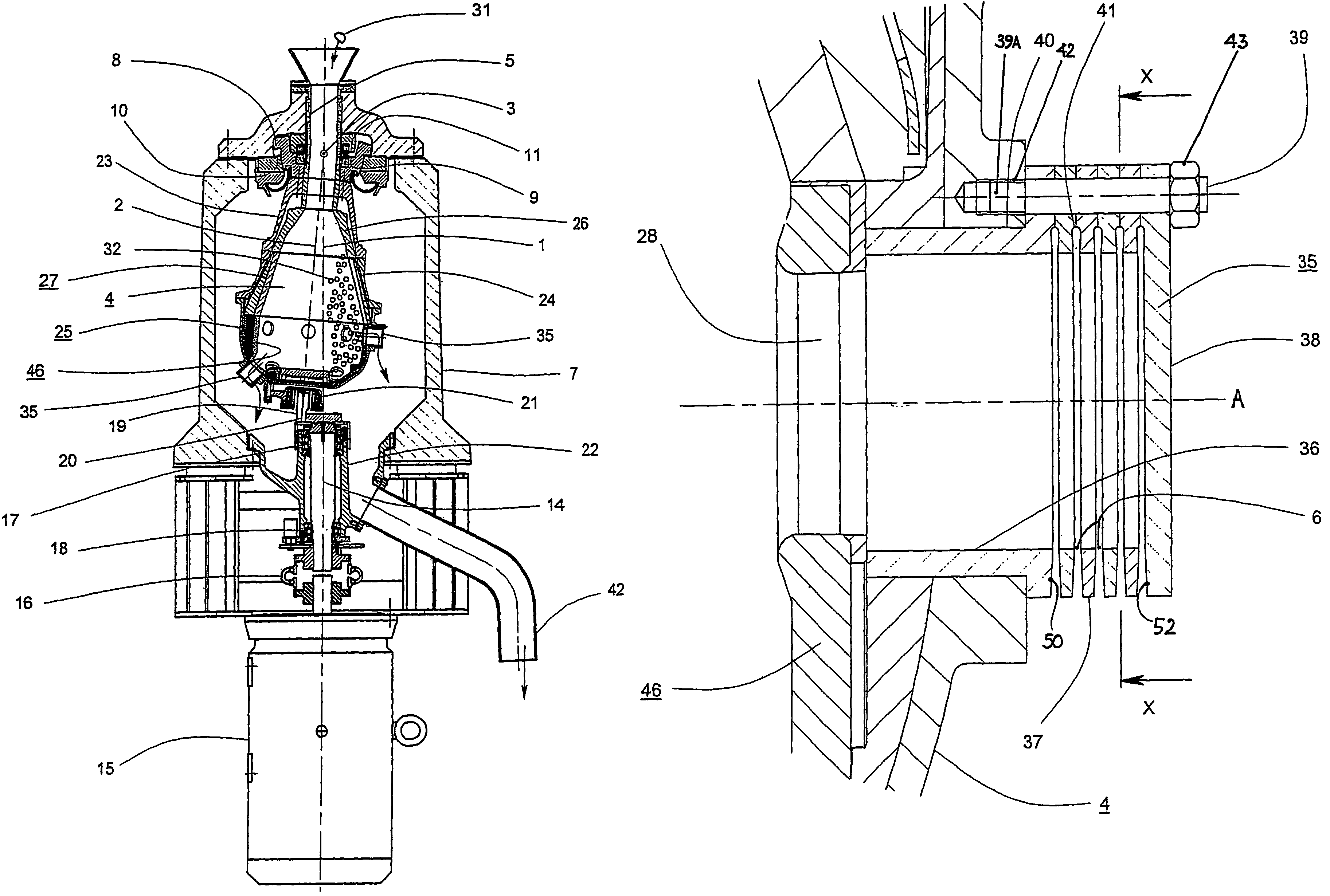
Soundproofing panel for turbomachine and turbomachine comprising such a panel
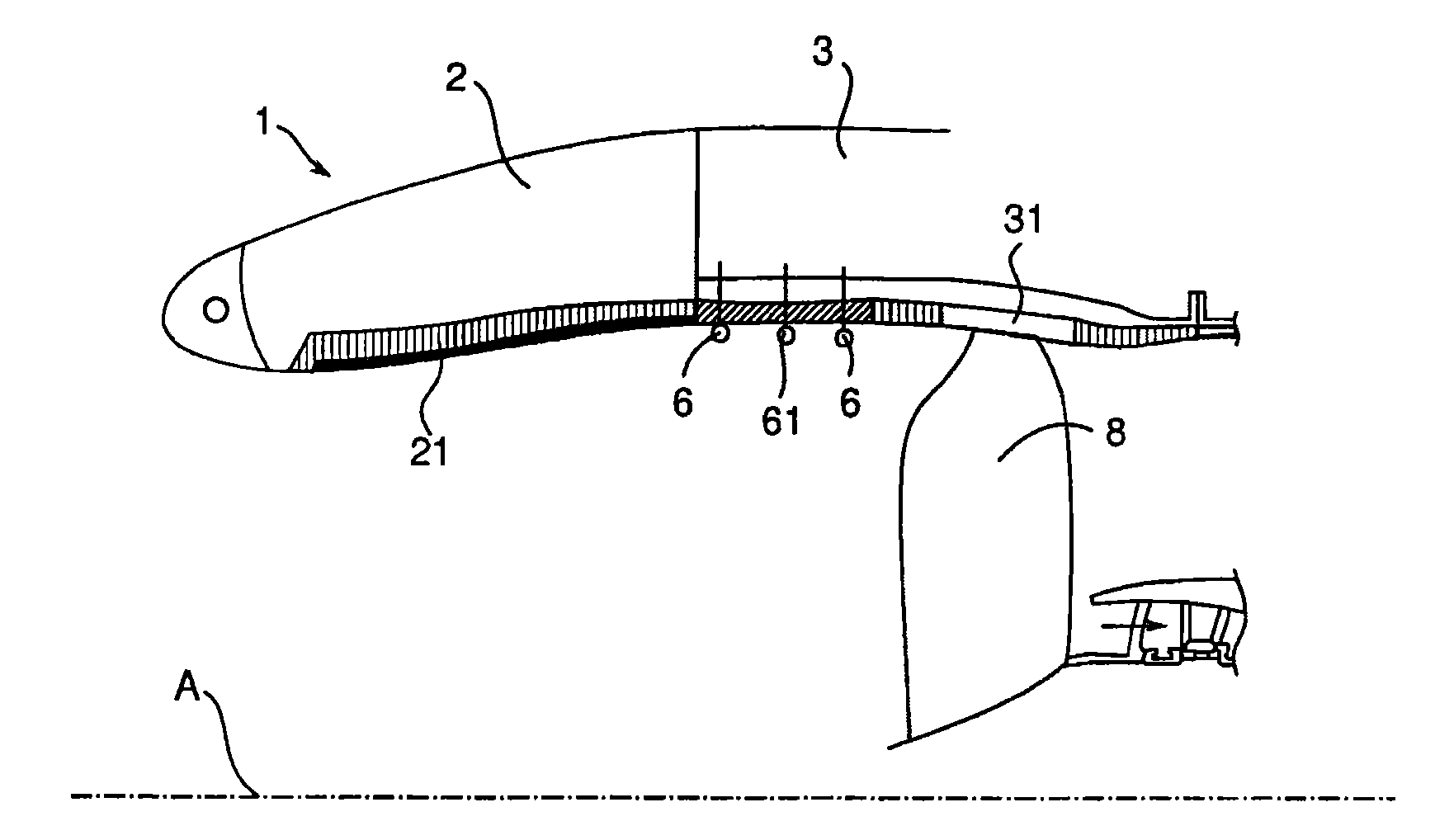
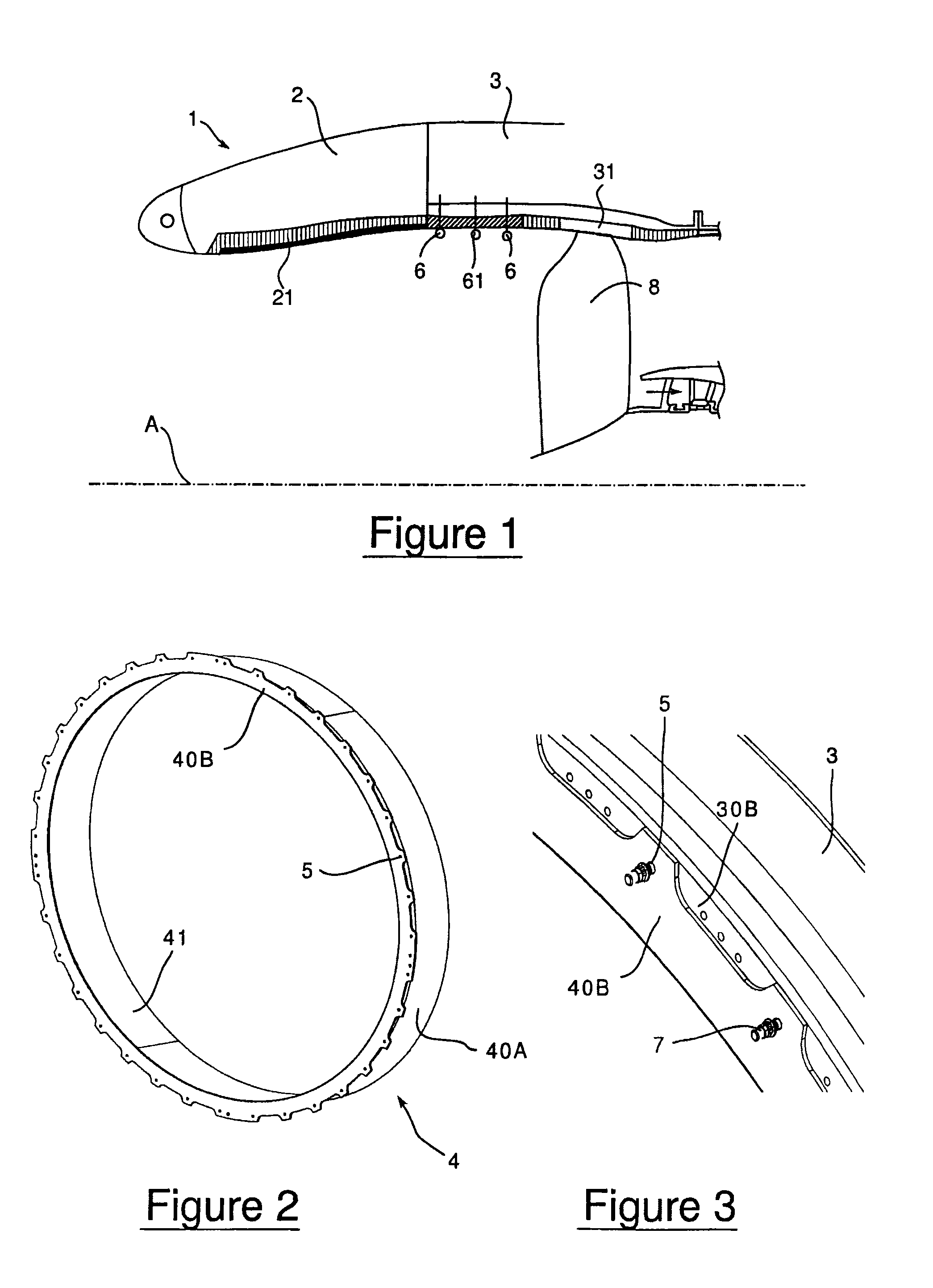
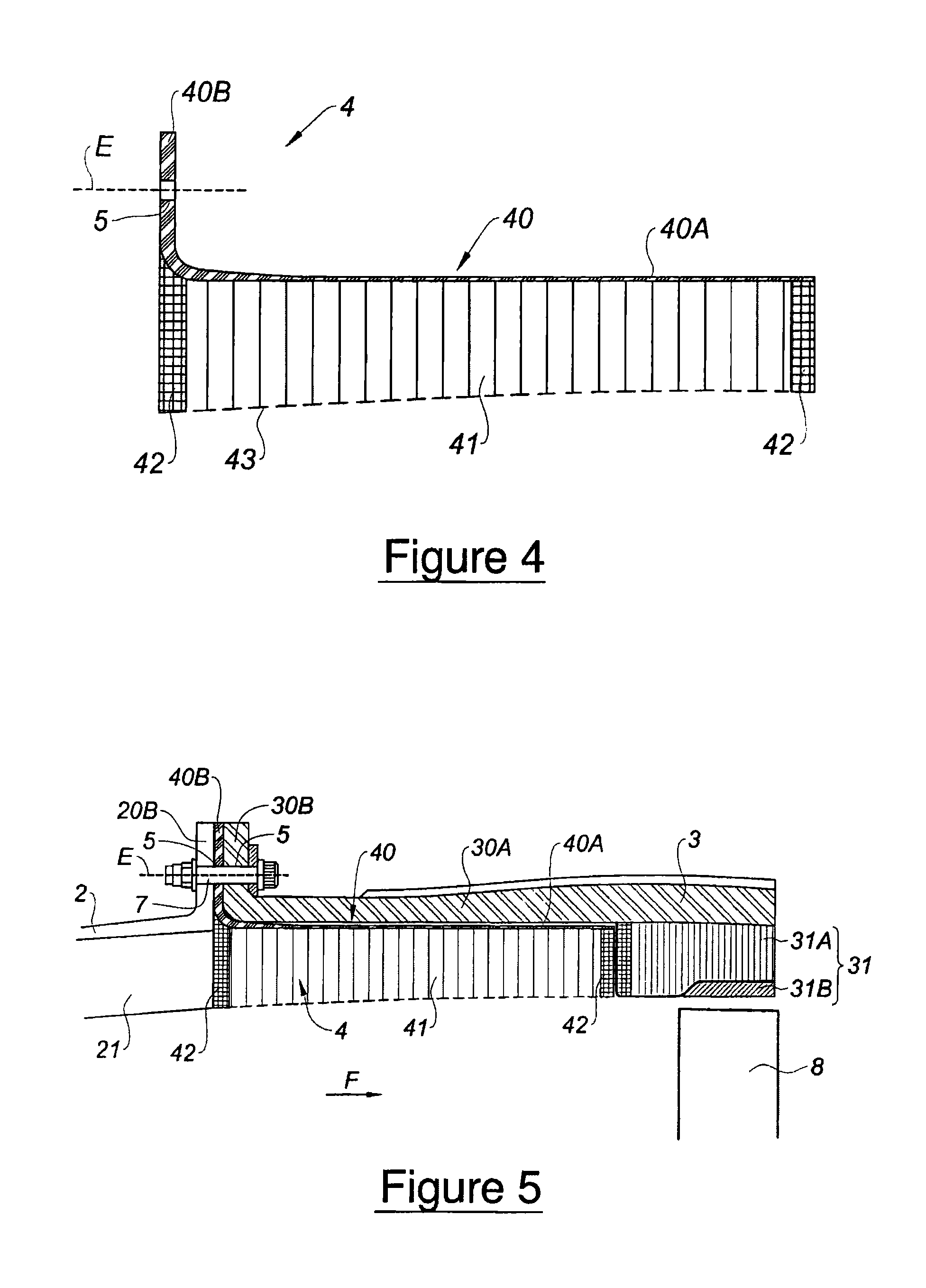
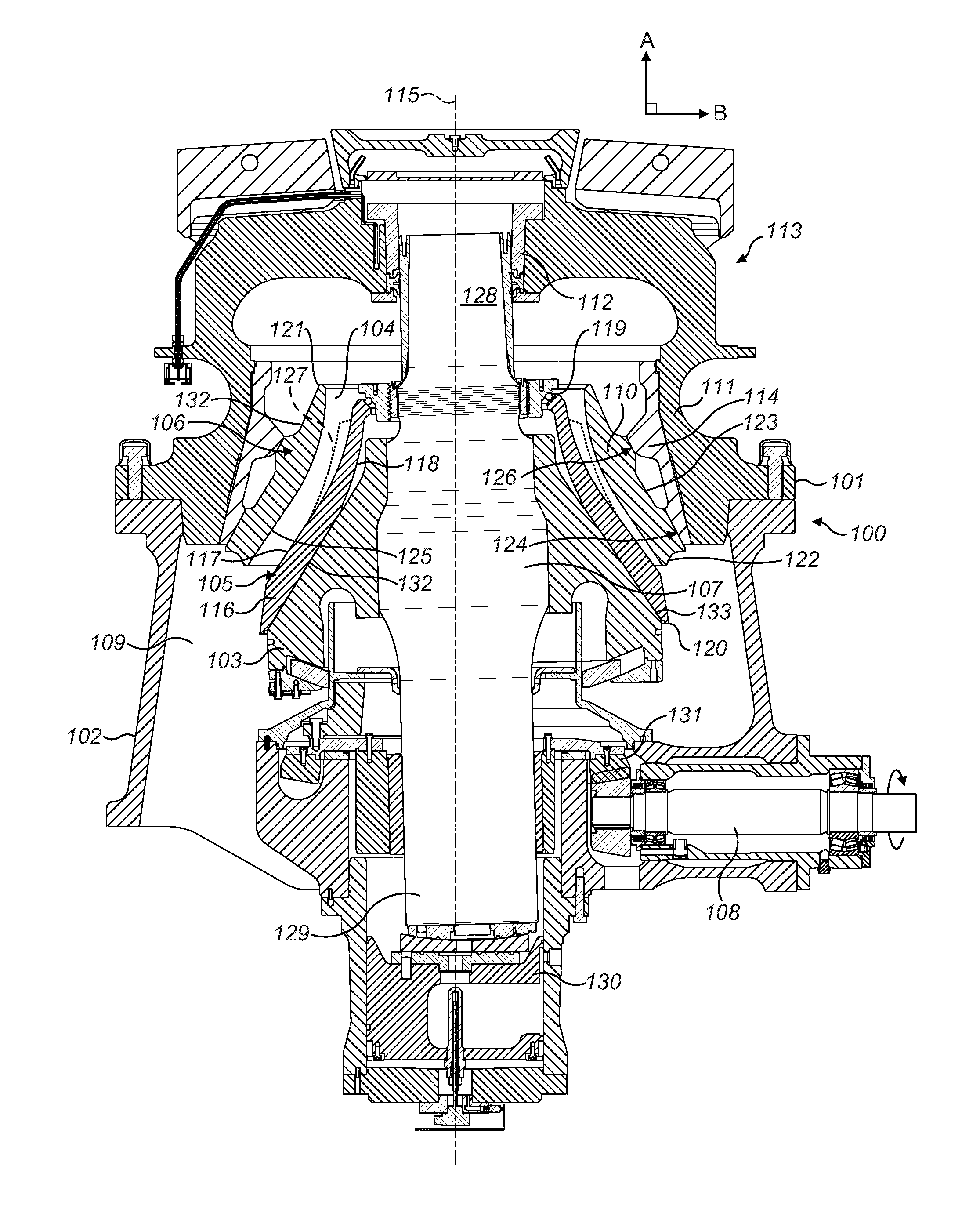
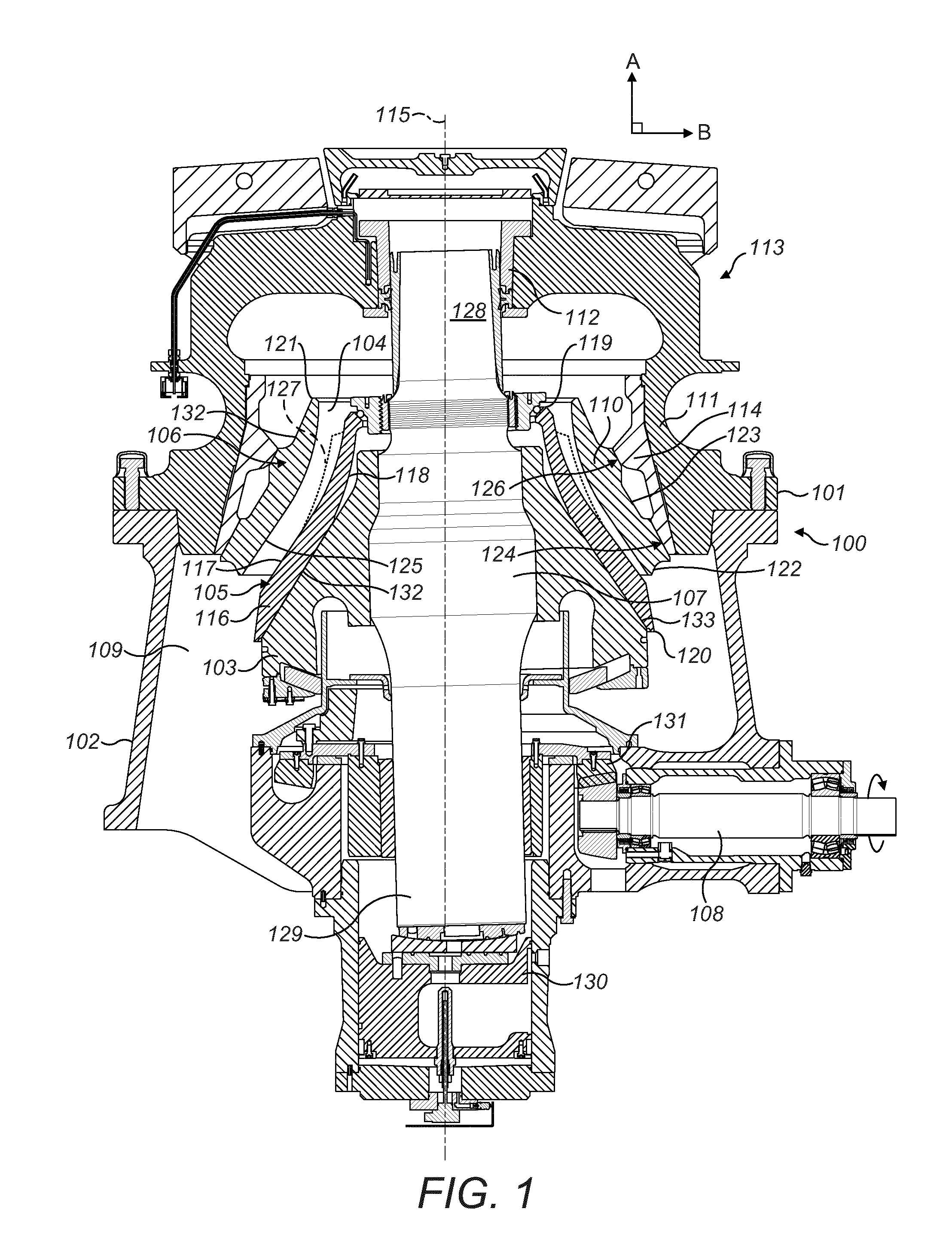
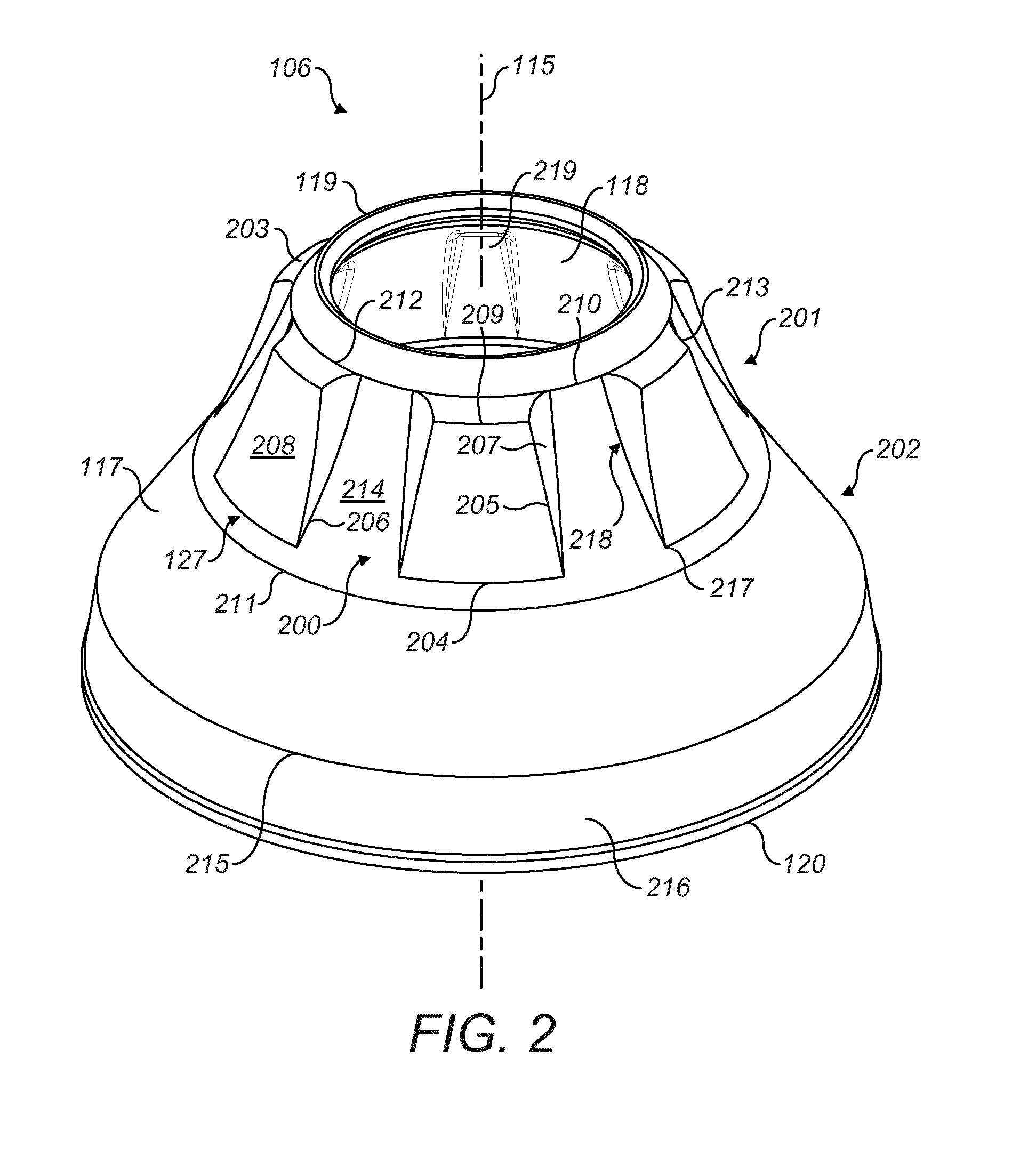
ActiveUS8544598B2Save timeReduce radial thicknessEngine manufacturePump componentsAirflowEngineering
A one-piece soundproofing panel which is attached within an circumferential air blower casing of a turbomachine, with an axis, in which circulates an airflow from upstream to downstream, is disclosed. The panel includes a circumferential rigid seat with a longitudinal cylindrical part, arranged to axially extend with respect to the axis A of the turbomachine, having an outside surface, intended to come to extend facing with an internal surface of the air blower casing, and an internal surface to which is applied a soundproofing coating; and an annular fastening flange, formed at the upstream end of the longitudinal cylindrical part, radially outwardly extending, the fastening flange being arranged to cooperate with a fastening flange of the air blower casing.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Covered stent and method of covering a stent
A radially deployable covered stent that predictably and dependably expands to an increased diameter state at relatively low deployment pressures while concomitantly minimizing the risk of tearing of the stent covering during expansion. The stent covering includes an inner cover and an outer cover that are bonded together through and around the stent structure to cover the stent. The stent cover is constructed from expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) having a structure of nodes interconnected by fibrils. The stent covering has a radial thickness of at least about 0.008″ and an average internodal distance (IND) of at least about 100 microns when the stent is in the reduced diameter, unexpanded state. The covered stent deploys at an average deployment pressure of less than or equal to about 10 atm. A method for covering a stent structure according to the present invention includes placing a compression member in the form of a tubular sleeve over the outer cover and heating the compressed covered stent to bond the inner cover to the outer cover. An adhesive in the form of an aqueous dispersion of PTFE can be applied to either the inner cover or the outer cover to facilitate bonding of the inner cover to the outer cover.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
