Method for preparing 2,5-dimethyl phenylacetic acid
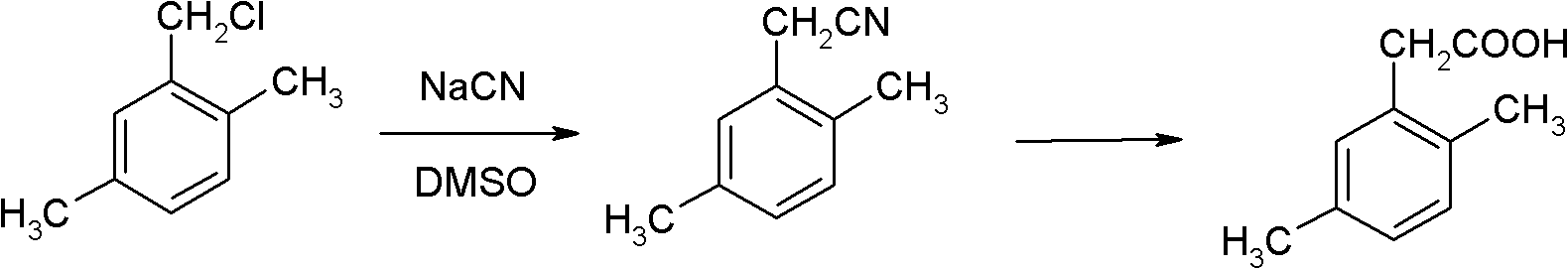
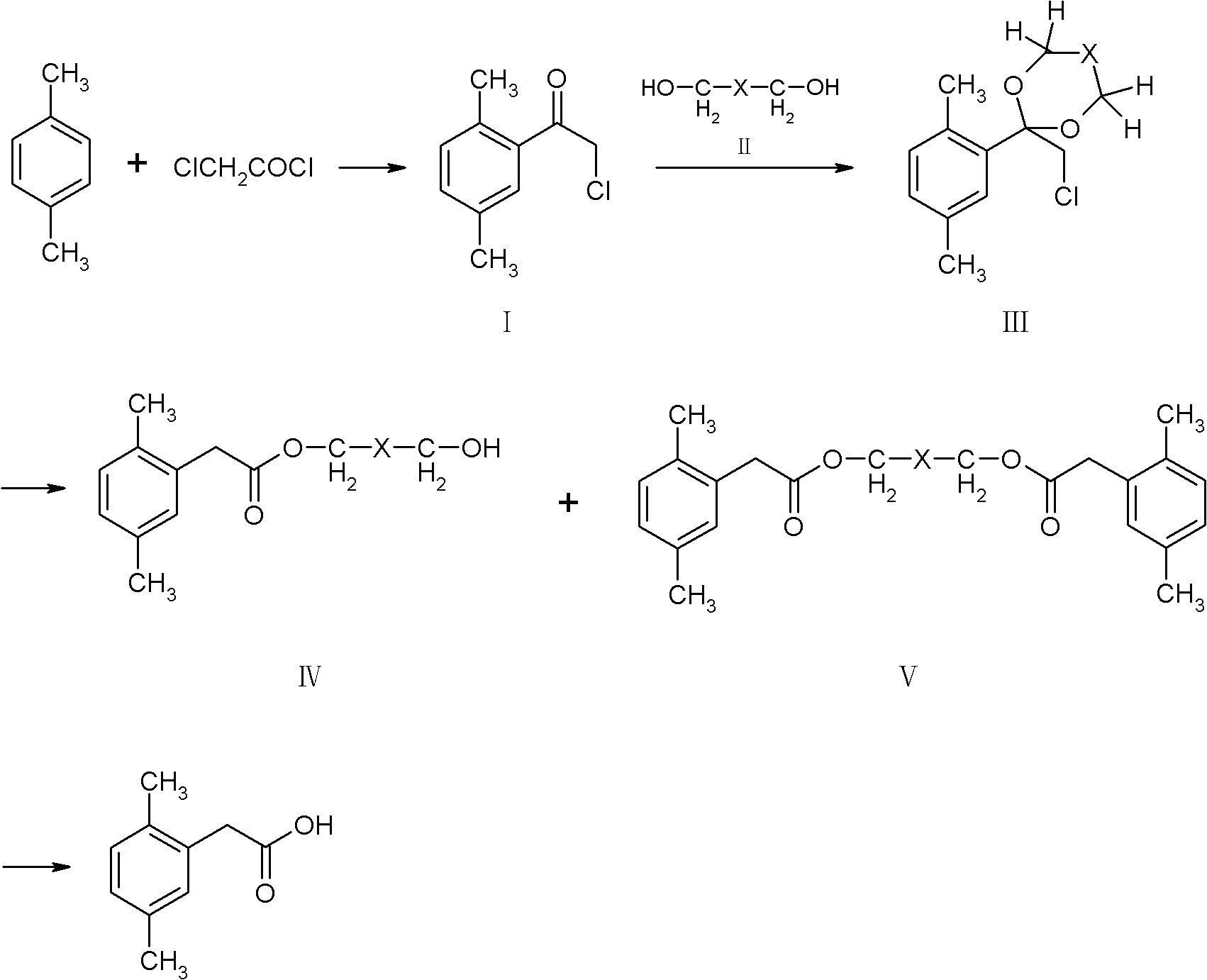
A technology of dimethylphenylacetic acid and p-xylene, which is applied to the preparation of carboxylic acid by carbon monoxide reaction, the preparation of halogenated hydrocarbons, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of complex reaction types, high raw material prices, and many synthesis steps, etc., Achieve the effects of high reaction yield, low production cost and reasonable process conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
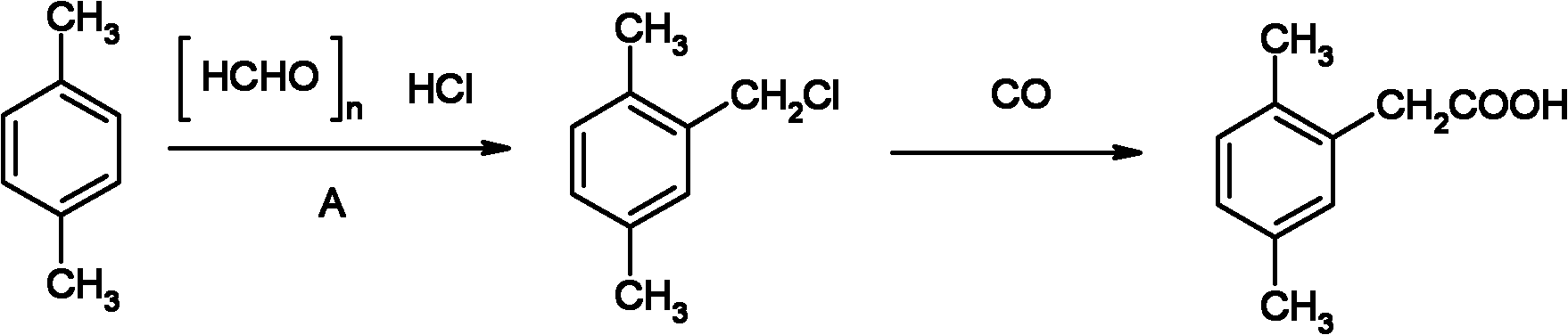
[0028] (1) Chloromethylation reaction
[0029] In a 500ml four-necked flask, add 48g of paraformaldehyde, 106g of p-xylene, 10g of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole bromide, and 3.2g of concentrated hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 36%. After stirring evenly, the temperature rises to Charge hydrogen chloride gas at 80-85°C, keep warm for 0.5 hours after the hydrogen chloride gas has been flushed, and then let it stand for stratification after cooling down to room temperature, the upper layer is the organic layer, and the lower layer is the water layer. The water layer is dehydrated under reduced pressure, and the dehydrated ionic liquid can be recycled. The organic layer was transferred to a 500ml four-neck flask for rectification under reduced pressure, and 139.3g of 2,5-dimethylbenzyl chloride was finally obtained after precipitation, with a yield of 90.1%.
[0030] (2) Carbonylation and hydrolysis reactions
[0031] In a 1000ml autoclave, add 70.0g of the above-mentioned...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) Chloromethylation reaction
