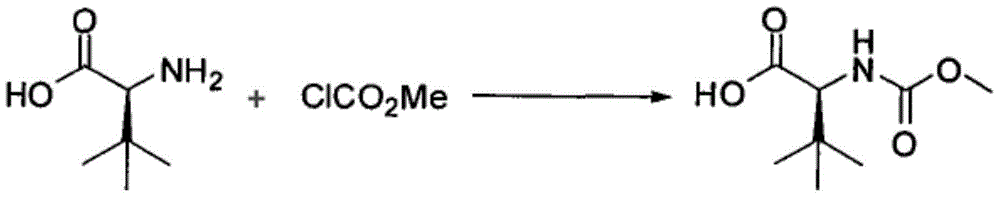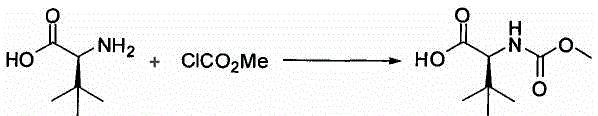Patents
Literature
35 results about "L-tert-leucine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
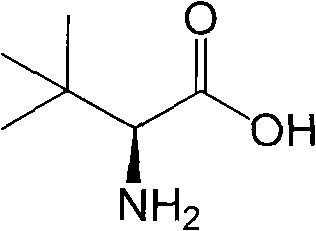
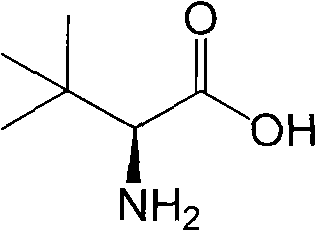
L-tert-Leucine can be used: • As a key precursor in the synthesis of a chiral phosphinooxazoline ligand, (S)-tert-butylPHOX. • In the synthesis of chiral copper(II) polymers that can catalyze the kinetic resolution of secondary alcohols by acylation.
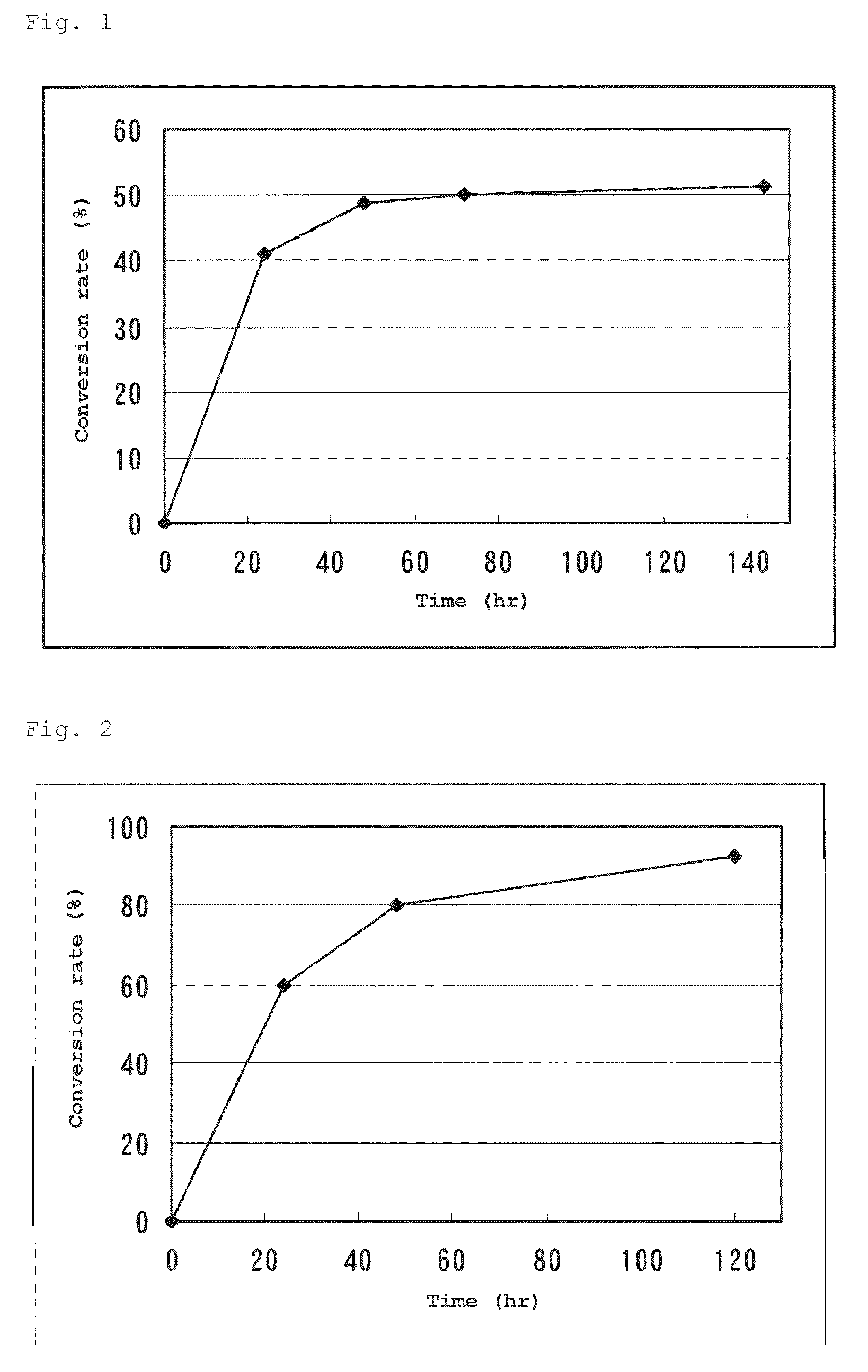
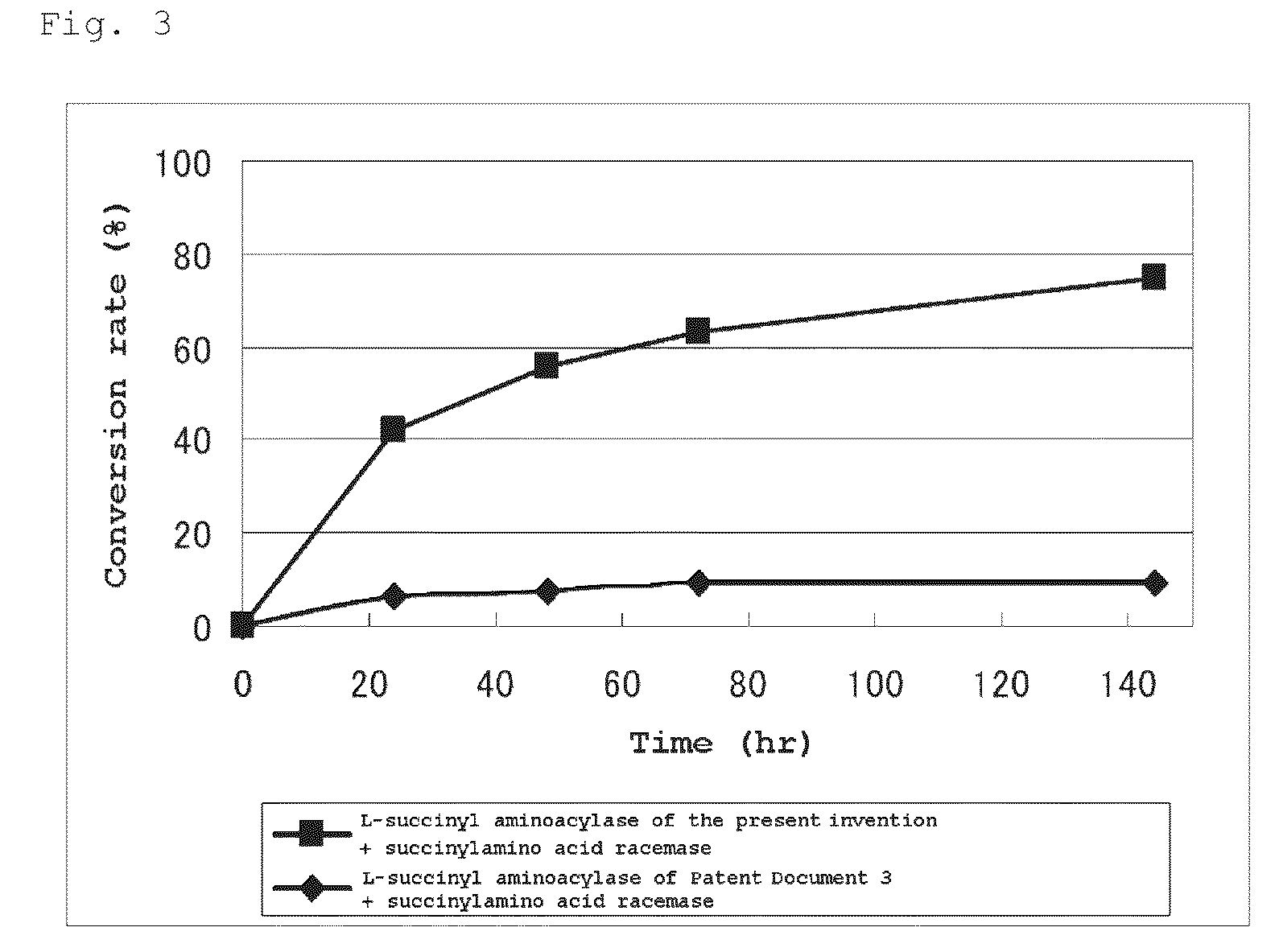
L-succinylaminoacylase and process for producing l-amino acid using it
ActiveUS20110244530A1Efficient productionSugar derivativesHydrolasesNucleic acid sequencingL-tert-leucine
The present invention provides an L-aminoacylase which is able to produce L-tert-leucine being useful as an intermediate for pharmaceuticals. A protein which is characterized in being represented by any of the following (a) to (d): (a) a protein coded by a gene consisting of a nucleic acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 1; (b) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 2; (c) a protein coded by a polynucleotide which hybridizes under a stringent condition with a nucleic acid sequence which is complementary to the nucleic acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 1 and having an L-succinylaminoacylase activity; and (d) a protein which consists of an amino acid sequence where one or several amino acid (s) is / are substituted, deleted, inserted and / or added in the protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 2 and has an L-succinylaminoacylase activity.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD +1
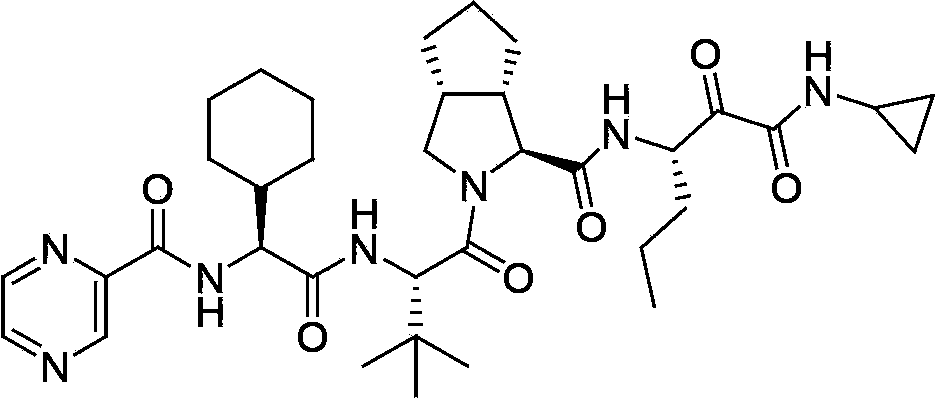
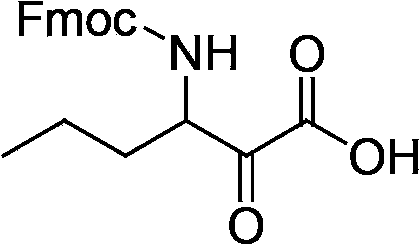
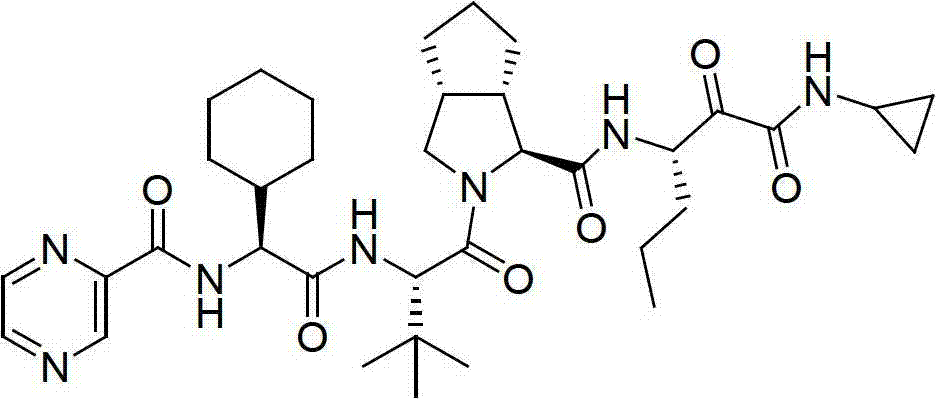
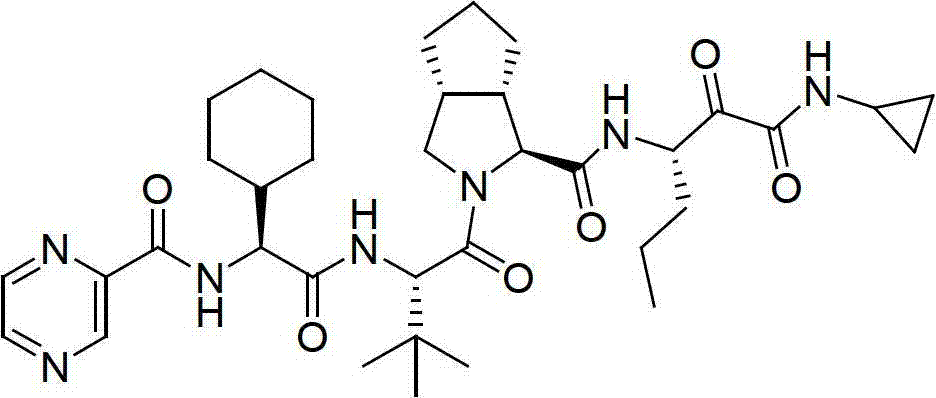
Method for preparing telaprevir
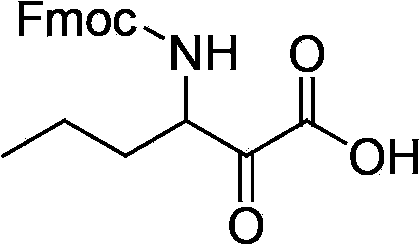
The invention relates to a new method for preparing telaprevir, which comprises the following steps: 1) orderly coupling the following 5 substances according to a Fmoc solid-phase synthetic method with a resin as a carrier to obtain peptide resin: amino acid Fmoc-P-OH, Fmoc-octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrole-1-carboxylic acid, Fmoc-L-tertiary leucine, Fmoc-2-cyclohexyl glycine, and 2-pyrazinecarboxylic acid; 2) allowing the peptide resin to react with a cyclopropylamine solution to obtain the telaprevir. The Fmoc is 9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl, and is connected with an amino, or with a nitrogen atom on a carbon atom connected with a carboxyl. The method for preparing telaprevir of the invention is simple in operation, low in cost, and high in yield.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