Rotating electrical machine apparatus
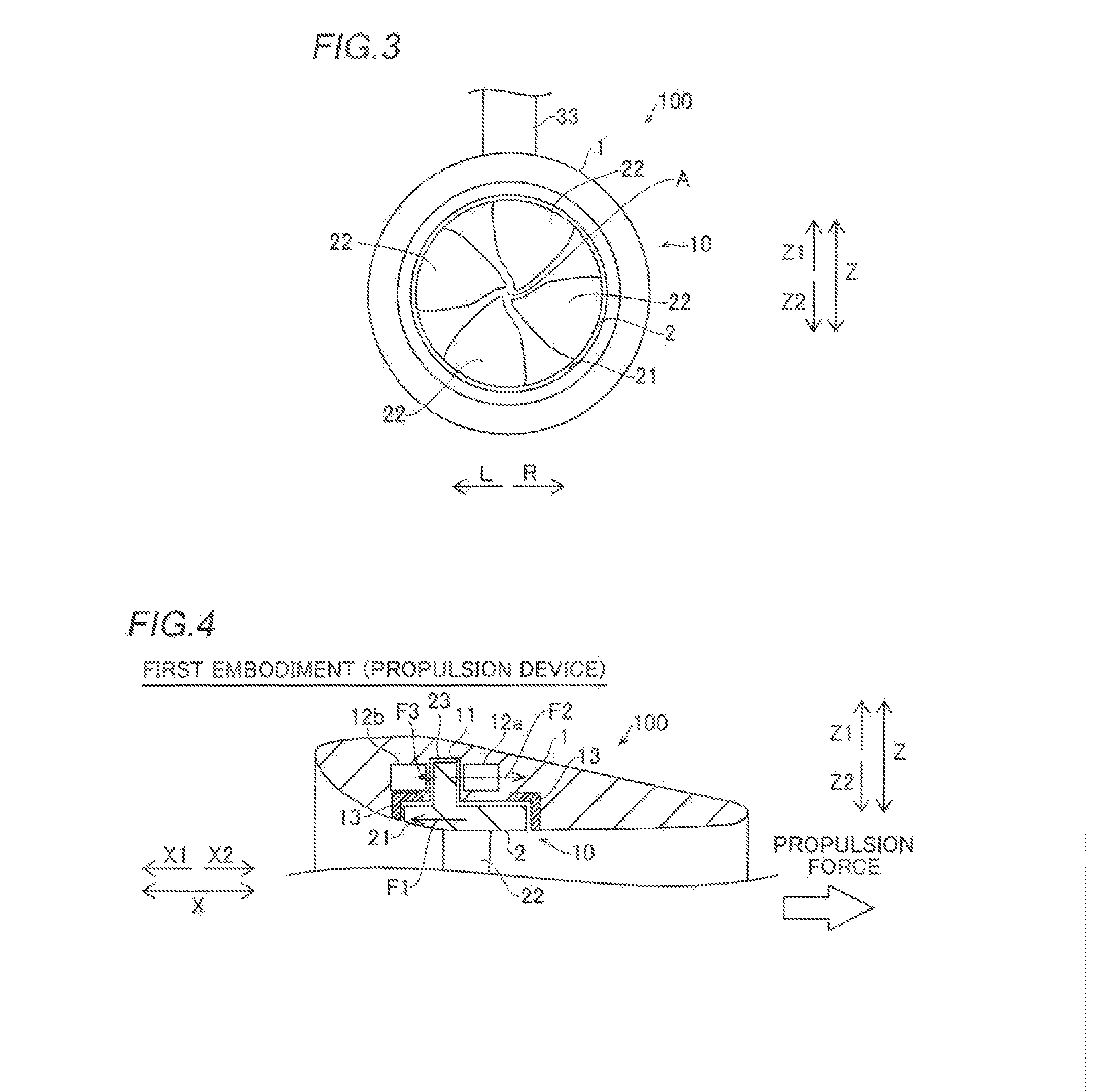
ActiveUS20160185431A1Reduce radial thicknessEasy formationRotary propellersOutboard propulsion unitsEngineeringMechanical engineering
In a rotating electrical machine apparatus, a rotor portion provided in a cylindrical portion and a stator portion provided in a recessed portion in which the rotor portion is housed are aligned along the rotation axis of a rim such that a force is generated in a direction opposite to the direction of a load that acts along the rotation axis of the rim of loads that act on the rim following rotation of a blade.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Electric wheel
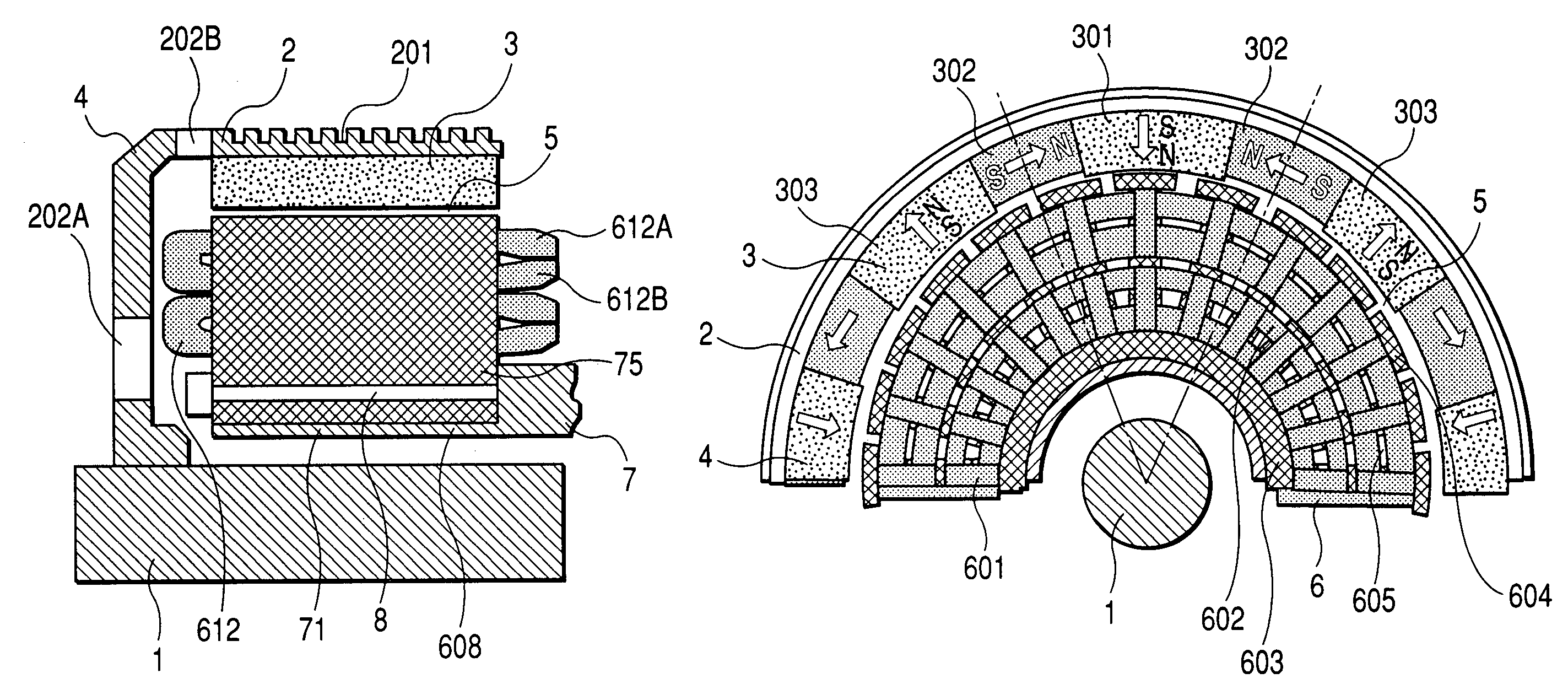
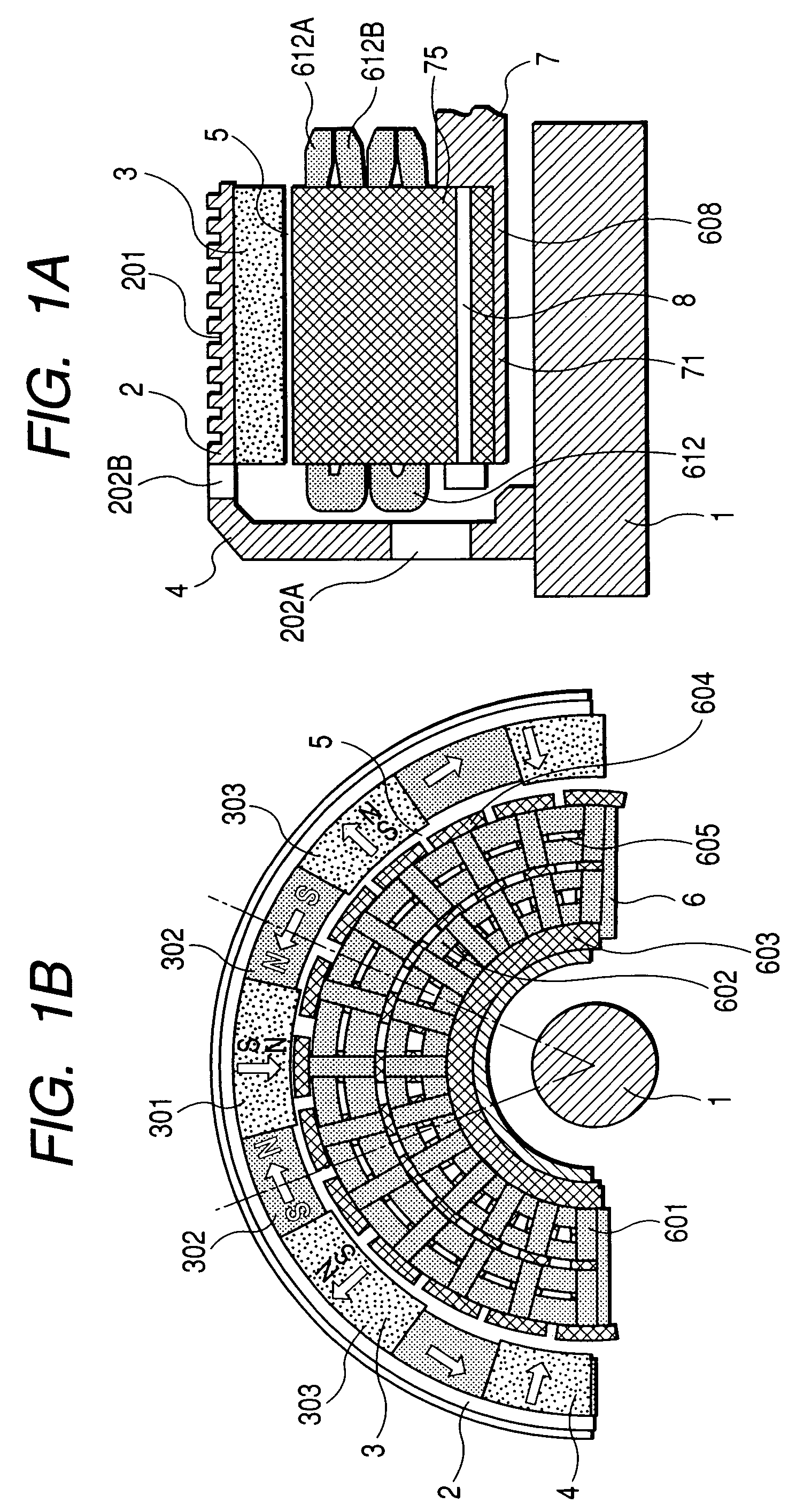
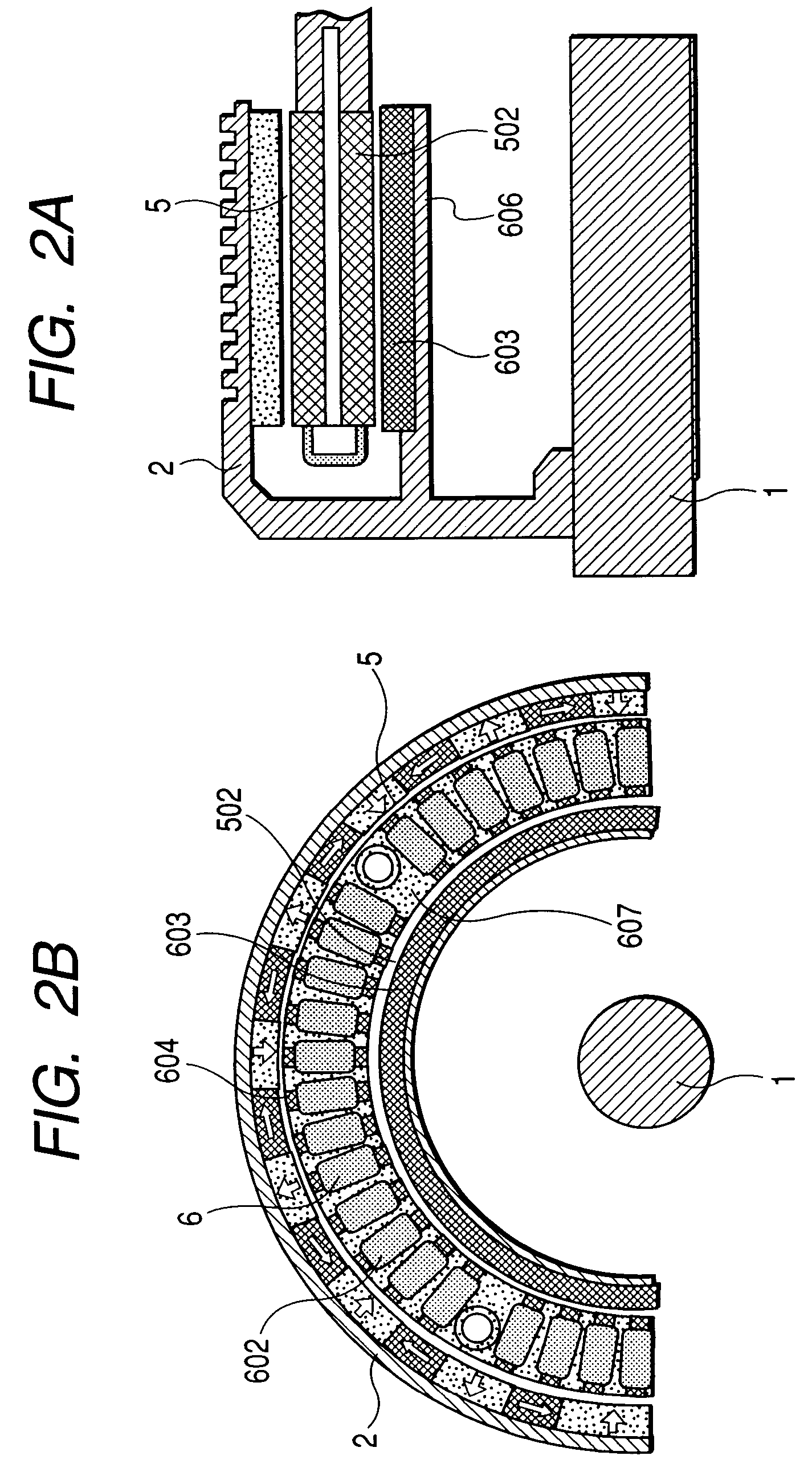
ActiveUS7462968B2Reduce radial thicknessIncrease the diameterMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric devicesElectrical polarityMagnetization
The rotor of the outer-rotor type wheel-in motor of the electric wheel includes a field generator facing the outer surface of the stator across from an electrical gap. The field generator includes pole magnets magnetized in the radial direction with respect to the rotation axis of the wheel-in motor, adjacent two of the pole magnets having opposite directions of magnetization so that magnet polarity of the field generator alternates at a predetermined pole pitch along the circumferential direction, yoke magnets magnetized in the circumferential direction each of which is put between corresponding adjacent two of the pole magnets to strengthen magnetic field formed by the pole magnets, and a field generator support member to which the field generator is fixed, the field generator support member being fixed to the rotary shaft which is rotatably supported by a wheel suspension system of a vehicle.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Turbine blade damping device with controlled loading
A damping structure for a turbomachine rotor. The damping structure including an elongated snubber element including a first snubber end rigidly attached to a first blade and extending toward an adjacent second blade, and an opposite second snubber end positioned adjacent to a cooperating surface associated with the second blade. The snubber element has a centerline extending radially inwardly in a direction from the first blade toward the second blade along at least a portion of the snubber element between the first and second snubber ends. Rotational movement of the rotor effects relative movement between the second snubber end and the cooperating surface to position the second snubber end in frictional engagement with the cooperating surface with a predetermined damping force determined by a centrifugal force on the snubber element.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Slotless motor for implantable axial flow blood pump
