Method for producing 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene by C9 aromatic hydrocarbon isomerization
A technology for the isomerization of trimethylene and aromatic hydrocarbons, which can be used in the fields of isomerization to produce hydrocarbons, organic chemistry, etc., and can solve the problem of high production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
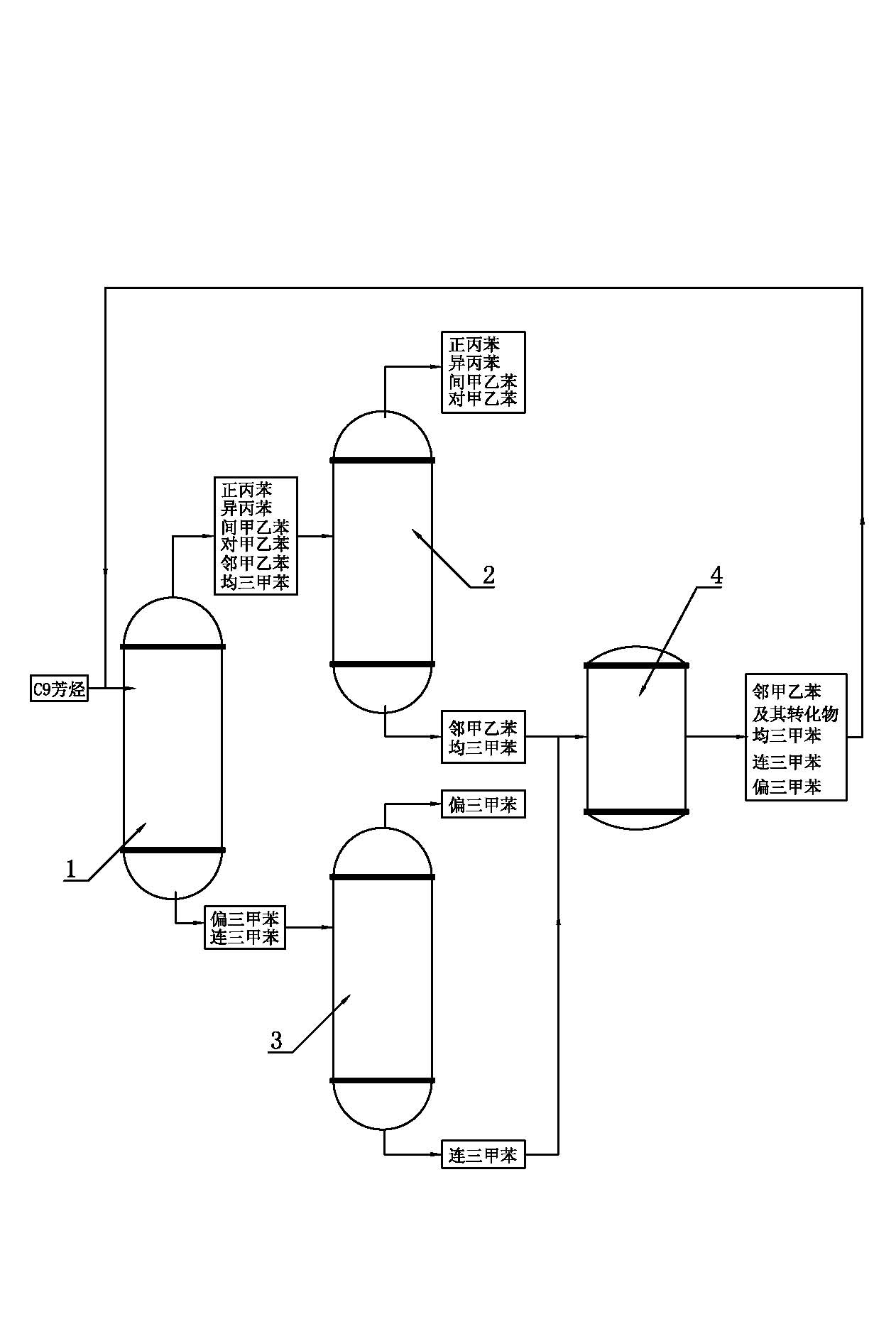
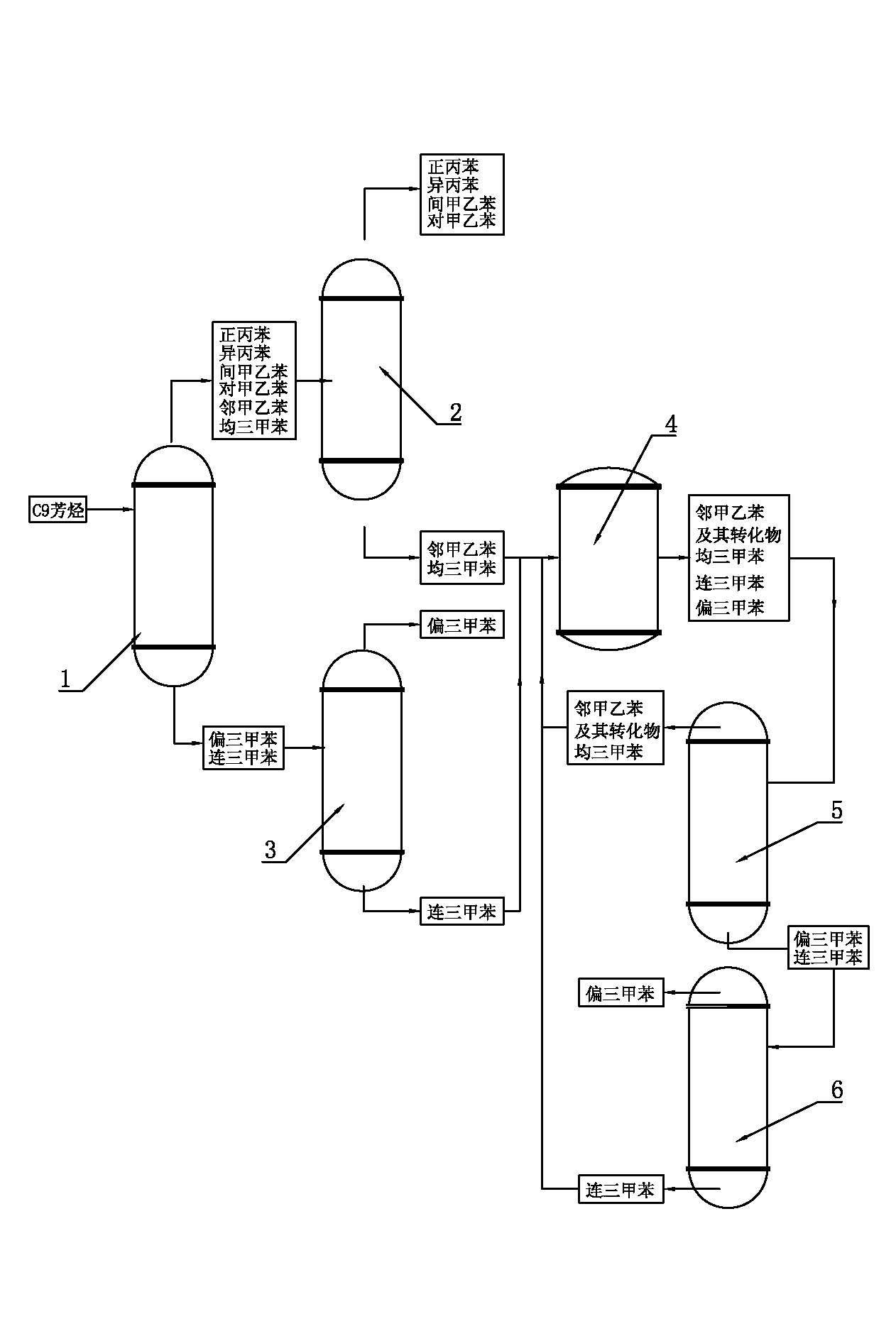
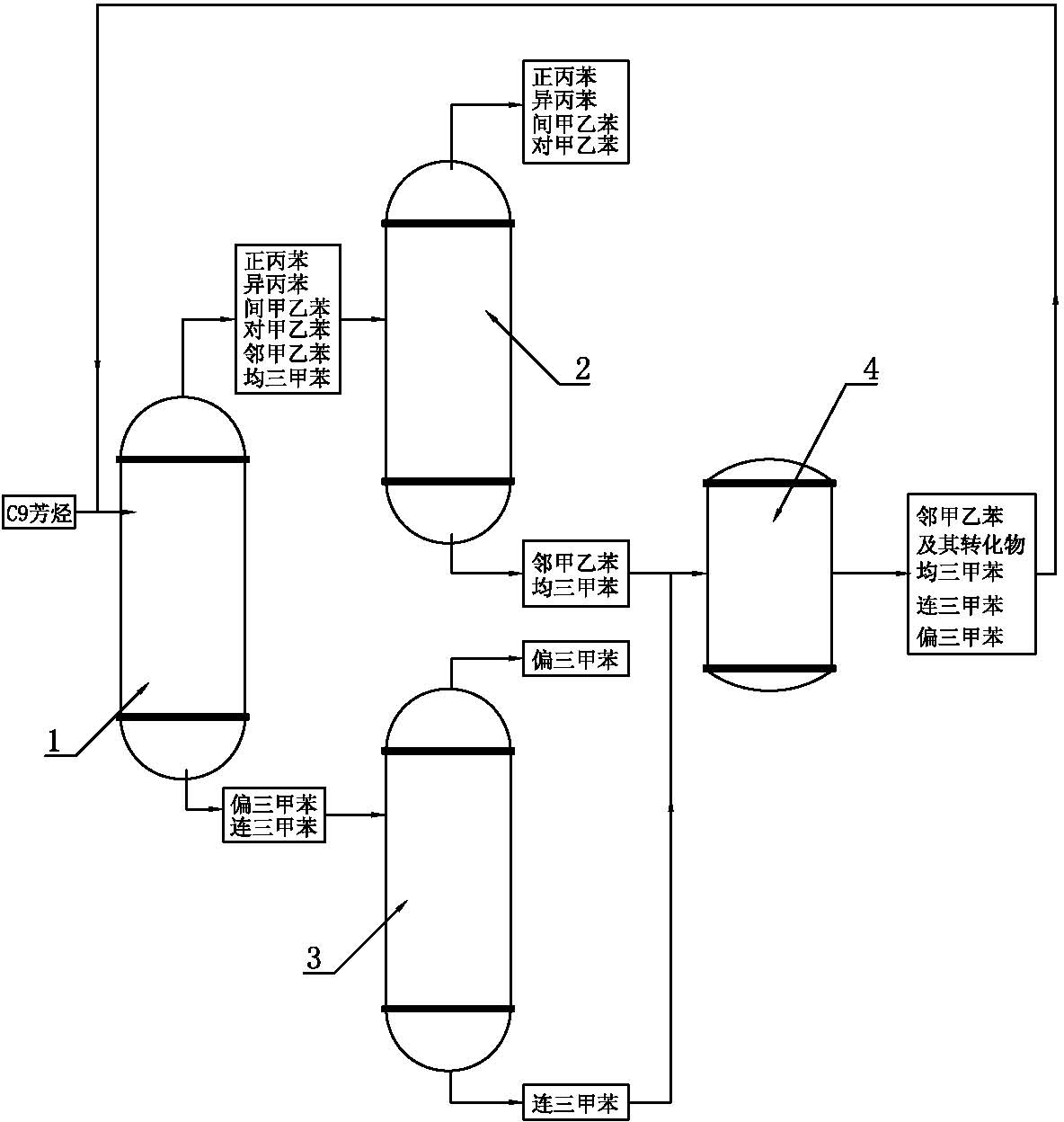
[0018] The method for producing trimethylbenzene by isomerization of C9 aromatic hydrocarbons, the steps are as follows:
[0019] 1) The C9 aromatics produced by petroleum cracking with a purity greater than or equal to 90% are delightened in the light removal tower 1, and the working temperature of the light removal tower 1 is controlled at 166°C~168°C (because it is difficult to control the temperature at a certain Therefore, it is appropriate as long as it fluctuates within a certain range, the same below), so that o-methylethylbenzene, m-methylethylbenzene, p-methylethylbenzene, mesitylene, and n-propyl ethylbenzene with a boiling point lower than 166°C After benzene and cumene are