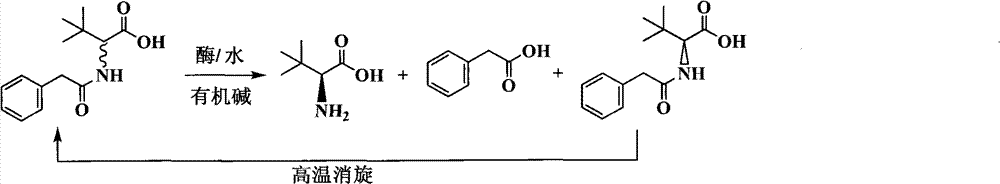
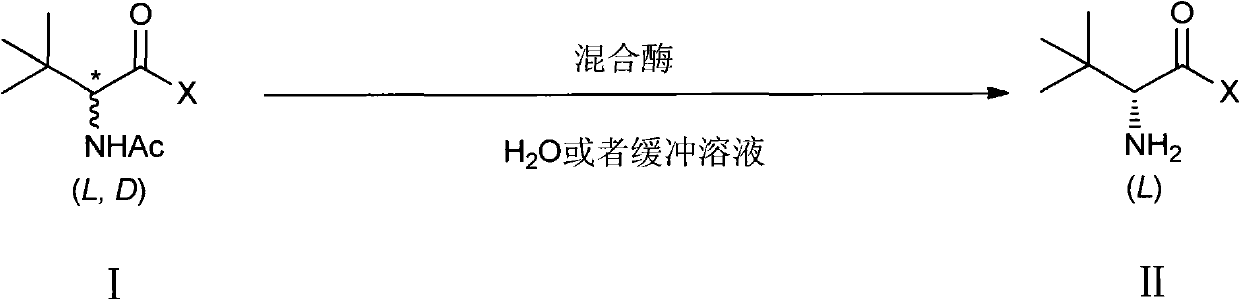
Method for preparing L-tertiary leucine compound by two enzyme system
The invention relates to a method for preparing a chiral compound based on splitting by adopting a biological enzyme preparation, in particular to a method for preparing an L-tertiary leucine compound by a two enzyme system. The method prepares the chiral L-tertiary leucine compound of the formula III by using the reaction of an N-acylating tertiary leucine compound of the formula II in water or a buffer solvent at 15 to 60 DEG C in the presence of the two enzyme system. The biological enzyme is a mixed enzyme of an acylating amino acid racemase (alanine racemase) and a hydrolase; and the preparation reaction equation is as follows, wherein X is any group of OH, NH2, NR1R2 and OR3 (wherein R1, R2, R3 are a C1-C5 straight chain, a branch chain and a one, two or three-halogen substituted alkane respectively). The invention can be implemented at room temperature and ensures simple operation and no pollution, while remarkably lowering the production cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
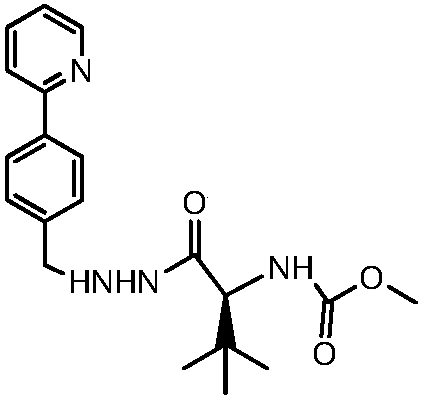
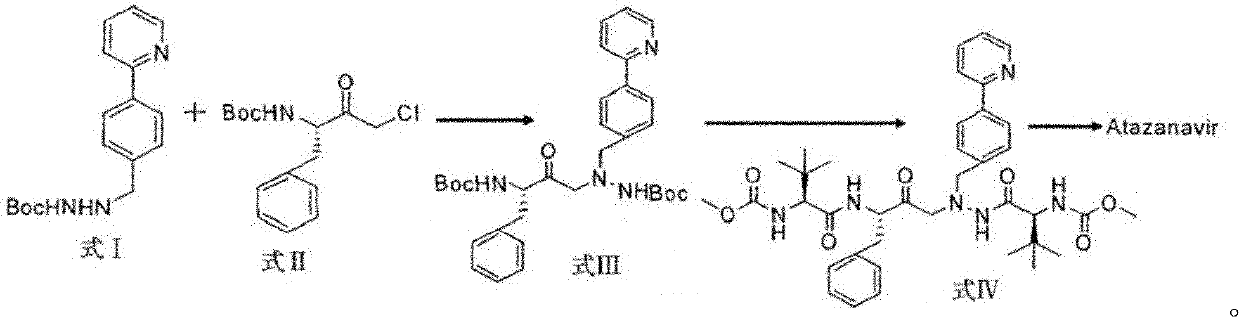
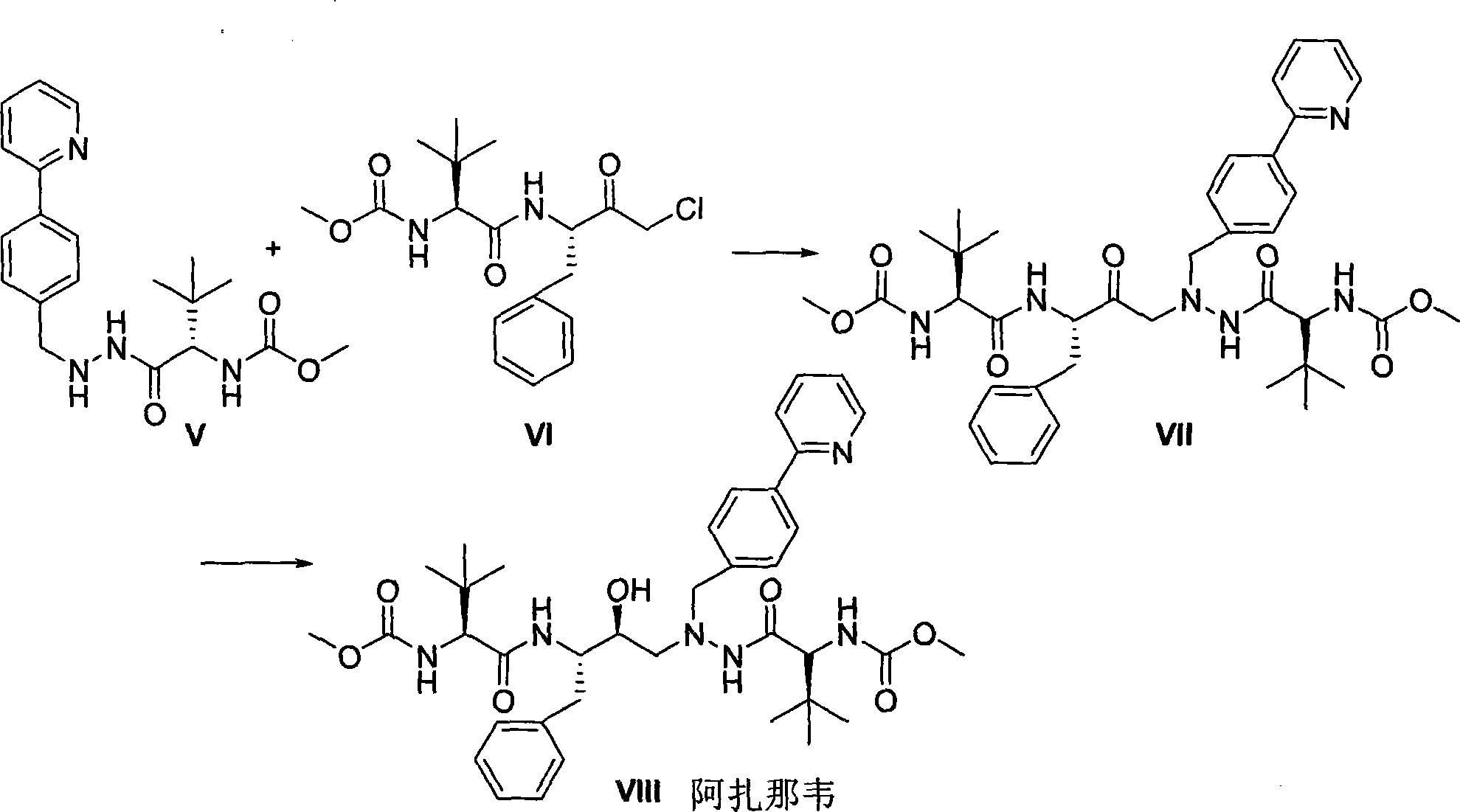
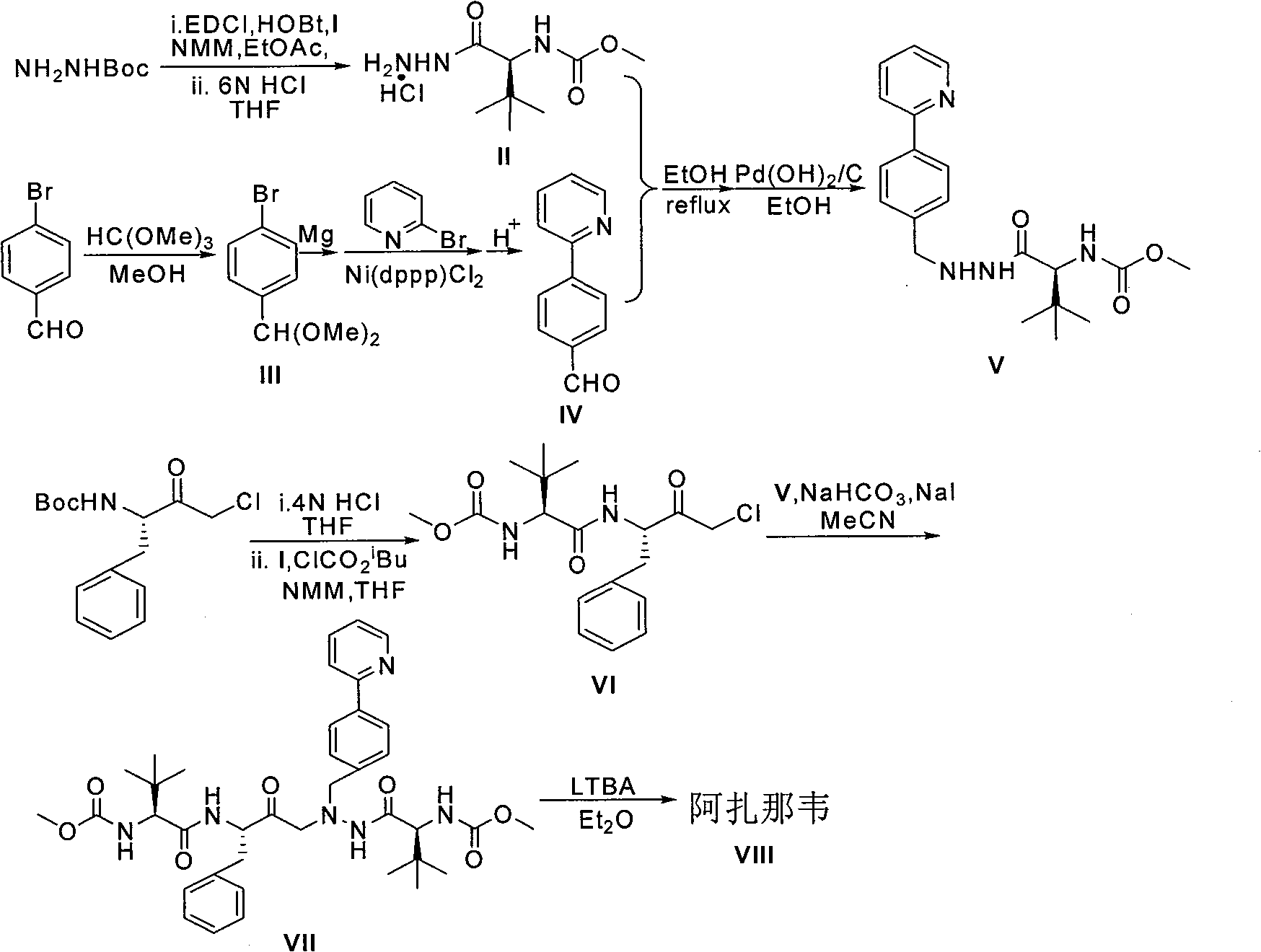
Novel method for synthesizing Atazanavir
InactiveCN102485713AMild reaction conditionsImprove securityOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionCarbamateTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
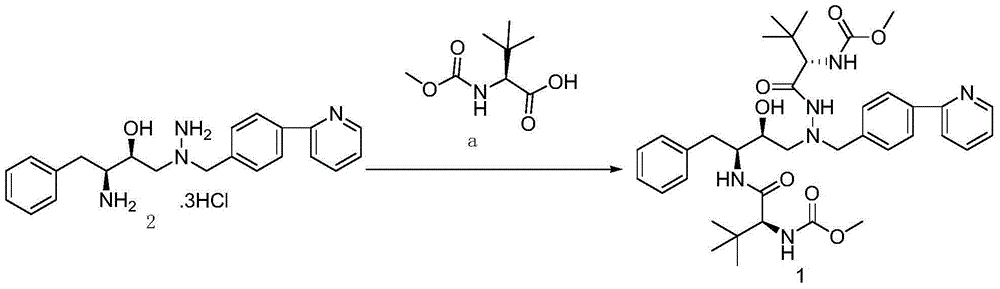
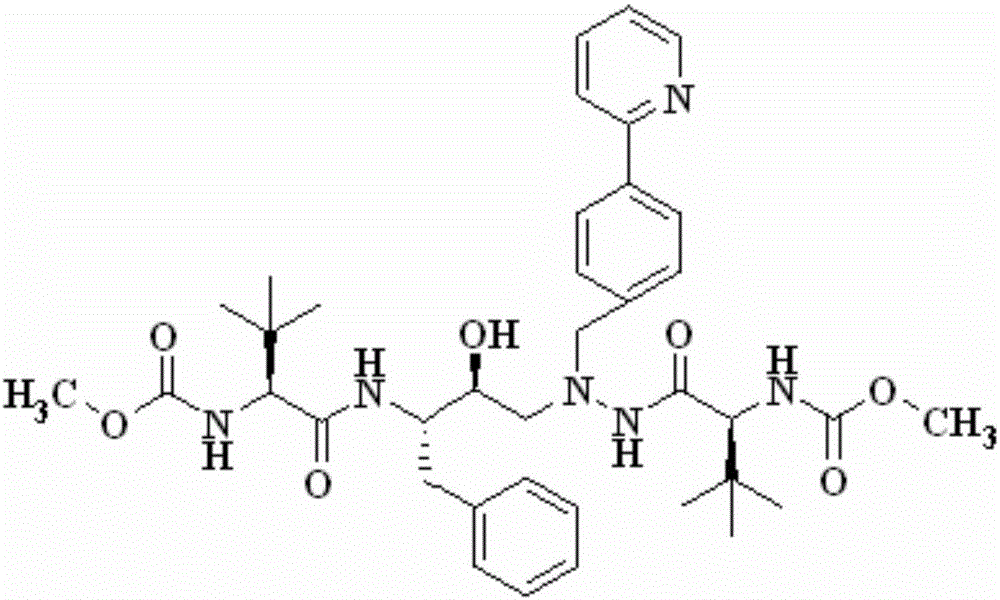
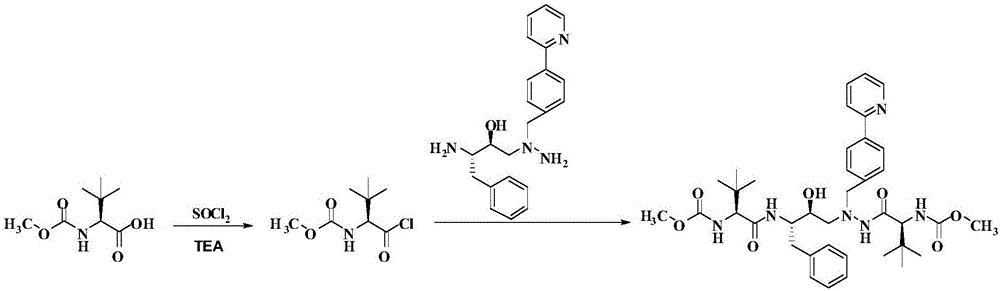
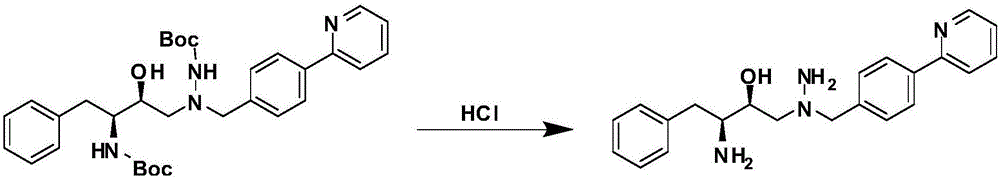
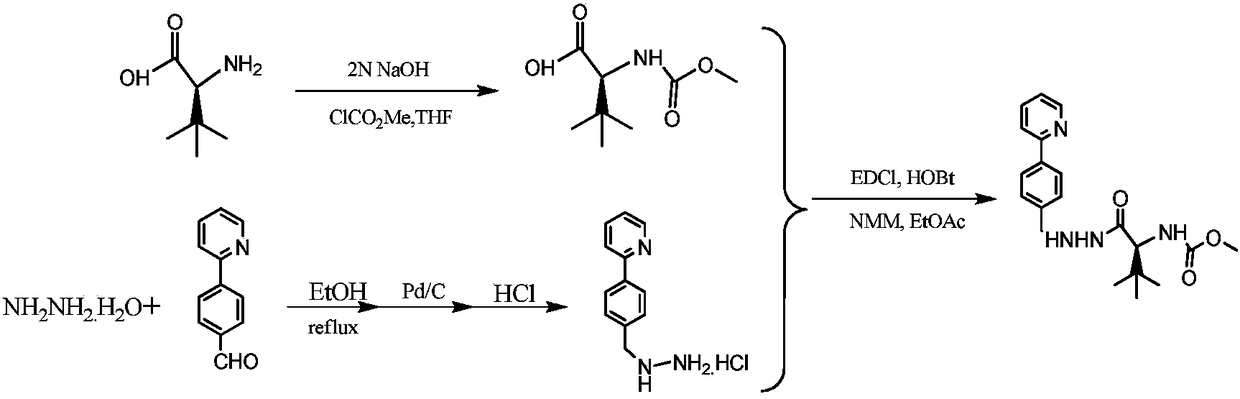
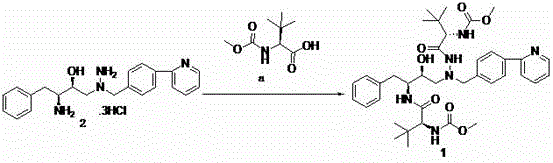
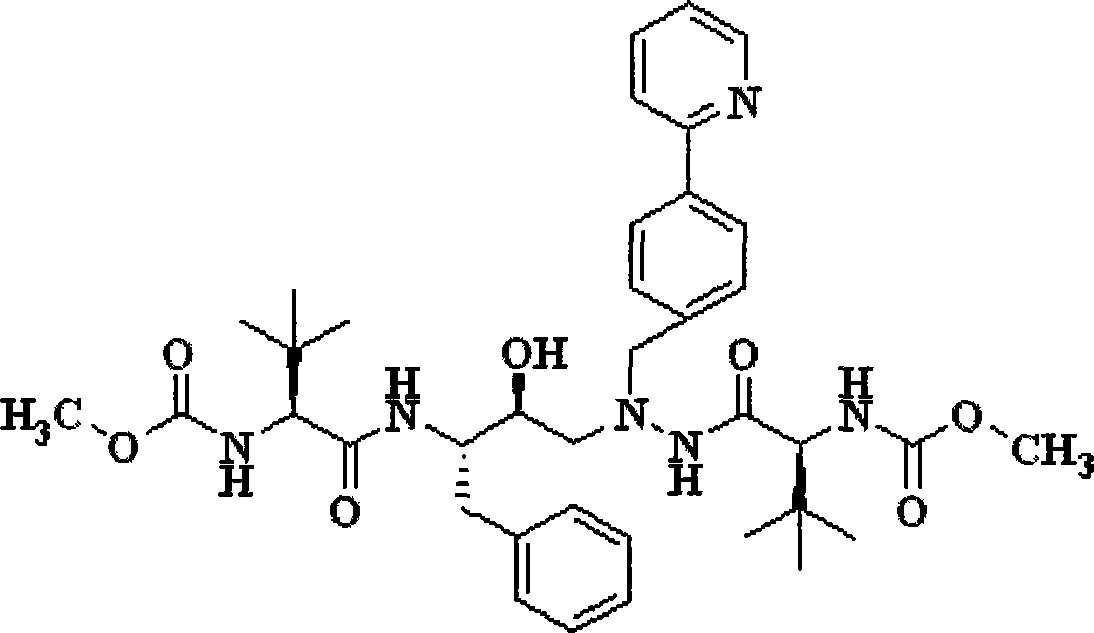
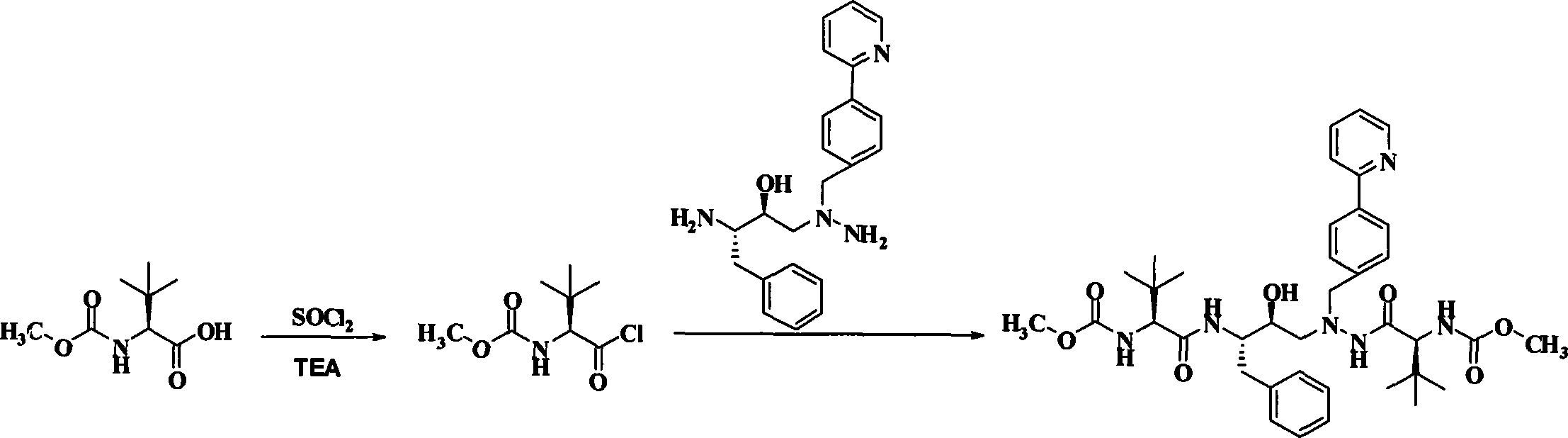
The invention discloses a novel method for synthesizing Atazanavir. The method comprises steps of: carrying out a nucleophilic substitution reaction on a compound shown as a formula I N-1-(t-butoxycarbony)-N-2-[4-(2-pyridyl) benzylidene]-hydrazine and a compound shown as a formula II (S)-4-chlorine-3-carbonyl-1-phenyl butane-2-tert-butyl carbamate to obtain an intermediate shown as a formula III; removing protective groups of the intermediate shown as a formula III and carrying out condensation reaction with N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine to obtain an intermediate shown as a formula IV; carrying out a reduction reaction on the intermediate shown as the formula IV; and a reaction formula is shown as below. The synthetic method has advantages of mild reaction conditions, high security, simple operation, simple purification treatment on end product, high purity, stable quality, easily available raw material, low price and high overall yield, so as to substantially reduce cost and apply to demand of large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACEBRIGHT PHARMA GRP +1
