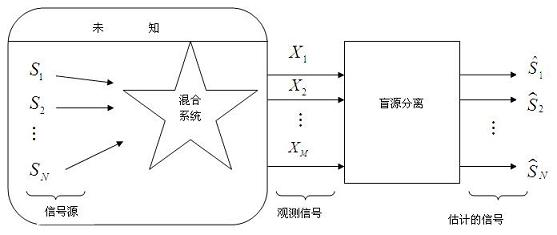
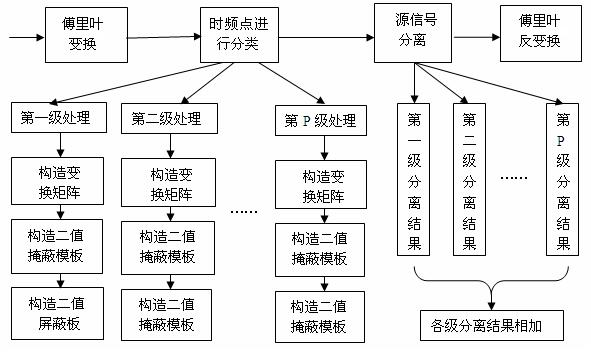
Matrix-transformation-based method for underdetermined blind source separation
An underdetermined blind separation and matrix transformation technology, applied in speech analysis, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as harsh conditions, strict signal sparsity requirements, and poor anti-noise performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Select 4 voice signals of different speakers from the voice library as the source signal, take 50000 points respectively, and perform linear instantaneous mixing in the time domain. The mixing matrix is as follows:
[0090]
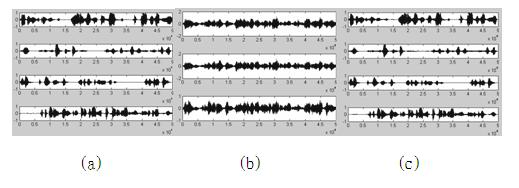
[0091] The obtained scattered mixed signal is transformed into the time-frequency domain by short-time Fourier transform. The frame length of the short-time Fourier transformed time-domain signal is 1024 points, the overlap between frames is 512 points, and the frequency domain resolution is 1024 points. The time-domain waveform of the original four-way voice signal is attached image 3 As shown in (a), the time-domain waveforms of the three-way observation signals after linear instantaneous mixing are shown in the attached image 3 Shown in (b), the four-way voice signal time-domain waveform that the present invention separates is as attached image 3 (c) shown. Compared image 3 (a) and image 3 (c) It can be seen that the recovery perfo...
Embodiment 2
[0097] One of the advantages of the present invention is that it lowers the requirement on the statistical characteristics of the source signal, and enables underdetermined separation of related source signals. Select one voice signal from the voice library, and then take different time periods of the voice to form four related source signals. The time-domain waveforms of the original four-way correlation signals are attached Figure 4 As shown in (a), the time-domain waveforms of the three-way observation signals after linear instantaneous mixing are shown in the attached Figure 4 Shown in (b), the time-domain waveforms of the four-way signals separated by the present invention are as attached Figure 4 (c) shown. The output signal-to-noise ratio of the separated signals is shown in Table 2.
[0098] Table 2 Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of four-way correlated speech output
[0099]
Embodiment 3
[0101] The invention can well solve the underdetermined separation of weak and sparse signals. The advantages of the present invention will be described below by taking noise with poor sparsity as an example. Select one noise and three different speech signals from the speech library. The time-domain waveforms of the original one-way noise and three-way voice signals are attached Figure 5 As shown in (a), the time-domain waveforms of the three-way observation signals after linear instantaneous mixing are shown in the attached Figure 5 Shown in (b), the four-way signal time-domain wave form that the present invention separates is as attached Figure 5 (c) shown. The output signal-to-noise ratio of the separated signals is shown in Table 3.
[0102] Table 3 One-way noise, three-way voice output signal-to-noise ratio SNR
[0103]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com