CdTe battery transition layer and preparation method thereof and CdTe battery
A transition layer and battery technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve the problems of rapid battery performance decay, unsuitability for large-scale industrial production, and complex transition layer preparation, so as to achieve stable battery performance and easy condition parameters The effect of simple control and preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
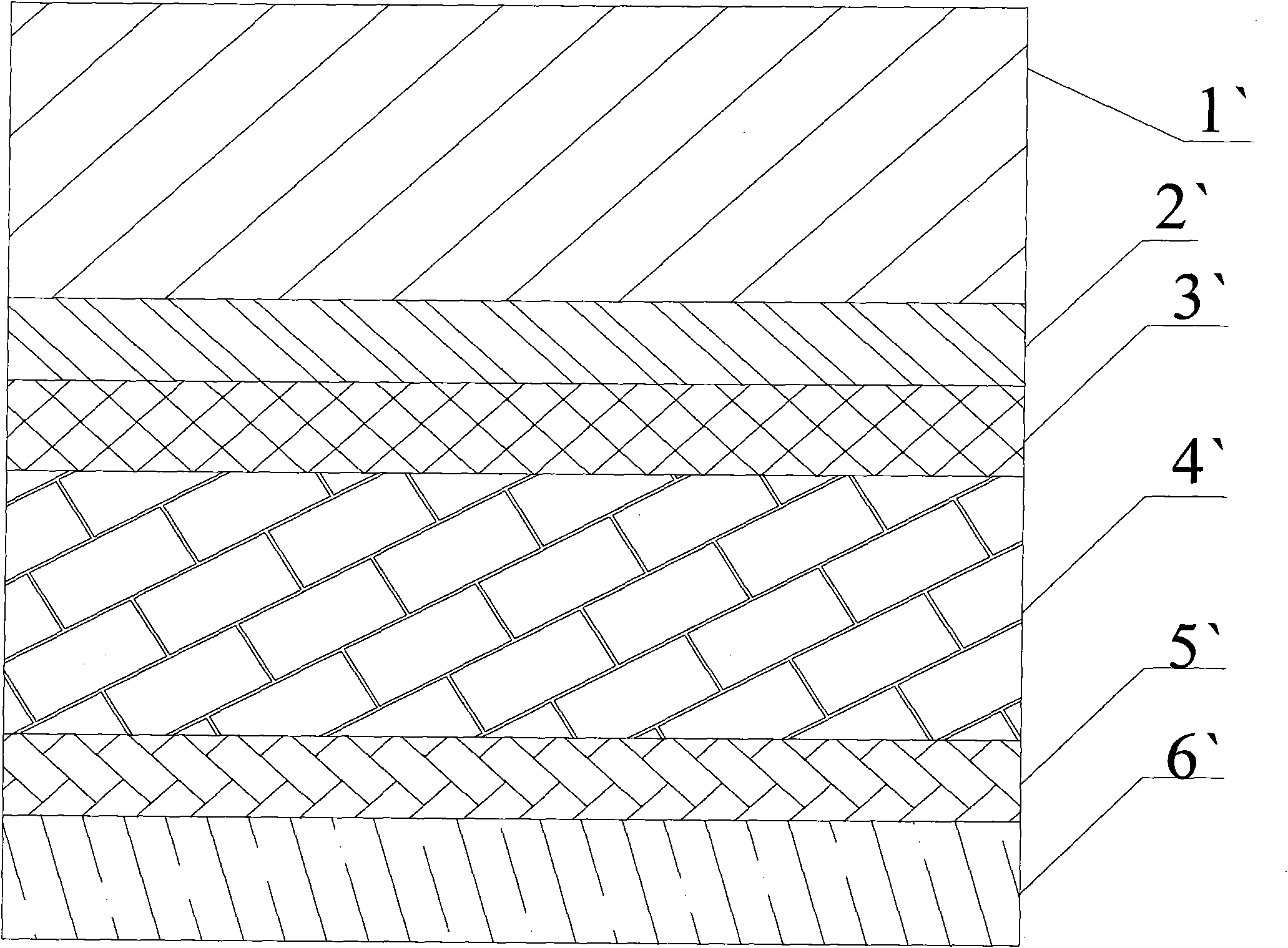
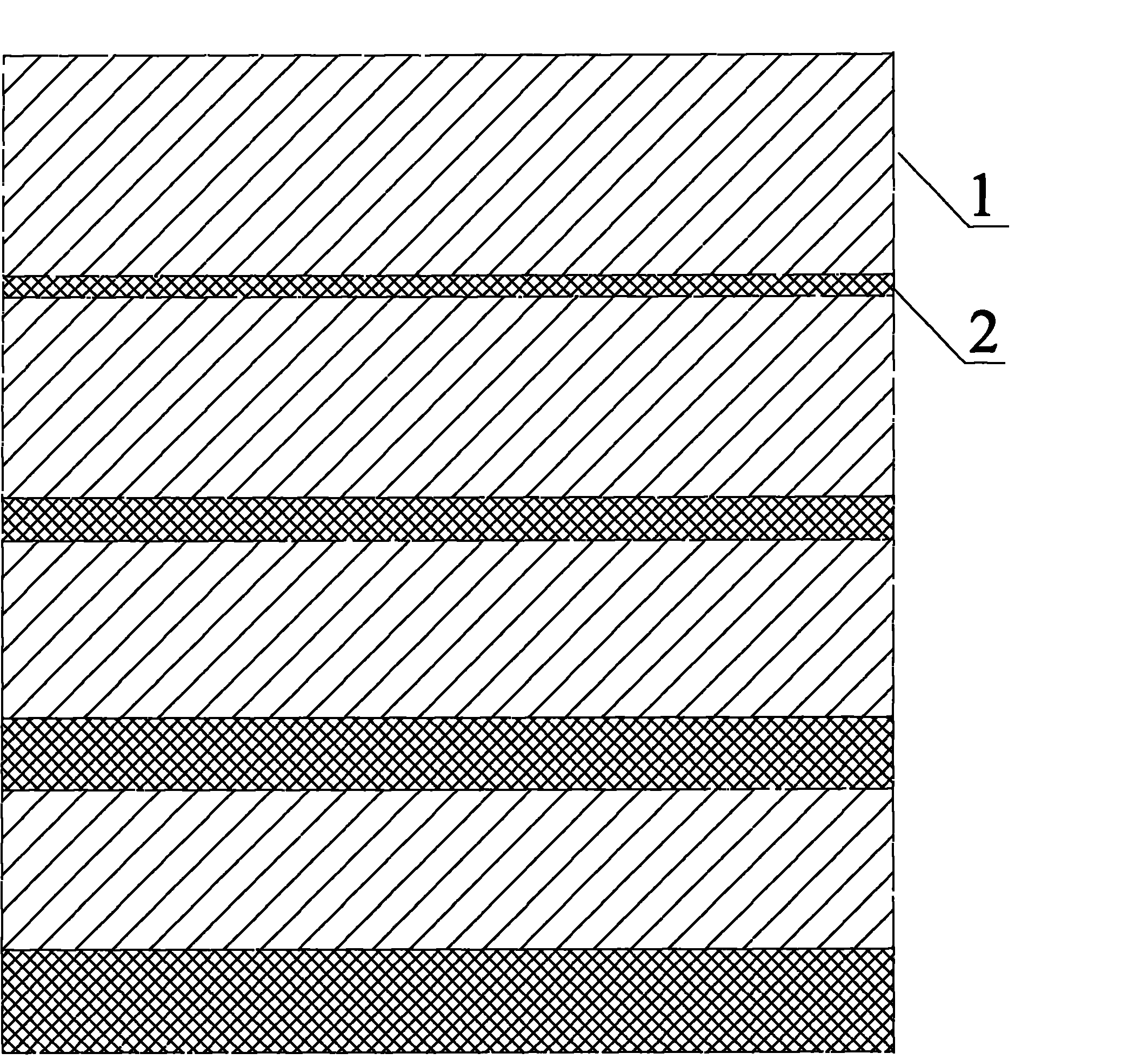
[0028] A preparation method for a transition layer of a CdTe battery, which comprises: first depositing a layer of ZnTe on the CdTe layer, and then alternately depositing a Cu layer and a ZnTe layer; In the range of ~40nm, the total thickness of the deposit is 25~120nm.
[0029] Wherein, the deposition can be realized by sputtering, electron beam evaporation and vapor deposition which are commonly used in the art.
[0030] The method of the present invention adopts single-source deposition, and the equipment is simple and the cost is cheap. At the same time, the atomic ratio of the product can be controlled by the thickness of the deposited film, which is relatively stable. The Cu layer is located behind the ZnTe film layer. By controlling the thickness of the ZnTe film layer, the diffusion depth of Cu can be controlled, so that it is not easy to diffuse into other film layers to form a wedge-shaped copper-doped transition. layer, which is beneficial to improve the short-circ...
Embodiment 1
[0041] A CdTe solar cell, which includes a glass substrate, a transparent conductive layer, a CdS layer, a CdTe layer, a transition layer and a back electrode layer stacked in sequence;
[0042] The glass substrate is ultra-white glass with a thickness of 2mm; the transparent conductive layer is FTO with a thickness of 1um; the purity of the CdS layer is 5N and the thickness is 200nm; the purity of the CdTe layer is 5N and the thickness is 5um.