Method for preparing telaprevir and intermediate thereof and intermediate
The invention relates to a new method for preparing telaprevir, which comprises the following steps: 1) orderly coupling the following 5 substances according to a Fmoc solid-phase synthetic method with a resin as a carrier to obtain peptide resin: -amino acid Fmoc-P-OH, -Fmoc-octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrole-1-carboxylic acid, -Fmoc-L-tertiary leucine, -Fmoc-2-cyclohexyl glycine, and -2-pyrazinecarboxylic acid; 2) cracking the peptide resin to obtain deprotected peptide; 3) allowing the deprotected peptide to react with cyclopropylamine under a liquid-phase condition to obtain the telaprevir; wherein the Fmoc is 9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl, and is connected with an amino, or with a nitrogen atom on a carbon atom connected with a carboxyl. The method for preparing telaprevir of the invention is simple in operation, low in cost, and high in yield.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
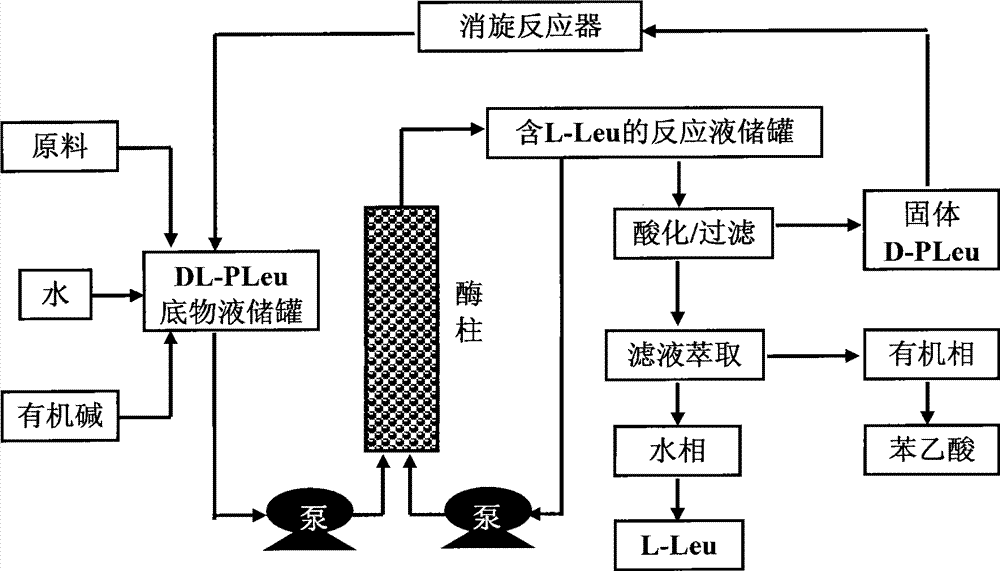
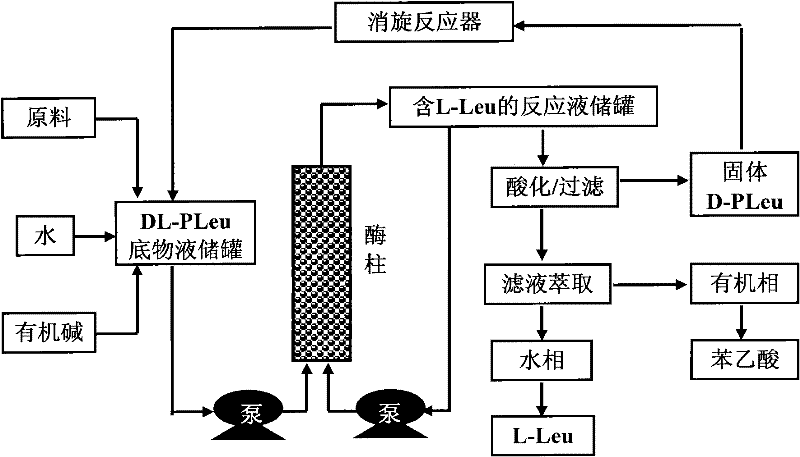
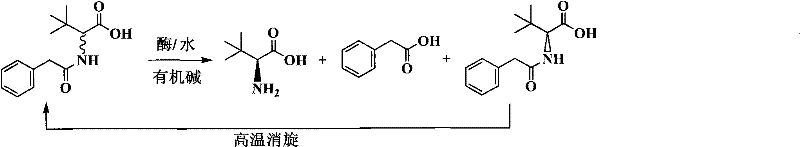
Continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine
ActiveCN102533888AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costFermentationSimple Organic CompoundsReflux
The invention relates to a method for preparing an optical isomer by continuously resolving a nitrogenous organic compound raceme with an enzyme, and particularly relates to a method for preparing L-tert-leucine by resolution with an aminoacylase, specifically a continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine. The method comprises the following steps: by using N-phenylacetyl-DL-tert-leucine and an inorganic alkali as raw materials and pure water as a reaction medium, preparing a substrate solution with a certain concentration; passing the substrate solution through an aminoacylase reaction column at a certain flow rate; under the enzyme catalytic actions, selectively hydrolyzing N-phenylacetyl-L-tert-leucine to generate L-tert-leucine and phenylacetic acid; and after the reaction finishes, acidifying the reaction solution, carrying out vacuum filtration to separate out unreacted N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine, and separating and extracting phenylacetic acid from the filtrate with an organic solvent, wherein the L-tert-leucine is in the water phase, and the unavailable N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine is racemized by high-temperature reflux and put into the resolving reaction again.
