Iron-making method by performing coal-based direct reduction in rotary hearth furnace and melting in gas melting furnace on lateritic-nickel ore
A gas-fired melting furnace and lateritic nickel ore technology, which is applied in the direction of rotary drum furnace, furnace, furnace type, etc., can solve the problems of large coke consumption, sintering pollution, and low reduction temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
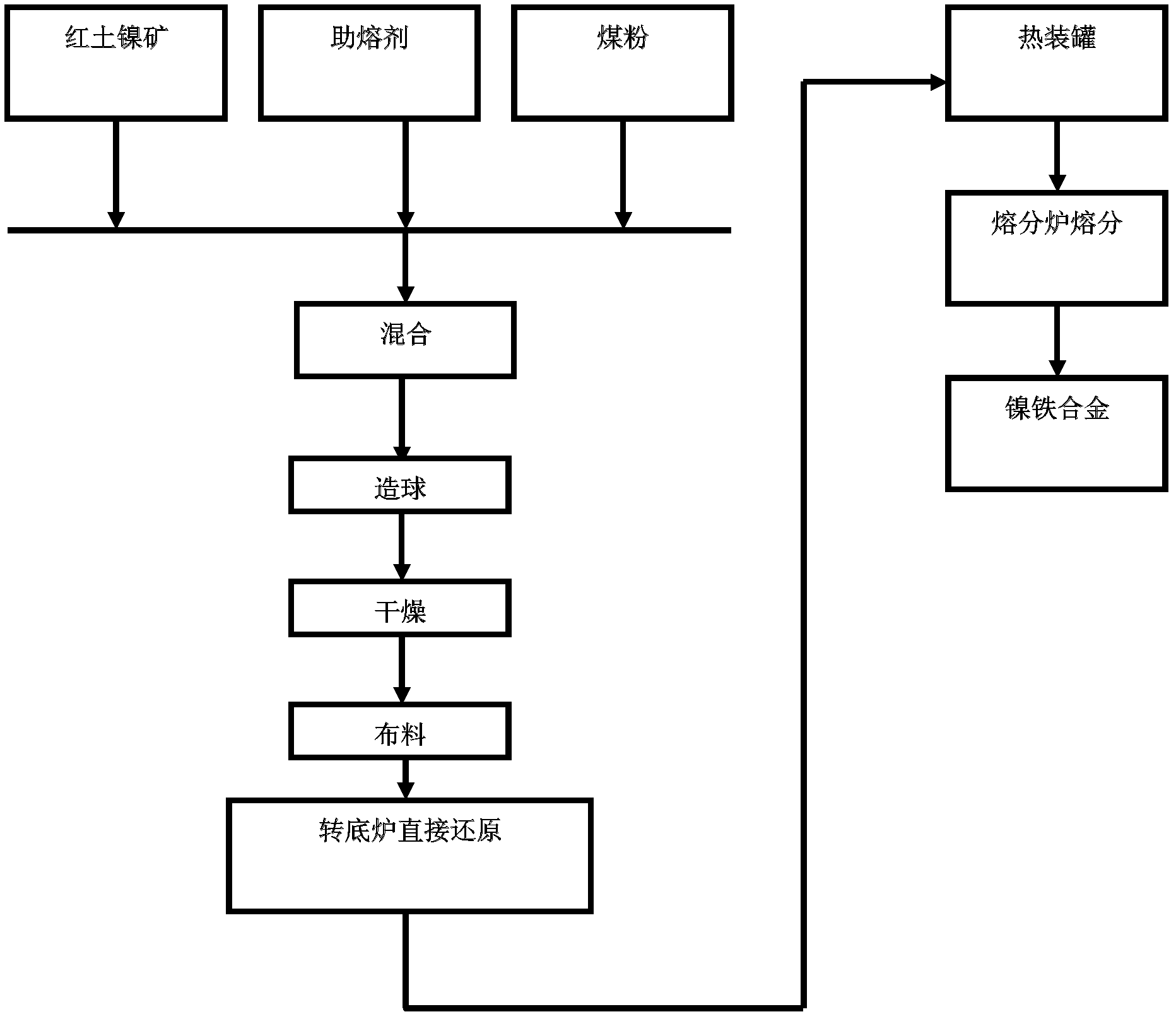
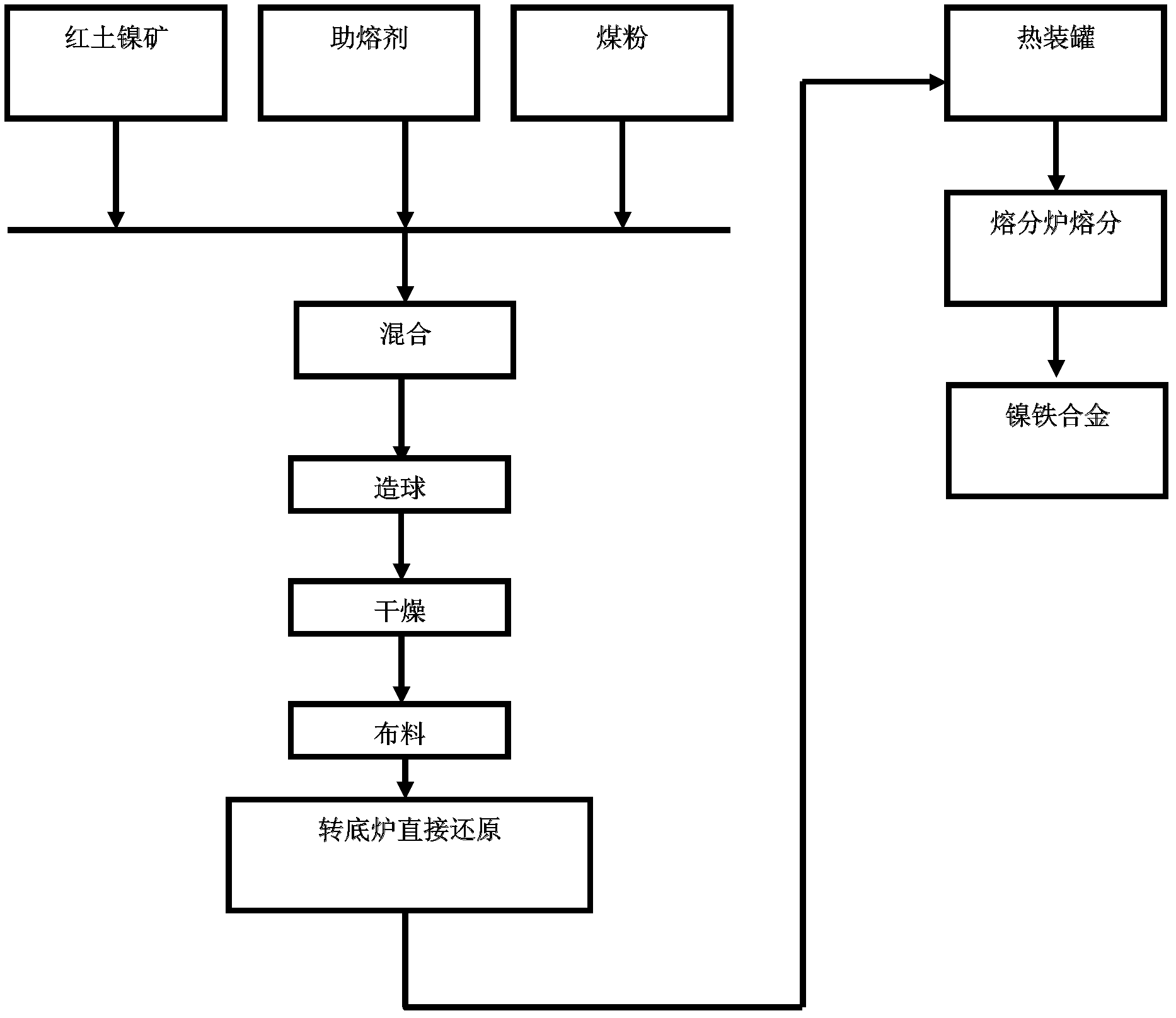
[0023] The laterite nickel ore containing 17.91% iron and 1.52% nickel in a certain place is mixed according to the ratio of laterite nickel ore: coal: limestone = 100:10:10, put into the rotary hearth furnace and roasted for 35 minutes, then hot charge The tank is sent to a gas melting furnace using gas as fuel for melting. The temperature of the gas melting furnace is 1420°C to 1600°C, and the melting time is 30 minutes. Finally, a nickel-iron alloy containing 14.607% nickel and 84.76% iron is obtained, and the yield of nickel is 95.68%. To produce one ton of pure nickel, 69.25 tons of laterite nickel ore containing 1.52% nickel and 58480Nm of gas are required 3 , power consumption 8128.72kwh.
[0024] In the present invention, the high-temperature reduction process of the rotary hearth furnace is used to reduce the nickel and iron in the laterite nickel ore, and then the heat is sent to the regenerative coal-gas melting furnace for melting after hot-filling; The temperatu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com