Microbial fuel cell and preparation method thereof
A technology of fuel cells and microorganisms, applied in biochemical fuel cells, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of undiscovered Pseudomonas electrical activity and undisclosed uses of Pseudomonas, and achieve electricity production conditions that are not harsh, Ease of operation and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: The electricity production of Pseudomonas MBR using glucose as fuel under aerobic conditions.
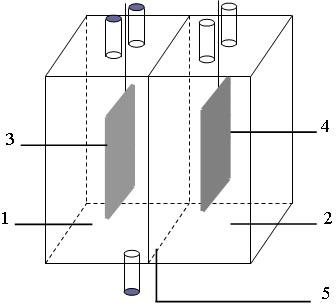
[0035] (1) Construction of microbial fuel cell device: In this example, a microbial fuel cell device using Pseudomonas MBR to generate electricity was constructed according to the existing technology and method, as shown in the attached figure 1 As shown, it includes four parts: anode chamber, cathode chamber, diaphragm and external circuit. In the figure, 1 is the anode chamber, 2 is the cathode chamber, 3 is the anode electrode, 4 is the cathode electrode, and 5 is the diaphragm. The volumes of the cathode and anode chambers are both 245ml, the cathode and anode are both 6 cm×5 cm carbon felt, and the cation exchange membrane is used as the diaphragm.
[0036] (2) Prepare anolyte. A component: NH 4 Cl 0.53 g, KH 2 PO 4 2.0g, MgSO 4 7H 2 0 0.5 g, FeCl 3 6H 2 O 0.005 g, CaCO 3 0.01 g, Na 2 CO 3 3.18 g, NaHCO 3 5.88 g, 800 mL of distilled water; B...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: Pseudomonas MBR uses glucose as fuel to produce electricity under anoxic conditions
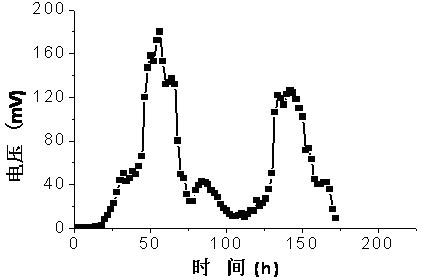
[0041] The experimental method and steps are basically the same as the operation of MFC1 in Example 1. The difference is that in this embodiment, the anode compartment of the microbial fuel cell MFC2 is aerated with air, so that the dissolved oxygen is maintained at 0.2~0.5 mg L -1 . Its electricity production curve is as image 3 As shown, the average cycle is about 10 days, and the COD removal rate of organic matter at the anode is 179 mg L -1 d -1 , the total removal rate was 81%.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Pseudomonas MBR uses glucose as fuel to produce electricity under anaerobic conditions
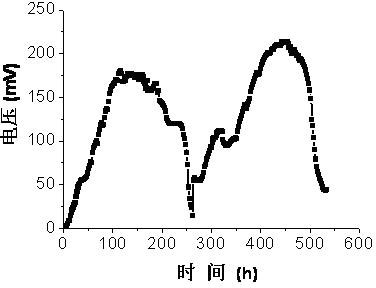
[0043] The experimental method and steps are basically the same as the operation of MFC1 in Example 1. The difference is that in this embodiment, when the microbial fuel cell MFC3 is started, the anode chamber is ventilated with nitrogen for 20 minutes to ensure anaerobic conditions. Its electricity production curve is as Figure 4 As shown, the average cycle is about 8 days, and the COD removal rate of organic matter at the anode is 272 mg L -1 d -1 , the total removal rate was 83%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com