PendingCN107104570AEliminate torqueReduce radial thicknessBlood pumpsMagnetic circuit stationary partsCopper wireBlood pump
The invention discloses a slotless motor for an implantable axial flow blood pump. The slotless motor comprises a stator iron core, a stator winding, a rotor rotating shaft and a rotor permanent magnet. The slotless motor is characterized in that the stator iron core is formed by axially punching a circular silicon steel sheet, the rotor permanent magnet is made of a permanent magnetic material and is supportive of radial magnetizing, a coil of the stator winding is positioned between the stator iron core and the rotor rotating shaft, the stator winding is pasted on the inner wall of the stator iron core which is cylindrical, and the stator iron core is of a tooth-slotless structure. A direct-current brushless slotless structure is adopted, so that tooth-slot torque is eliminated, and copper loss is lowered. A triphase winding is divided into two layers of structures, copper wires at the end are arranged regularly, and thickness is consistent with that of a central portion, so that radial thickness of the end of the motor is reduced. High-heat-conductivity epoxy resin is used to fix the stator winding, so that the problem that the coil generates heat is solved effectively, the motor winding is fixed, and electromagnetic vibration and noise are avoided.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Turbine Blade Damping Device With Controlled Loading
A damping structure for a turbomachine rotor. The damping structure including an elongated snubber element including a first snubber end rigidly attached to a first blade and extending toward an adjacent second blade, and an opposite second snubber end positioned adjacent to a cooperating surface associated with the second blade. The snubber element has a centerline extending radially inwardly in a direction from the first blade toward the second blade along at least a portion of the snubber element between the first and second snubber ends. Rotational movement of the rotor effects relative movement between the second snubber end and the cooperating surface to position the second snubber end in frictional engagement with the cooperating surface with a predetermined damping force determined by a centrifugal force on the snubber element.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Rim driving propeller with dummy shaft structure