[0043] The transition layer is to deposit a 30nm ZnTe layer, a 4nm Cu layer, a 25nm ZnTe layer, and a 5nm Cu layer sequentially on the CdTe layer.
[0044] The back electrode layer is a Ni layer with a thickness of 200nm.
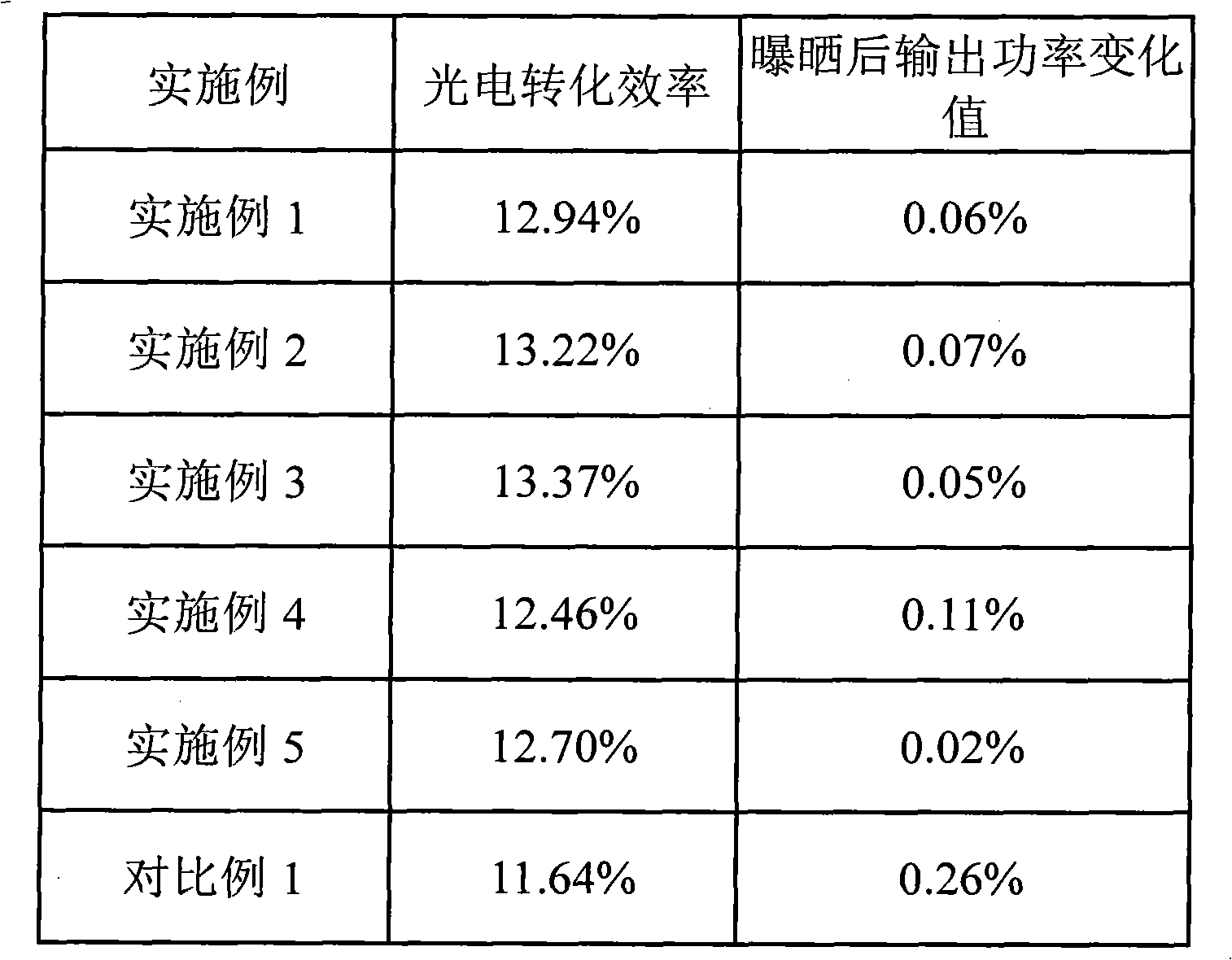
[0045] The battery is denoted as A1.
Embodiment 2
[0047] The difference from Example 1 is that the transition layer is sequentially deposited on the CdTe layer with a 25nm ZnTe layer, a 3nm Cu layer, a 20nm ZnTe layer, a 4nm Cu layer, a 15nm ZnTe layer, and a 5nm Cu layer.
[0048] Other parts are with embodiment 1.
[0049] The battery is denoted as A2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Total thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com