Microspheric precious metal adsorbent and preparation method thereof
A precious metal and adsorbent technology, applied in the field of adsorption, can solve the problems of small adsorption capacity of precious metals, inconvenient use and regeneration, unfavorable use and regeneration, etc., and achieve strong practical use value, excellent adsorption performance, and excellent adsorption performance of precious metals.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
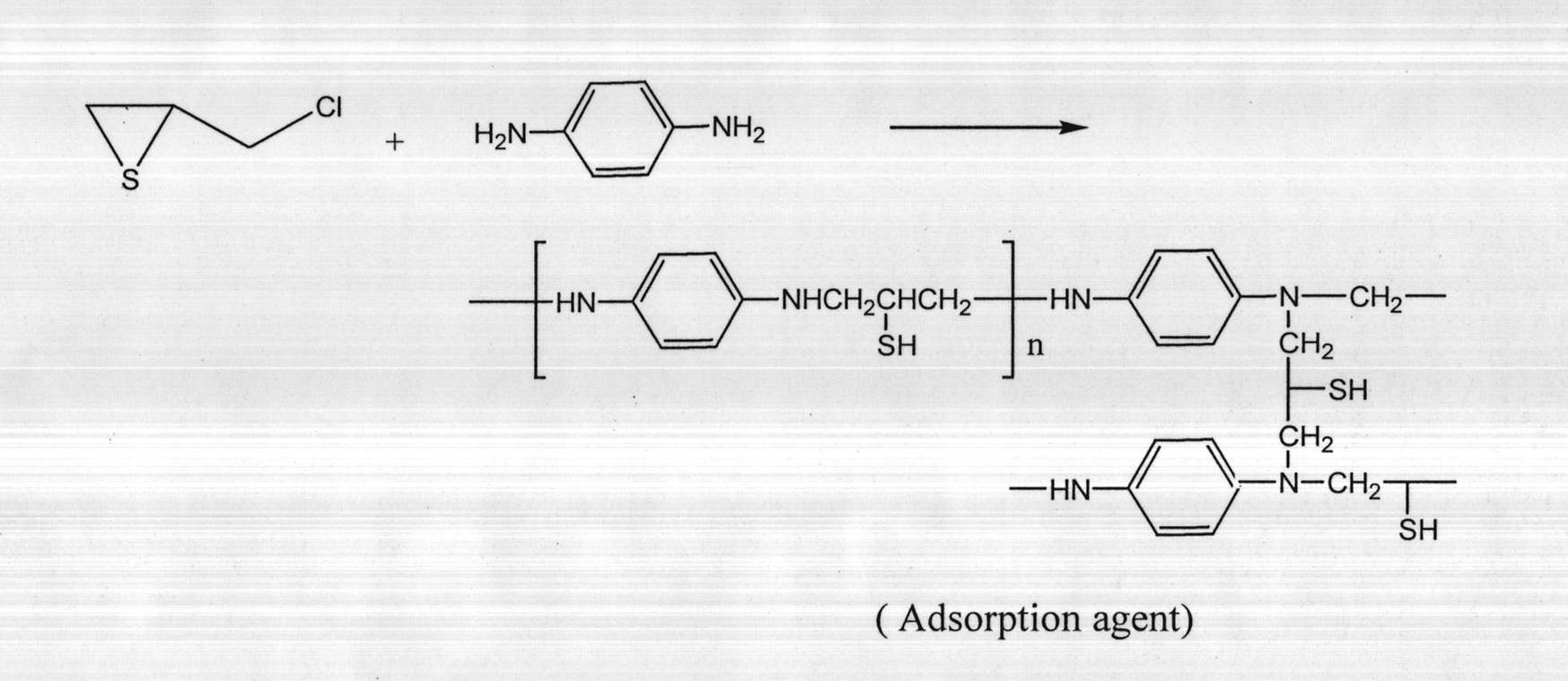
[0018] Put 80ml of distilled water, 4.0g (0.037mol) of p-phenylenediamine, and 2.0g of sodium chloride together into a 250ml reaction flask, stir magnetically for 24 hours, then add 20ml of polyvinyl alcohol solution (20g / L), press thiochloride The molar ratios of propane and p-phenylenediamine are: 1:2, 1:1, 2:1 Add epithichloropropane, mechanically stir together at 25°C, heat up to 70°C after 40min, and stop the reaction after 6h.
[0019] The prepared adsorbent is soaked in acidic and alkaline solutions in sequence, extracted with acetone for 24 hours, washed with water and ethanol in sequence, and dried in vacuum at constant temperature to obtain a microspherical shape. The resulting product numbers are PAC1, PAC2, and PAC3 in sequence.
[0020] Table 1 The content of each element of the microspherical adsorbent
[0021]
[0022] Use a digital camera to take pictures of the appearance of PAC2, see the results figure 1 . Microspheres with uniform particles and regular...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Accurately weigh 0.100 g of the microspherical adsorbent prepared in Example 1, place it in a 100 ml conical flask with a stopper, add a certain concentration of metal ion solution, and vibrate in a constant temperature oscillator for 24 hours (use black to absorb Ag(Ⅰ). wrap the bottle with paper to avoid light), use an atomic absorption meter to measure the concentration of metal ions in the solution before and after adsorption, and calculate the adsorption capacity according to the following formula:
[0026] Q=(C 0 -C)V / W
[0027] Where Q is the adsorption capacity (mmol / g), C 0 is the concentration (mol / L) of metal ions before adsorption, C is the concentration (mol / L) of metal ions after adsorption, W is the dry weight of chelating agent (g), and V is the solution volume (ml).
[0028] The adsorption capacity of table 2 microsphere type adsorbent (mmol / g)
[0029]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com