ActiveCN114056529ALow flow resistanceReduce radial thicknessPropulsive elementsImpellerFriction loss
The invention discloses a rim driving propeller with a dummy shaft structure, which comprises an annular guide pipe, a dummy shaft is coaxially arranged in the annular guide pipe, a bearing is coaxially and fixedly sleeved outside the dummy shaft, an impeller is coaxially and fixedly sleeved outside the bearing, and a rim motor rotor is coaxially and fixedly sleeved outside the outer edge of the impeller. The rim motor stator matching the rim motor rotor is coaxially embedded in the inner wall of the annular guide pipe, and a rear guide vane with the outer edge connected to the inner wall of the annular guide pipe is coaxially and fixedly arranged at the position, located behind the bearing, outside the dummy shaft in a sleeving mode. According to the invention, the space structure of the dummy shaft under the large hub ratio scale of the impeller is reasonably utilized, and the bearing is arranged at the hub, which means that the diameter is smaller, the linear speed is smaller during working, and the friction loss is reduced; and meanwhile, only the rim motor stator is placed in the annular guide pipe, the structural form is simpler, the radial thickness of the annular guide pipe is reduced, structural optimization of the annular guide pipe is more facilitated, and the flow resistance during working of the pump-jet propeller is reduced.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Ball bearing cage
ActiveCN101443568AReduce quality problemsReduce inertiaBall bearingsBearing componentsBall bearingMechanical engineering
Ball bearing cage (4) consisting of a bead ring (7) and a substantially axial portion (8) fitted with claws (11) that define alveolus (9) for balls and joining on the bead (7), the substantially axial portion (8) stretching axially on one portion of the alveolus (9). The substantially axial portion (8) presents an external diameter inferior to the external diameter of the bead (7), the external diameter of the substantially axial portion being comprised between the primitive diameter of the cage reduced to half of the radial thickness of the diameter of the bead and the primitive diameter increased to half of the radial thickness of the bead.
Owner:AB SKF
Three-cooling type fuel rod and fuel assembly
ActiveCN106782681AReduce radial thicknessReduce radial thermal expansionFuel elementsNuclear energy generationNuclear engineeringCooling channel