Owner:瑞博(杭州)医药科技有限公司
Method for preparing highly pure L-tertiary leucine through biological process
ActiveCN103966275AHigh selectivityMild conditionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationChemical synthesisSelf induction
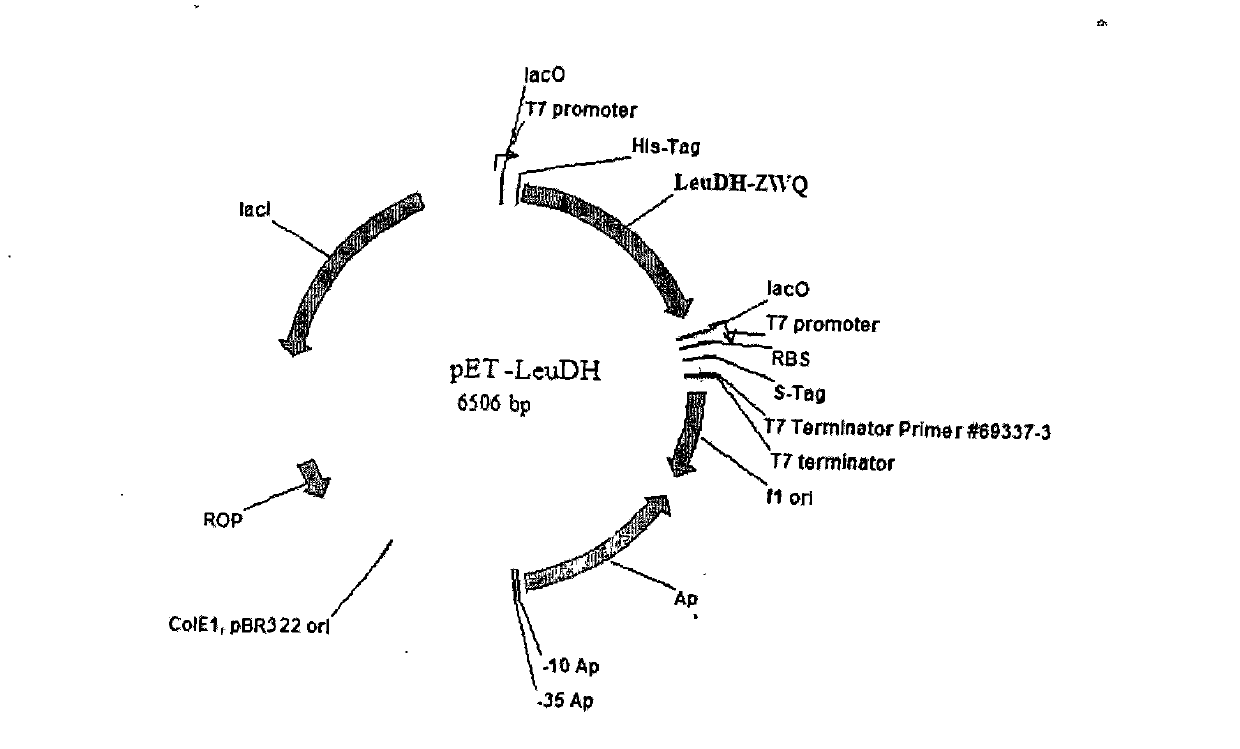
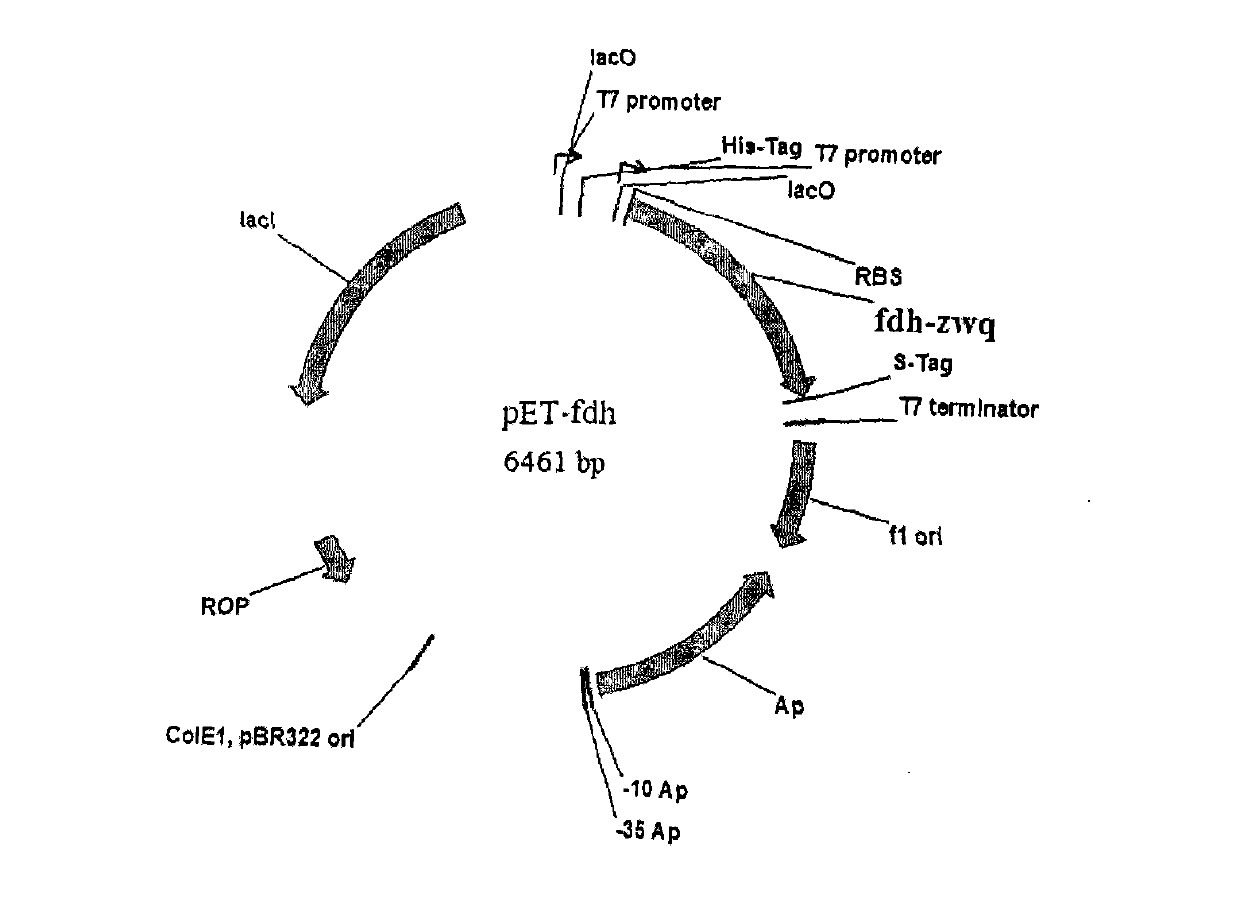
The invention discloses a method for preparing highly pure L-tertiary leucine through a biosynthesis process. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating an Escherichia coli seed liquid expressing leucine dehydrogenase gene and formic dehydrogenase gene into in a fermenting culture medium of a self-induction system, carrying out fermenting culture, centrifuging to obtain crude thalli, and adding a buffer solution to obtain a cell suspension; adding substrates comprising trimethylpyruvic acid and ammonium formate, and carrying out a biological catalysis reaction to obtain an trimethylpyruvic acid conversion solution; and centrifuging the conversion solution, adjusting the pH value of the solution, carrying out column chromatography, precipitating, and concentrating to obtain highly pure L-tertiary leucine. The method fully uses the high effectiveness, the specificity and the mildness of an enzyme; and compared with traditional chemical synthesis methods, the method disclosed in the invention has the advantages of high selectivity, mild conditions, simple process, low cost, small pollution and the like.
Owner:山东斯递尔化工科技有限公司
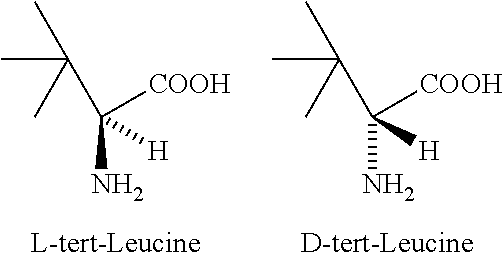
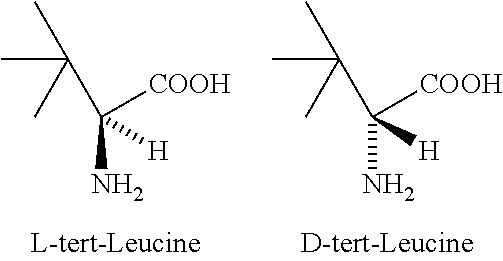
Method for simultaneously preparing D-tert-leucine and L-tert-leucine
InactiveCN105399642AUnfavorable solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationAminolysisN-Butanol
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously preparing D-tert-leucine and L-tert-leucine. The method comprises the following steps: 1, reacting n-butanol with 1,1-dichloroethylene to obtain a 3,3-dimethylbutyric acid product; 2, adding a catalyst to the 3,3-dimethylbutyric acid product, introducing air and chlorine, and carrying out a chlorination reaction to obtain 2-chloro-3,3-dimethylbutyric acid; 3, carrying out an aminolysis reaction on 2-chloro-3,3-dimethylbutyric acid to obtain D, L-tert-leucine; 4, carrying out acetylation and chloroacetylation on the obtained D, L-tert-leucine, and using L-thermal stability amino acid acylase splitting and other treatments to respectively obtain D-tert-leucine and L-tert-leucine; and 5, racemizing acetylated and chloroacetylated D-tert-leucine recovered after splitting, and carrying out cycle splitting. N-butanol and 1,1-dichloroethylene with low cost are used as initial raw materials. The cost of the method is substantially lower than that of a biological reduction method.
