Micro-slit-structure-based full PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) micro-fluidic cell capturing chip and manufacturing method thereof
A microfluidic, cell technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, enzymology/microbiology devices, bioreactors/fermenters for specific purposes, etc. Achieve the effects of high capture efficiency, simple and feasible modification and integration operations, and simple production methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1. Fabrication of a double-layer structure cell capture chip:
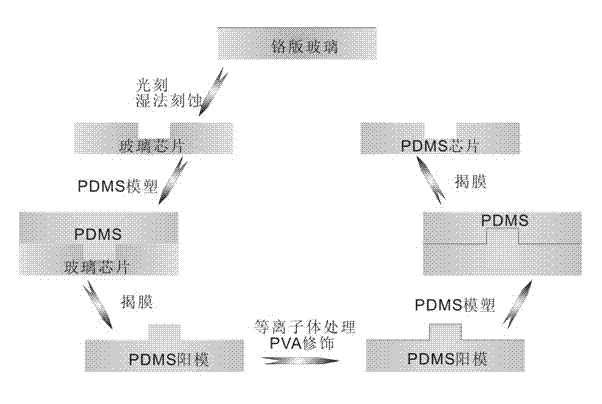
[0028] 1. Use as figure 1 Prepare PDMS microchannel chips in the manner shown.
[0029] Step 1. Fabrication of glass channels: glass chip channels are prepared using standard photolithography and chemical wet etching techniques. Using a commercial uniform colloidal chromium plate, photolithography is carried out according to the channel design pattern, and the etching depth is 30-50 μm;
[0030] Step 2. Make the upper and lower layers of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannel sheets: use the above-mentioned glass chip as a negative template, cast a certain amount of PDMS on it, heat and solidify, and get a corresponding positive mold after peeling off structured PDMS chips. After the PDMS positive mold is treated with air plasma, the surface is quickly spin-coated with an aqueous solution of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with a mass percentage concentration of 0.1-0.5%, and dried under an infrared lamp...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2. Using a double-layer structure cell capture chip to capture and release cells:
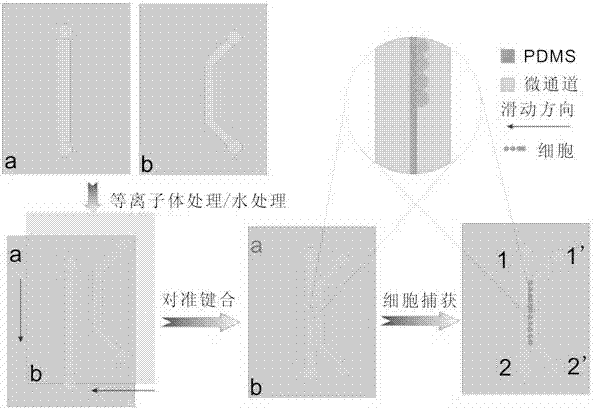
[0035] In order to characterize the capture effect of the chip on cells, we used different channel combinations to make micro-slits and captured the suspended BGC-823 cell samples. The results are as follows: image 3 shown. The steps are:
[0036] Step 1. Inject the cell suspension at the entrance of the upper channel. Due to the difference in hydrostatic pressure, the cells flow to the solution to the outlet and shunt to the lower channel. Blocked by the slit, the cells are continuously arranged and aggregated on the slit along the flow direction to form a capture. Excess cells are discharged from the outlet along with the suspension; the captured cells can also be washed while maintaining the pressure.
[0037] Step 2. Aspirate the sample solution from the inlet, inject the buffer solution into the inlet and outlet of the lower channel, reverse the pressure of the liquid, ev...
Embodiment 3
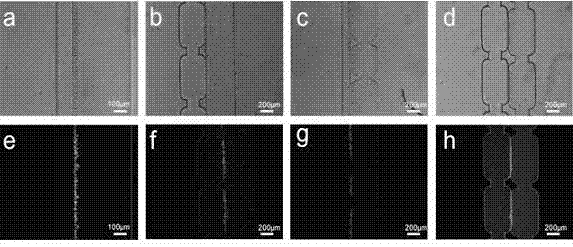
[0038] Example 3. Using a double-layer structure cell capture chip to capture several cells or a single cell:
[0039] In order to characterize the capture performance of the chip for a small number of cells, we captured several and single cells by reducing the length of the slit and using staggered bonding. The results are as follows Figure 4 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Etching depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com