The invention discloses a three-cooling type fuel rod and a fuel assembly. The three-cooling type fuel rod comprises a rod body, wherein the rod body comprises an inner cladding, a middle cladding, an outer cladding, a first pellet and a second pellet; the middle cladding and the outer cladding are sequentially sheathed on the exterior of the inner cladding; the first pellet is arranged in the inner cladding, and the second pellet is arranged between the middle cladding and the outer cladding; an annular gap between the middle cladding and the outer cladding forms an inner cooling passage for a coolant to pass through. Compared with the solid pellet in the prior art, the three-cooling type fuel rod has the advantages that by arranging multiple claddings and the inner pellet, at the premise of same reactor core uranium charging amount, the radial thickness of the pellet is greatly reduced, so that the self-shield effect is obviously reduced, and the remaining amount of crackable material is reduced; the radial thickness of the pellet is greatly reduced, the radial expansion amount of the pellet is also reduced, the PCMI (pellet and cladding mechanical interaction) load under the special accident condition of a reactor is reduced, and the probability of PCMI failure of the fuel rod is further reduced.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +2
Permanent magnet rotor
InactiveUS20150145367A1Reduce magnetic leakageEnhance performanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetBrushless motors
A rotor for a brushless motor includes a shaft, a rotor core and a number of permanent magnets. The rotor core includes inner and outer annular portions. The inner annular portion has a central hole for receiving the shaft. The outer annular portion includes a number of sector segments arranged in a ring, with adjacent sector segments defining a slot there between for receiving a corresponding permanent magnet. Radially outer ends of adjacent sector segments are interconnected by a connector. The sector segments include first sector segments and second sector segments arranged alternately. The first sector segments are separated from the inner annular portion. The second sector segments are each connected to the inner annular portion by connecting arms.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC INTERNATIONAL AG
Crushing shell with profiled crushing surface
ActiveUS20160346786A1Capacity balanceIncreased reduction potentialGrain treatmentsCrusherClassical mechanics
