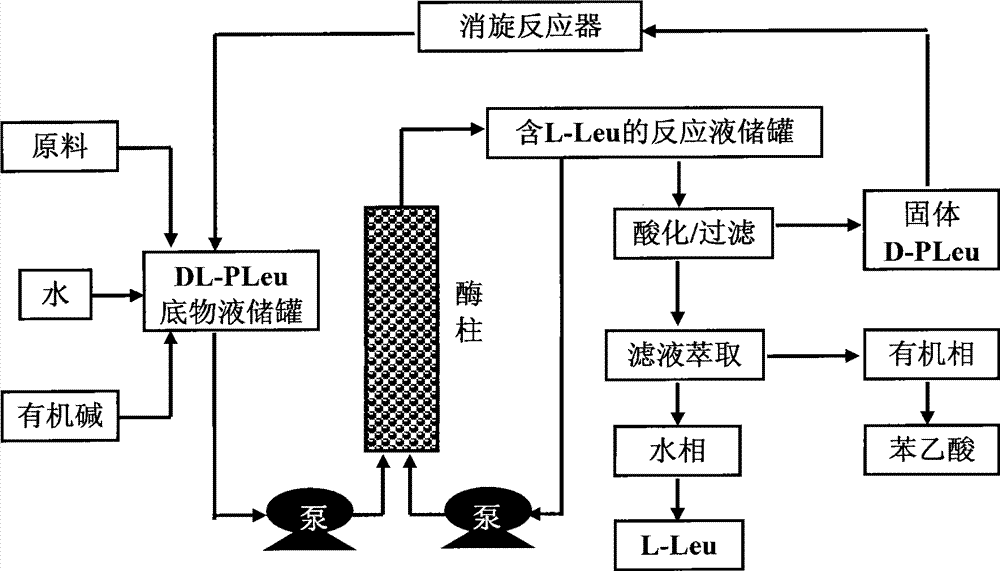
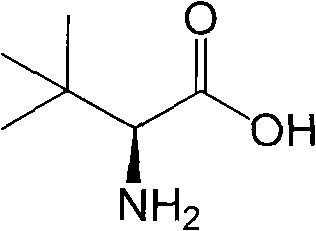
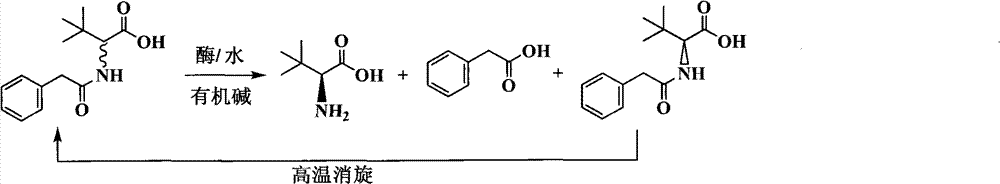
Continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine
A technology of tert-leucine and enzymatic method, which is applied in the field of splitting and preparing L-tert-leucine by using aminoacylase, can solve the problems of large solvent consumption, low production efficiency and complexity, and achieve high raw material utilization rate , reduced usage, low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Add 200g of N-phenylacetyl-DL-tert-leucine into 2000mL of pure water, and fully dissolve 165mL of 5M sodium hydroxide to prepare a substrate solution with a substrate concentration of 9.24% and a pH of 7.0. The product solution was passed through the Bacillus megaterium penicillin acylase reaction column at a flow rate of 1000mL / h, and the reaction was carried out at a room temperature of about 25°C. The conversion rate was determined to be 16.4% by sampling after 1 hour of reaction, and 49.7% after reaction 6 hours. Collect the reaction solution, and replace the remaining reaction solution in the column with 200mL pure water to finally obtain 2200mL of the reaction solution containing L-tert-leucine, add 166mL of 5M hydrochloric acid dropwise, filter under reduced pressure to obtain a white precipitated solid, and dry it in an oven at 60°C. Weighing 103.2g, the unreacted substrate content is 91.3%, which is N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine. Take 1g of solid methanol and di...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Add 400g of N-phenylacetyl-DL-tert-leucine into 2000mL of pure water, and fully dissolve 331mL of 5M sodium hydroxide to prepare a substrate solution with a substrate concentration of 17.16% and a pH of 7.0. The product solution passed through the immobilized Amano aminoacylase reaction column at a flow rate of 500mL / h, and the reaction was carried out at a room temperature of about 25°C. After 2 hours of reaction, the conversion rate was measured to be 12.7%, and after 12 hours of reaction, the conversion rate was analyzed to be 48.3%. Collect the reaction solution, and replace the remaining reaction solution in the column with 200mL pure water to finally obtain 2350mL of the reaction solution containing L-tert-leucine, add 333mL of 5M hydrochloric acid dropwise, filter under reduced pressure to obtain a precipitated solid, dry it in an oven at 60°C, weigh The weight is 210.8g, which is 89.7% of the unreacted substrate content, mainly N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine and t...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Add 300 g of the substrate obtained by racemization of Example 1 and Example 2 (N-phenylacetyl-DL-tert-leucine content 90.2%, the rest is phenylacetic acid) into 2000 mL of pure water, fully dissolve 275 mL of 5M sodium hydroxide, and prepare To form a substrate solution with a substrate concentration of 11.89% and a pH of 7.0, use a constant flow pump to pass the substrate solution through the Alcaligenes faecalis penicillin acylase reaction column at a flow rate of 1000mL / h, and react at a room temperature of about 25°C for 3 hours The conversion rate was determined to be 28.3% by sampling, and the conversion rate was analyzed after 7 hours of reaction to be 48.3%. Collect the reaction solution, and replace the remaining reaction solution in the column with 200mL pure water to finally obtain 2300mL of the reaction solution containing L-tert-leucine, add 279mL of 5M hydrochloric acid dropwise, filter under reduced pressure to obtain a white precipitated solid, and dry i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com