Owner:NANJING Y BIO PHARMA CO LTD
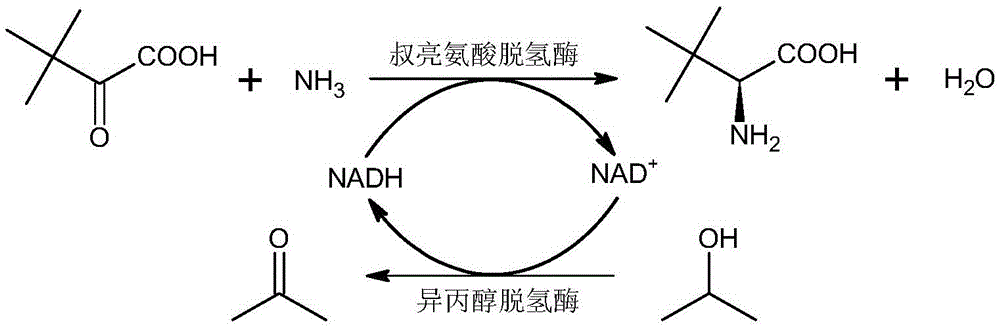
Method for synthesizing L-tertiary leucine through double enzymes
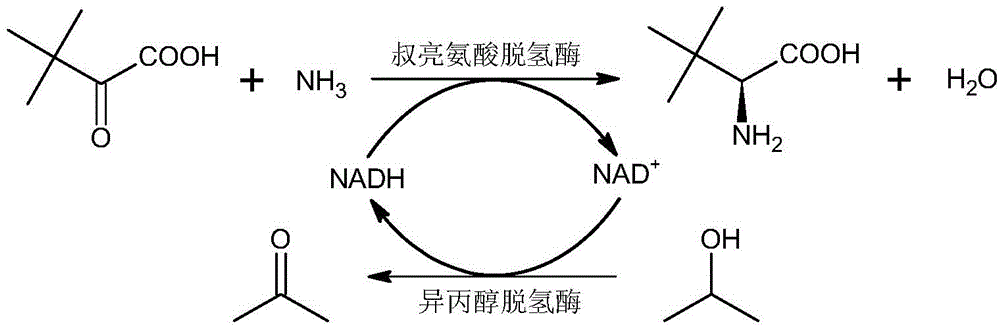
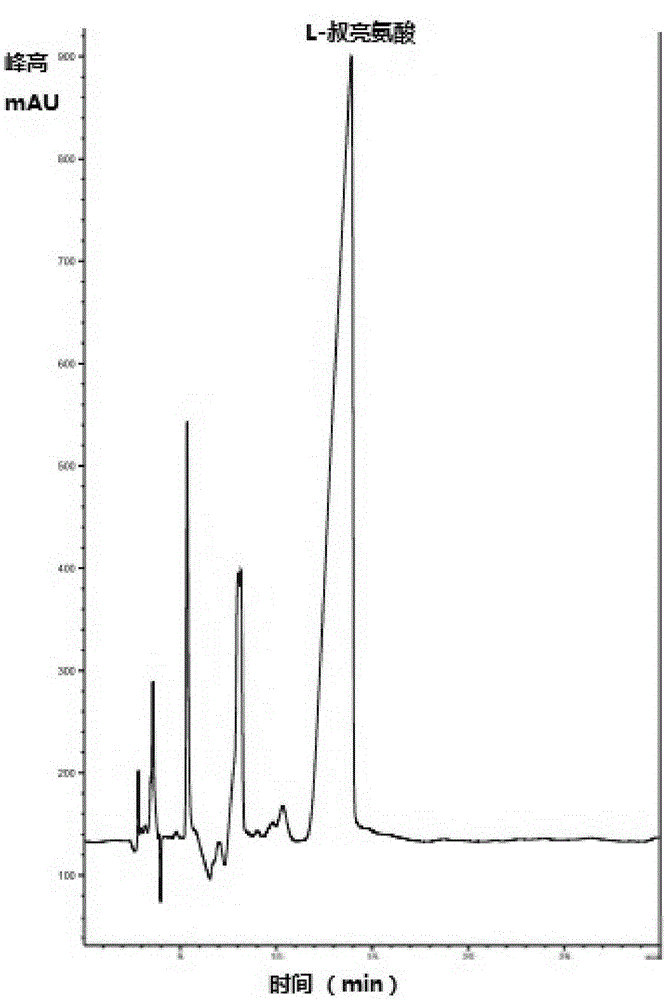
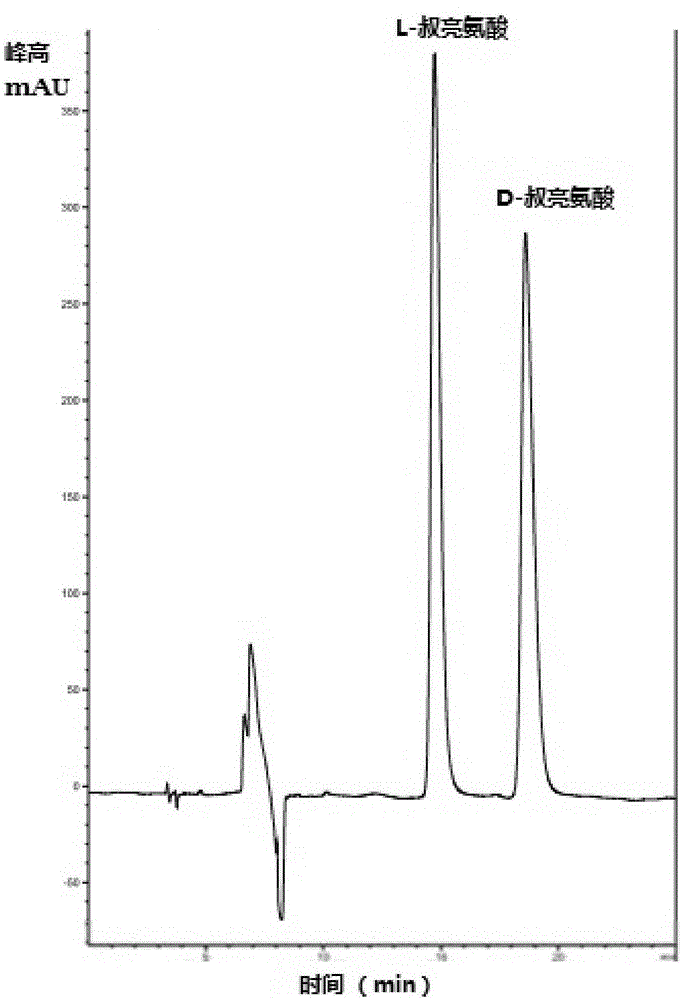
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing L-tertiary leucine through double enzymes. A coenzyme NADH is coupled and mediated by utilizing leucine dehydrogenase and isopropanol dehydrogenase, and NAD+ can be rapidly reduced into NADH through the isopropanol dehydrogenase under the action of isopropanol with the final concentration being about 10 percent in a reaction solution, so that the reaction speed is increased, the reaction time is shortened, the reaction efficiency is improved, the space time yield is increased, the amount of double enzymes is low and is not higher than 3 percent of the mass of substrates, the reaction cost is reduced, the purity of the reaction product is over 99%ee, and recrystallization and resolution are not needed.
Owner:ENZYMASTER NINGBO BIO ENG CO LTD
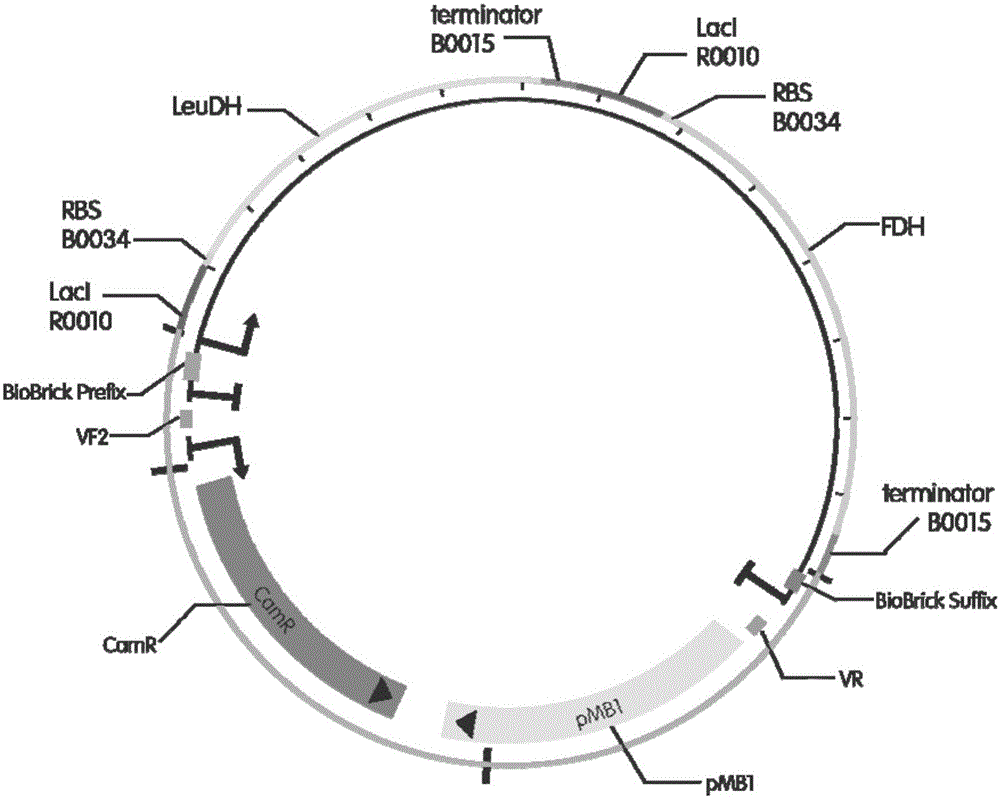
Method for preparing L-tertiary leucine based on biological brick tandem double enzymes
InactiveCN105154488AImprove conversion rateGood chiral selectivityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliBrick
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-tertiary leucine based on biological brick tandem double enzymes. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a tandem biological brick element capable of realizing tandem expression of leucine dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase; (2) introducing the tandem biological brick element into Escherichia coli (E.coli) so as to construct E.coli engineering bacteria based on tandem expression of leucine dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase; (3) inoculating the E.coli engineering bacteria into a liquid enlarged culture medium containing chloromycetin for carrying out culture and induced expression to obtain fermentation liquid, carrying out refrigerated centrifugation to obtain cells, and re-suspending and washing with a buffer solution so as to obtain cell sap; and (4) putting the cell sap, trimethylpyruvic acid, amino donors, coenzymes and cosubstrates for regeneration of the coenzymes in a buffer system for carrying out vibration reaction, and carrying out whole-cell catalysis asymmetric reductive amination to obtain the product, namely L-tertiary leucine. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the product conversion rate is high, the chiral selectivity is better, the reaction conditions are mild, the operation is simple, the expensive coenzymes can be regenerated, and the cost is saved by expressing the double enzymes with single cells.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for producing L-tert-leucine
InactiveCN102978251AReduce dosageIncreased space-time yieldFermentationEnzyme catalysisL-tert-leucine
The invention relates to the fields of biological pharmacy and biochemical engineering, and in particular relates to a method for producing L-tert-leucine. The method comprises the step of synthesizing L-tert-leucine through the L-tert-leucine dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase enzymic method, wherein in the enzyme catalysis step, the enzyme feeding amount is 4 percent (w / w) of a substrate, the coenzyme feeding amount is 0.2 percent (w / w) of the substrate, the space time yield is 100g / d / L, the product purity is more than 98 percent, and the optical purity is more than 99 percent. Compared with the traditional preparation process, the method has the advantages that the catalyst enzyme amount is effectively reduced, the product is high in purity and high in yield, the process flow is simple, special equipment requirements are avoided, the method is suitable for industrial production, and the product can be widely applied to chemical intermediates and medical intermediates.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
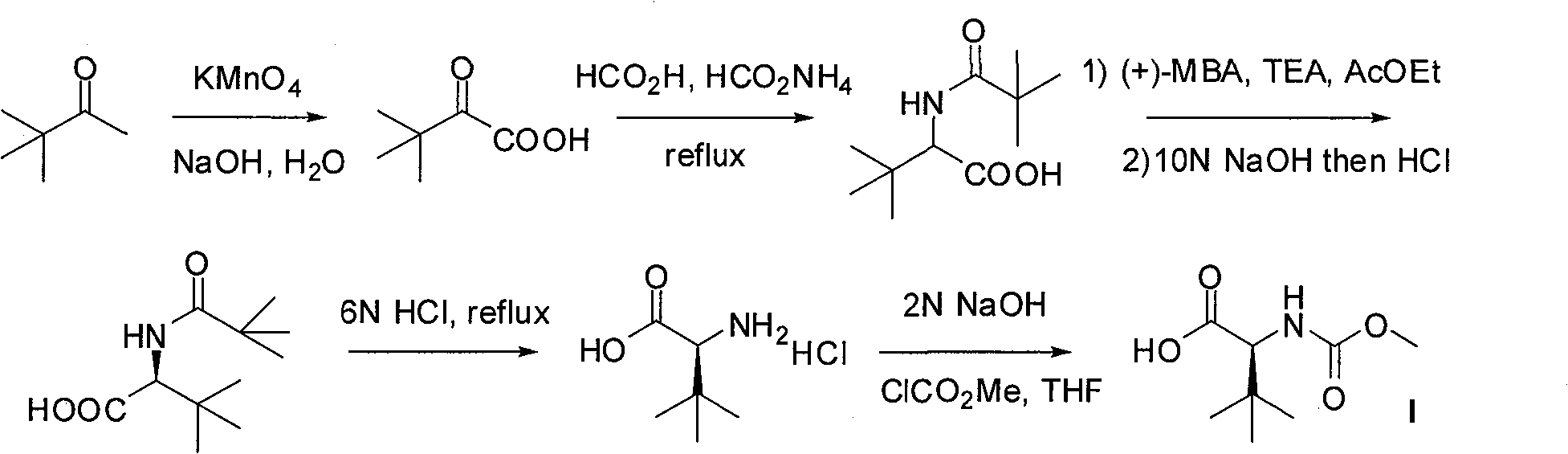
Process for the preparation of enantiomerically pure tert-leucine
ActiveUS8835676B2Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationEnantiomerDiastereomer
