Photovoltaic millimeter wave power synthesis circuit
A power synthesizing circuit, a technology of optically generating millimeter waves, applied in the directions of power amplifiers, high-frequency amplifiers, etc., can solve the problems of inability to increase the cut-off frequency of photodetectors, limit the response speed of photodetectors, system linearity and high cost, and improve the Power synthesis efficiency, improving circuit standing wave ratio, satisfying the effect of high power and large bandwidth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
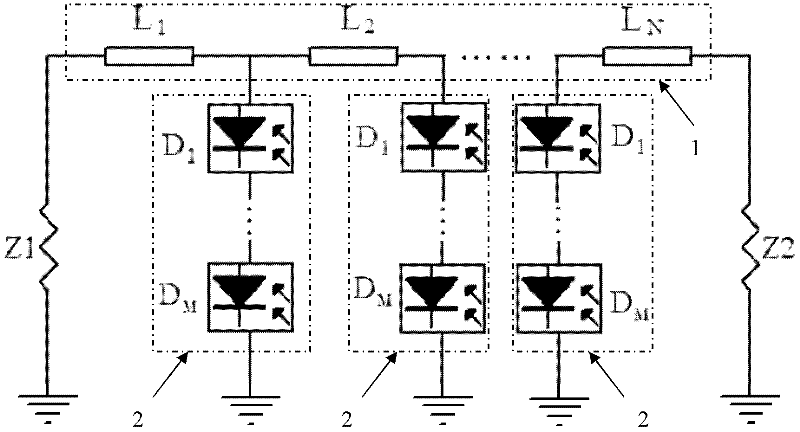
[0030] Embodiment one: if figure 2 As shown, an optically-generated millimeter-wave power synthesis circuit includes a first load Z1, a second load Z2 and a microstrip line group 1. The microstrip line group 1 is composed of N sections of microstrip lines in series. The microstrip line group 1 One end of the first load Z1 is connected to one end of the first load Z1, the other end of the microstrip line group 1 is connected to one end of the second load Z2, the other end of the first load Z1 and the other end of the second load Z2 are grounded, and the microstrip line group 1 A photoelectric conversion module 2 is connected to the common connection end of each adjacent two sections of microstrip lines, and each photoelectric conversion module 2 is grounded. The photoelectric conversion module 2 is formed by serially connecting M photoelectric conversion units. The photoelectric conversion unit is one A photodiode, the cathodes and anodes of M photoelectric conversion units ar...
Embodiment 2
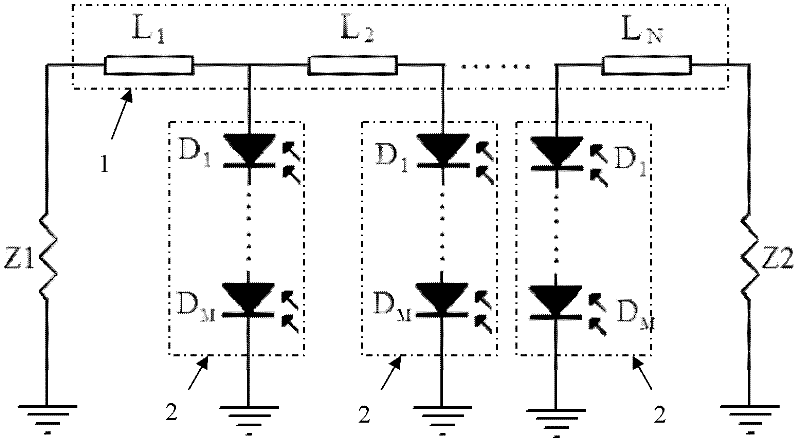
[0031] Embodiment two: if image 3 As shown, an optically-generated millimeter-wave power synthesis circuit includes a first load Z1, a second load Z2 and a microstrip line group 1. The microstrip line group 1 is composed of three sections of microstrip lines in series. One end of the first load Z1 is connected to one end of the first load Z1, the other end of the microstrip line group 1 is connected to one end of the second load Z2, the other end of the first load Z1 and the other end of the second load Z2 are grounded, and the microstrip line group 1 A photoelectric conversion module 2 is connected to the common connection end of each adjacent two sections of microstrip lines, and each photoelectric conversion module 2 is grounded. The photoelectric conversion module 2 is composed of two photoelectric conversion units in series, and the photoelectric conversion unit is Photodiodes, the cathodes and anodes of the two photoelectric conversion units are connected in series, and...
Embodiment 3
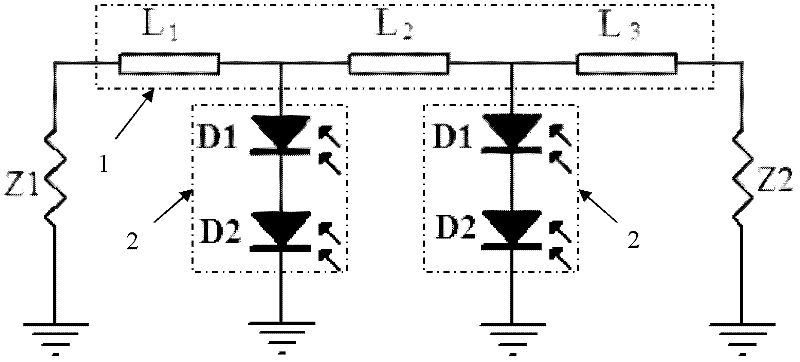
[0033] Embodiment three: as Figure 6As shown, an optical-generated millimeter-wave power synthesis circuit includes a first load Z1, a second load Z2 and a microstrip line group 1. The microstrip line group 1 is composed of four sections of microstrip lines in series. One end of the first load Z1 is connected to one end of the first load Z1, the other end of the microstrip line group 1 is connected to one end of the second load Z2, the other end of the first load Z1 and the other end of the second load Z2 are grounded, and the microstrip line group 1 A photoelectric conversion module 2 is connected to the common connection ends of every two adjacent microstrip lines, and each photoelectric conversion module 2 is grounded. Photodiode, the cathode and anode of the two photoelectric conversion units are connected in series, the first photoelectric conversion unit D in the photoelectric conversion module 2 1 The anode of the anode is connected to the microstrip line group 1, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com