Method for isolating cell free apoptotic or fetal nucleic acids
A cell nucleic acid and nucleic acid technology, applied in the fields of separation of fetal nucleic acid, separation of apoptosis or fetal nucleic acid, identification of fetal genetic composition, and can solve the problem of lack of prenatal examination or screening of pregnant women
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Preparation of DNA binding beads
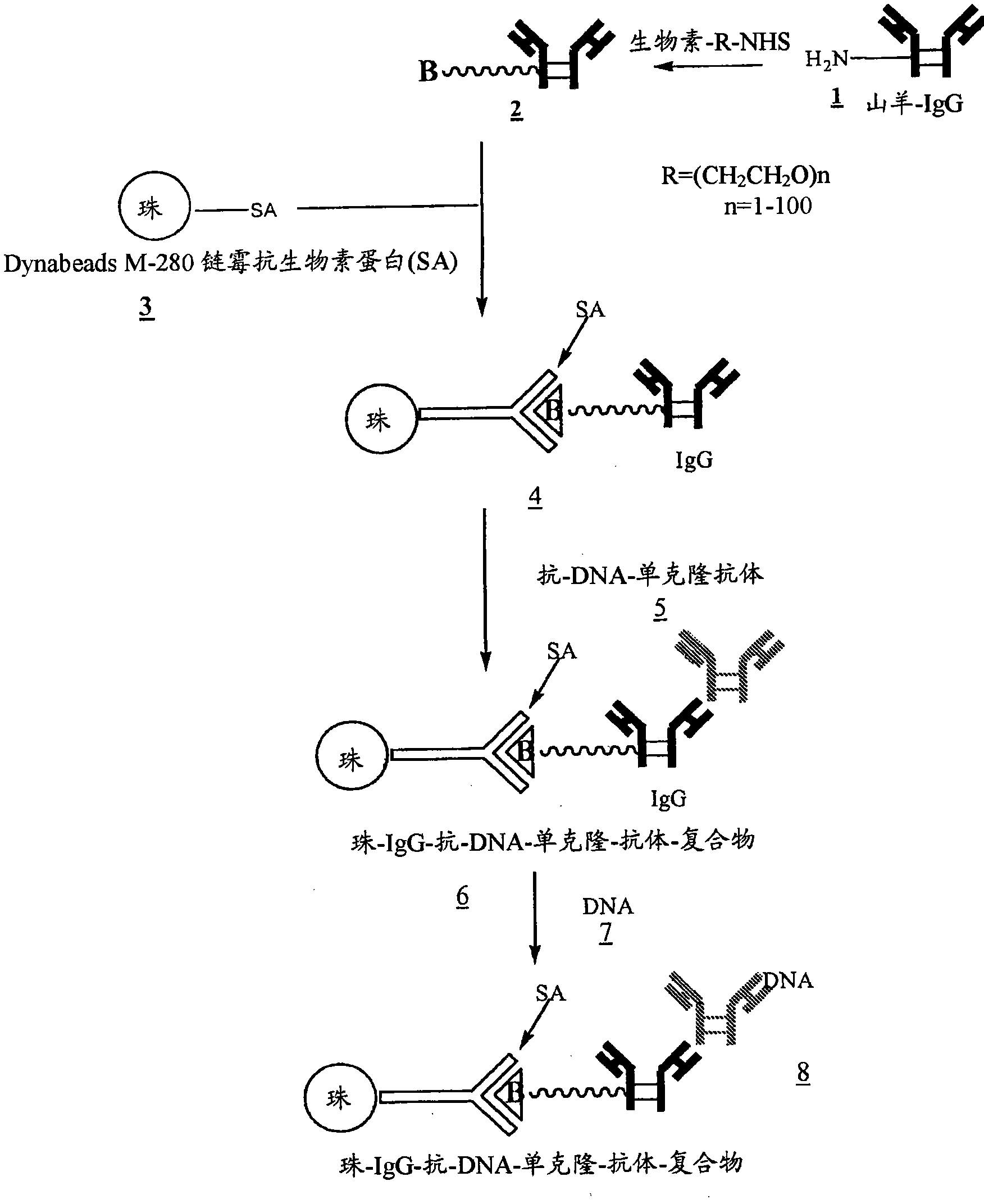
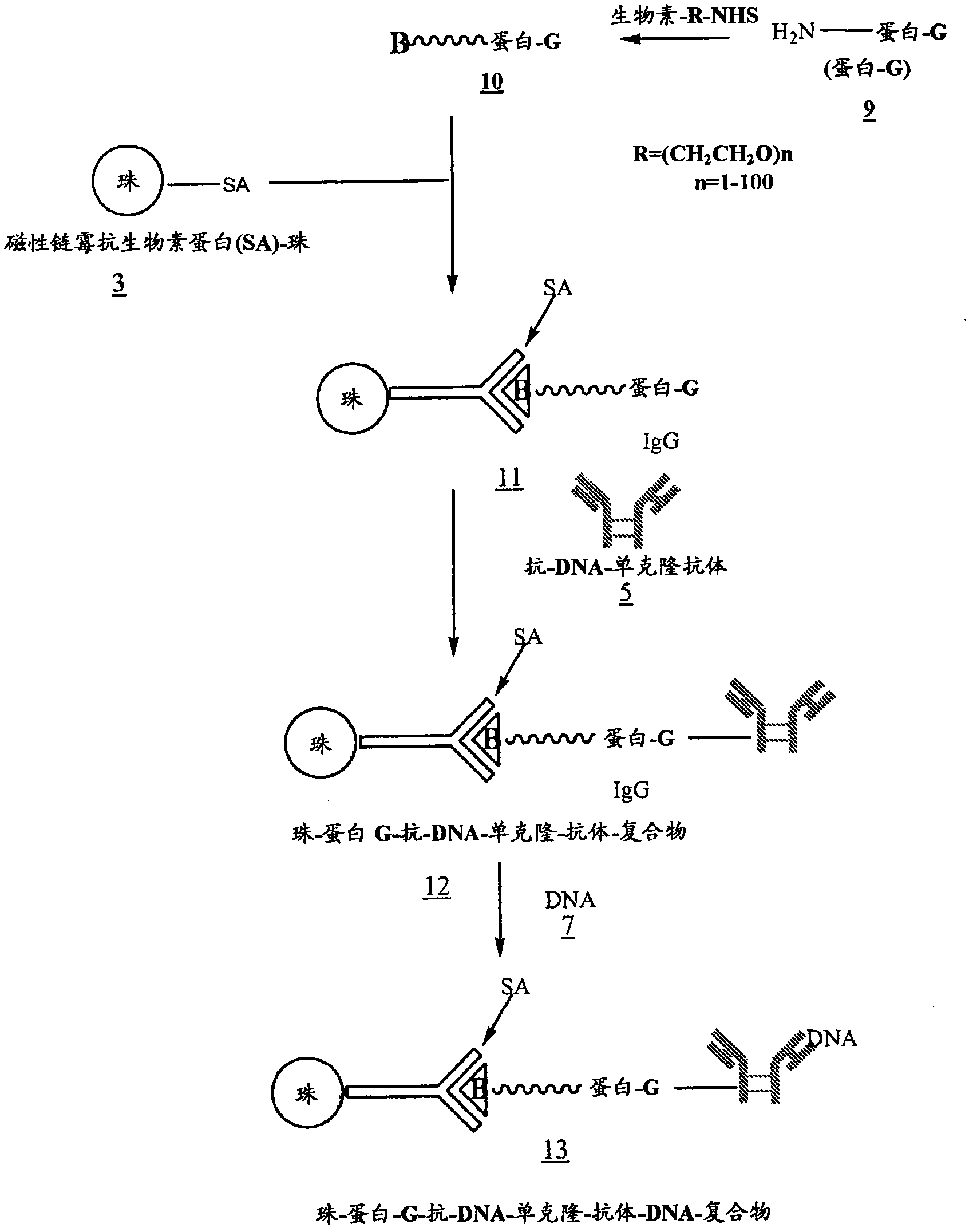
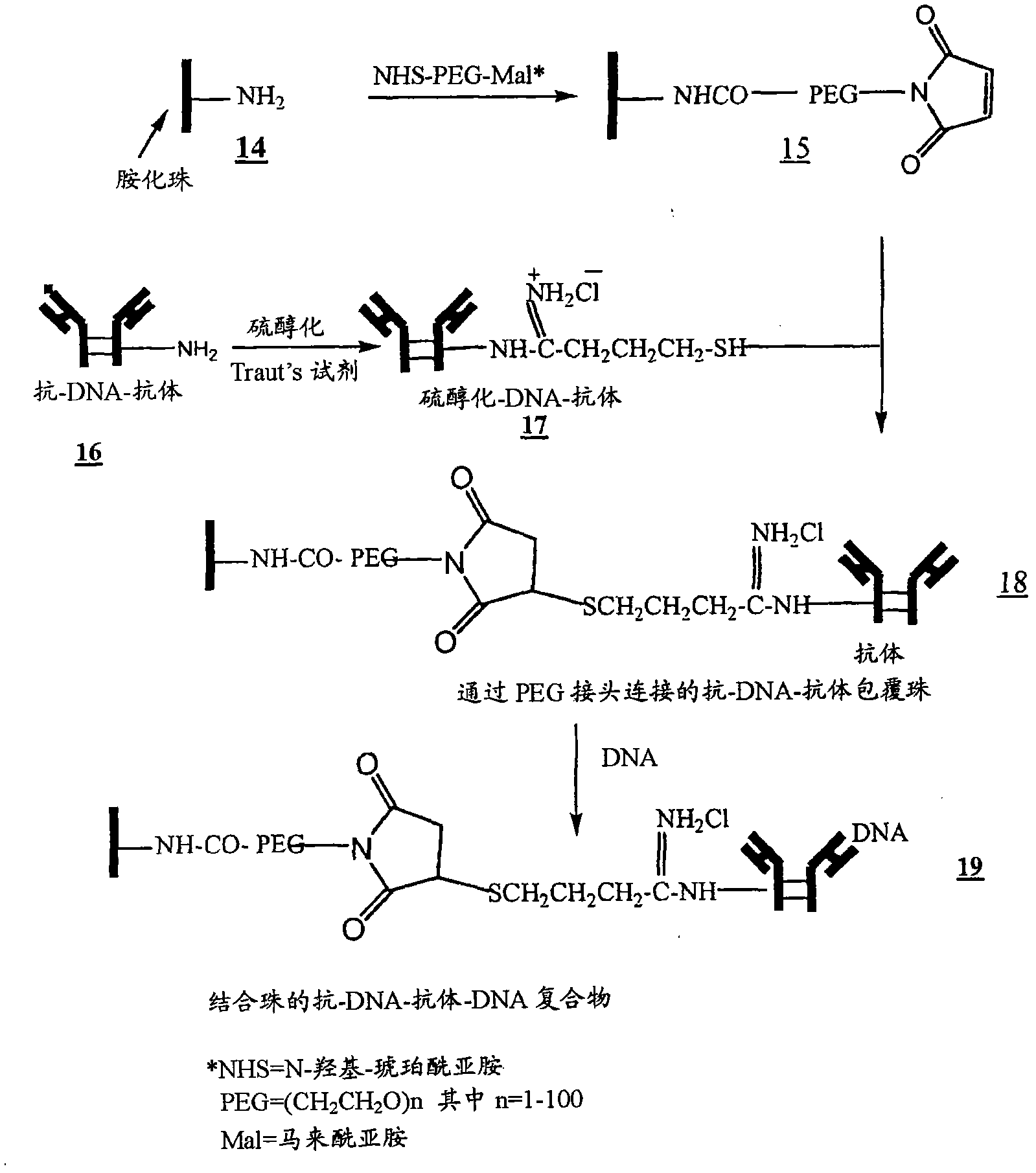
[0034] figure 1 , 2 and 3 outline the steps involved in the preparation of magnetic beads conjugated to anti-DNA-antibodies via IgG, protein-G and NHS-PEG-maleimide, respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Procedure for Isolating Fetal DNA from Maternal Blood