vaporized and leave the light removal tower 1 from the top of the tower, they enter the first rectification tower 2; the unisexylene and trimethylbenzene with a boiling point higher than 168°C retained at the bottom of the light removal tower 1 are sent to the second distillation tower. Second d...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The method for producing trimethylbenzene by isomerization of C9 aromatic hydrocarbons, the steps are as follows:
[0026] 1) The C9 aromatics produced by petroleum cracking with a purity greater than or equal to 90% are subjected to light removal treatment in the light removal tower 1, and the working temperature of the light removal tower 1 is controlled at 166°C~168°C (so that the adjacent boiling point is lower than 166°C) Methylbenzene, m-methylethylbenzene, p-methylethylbenzene, mesitylene, n-propylbenzene and isopropylbenzene are vaporized and leave the light removal tower 1 from the top of the tower, and then enter the first rectification tower 2; the bottom of the light removal tower 1 is retained Pyrylene and trimethylbenzene whose boiling point is higher than 168°C are transported to the second rectification tower 3;
[0027] 2) In the second rectification tower 3, the rectification temperature is 169.5°C to 175°C, and the trimethylbenzene leaves from the top...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The method for producing trimethylbenzene by isomerization of C9 aromatics, the steps are as follows:
[0033] 1) The C9 aromatics with a purity greater than or equal to 90% after extraction of mesitylene are subjected to light removal treatment in the light removal tower 1, and the working temperature of the light removal tower 1 is controlled at 166°C~168°C (so that the boiling point is lower than 166 The o-methylethylbenzene, m-methylethylbenzene, p-methylethylbenzene, mesitylene, n-propylbenzene and cumene at ℃ are vaporized and leave the light removal tower 1 from the top of the tower, and then enter the first rectification tower 2; Pyrylene and trimethylbenzene with a boiling point higher than 168°C retained at the bottom of the tower are sent to the second rectification tower 3;
[0034] 2) In the second rectification tower 3, the rectification temperature is 169.5°C to 175°C, and the trimethylbenzene leaves from the top of the second rectification tower 3 and is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com