Owner:DIVI S LAB LTD
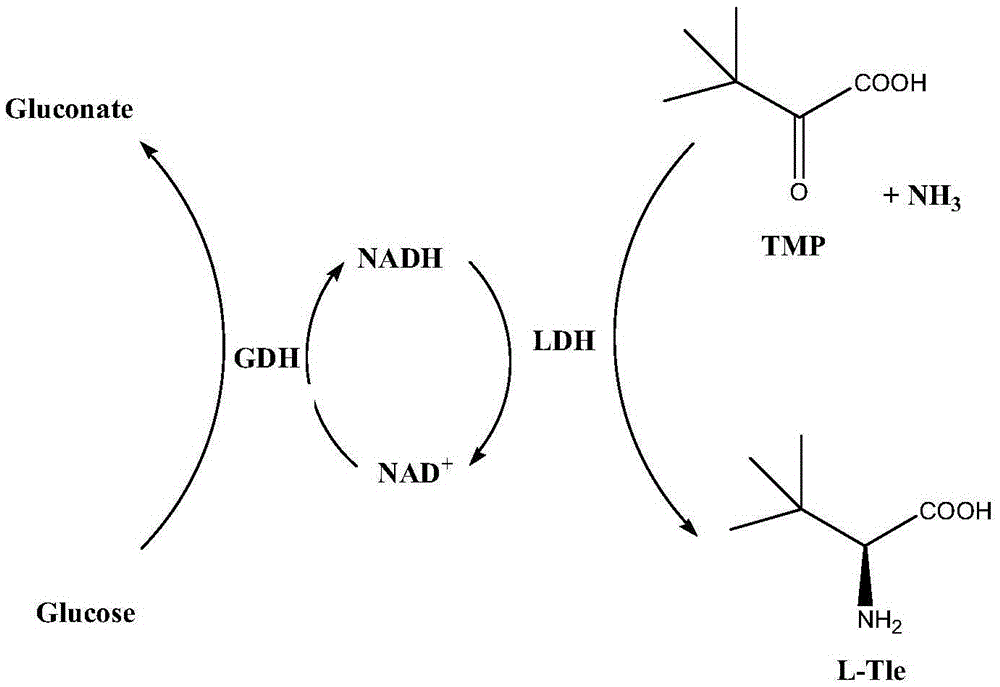
Method for preparing L-tert-leucine by coupling leucine dehydrogenase with glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveCN105603016AAchieve recyclingAchieve zero additionOrganic chemistryFermentationHigh concentrationNiacin
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-tert-leucine by coupling leucine dehydrogenase with glucose dehydrogenase, belonging to the technical field of enzyme engineering and chiral medical intermediate preparation. The method comprises the following steps: adding substrates trimethylpyruvic acid and glucose into a reaction system; adjusting the pH value of the system to 8.0-9.0; and adding a crude enzyme (containing leucine dehydrogenase, glucose dehydrogenase and coenzyme) with broken co-expressed strain and cultured by a culture medium added with substances such as niacin, and then starting reactions while controlling the temperature at 25-30 DEG C and pH value at 8.0-9.0 in the reaction process to generate L-tert-leucine. In the invention, a system in which leucine dehydrogenase is coupled with glucose dehydrogenase is adopted, and the L-tert-leucine is prepared by use of the coenzyme contained in the thalli; and the method has the characteristics of high concentration of single-batch reaction substrates, high reaction efficiency, no coenzyme addition and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
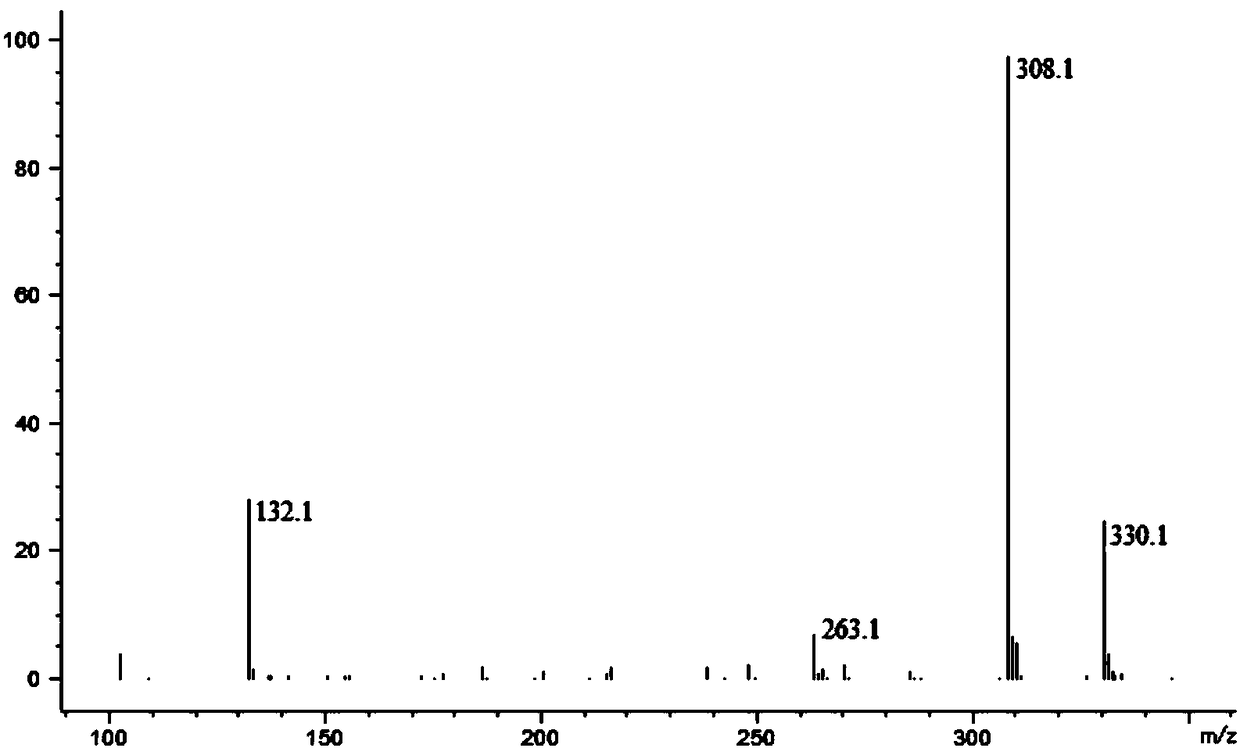
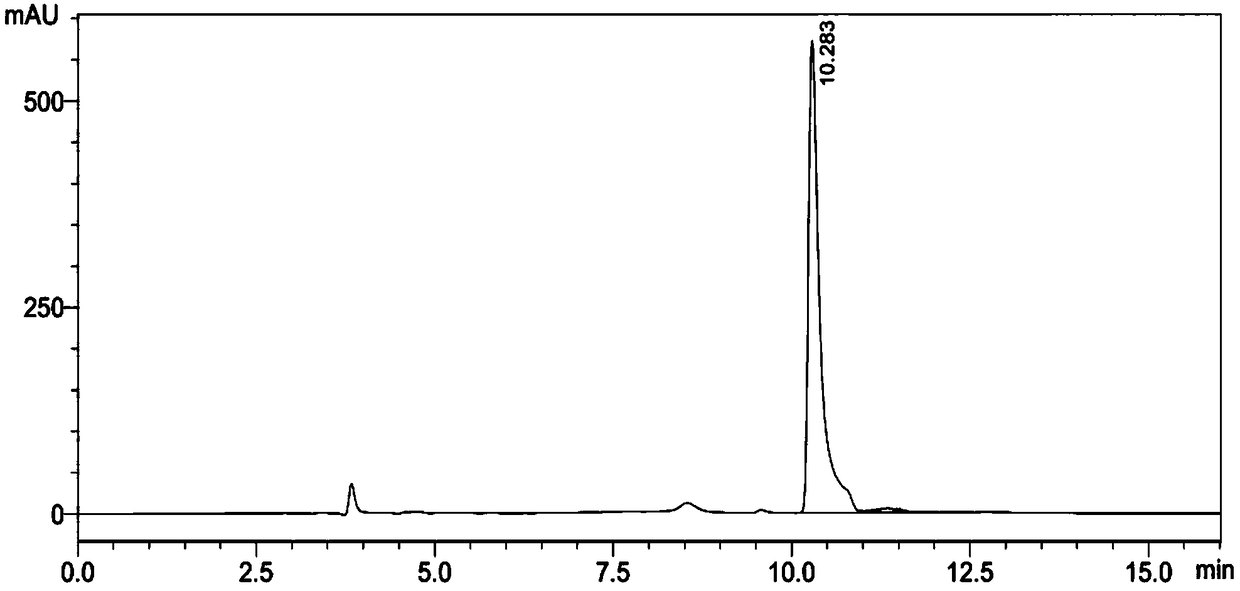
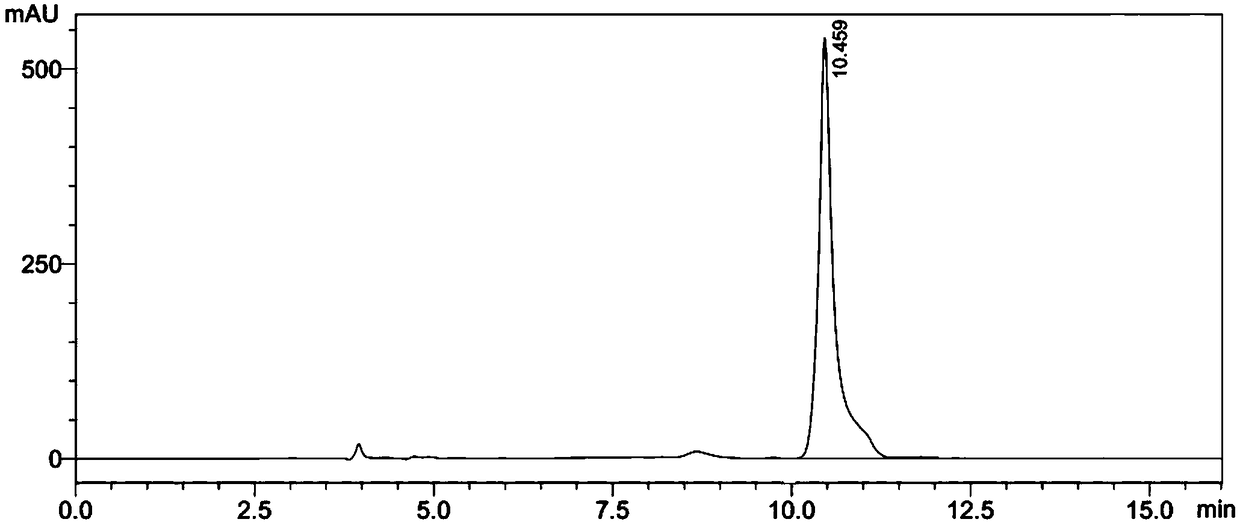
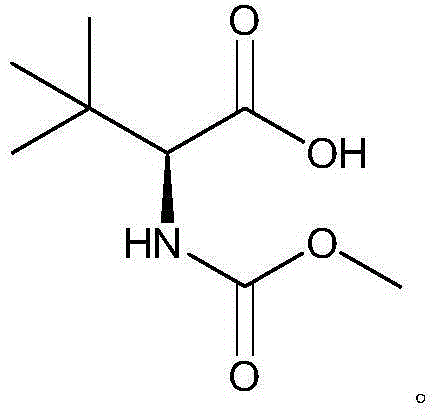
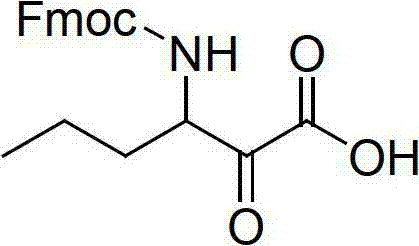
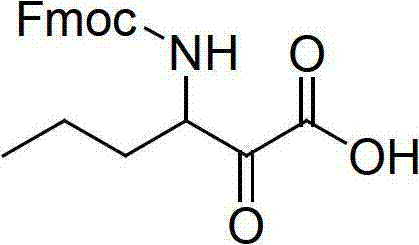
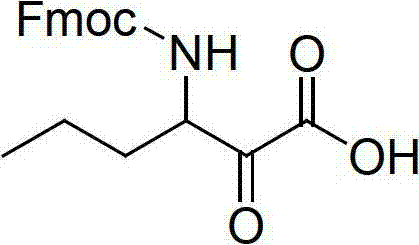
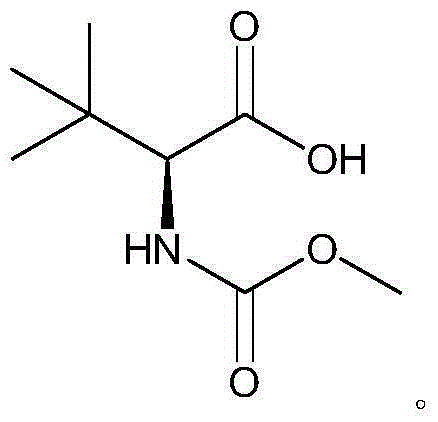
Preparation method of N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine
ActiveCN105111105ASuitable for industrial productionHigh purityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationDiastereomerL-tert-leucine
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIUZHOU PHARM CO LTD
Novel method for preparing atazanavir monomer
The invention discloses a method for preparing an atazanavir monomer. The method is applied to the technical field of medicines and comprises steps as follows: at the proper temperature, weak base is used as an acid-binding agent, under a certain organic solvent condition, N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine firstly reacts with thionyl chloride to produce N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine acyl chloride, then the N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine acyl chloride and 1-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)-phenyl]-4(S)-hydroxyl-5(S)-2,5-diamino-6-phenyl-2-azahexane have an amide formation reaction at the room temperature, and the atazanavir monomer is obtained. The method has the advantages as follows: (1), the thionyl chloride is cheap, so that the costs of raw materials are effectively reduced, and the method is suitable for industrialization; (2), the produced pollution is less and is converted into soluble effluent brine after after-treatment, so that the method is relatively environment-friendly; (3), the operation is simple, the product yield is high, separation and purification are easy, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NORTHEAST PHARMA GRP
Preparation method of N- methoxycarbonyl group-L- tertiary leucine
ActiveCN103159647ASuitable for industrial productionHigh purityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationDiastereomerTert-leucine
The invention relates to a preparation method of MOC-L-tertiary leucine, in particular to a method for splitting 2-methoxy group acylamino-3, 3-dimethyl butyric acid to prepare the MOC-L-tertiary leucine. Two kinds of diastereoisomer amine salt of the 2-methoxy group acylamino-3, 3-dimethyl butyric acid are formed through the 2-methoxy group acylamino-3, 3-dimethyl butyric acid and a resolving agent amine compound, MOC-L-tertiary leucine amine salt is obtained through separation, and the MOC-L-tertiary leucine is obtained by utilizing of the free acid MOC-L-tertiary leucine amine salt. The preparation method is low in cost, simple and reasonable in technique, high in product purity and suitable for industrial production of the MOC-L-tertiary leucine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIUZHOU PHARM CO LTD