[0034] In a 500ml four-neck flask, add 24g of paraformaldehyde, 53g of p-xylene, 4.9g of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, and 1.6g of concentrated hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 36%, and heat up after stirring When the temperature rises to 80-85°C, hydrogen chloride gas is filled. After the hydrogen chloride gas is filled, it is kept for 0.5 hours. After cooling down to room temperature, it is allowed to stand for stratification. The upper layer is the organic layer, and the lower layer is the water layer. The water layer is dehydrated under reduced pressure, and the dehydrated ionic liquid can be recycled. The organic layer was transferred to a 500ml four-neck flask for rectification under reduced pressure, and 70.6g of 2,5-dimethylbenzyl chloride was finally obtained after precipitation, with a yield of 91.3%.
[0035] (2) Carbonylation and hydrolysis reactions
[0036] In a 1000ml autoclave, add the above-me...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Chloromethylation reaction
[0039] In a 250ml four-necked flask, add 36.0g of paraformaldehyde, 84.8g of p-xylene, 14.0g of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole chloride, 2.4g of concentrated hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 36%, and heat up after stirring evenly. Fill in hydrogen chloride gas when the temperature rises to 80-85°C, keep the temperature for 0.5 hours after the hydrogen chloride gas is filled, let it stand and separate after cooling down to room temperature, the upper layer is the organic layer, and the lower layer is the water layer. The water layer is dehydrated under reduced pressure, and the dehydrated ionic liquid can be recycled. The organic layer was transferred to a 250ml four-neck flask for rectification under reduced pressure, and 113.4g of 2,5-dimethylbenzyl chloride was finally obtained after precipitation, with a yield of 91.7%.
[0040] (2) Carbonylation and hydrolysis reactions
[0041] In a 1000ml autoclave, add the above-mentioned re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com