Methods and systems for deacidizing gaseous mixtures
A technology for degassing and acid gas, used in separation methods, gas treatment, carbon compounds, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
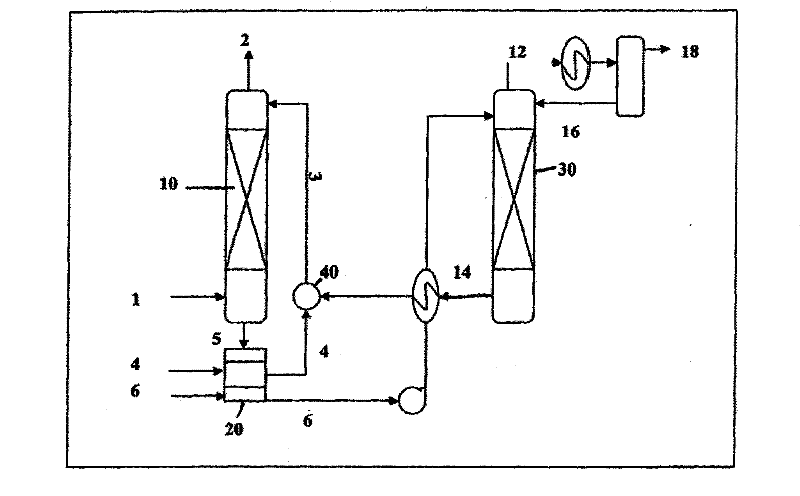
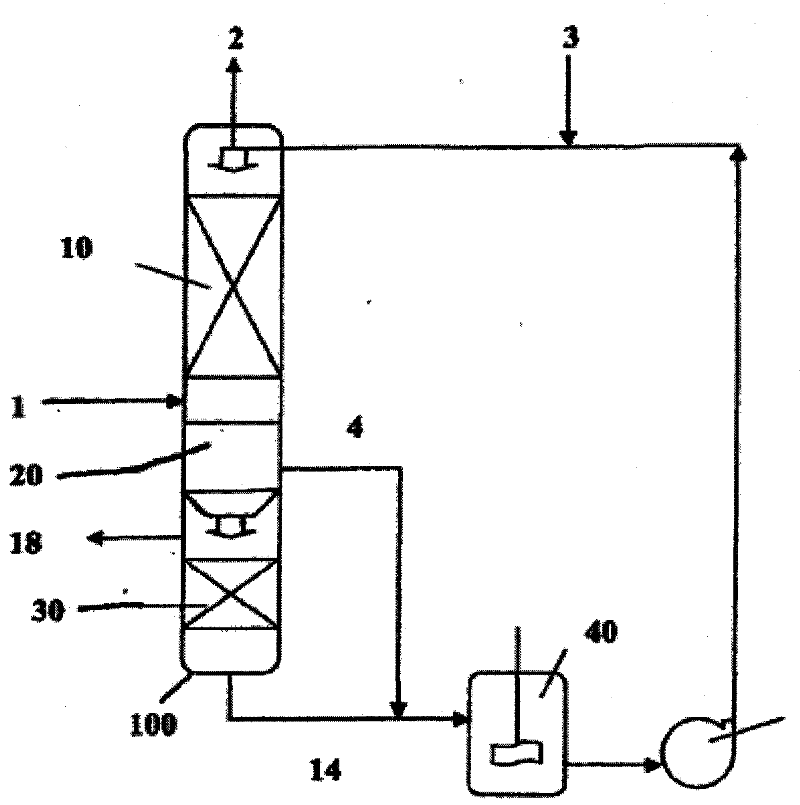
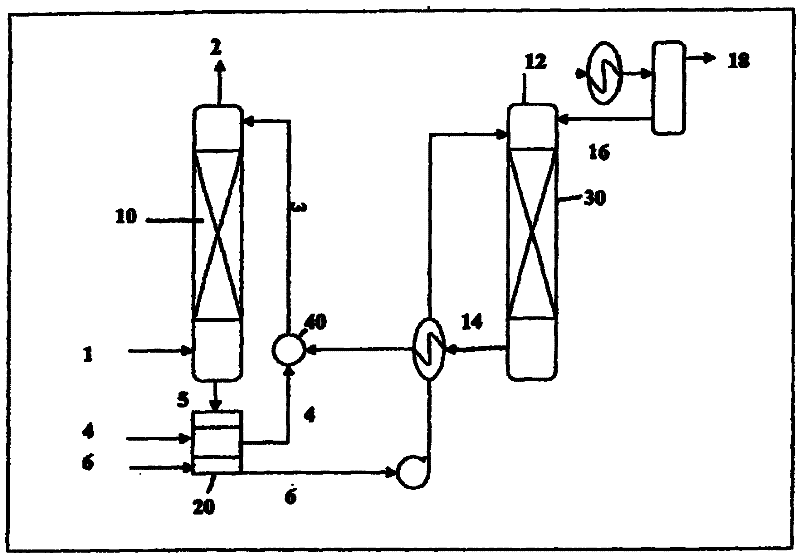
[0066] The absorbent contains 2 phases, an organic phase and a carrier phase, and the mixed gas containing carbon dioxide is fed into a stirred absorption unit at 25°C to 45°C at atmospheric pressure. The organic phase is composed of 20% monoethanolamine by volume and 80% decanol by volume, and the carrier phase is composed of the reaction product of ethanolamine and carbon dioxide.
[0067] When the organic phase comes into contact with the gas mixture, carbon dioxide is chemically absorbed by the organic phase by reacting with ethanolamine in the organic phase. The absorbed carbon dioxide exists as a reaction product with ethanolamine. The reaction products are transferred to the carrier phase through the interface between the organic phase and the carrier phase, where they accumulate. After absorbing the carbon dioxide gas, the absorbent is identified and separated by gravity into a first acid-lean gas phase and an acid-rich gas phase. The first acid-lean gas phase, consi...
Embodiment 2
[0069] An absorbent consists of an organic phase, a carrier phase, and two liquid phases. The carbon dioxide-containing gas mixture is supplied to a stirred absorption unit at 25°C to 45°C at atmospheric pressure. The organic phase consists of 20% dibutylamine and 80% isooctyl alcohol by volume. The carrier phase contained 150 g / l of potassium carbonate in water.
[0070] When the organic and mixed gas phases come into contact, carbon dioxide is chemically absorbed by the organic phase through the reaction with dibutylamine in the organic phase. The absorbed carbon dioxide exists as the reaction product of carbon dioxide and dibutylamine. The reaction product is further reacted with potassium carbonate in the carrier phase to form potassium bicarbonate, so that it is transferred to the carrier phase through the interface between the organic phase and the carrier phase. Thus, the absorbed carbon dioxide ends up in the carrier phase as (in the form of) potassium bicarbonate. ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] The absorbent includes two liquid phases, an organic phase and a carrier phase, and a mixed gas containing carbon dioxide is supplied to a stirring absorption unit at 25°C to 45°C under one atmospheric pressure. The organic phase consists of 20% dibutylamine and 80% isooctyl alcohol by volume. The carrier phase is an aqueous solution.
[0076] When the organic phase is in contact with the mixed gas phase, carbon dioxide is chemically absorbed by the organic phase by reacting with dibutylamine in the organic phase. Absorbed carbon dioxide exists as the reaction product of carbon dioxide and dibutylamine. The reaction product then transfers to the carrier phase through the interface between the organic phase and the carrier phase and accumulates there.
[0077] The absorbent is defined after absorbing carbon dioxide gas and separated by gravity into a first acid-lean gas phase and an acid-rich gas phase. The first acid-lean gas phase contains unreacted dibutylamine, is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com