A gyratory crusher crushing shell having a mount face for contacting a support region of the crusher and a crushing face to contact material to be crushed and passing through the crushing zone. The crushing shell includes a plurality of wedges project radially from the crushing surface, the wedges being spaced apart in a circumferential direction around the axis to define channels extending axially between the wedges.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
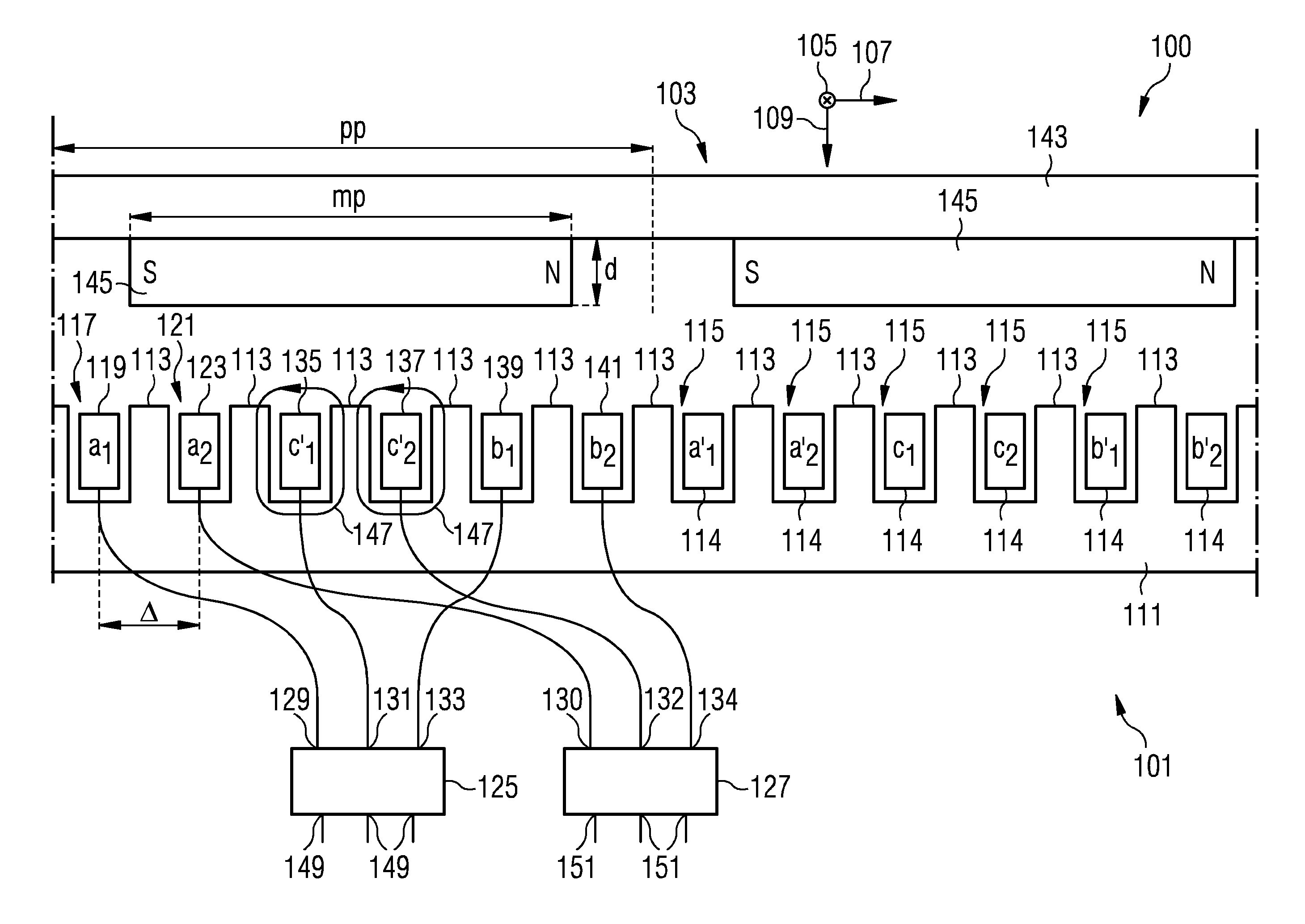
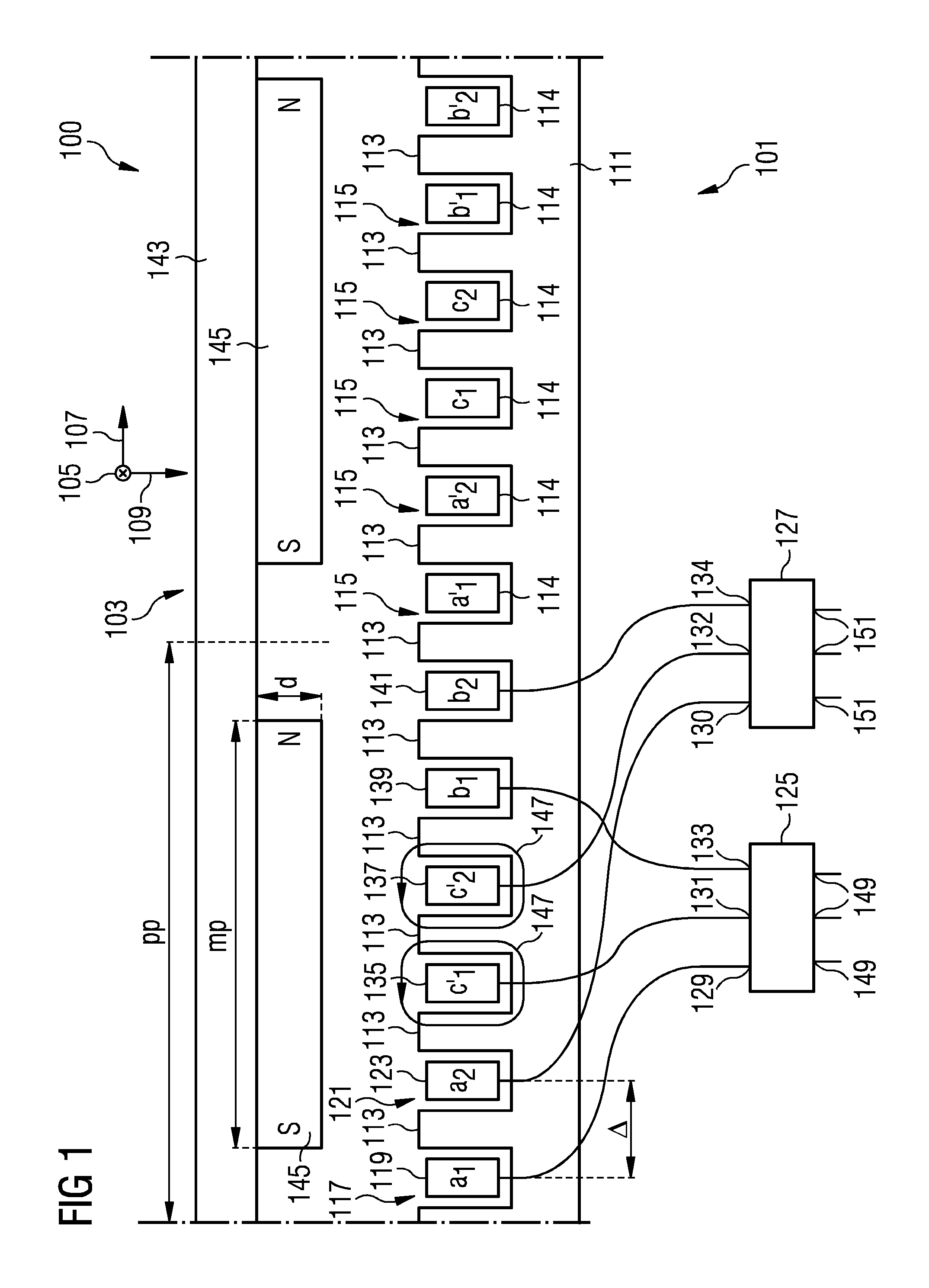
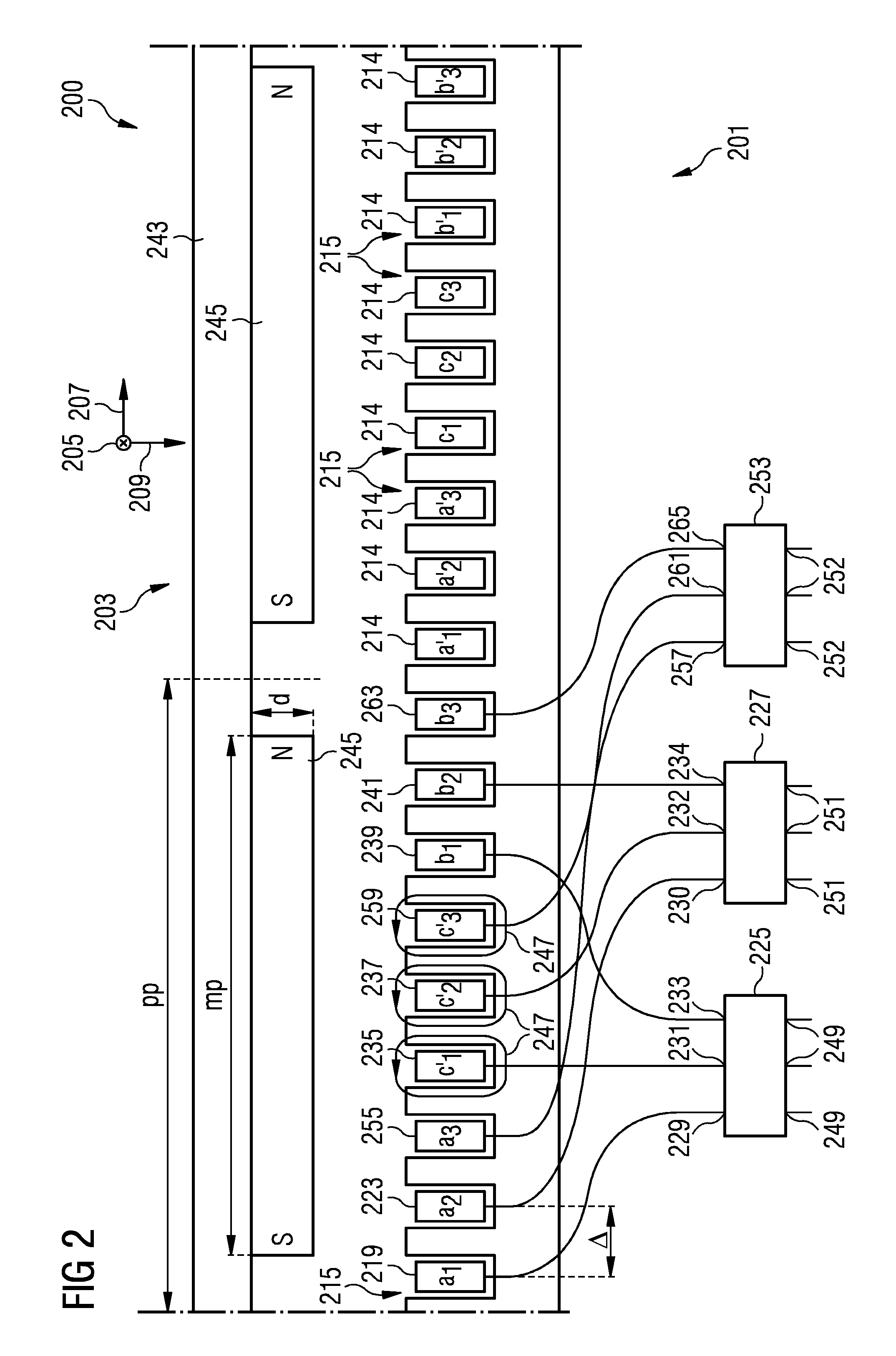
Stator arrangement and electrical generator
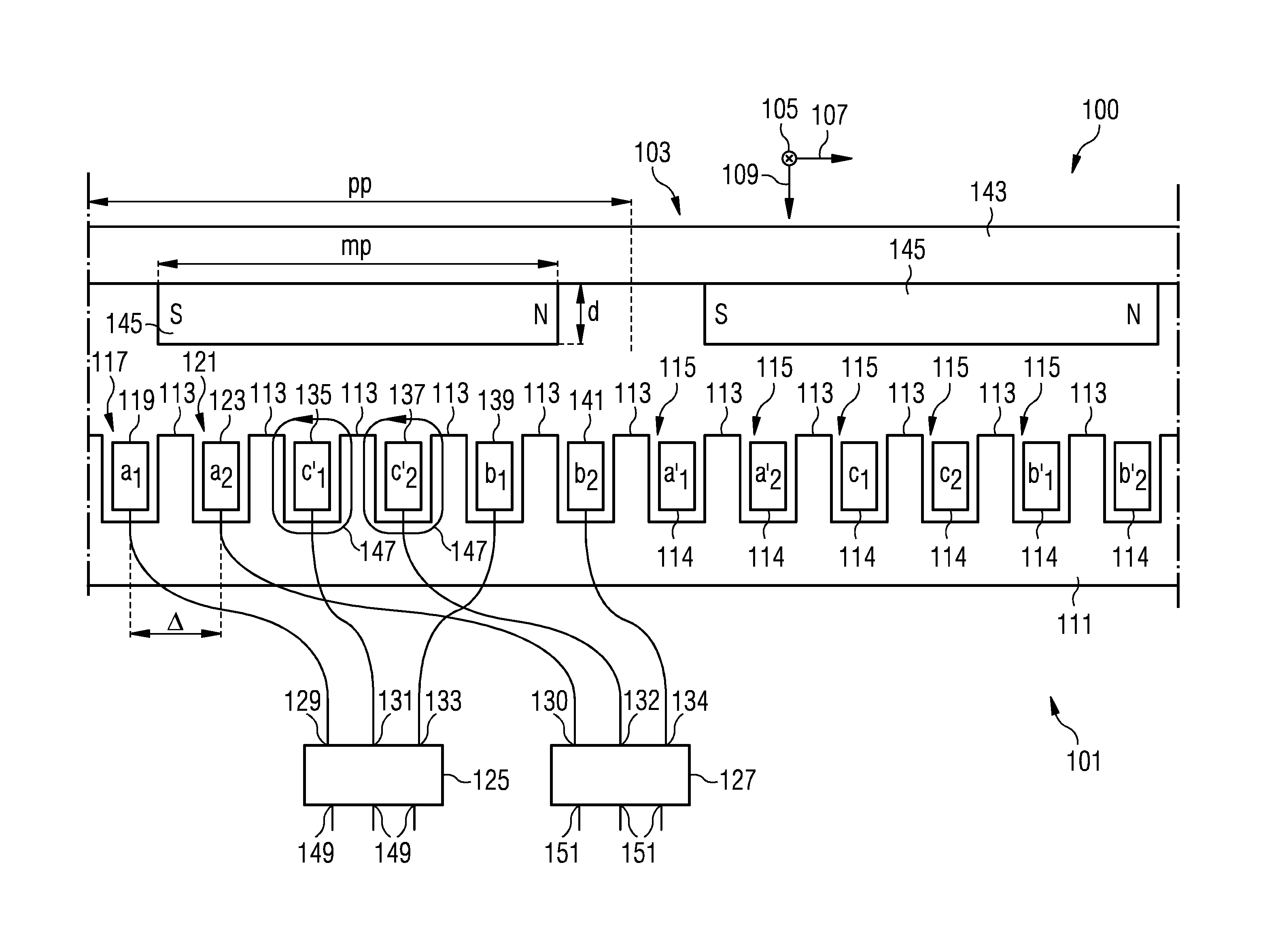
ActiveUS20140015498A1Energy delivered is increasedReduce deliveryMagnetic circuit stationary partsMechanical energy handlingEngineeringDynamo
A stator arrangement includes a stator extending in a circumferential direction and plural teeth alternating with plural slots arranged along the circumferential direction. A first wire is arranged in a first slot of the plural slots. A second wire is arranged in a second slot of the plural slots, wherein the second slot is circumferentially adjacent to the first slot. A first converter has an input terminal connected to the first wire and a second converter has an input terminal connected to the second wire.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
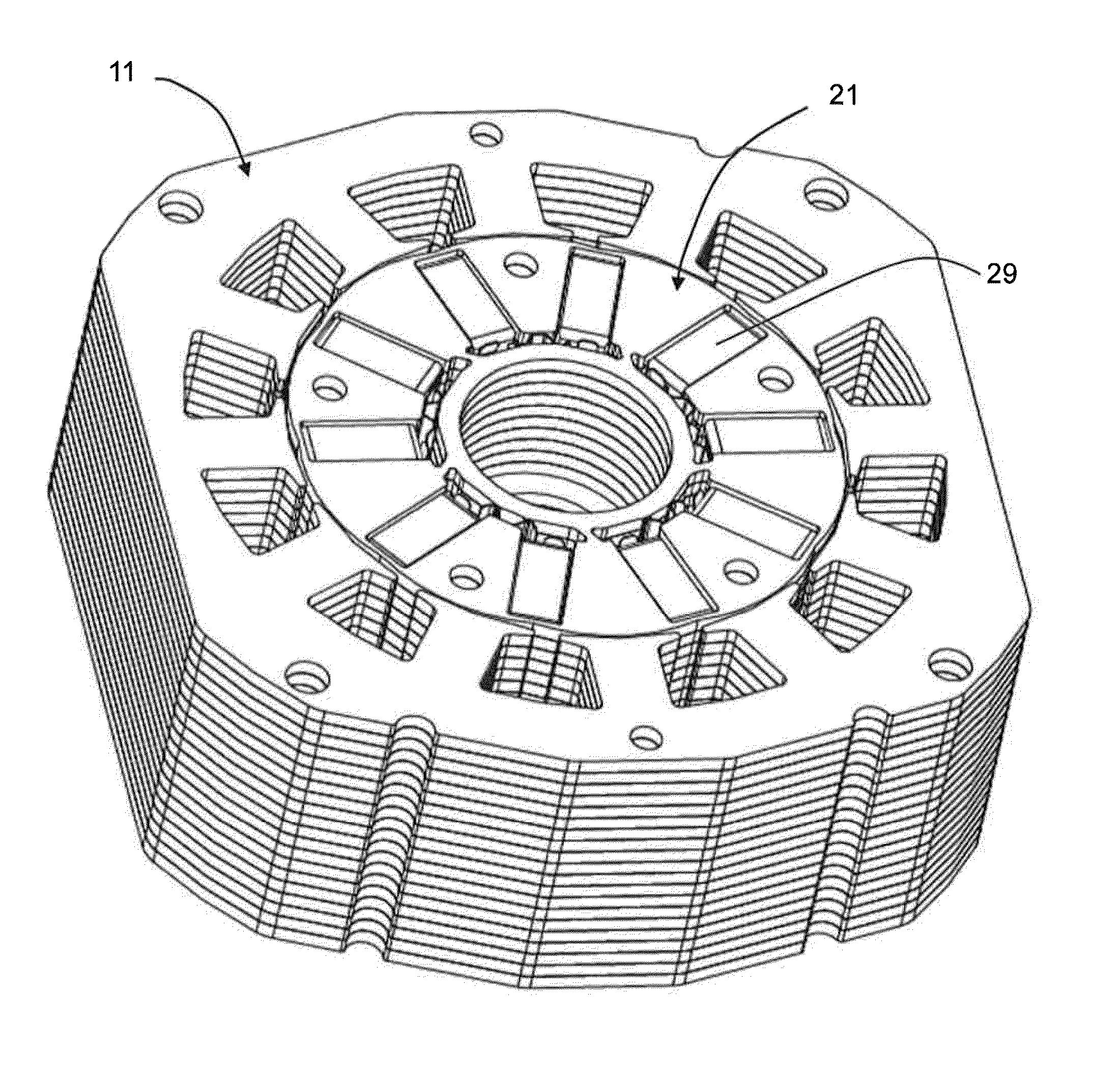
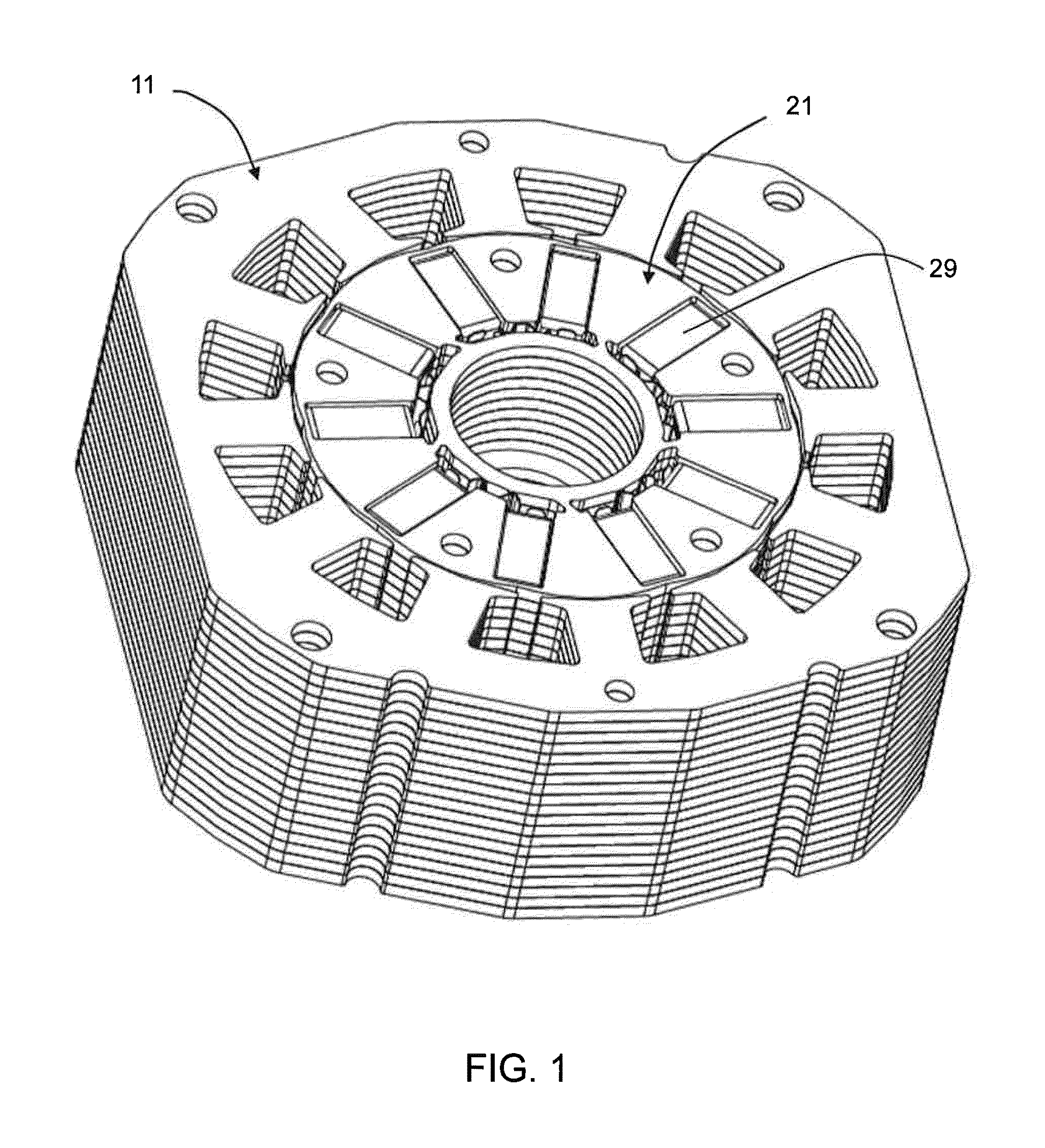
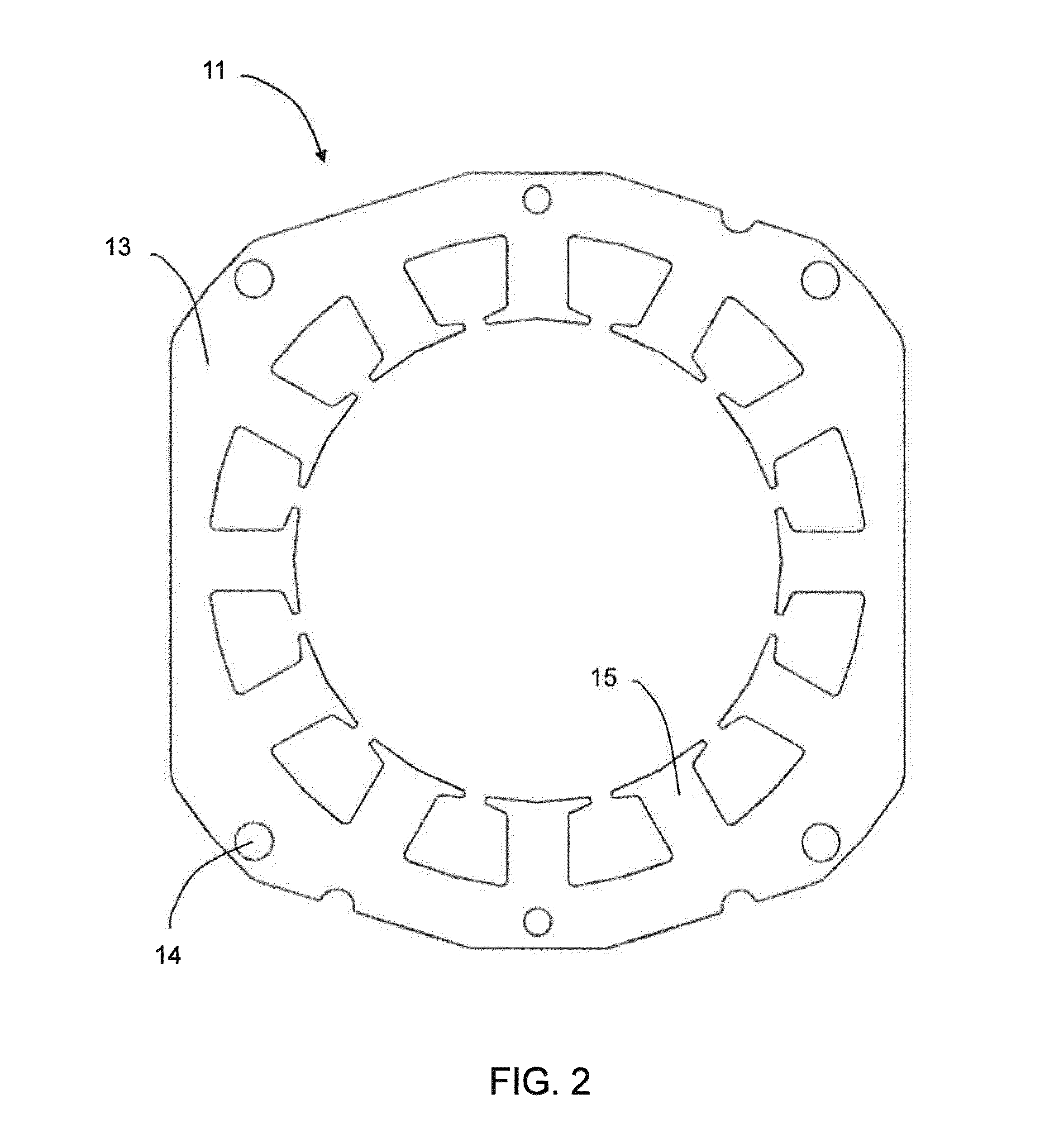
Rotor structure of large-shaft-diameter built-in permanent magnet motor and motor thereof
PendingCN112688458AReduce vibrationReduce noiseMagnetic circuit rotating partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionElectric machineryEngineering
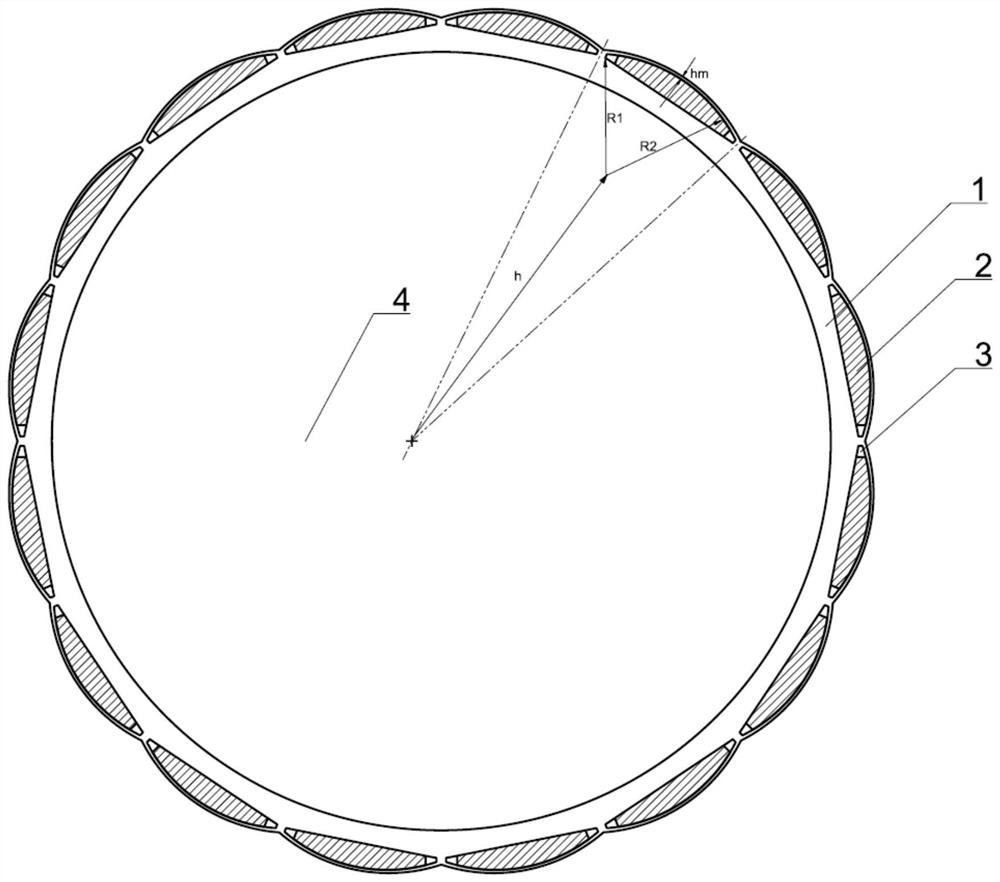
The invention discloses a rotor structure of a large-shaft-diameter built-in permanent magnet motor. The rotor structure comprises a rotor core; 2p semi-fusiform magnetic steel grooves are uniformly formed in the rotor core in the circumferential direction, wherein p is the number of pole pairs; each magnetic steel groove arc surface is a semi-fusiform arc edge, the point of the semi-fusiform arc edge close to the arc direction and away from the circle center h of the rotor core is used as the circle center, the length R1 is used as the radius, and each magnetic steel groove bottom surface is a semi-fusiform straight edge. Semi-fusiform permanent magnets are fixed in the magnetic steel grooves, and the arc surfaces of the semi-fusiform permanent magnets and the arc surfaces of the magnetic steel grooves are the same in circle center position and equal in radius; and the outer surface of the rotor core is an eccentric arc parallel to the arc surfaces of the magnetic steel grooves. By adopting the rotor structure of the large-shaft-diameter built-in permanent magnet motor, vibration and noise generated by the motor can be reduced under the condition that the performance of the motor is not lost, the radial thickness of the rotor core is reduced, and the space utilization rate of the rotor structure is improved.