Microstructure optical fiber with large mode area
A technology of micro-structured optical fiber and large mode field, which is applied in the direction of cladding optical fiber, multi-layer core/clad optical fiber, optical waveguide and light guide, etc., which can solve the problems of increased manufacturing difficulty, low bending loss, and complex structure, and achieve structural Effects of simplicity, low bending loss, and low binding loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
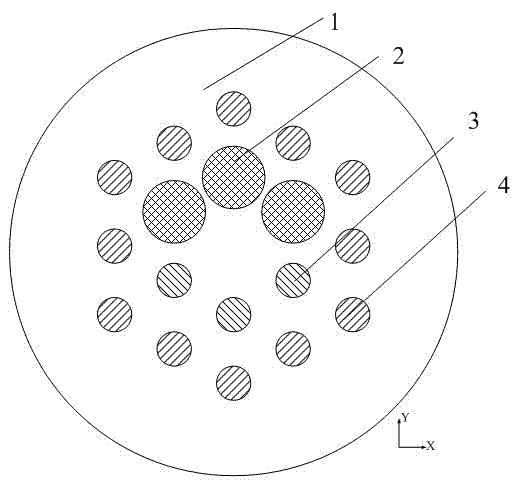
[0050] The cross-sectional structure of the optical fiber is as figure 1 shown. The matrix material is pure quartz, and the hole material is doped quartz material. The pore period Λ of the cladding is 46 μm, and the pore diameter d of the first type of pore 2 2 is 42 μm. Hole diameter d of the second type of hole 3 and the third type of hole 4 3 and d 3 Both are 23 μm. The first type of hole 2, the second type of hole 3 and the third type of hole 4 have the same refractive index, which is 0.004 lower than that of the matrix material. When the transmission wavelength is 1064 nm, the fundamental mode field area in the straight fiber is greater than 1800 μm 2 , when the bending radius is 20 cm, the mode field area of the fundamental mode reaches 1000 μm 2 -- above. When the bending radius of the optical fiber reaches 5 cm, the fundamental mode loss is still less than 0.01 dB / m. When the fiber is straight, its fundamental mode leakage loss is less than 0.01 dB / m, and i...
Embodiment 2
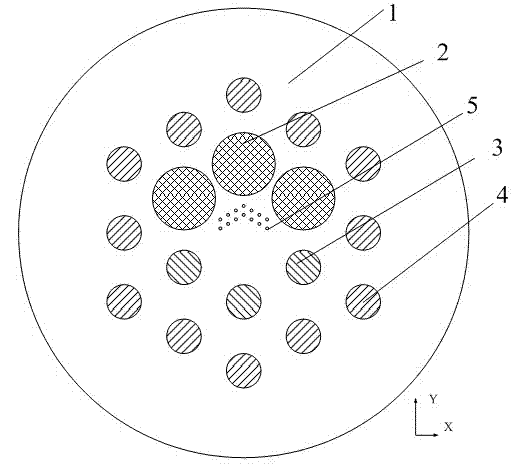
[0052] The cross-sectional structure of the optical fiber is as figure 2 shown. The matrix material is pure quartz, and the hole material is doped quartz material. The period Λ of the cladding pores is 46 μm, and the pore diameter d of the first type of pores 2 2 is 42 μm. Hole diameter d of the second type of hole 3 and the third type of hole 4 3 and d 4 Both are 23 μm, and the refractive index of the first type of hole 2, the second type of hole 3 and the third type of hole 4 is the same, which is 0.004 lower than that of the matrix material. Period Λ of the fourth type of hole 5 5 6 μm, hole diameter d 5 At 2 μm, the refractive index of the hole is 0.001 lower than that of the matrix material. When the transmission wavelength is 1064 nm, the fundamental mode field area of the straight fiber can reach 1600 μm 2 above; when the fiber bending radius is 50 cm, the mode field area of the fundamental mode is greater than 1500 μm 2 ; When the fiber bending radius is ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The cross-sectional structure of the optical fiber is as figure 2 shown. The matrix material is pure quartz, and the hole material is doped quartz material. The period Λ of the cladding pores is 46 μm, and the pore diameter d of the first type of pores 2 2 is 42 μm. Hole diameter d of the second type of hole 3 and the third type of hole 4 3 and d 4 They are 28 μm and 23 μm respectively, and the refractive index of the first type of hole 2 , the second type of hole 3 and the third type of hole 4 is the same, which is 0.004 lower than that of the matrix material 1 . Period Λ of the fourth type of hole 5 5 6 μm, hole diameter d 5 At 2 μm, the refractive index of the hole is 0.002 lower than that of the matrix material. When the transmission wavelength is 1064 nm, the fundamental mode field area in straight fiber can reach 1200 μm 2 above. When the fiber bending radius is 15 cm, the mode field area of the fundamental mode is still 1200 μm 2 above. When the fib...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com