Wireless equipment and packet scheduling method thereof, and transmission method of wireless system
A wireless device and transmission method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as performance bottlenecks, difficult to accurately predict, delay and jitter requirements, etc., to achieve good data packet delay performance, suppress delay inconsistency, and good scalability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
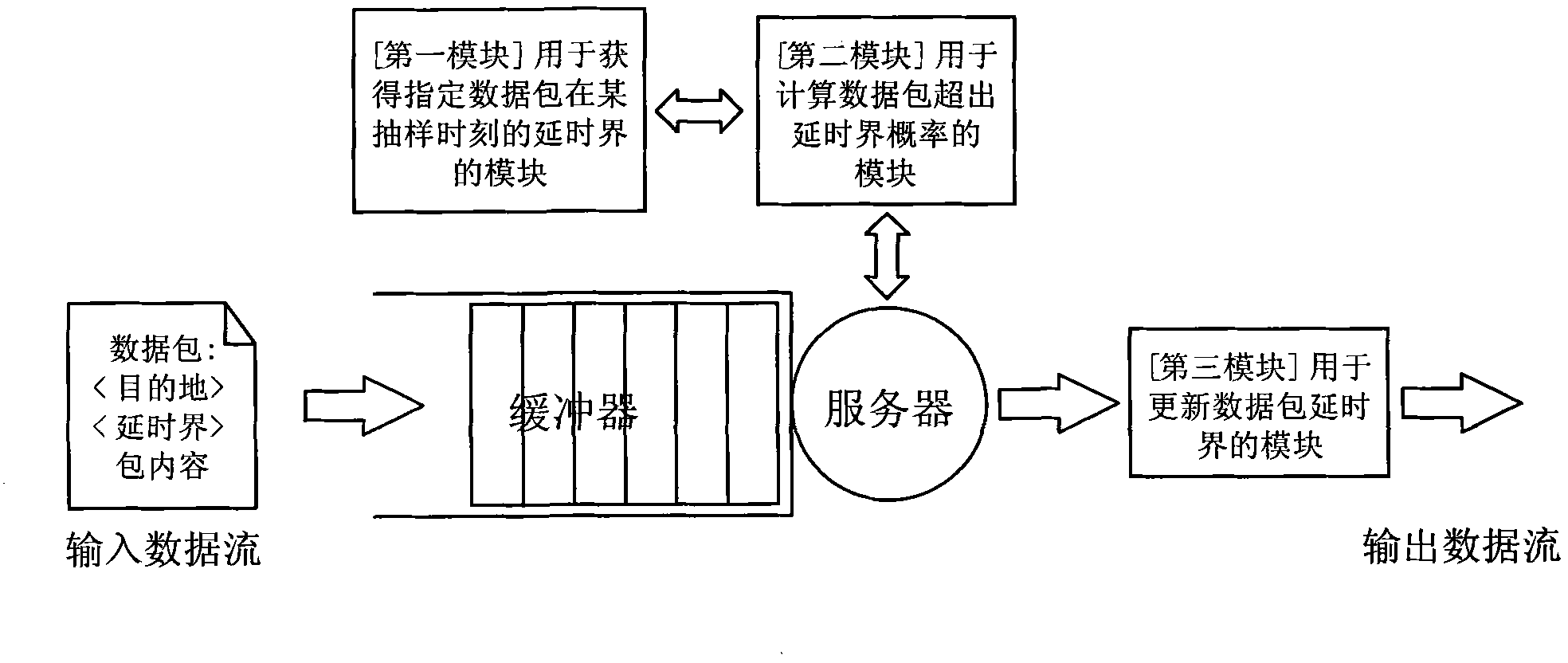
[0042] This embodiment provides a data packet scheduling method, and the details of the method are as follows:
[0043] [The concept of "delay circle"]
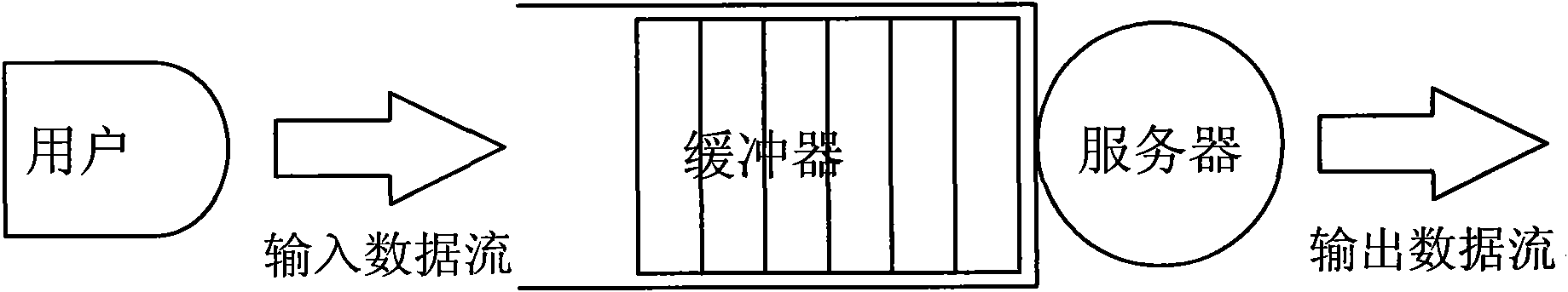
[0044] The packet delay bound (Packet Delay Bound, PDB) refers to the upper limit of the delay allowed by the data packet, which is determined by the "initial delay bound" of the data packet and the "experienced delay" of the data packet , whose mathematical expression is
[0045] Delay bound = initial delay bound - experienced delay (1)
[0046] When the "experienced delay" of a data packet exceeds its "initial delay bound", this data packet becomes an expired data packet. Different application services have different processing methods for expired data packets. In the system, it is assumed that before the data packet enters the queuing system, the data packet will carry the information of the destination and the delay boundary, and after the data packet enters the queuing system, the delay boundary information carried by ...