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Turbine blade damping device with controlled loading
A damping structure for a turbomachine rotor. The damping structure includes an elongated snubber element including a first snubber end rigidly attached to a first blade and extending toward an adjacent second blade, and an opposite second snubber end defining a first engagement surface positioned adjacent to a second engagement surface associated with the second blade. The snubber element has a centerline extending radially inwardly in a direction from the first blade toward the second blade along at least a portion of the snubber element between the first and second snubber ends. Rotational movement of the rotor effects relative movement between the first engagement surface and the second engagement surface to position the first engagement surface in frictional engagement with the second engagement surface with a predetermined damping force determined by a centrifugal force on the snubber element.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
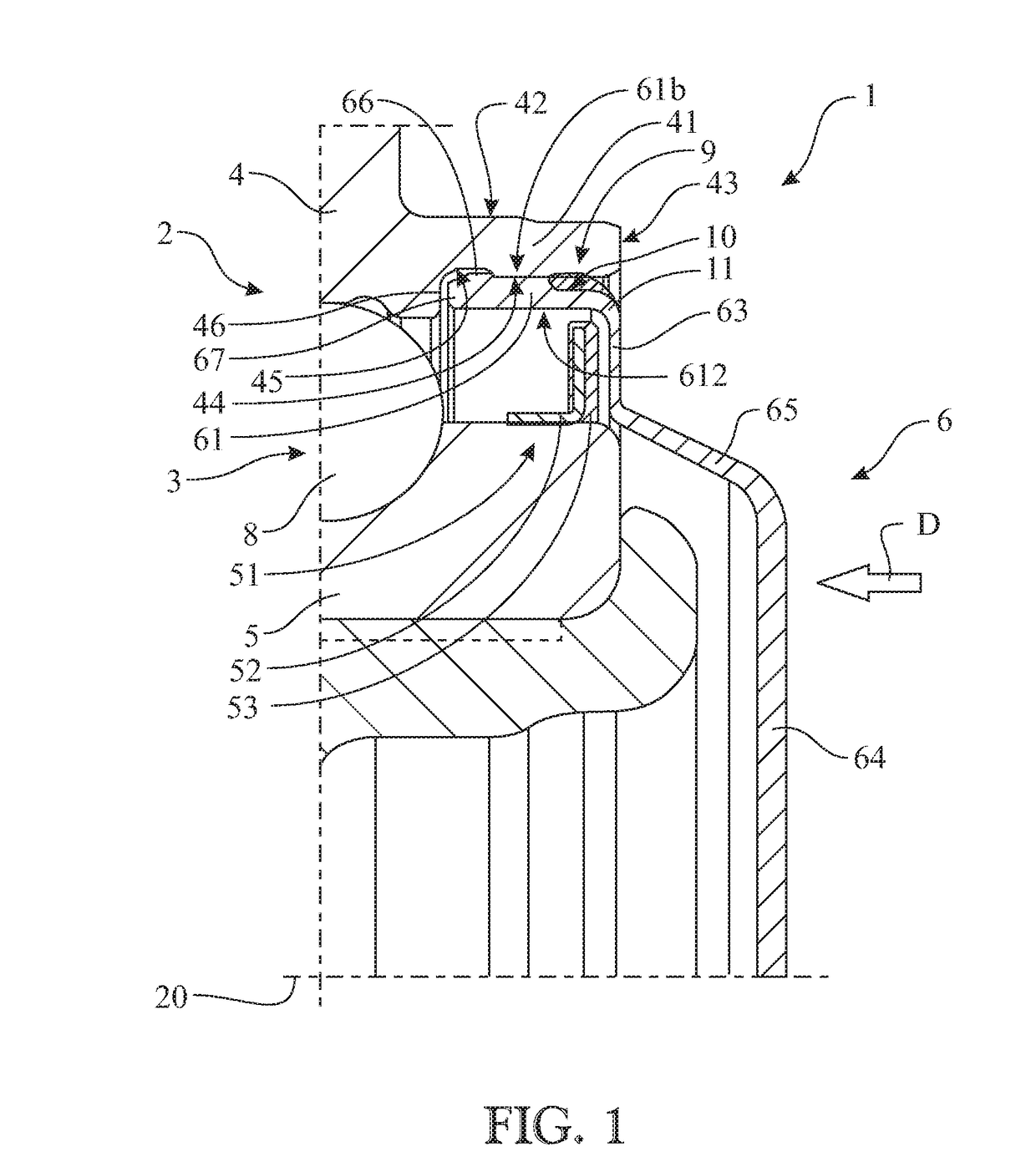
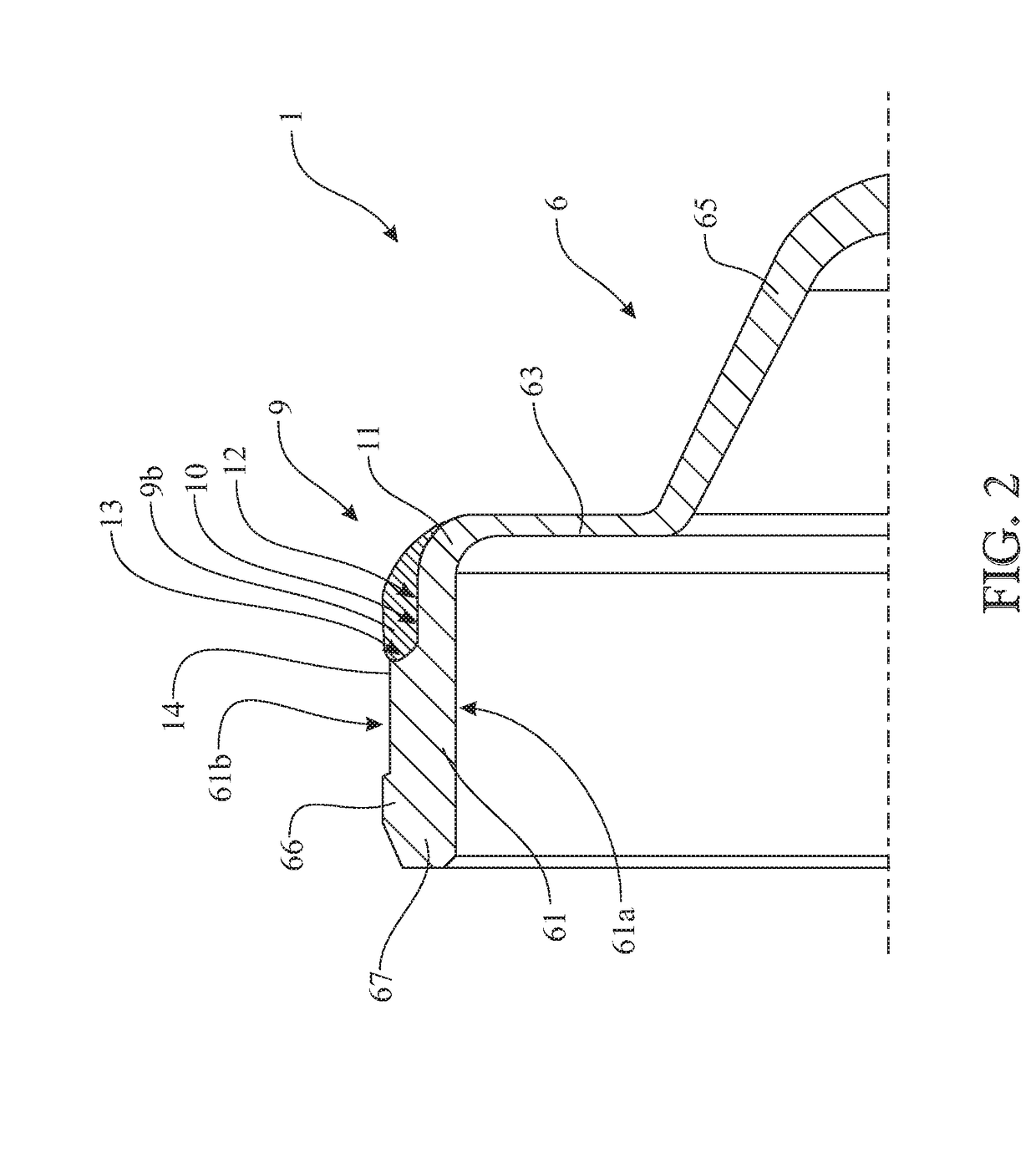
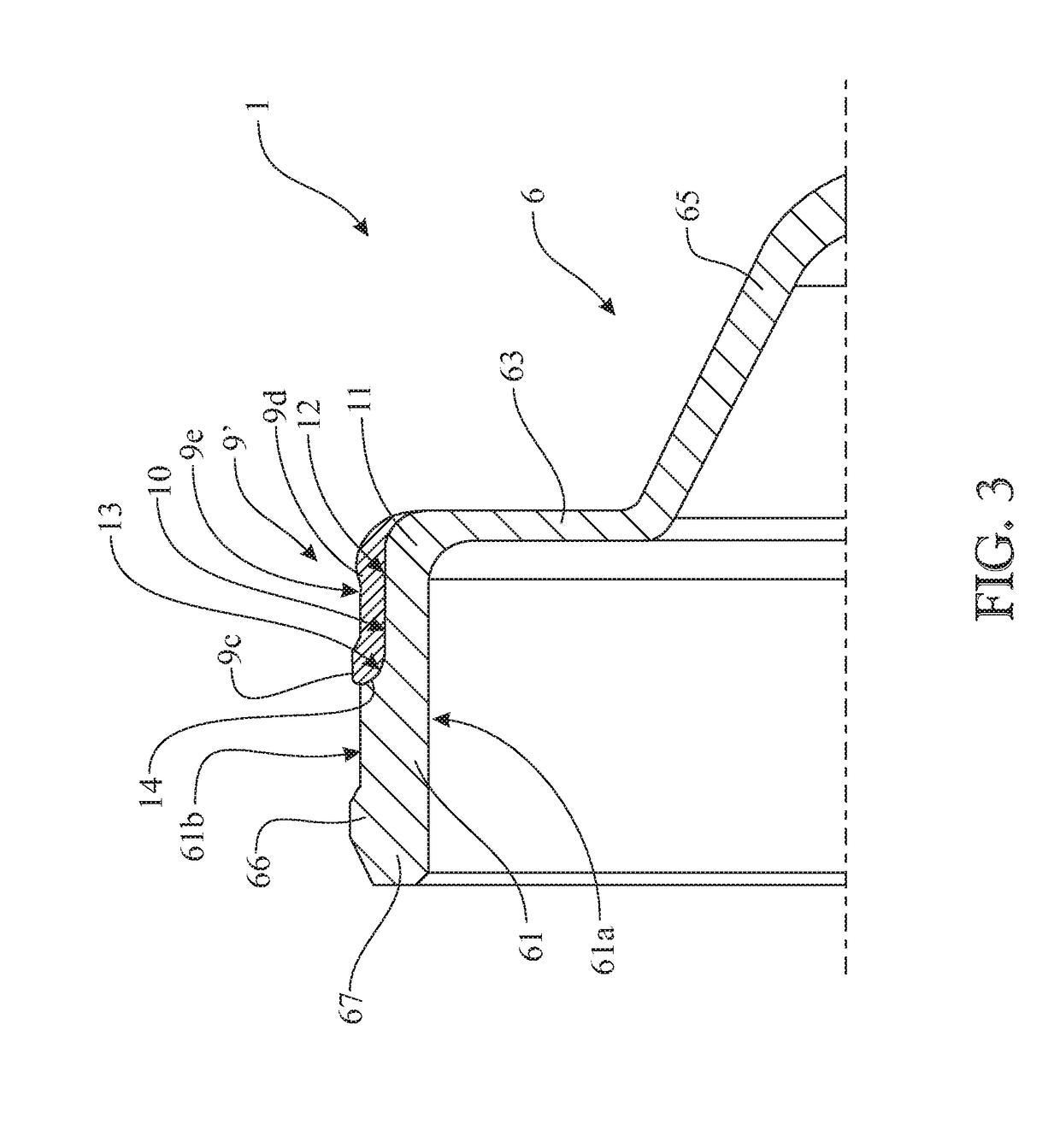
Sealing device for a hub/wheel assembly and hub/wheel assembly having such a sealing device
ActiveUS20190070898A1Reduce radial thicknessRoller bearingsBearing assemblyThermoplastic elastomerEngineering
A sealing device for a hub / wheel assembly with a roller bearing, the sealing device comprising a guard, made of plastic, which is coupled to an outer ring of the bearing so as to seal off the bearing, and which has a cylindrical mounting wall having an outer lateral surface coupled to an inner lateral surface of a collar of the outer ring. The sealing device includes a snap-engagement tooth for engaging with the collar made along the outer lateral surface so that the snap-engagement tooth snap-fits in a contoured annular groove made along the collar about the axis and an annular gasket made of thermoplastic elastomer being co-injection-molded inside a gripping seat made in the cylindrical mounting wall on the same side as the snap-engagement tooth, substantially at a corner defined between the cylindrical mounting wall and an annular reading wall transverse to the cylindrical mounting wall.
