Method for manufacturing semiconductor device structure
A device structure and semiconductor technology, applied in the fields of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, and electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of increased driving current of semiconductor device structures, lack of semiconductor devices, and large on-chip resistance, etc., to avoid Shadow effect, improved electrical performance, reduced drive current effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
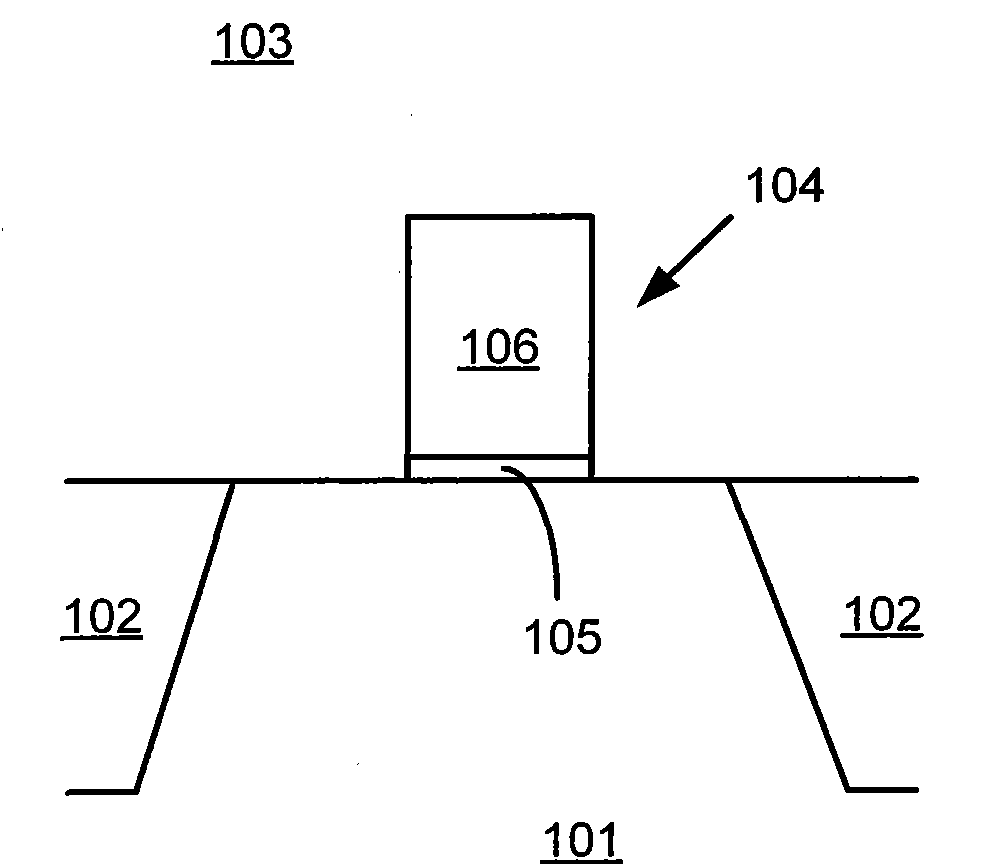
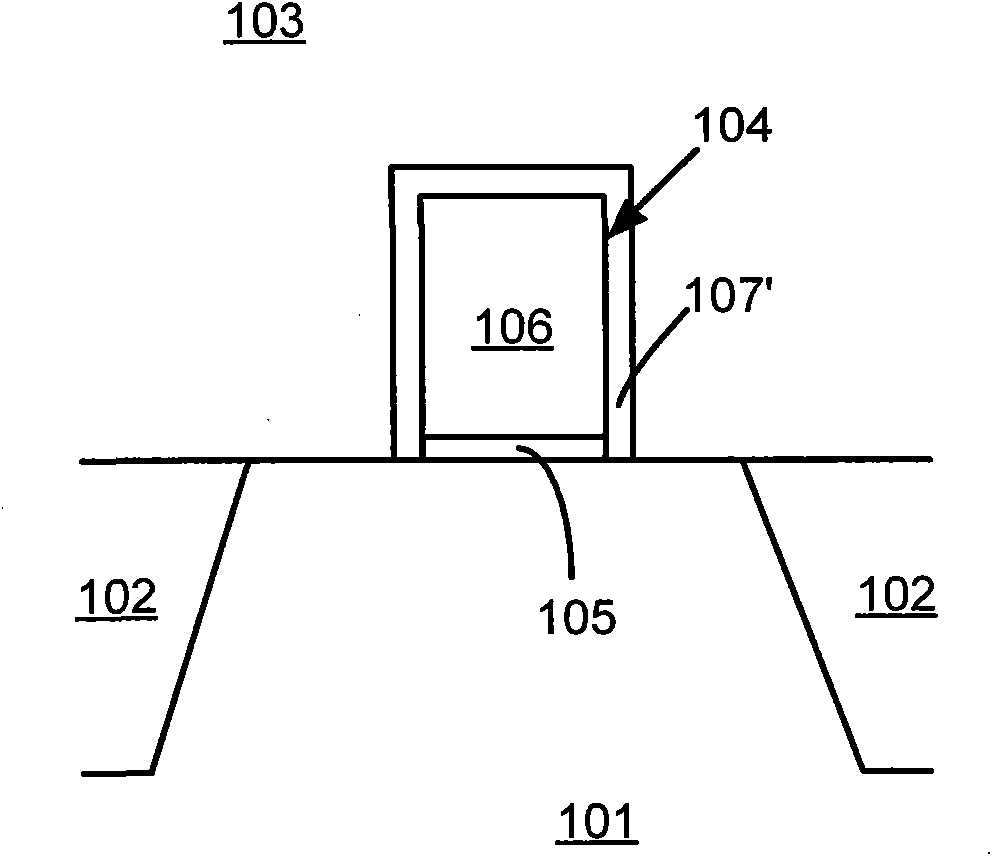
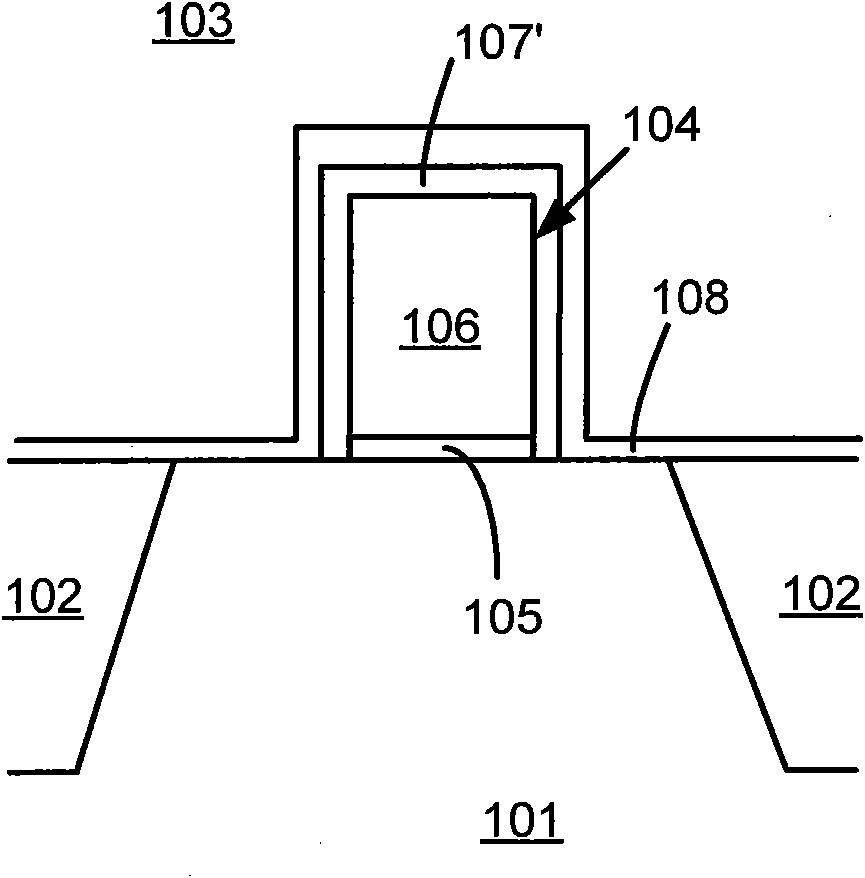
[0031] In the following description, numerous specific details are given in order to provide a more thorough understanding of the present invention. It will be apparent, however, to one skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without one or more of these details. In other examples, some technical features known in the art are not described in order to avoid confusion with the present invention.
[0032] In order to thoroughly understand the present invention, detailed steps will be presented in the following description, so as to explain how the present invention improves the process of fabricating semiconductor device structures to solve the problems in the prior art. Obviously, the practice of the invention is not limited to specific details familiar to those skilled in the semiconductor arts. Preferred embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, however, the present invention may have other embodiments besides these detailed d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com