Method for manufacturing substrate for electronic device, method for manufacturing electronic device, substrate for electronic device, and electronic device
A technology of electronic devices and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the field of improving the light extraction structure of optical devices, and can solve problems such as extraction, failure, and inability to extract emitted light
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
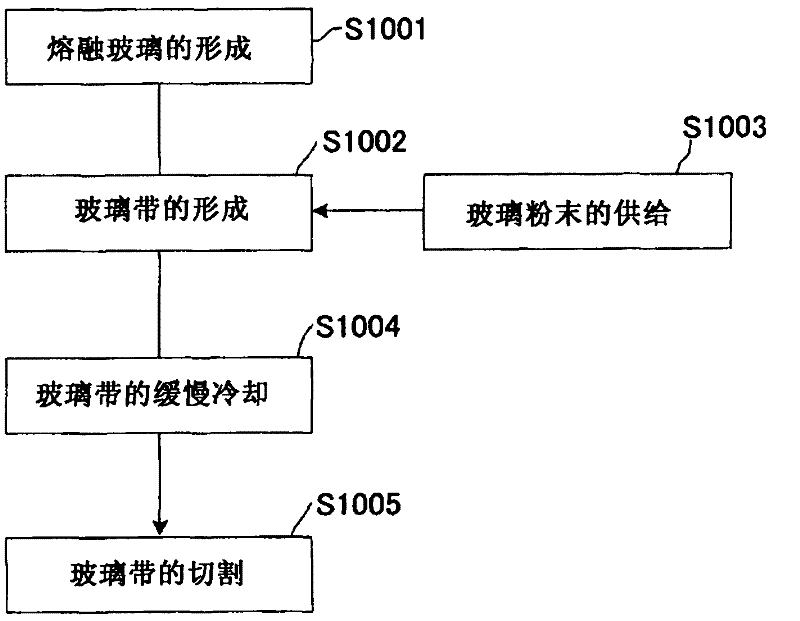
[0047] The manufacturing method of the electronic device substrate of the present invention, such as process flow figure 1 As shown, it is characterized in that it includes the following steps: a step of heating and melting glass raw materials or glass to produce molten glass (step S1001); continuously supplying molten glass to a bath of a molten metal bath (molten metal tank) containing molten metal surface to form a continuous glass ribbon forming process (step S1002); supply glass powder with a desired composition on the continuous glass ribbon, and form a scattering layer by melting the glass powder (step S1003); The process of slowly cooling the continuous glass ribbon with a scattering layer (step S1004); the process of cutting the slowly cooled continuous glass ribbon with a scattering layer to obtain a glass substrate with a scattering layer (step S1005).
