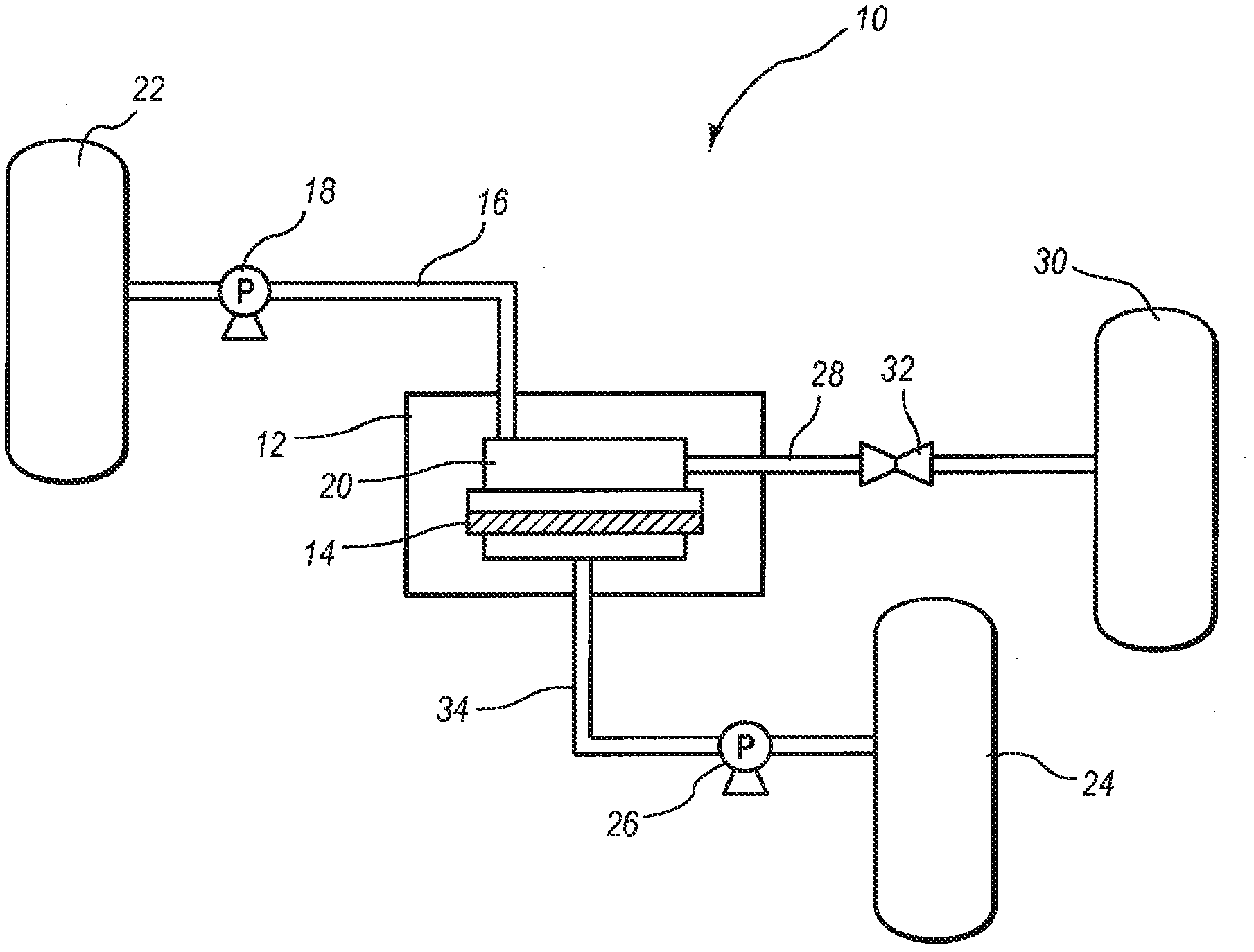
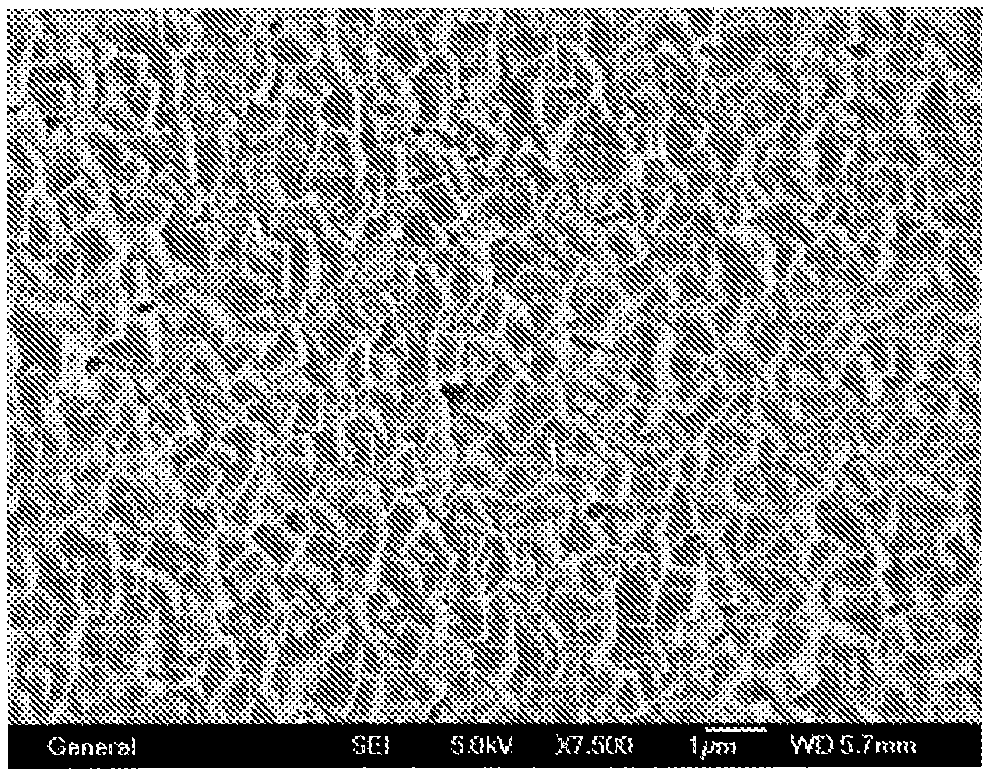
Zeolite membrane and methods of making and using same for water desalination
一种沸石膜、水脱盐的技术,应用在化学仪器和方法、膜、膜技术等方向,能够解决成本高等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1: Manufacture of silicalite-1 film
[0058] Example 1 describes a method of making a silicalite zeolite membrane suitable for water desalination. To 8 ml TEOS was added TPAOH solution (16 g; 15.4%) in a Teflon-lined autoclave at 140°C. After 24 hours, MFI (silicalite) nano-seeds with a size of 150 nm were obtained. By mixing seed particles with water and using NH 3 Aqueous solution The pH of the solution was adjusted to 10 to prepare a suspension (20 g / L) of zeolite seed particles. Adjusting the pH to 10 helps prevent seed particles from clumping together in suspension.
[0059] A coarse glass frit with a pore size of 20 μm was used as a support and washed 5 times with deionized water under ultrasonic oscillation and dried at 85 °C. The frit is then wetted and then immediately coated with the seed suspension by dropwise addition. Only a small amount of seed suspension is required, and the aqueous layer evaporates quickly to leave only a seed deposit on the...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2: Water Desalination Using Membranes
[0062] Example 2 describes a method of using the membrane of Example 1 for seawater desalination using reverse osmosis. A number of membranes fabricated according to the method of Example 1 were tested using reverse osmosis. The reverse osmosis experiments were performed at room temperature and standard atmospheric pressure. Preparation containing 3.5% NaCl, KCl, CaCl 2 , MgCl 2 The solution. The filtrate was analyzed by ICP for ion content. Measure the amount of permeate by weighing the liquid nitrogen cold trap before and after infiltration. Each separation experiment was performed for about 7-8 hours. After the separation experiment, the membrane was washed with distilled water and dried for the next experiment. Separation characteristics can be defined in terms of flux and cation rejection as follows: flux = P / (S x T), cation rejection (R) = (C 进料 -C 渗透物 ) / C 进料 , where P represents the amount of permeate (Kg)...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Using membranes to treat simulated seawater
[0066] Example 3 describes a method of using the membrane of Example 1 for seawater desalination using reverse osmosis. Example 3 was carried out under the same conditions as in Example 2, except that different salt concentrations were used in the feed. Specifically, the salt concentration in the feed of Example 3 mimics naturally occurring seawater. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0067] Table 2
[0068] ion type
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com