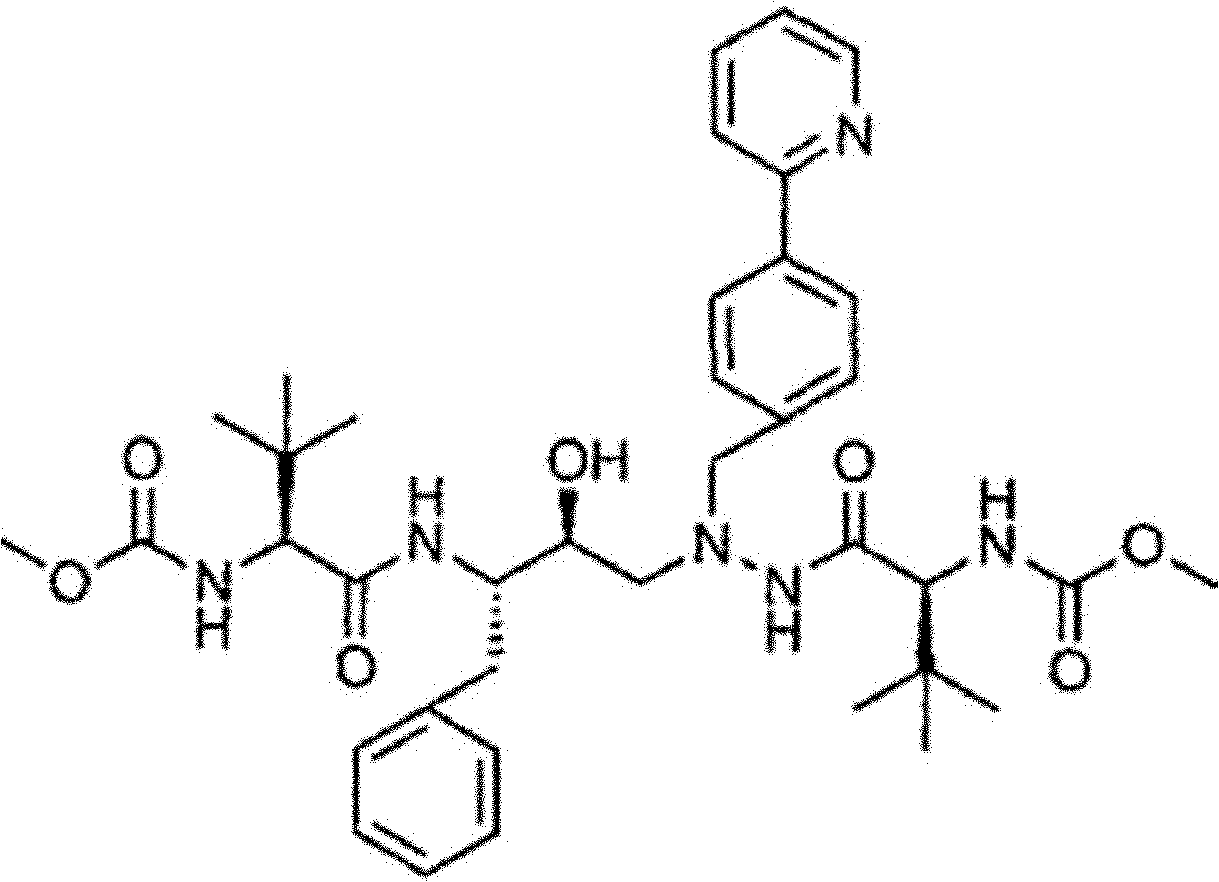
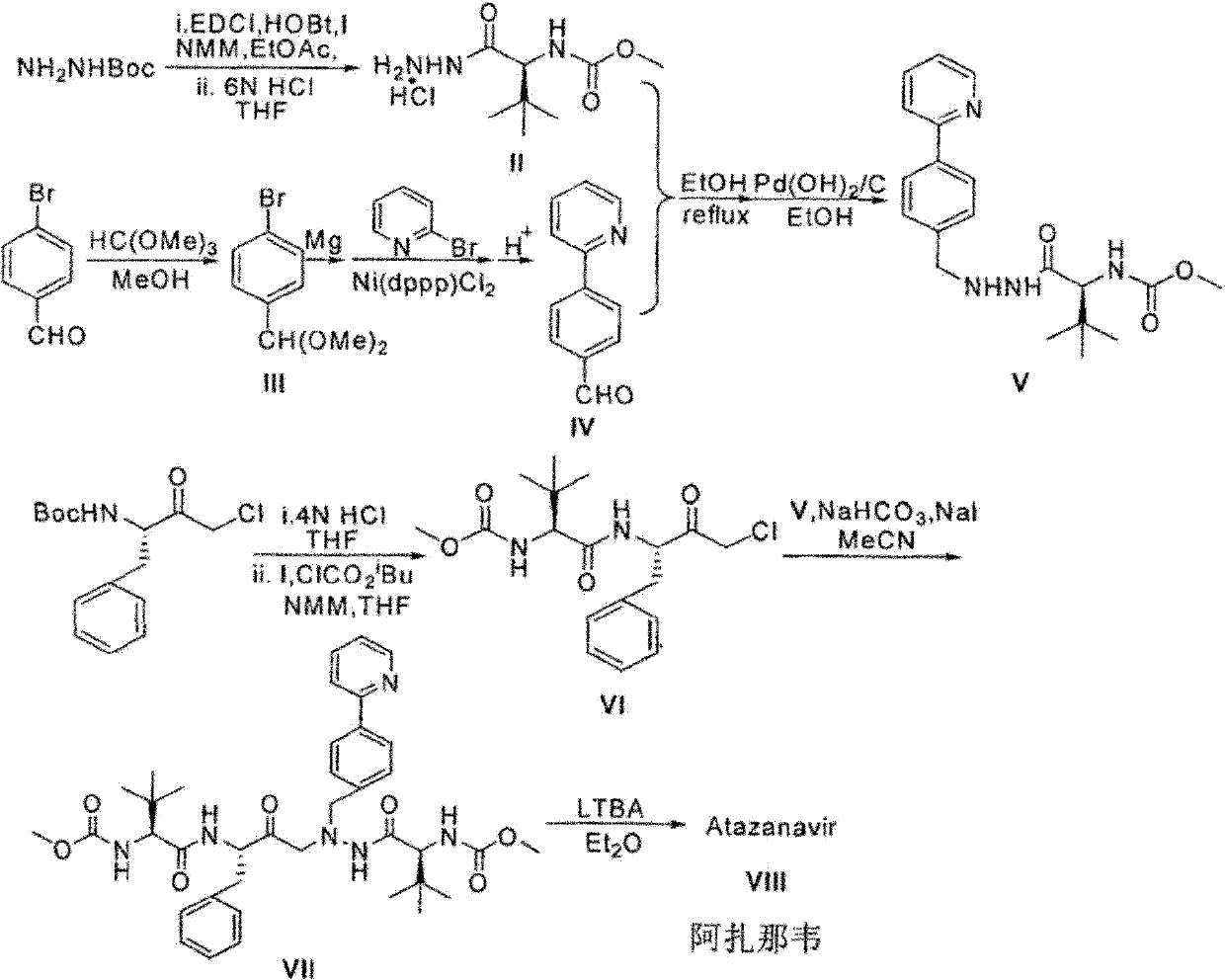
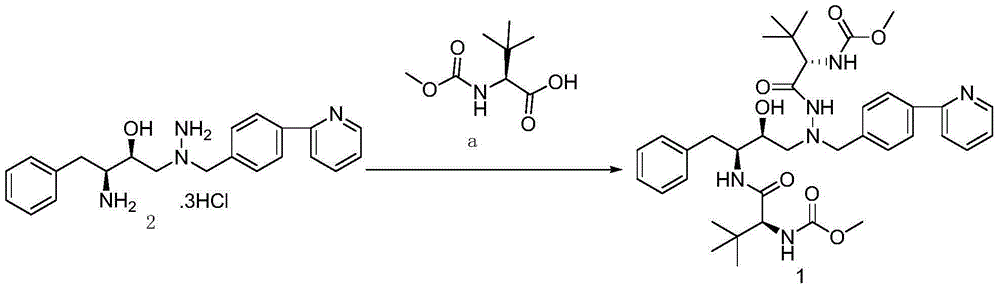
Novel synthetic method of HIV-1 protease inhibitor atazanavir
InactiveCN101391978BLow priceEasy recrystallization purificationOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionMethyl carbamateMethyl carbazate
The invention relates to a new synthetic method of an HIV-1 protease inhibitor, Atazanavir, which adopts a convergent-typed synthetic strategy, introduces a construction unit, methoxycarbonyl-tert-lencyl, as an N atom protecting group in the whole early synthetic stage, and takes the diastereomeric selective reduction of aminoketone as the key and final reaction step of the new process. The method comprises the steps that: the compound of formula V, namely, N-1-[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucine]-N-2-[4-(2-pyridyl)-phenmethyl]hydrazine, and the compound of formula VI, namely, (S)-1-((S)-4-chlorine-3-carbonyl-1-phenyl butane-2-yl-2-amino)-3, 3-dimethyl-1-carbonyl butane-2-yl-methyl carbamate, are treated with nucleophilic substitution reaction to generate the compound of formula VII, namely, 1-[4-(2-pyridyl)phenyl]-5(S)-2, 5-bis{[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucineyl] amino}-4-carbonyl-6-phenyl-2-azahexane; and the compound of formula VII is treated with reduction reaction to generate the Atazanavir. The invention has the advantages of less process route steps, easily-controlled reaction conditions, simple and convenient operation, low-price and easily-obtained raw material, high product yield, low cost and being suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
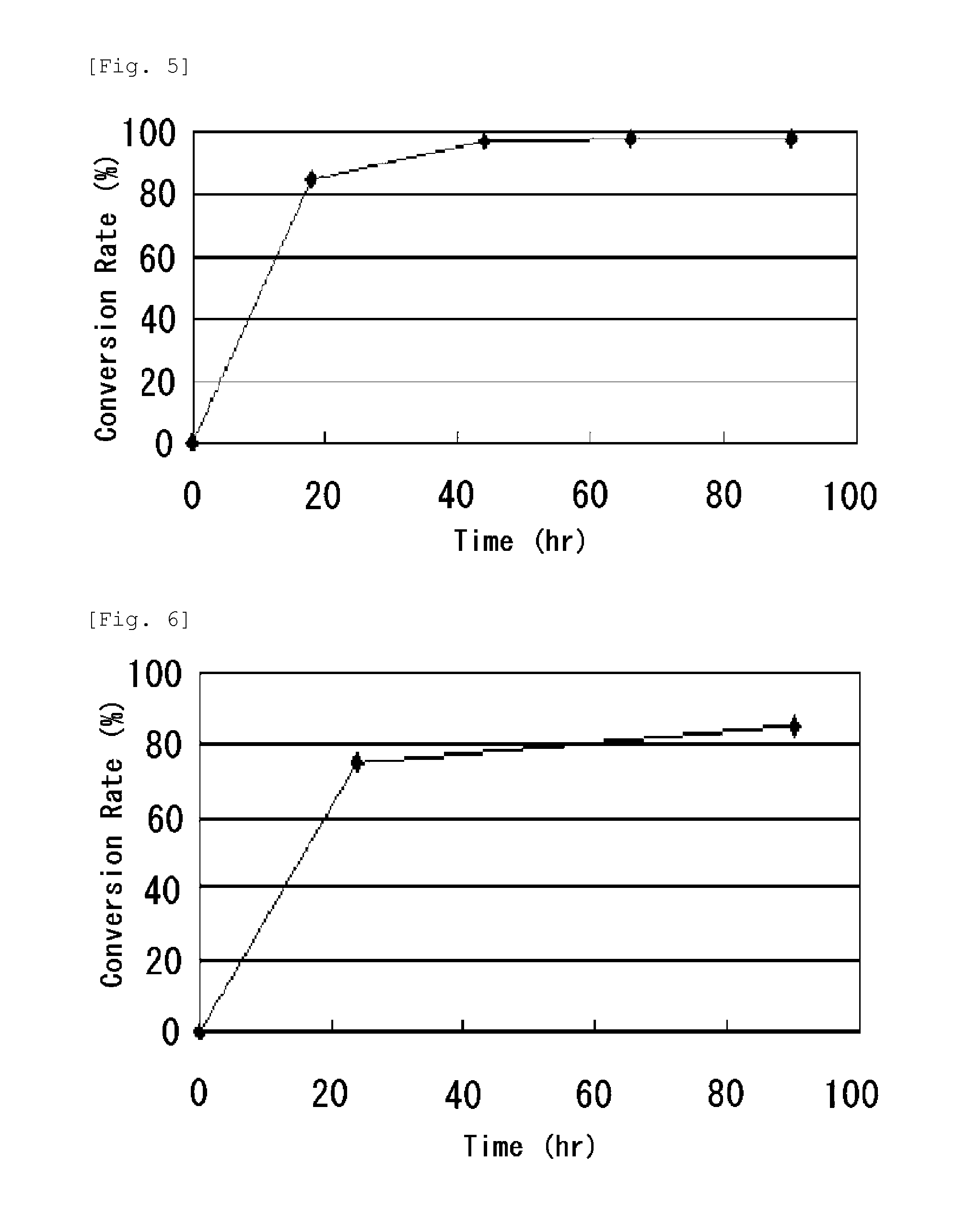
Method of producing n-[(2S)-sulfanyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl)butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide and intermediate thereof
InactiveUS6960567B2Increase productionReduce presencePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesPhenacylL-tert-leucine
Process for producing N-[(2S)-sulfanyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl) butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide by forming an intermediate compound N-[(2S)-thiobenzoyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl)butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide by an improved process that substantially reduces the presence of contaminants in the reaction mixture.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Biotransformation method for L-tert-leucine
InactiveCN108570486AReduce manufacturing costReduce acidificationOrganic compound preparationOxidoreductasesDrug biotransformationL-tert-leucine
The invention discloses a biotransformation method for L-tert-leucine. The method includes the following steps: establishing a transformation system by utilizing sodium trimethylpyruvate as a substrate, utilizing coenzyme NAD+ and immobilized leucine dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase as a biocatalyst and by adding an ammonium salt; and performing a biotransformation reaction to obtain a transformation liquid containing the L-tert-leucine. The biotransformation method utilizes the immobilized leucine dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase as the biocatalyst which can still have enzyme activity after ten times of reuse, and an expensive coenzyme and enzyme can be recycled, so that the production cost is saved; a self-made sodium trimethylpyruvate solution is utilized as the substrate,so that the preparation process is simplified, the production cost is saved, and purification is convenient; and the purity of a prepared L-tert-leucine crystal reaches 98.5% or above, and the optical purity is 99% or above. Process flow is simple, no special requirements are for equipment, and industrialization production is suitable. HPLC-MS and HPLC are utilized to monitor until the substrateis completely utilized.