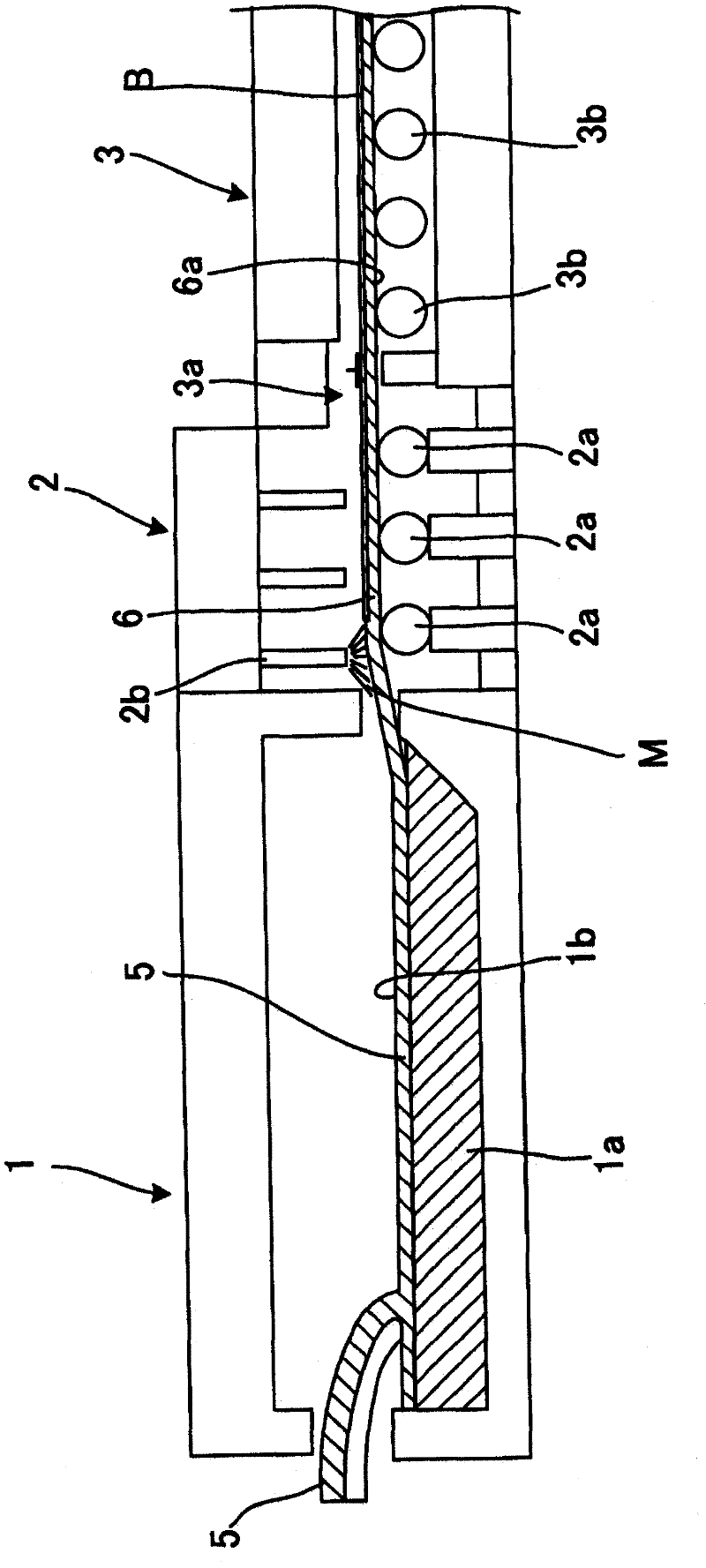
[0048] figure 2 It is a schematic cross-sectional view showing a part of the manufacturing equipment used in th...
no. 2 approach
[0088] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
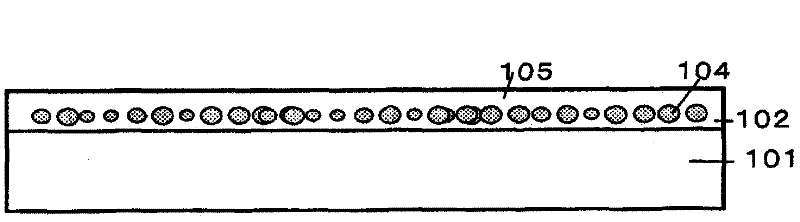
[0089] In addition, in the first embodiment, the glass layer as the scattering layer B is formed by spraying the suspension from the nozzle 2b at the entrance of the transport chamber 2 while forming the glass ribbon 6 as the substrate. In the second embodiment, as Figure 5 As shown in the enlarged view of the main part of the manufacturing device, it is characterized in that the scattering layer B is formed by directly spraying the glass powder onto the substrate (glass ribbon 6) by electrostatic powder spraying. This implementation uses roughly as figure 2 Shown is the same device as the device of Embodiment 1, but an electrostatic powder spraying device is provided on the back side of the glass ribbon (refer to figure 2 ), a scattering layer forming device is installed at the entrance of the slow cooling chamber 3, and nip portions (not shown) are provided at predetermined intervals instead ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com