Method and culture medium for enhanced detection of mycobacterium
A technology of mycobacteria and culture medium, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of slow growth rate, hindering the detection of mycobacteria, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
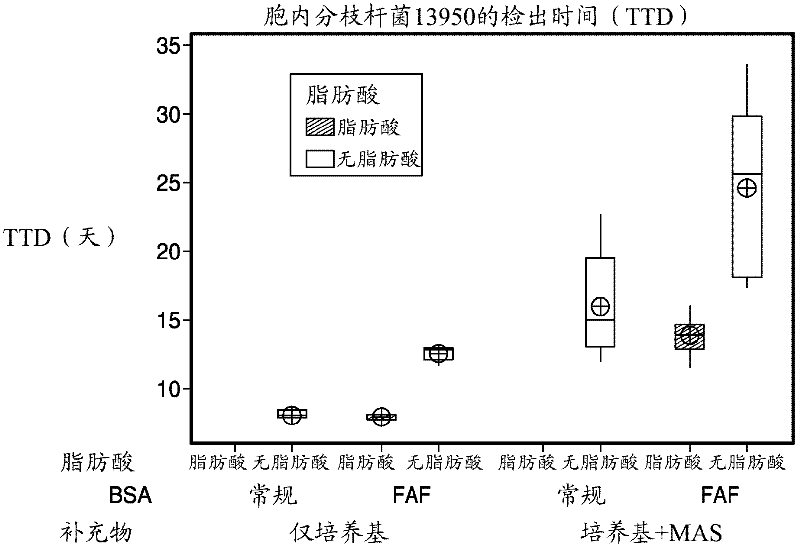
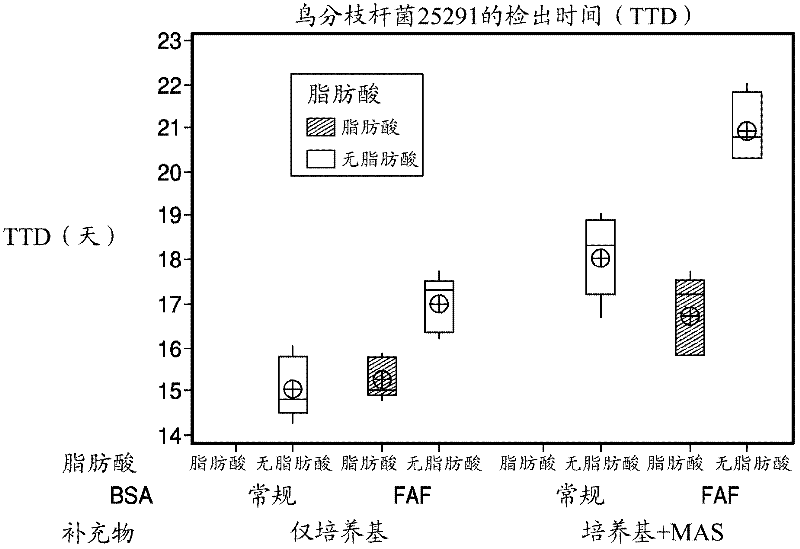
[0084] Example 1. TTD of different mycobacterial strains with and without fatty acid supplementation
[0085] To assess the effect of long-chain fatty acids (FA) on mycobacterial growth, fatty acid-free (FAF) BSA from Proliant, Inc. (Ames, Iowa) was selected. Based on fatty acid profile and growth performance, five long-chain fatty acids: myristic acid (C14:0), palmitic acid (C16:0), stearic acid (C18:0), oleic acid (C18:1) and linoleic acid (C18:2) was identified as a possible fatty acid supplement. Novel supplement formulations with FAF BSA were prepared and tested with and without 5 fatty acids (see Table 1 for novel supplement formulations). Target levels of fatty acid supplementation were based on fatty acid content obtained from previous assessments. The concentration of FAF BSA used was 10 g / L. Loss of fatty acids during filtration of the novel supplement was determined by fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) analysis. The recovery of fatty acids was observed to be >80% a...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2. TTD of mycobacterial strains with and without α-ketoglutarate
[0098] To further improve the TTD of mycobacteria, the CO-producing pathway in mycobacterial cells was selected 2 Substrates and / or cofactors of enzymes including α-ketoglutarate, isocitrate, L-malate, oxaloacetic acid, lactate ) and L-arginine. Novel supplements with fatty acids were prepared and filter sterilized as described above. The substrates were added to the novel supplements at different concentrations.
[0099] Inspection 0.5×10 3 4 species of mycobacteria in CFU / ml. The effect of different concentrations of α-ketoglutarate on the growth (ie TTD of growth) of M. avium, M. intracellulare and M. tuberculosis cultures was studied. Using the new autoclavable BacT / ALERT MP flasks (as described above). 0.5 ml of the novel supplement with varying amounts of α-ketoglutarate was added to the novel BacT / ALERT before inoculating the MP flask with the mycobacterial culture MP culture flas...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Example 3. TTD of Mycobacterium species with conventional MAS
[0105] Through studies including polymyxin B (POLY B), amphotericin B (AMP B), nalidixic acid (NA), trimethoprim (TMP), azlocillin (AZL) and vancomycin (VAN ) of the 6 drugs determined the effectiveness of conventional MAS against mycobacterial growth. These studies were also performed to identify drugs and their concentrations that have adverse effects on mycobacterial growth.
[0106] For growth performance, conventional / old RFs were prepared and 6 antimicrobial agents were added at different concentrations. The selected concentration is a level 25-50% lower or higher than the concentration of conventional MAS, which is polymyxin B (POLY B) at 1000 units / ml, amphotericin B at 180 μg / ml ( AMP B), nalidixic acid (NA) at 400 μg / ml, trimethoprim (TMP) at 10.5 μg / ml, azlocillin (AZL) at 34 μg / ml, and vancomycin (VAN) at 5 μg / ml .
[0107] Growth of M. intracellulare, M. kansasii, M. scrofula, and M. tuberc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com