Embodiment 2
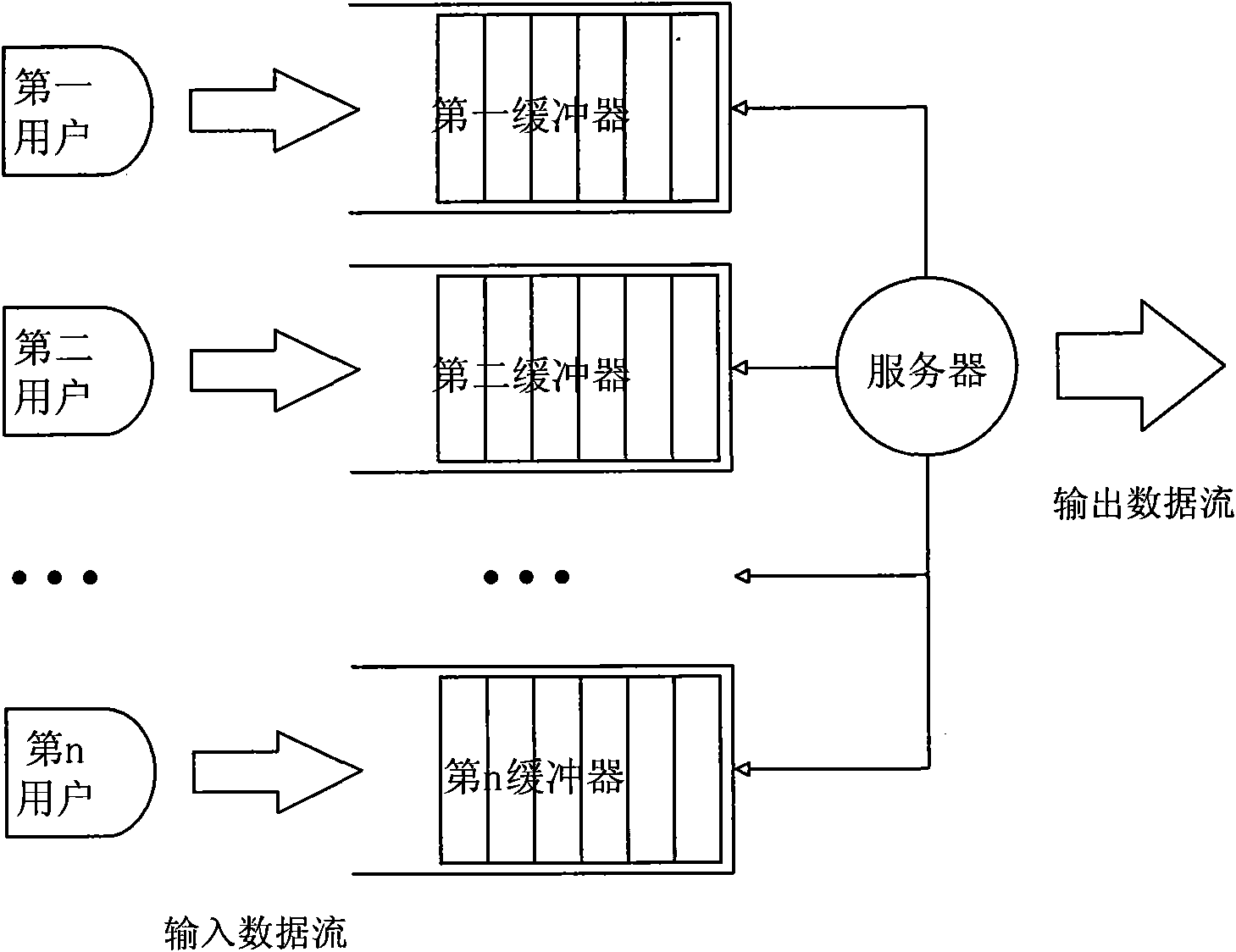
[0059] This embodiment provides a wireless device capable of implementing the data packet scheduling method described in Embodiment 1.
[0060] This embodiment works in a wireless system where wireless devices can communicate with each other. Here, mutual communication means that the wireless devices in this wireless system need to know the addresses and routing paths of other wireless devices, that is, each wireless device Each maintains a routing table (the routing table may be manually fixed, or may be regularly updated by other methods such as Routing Information Protocol). Such as Figure 4 As shown, wireless devices 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 together form such a wireless system, and at the moment, wireless device 2 maintains a routing table as shown below.
[0061] Table 1: Routing Table for Wireless Device 2
[0062] destination
routing path
[0063] wireless device 1
wireless device 1
wireless device 2
local
wireless dev...
Embodiment 3
[0087] This embodiment proposes a transmission method for a wireless system. By making corresponding amendments to Table 2, it is possible to reduce the computational complexity of scheduling without any loss in scheduling performance, and to prioritize scheduling with the shortest deadline. The modified table As shown in Table 4. Packets are first classified according to destination. For data packets going to the same destination, the priority of the data packets can be sorted according to the delay bound (not the probability of exceeding the delay bound); for data packets destined for different destinations, the server defines according to the probability of exceeding the delay bound its priority. In other words, when there are 5 data packets shown in Table 4 in the buffer, the server does not need to calculate the probability of exceeding the delay bound of these 5 data packets one by one, but only needs to calculate data packet 1 (because it is going to the wireless The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com