[0036] Beads coated with anti-DNA antibody 6 ( figure 1 ), 12( figure 2 ), or 18( image 3 ) to process 2ml of maternal blood. Use enough beads carrying at least 100 μg of anti-DNA antibody. Gently swirl the samples for 15 min at room temperature to ensure that the beads are well mixed with the blood. The samples were then placed in a magnetic separator for 1-2 minutes before removing the supernatant. The beads were then washed 3 times with 2M NaCl, 10 mM Tris.HCl, 1 mM EDTA (pH 7.0). The beads were then digested with proteinase K in 200 μl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris.HCl, 25 mM EDTA, 1% SDS at 55°C for 1 hour. After proteinase K inactivation at 95 °C for 10 min, the supernatant was ethanol precipitated by adding 2 volumes of absolute ethanol and cooling the samples at −80 °C for 20 min. Wash the DNA pellet once with 90% ethanol.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Determination of gender
[0038] The DNA from Example 2 was used as a template in PCR using primers and probes to determine fetal sex. After rinsing with 90% ethanol, the DNA pellet was dried, dissolved in 80 μl of water and analyzed for fetal sex by PCR. Using one or more TaqMan probes for Y chromosome sequence labeling, dual-labeled probes, 18-22 base oligonucleotides with a reporter fluorophore at the 5' end and a quencher fluorophore at the 3' end acid probe, and one or more primers to detect Y chromosome sequences.
[0039] SRY (Sex Determining Region Y) primers were used to target sex determining genes present on the Y chromosome of humans and other primates. The SRY gene encodes the testis determinant, also known as the SRY protein. Use FCY primers to target another commonly used marker in the Y chromosome. The β-hemoglobin gene, a housekeeping gene present in total DNA, was used as an internal control in each PCR reaction. As shown below, all 5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com