Owner:AB SKF
Dental abutment, abutment and screw assembly, and dental implant system
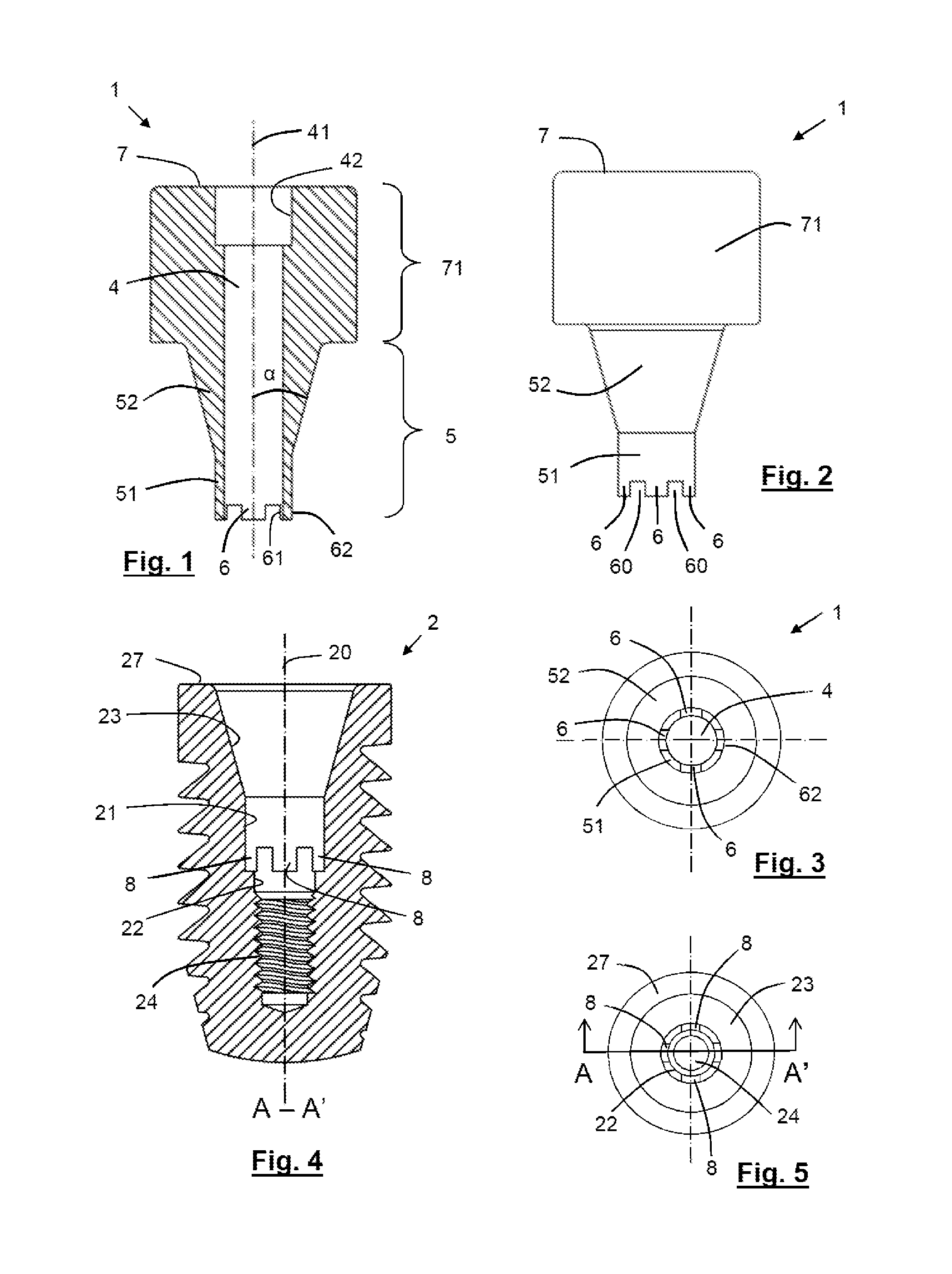
InactiveUS20160008104A1Reduce radial thicknessEffectiveDental implantsDental prostheticsEngineeringDental implant
The invention relates to a dental abutment with internal connection to an implant and fixing by means of a fixing screw. The abutment is provided, apically at the connection end thereof with anti-rotation means for positioning and fixing the orientation of the abutment with respect to the implant, and with a through hole configured for the passage therethrough of the fixing screw, the axis of which extends in the longitudinal direction to the apical connection end. The anti-rotation means comprise a plurality of longitudinal protrusions separated from each other which extend in the direction parallel to the axis of the through hole at the apical connection end, the protrusions being equidistant with respect to said axis and being configured as merlons such that the separation space between two adjacent protrusions is connected to the through hole.
Owner:TERRATS TRIQUELL MONTSERRAT
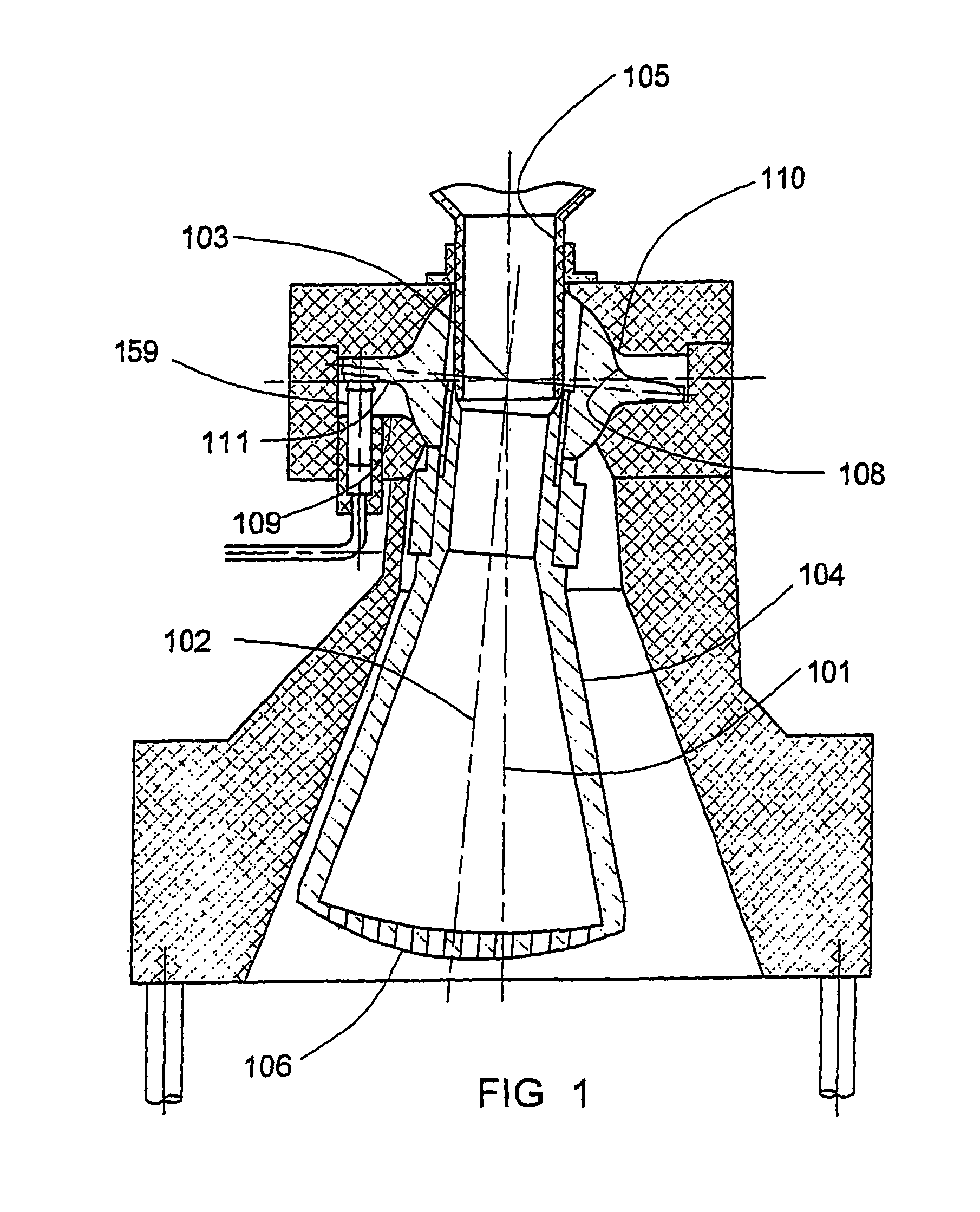
Discharge from grinding mills
ActiveUS7757986B2Mitigated, ameliorated or avoidedEffective clampingGrain treatmentsSortingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A screening element can be mounted at a discharge passage of a grinding mill chamber. The discharge passage is positioned in use to receive ground particles moving thereinto in a discharge direction. The screening element comprises one or more openings defined therein which are oriented such that ground particles pass therethrough in a direction that is oblique with respect to the discharge direction. The grinding mill chamber may form part of a centrifugal grinding mill.
Owner:F L SMIDTH & CO AS
Turbine blade damping device with controlled loading
InactiveUSRE45690E1Decrease radial thicknessReduce radial thicknessEngine manufactureBlade accessoriesTurbine bladeEngineering
A damping structure for a turbomachine rotor. The damping structure including an elongated snubber element including a first snubber end rigidly attached to a first blade and extending toward an adjacent second blade, and an opposite second snubber end positioned adjacent to a cooperating surface associated with the second blade. The snubber element has a centerline extending radially inwardly in a direction from the first blade toward the second blade along at least a portion of the snubber element between the first and second snubber ends. Rotational movement of the rotor effects relative movement between the second snubber end and the cooperating surface to position the second snubber end in frictional engagement with the cooperating surface with a predetermined damping force determined by a centrifugal force on the snubber element.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Stator arrangement and electrical generator
ActiveUS9553536B2Reduce deliveryLow coercivityMagnetic circuit stationary partsMechanical energy handlingDynamoElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Inner-rotor-type motor and electric tool provided with same
ActiveUS10491072B2Reduce axial thicknessMaintain strengthAssociation with control/drive circuitsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionPower toolClose contact
An inner-rotor-type motor is configured such that a projecting portion is formed on an inner circumferential surface of a housing, a recess portion is formed on an outer circumferential surface of a stator, the stator is positioned with respect to the housing by the recess portion and the projecting portion being fitted to each other, the stator is configured by an annular insulator having an attachment surface being brought into close contact with a core end surface at one axial end of a stator core, a sensor substrate is attached to the insulator so as to be capable of detecting a rotation angle of a rotor, the recess portion of the stator is configured by a cutout portion being formed in an area that is a part of an outer circumferential surface of the insulator and includes a portion that is brought into close contact with the core end surface.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Crushing shell with profiled crushing surface
ActiveUS10537895B2Capacity balanceIncreased reduction potentialGrain treatmentsClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com