Owner:南宁信肽生物技术有限责任公司
Preparation method of N- methoxycarbonyl group-L-tertiary leucine
ActiveCN105085321ASuitable for industrial productionHigh purityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparation3-methylbutyric acidDiastereomer
The invention relates to a preparation method of MOC (methoxycarbonyl group)-L-tertiary leucine, in particular to a method for preparing the MOC-L-tertiary leucine by separating 2-methoxyamide-3, 3-methylbutanoic acid. The method comprises the following steps of forming two kinds of diastereoisomer amine salts by using the 2-methoxyamide-3, 3-methylbutanoic acid and a resolving agent which is an amine compound; separating the two kinds of diastereoisomer amine salts to obtain MOC-L- tertiary leucine amine salt; and performing acid dissociation on the MOC-L- tertiary leucine amine salt to obtain the MOC-L-tertiary leucine. The method is low in cost, a technology is simple and reasonable, the purity of products is high, and the method is suitable for industrial production of the MOC-L-tertiary leucine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIUZHOU PHARM CO LTD
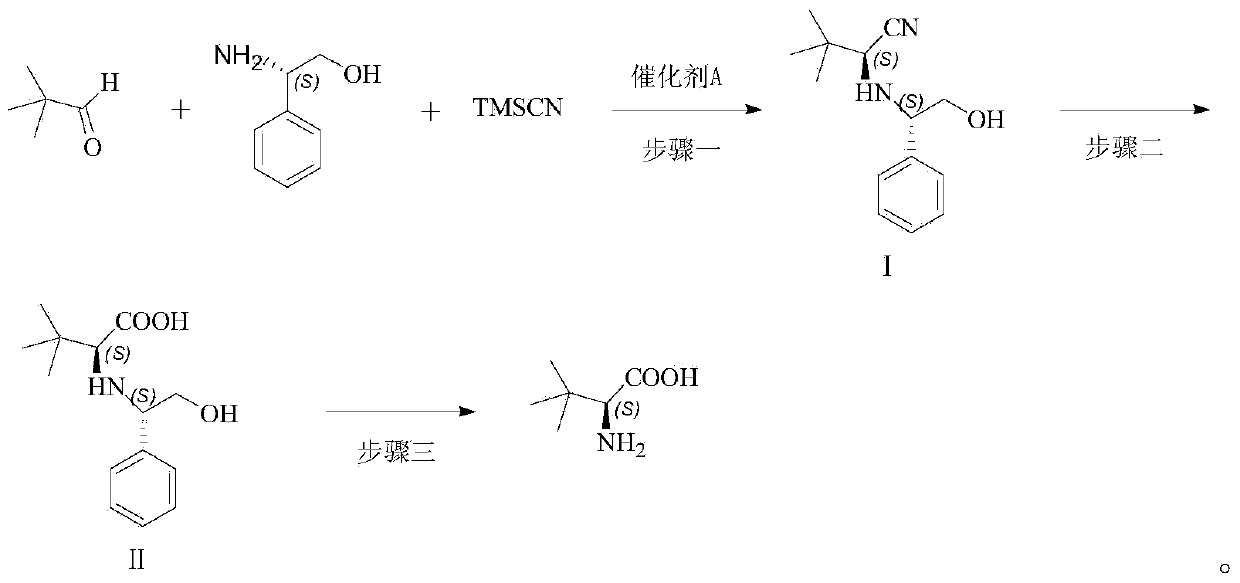
New method for preparing L-tertiary leucine
ActiveCN104193629AReduce pollutionHigh stereoselectivityOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationTrimethylsilyl cyanideSolvent free
The invention discloses a new method for preparing L-tertiary leucine. The new method comprises the following steps: 1, performing asymmetric cyanosilylation reaction on pivalaldehyde, L-phenylglycinol and trimethylsilyl cyanide in the presence of a catalyst A, and carrying out posttreatment to obtain a compound I; 2, hydrolyzing the compound I under acidic condition, and carrying out posttreatment to obtain a compound II; 3, performing catalytic hydrogenation reaction on the compound II to obtain L-tertiary leucine, wherein the catalyst A is magnesium diiodide, magnesium dibromide, magnesium dichloride, magnesium perchlorate or magnesium trifluoromethanesulfonate. The stereochemistry of the L-tertiary leucine can be constructed with high selectivity under solvent-free condition by adopting a magnesium catalyzed three-component one-pot asymmetric cyanosilylation reaction through cheap and easily available organic raw materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of method for preparing atazanavir monomer
A method for preparing atazanavir monomers applied in the field of medical technology, at an appropriate temperature, with a weak base as an acid-binding agent and a certain organic solvent, N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine The acid first reacts with thionyl chloride to generate N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine acid chloride, and then reacts with 1-[4-(pyridin-2-yl)-phenyl]-4(S)-hydroxy-5 (S)-2,5-diamino-6-phenyl-2-azidine was subjected to an amide reaction at room temperature to obtain atazanavir monomer. The invention has the following advantages (1) thionyl chloride is cheap, effectively reduces the cost of raw materials, and is suitable for industrialization; (2) the pollution produced is less, because it becomes soluble waste brine after post-treatment, and the environment is relatively friendly; ( 3) The operation is simple, the product yield is high, and it is easy to separate and purify, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NORTHEAST PHARMA GRP
Method for preparing telaprevir and intermediate thereof and intermediate
The invention relates to a new method for preparing telaprevir, which comprises the following steps: 1) orderly coupling the following 5 substances according to a Fmoc solid-phase synthetic method with a resin as a carrier to obtain peptide resin: -amino acid Fmoc-P-OH, -Fmoc-octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrole-1-carboxylic acid, -Fmoc-L-tertiary leucine, -Fmoc-2-cyclohexyl glycine, and -2-pyrazinecarboxylic acid; 2) cracking the peptide resin to obtain deprotected peptide; 3) allowing the deprotected peptide to react with cyclopropylamine under a liquid-phase condition to obtain the telaprevir; wherein the Fmoc is 9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl, and is connected with an amino, or with a nitrogen atom on a carbon atom connected with a carboxyl. The method for preparing telaprevir of the invention is simple in operation, low in cost, and high in yield.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
L-succinylaminoacylase and process for producing L-amino acid using it
The present invention provides a L-succinylacylase consisting of: (a) a protein coded by a gene consisting of a nucleic acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 1; (b) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 2; (c) a protein coded by a polynucleotide which hybridizes under a stringent condition with a nucleic acid sequence which is complementary to the nucleic acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 1 and having an L-succinylaminoacylase activity; or (d) a protein which consists of an amino acid sequence where one or several amino acid(s) is / are substituted, deleted, inserted and / or added in the protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 2 and has an L-succinylaminoacylase activity. This enzyme is able to produce a sterically bulky unnatural amino acid such as L-tert-leucine etc. which is useful as an intermediate for pharmaceuticals.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD +1
Continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine
ActiveCN102533888BIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costFermentationSimple Organic CompoundsReflux
The invention relates to a method for preparing an optical isomer by continuously resolving a nitrogenous organic compound raceme with an enzyme, and particularly relates to a method for preparing L-tert-leucine by resolution with an aminoacylase, specifically a continuous enzymatic method for producing L-tert-leucine. The method comprises the following steps: by using N-phenylacetyl-DL-tert-leucine and an inorganic alkali as raw materials and pure water as a reaction medium, preparing a substrate solution with a certain concentration; passing the substrate solution through an aminoacylase reaction column at a certain flow rate; under the enzyme catalytic actions, selectively hydrolyzing N-phenylacetyl-L-tert-leucine to generate L-tert-leucine and phenylacetic acid; and after the reaction finishes, acidifying the reaction solution, carrying out vacuum filtration to separate out unreacted N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine, and separating and extracting phenylacetic acid from the filtrate with an organic solvent, wherein the L-tert-leucine is in the water phase, and the unavailable N-phenylacetyl-D-tert-leucine is racemized by high-temperature reflux and put into the resolving reaction again.
Owner:瑞博(杭州)医药科技有限公司
PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ENANTIOMERICALLY PURE tert-LEUCINE
ActiveUS20120245379A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationEnantiomerDiastereomer
Enantiomerically pure L-tert-leucine and D-tert-leucine were prepared from (DL)-tert-leucine by diastereomeric salt formation using dibenzoyl-d-tartaric acid as the resolving agent.
Owner:DIVI S LAB LTD
Printing and dyeing industry sewage treating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106587210AQuick resultsNo secondary pollutionWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentMagnesium saltPollution
The invention discloses a printing and dyeing industry sewage treating agent and a preparation method thereof. The printing and dyeing industry sewage treating agent is prepared from, by weight, 20-25 parts of diatomite, 0.5-2 parts of alpha-bromocinnamaldehyde, 1-5 parts of Boc-L-tert-leucine, 5-8 parts of calcium carbonate, 10-25 parts of coal gangue, 5-8 parts of tobacco stalk, 1-3 parts of sodium tartrate, 0.5-5 parts of (diphenylhydroxymethyl)pyrrolidine, 8-15 parts of fly ash, 5-10 parts of wormcast and 5-10 parts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium magnesium salt. According to the printing and dyeing industry sewage treating agent, a synergistic effect is exerted through raw material compounding, the content of COD, BOD, SS and NH3-N in printing and dyeing sewage can be effectively decreased, and the chromaticity and the dye concentration of the printing and dyeing sewage can be significantly reduced; the preparation method and the sewage treatment method are simple, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the cost is low, and the sewage treating agent is safe and effective; in addition, the printing and dyeing industry sewage treating agent has the advantages of being capable of rapidly achieving the effects and free of secondary pollution.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU ZHANGMENG NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Synthetic method of atazanavir intermediate
InactiveCN108069893ALow costMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryBenzaldehydeHydrogenation reaction
The invention discloses a synthetic method of an atazanavir intermediate of N-1-[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucine]-N-2-[4-(2-pyridyl)-benzyl] hydrazine. The synthetic method comprises (1) amidationreaction, (2) condensation and hydrogenation reaction and (3) condensation reaction. L-tert-leucine and methylchloroformate are subjected to amidation reaction to obtain N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine, then 4-(2-pyridyl)-benzaldehyde and hydrazine hydrate are subjected to condensation reaction and hydrogenation reaction to obtain 2-[4-(2-pyridyl)-benzyl] hydrazine hydrochloride, and the 2-[4-(2-pyridyl)-benzyl] hydrazine hydrochloride and the N-methoxycarbonyl-L-tert-leucine are subjected to condensation reaction to obtain the atazanavir intermediate of the N-1-[N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-tert-leucine]-N-2-[4-(2-pyridyl)-benzyl] hydrazine. The synthetic method of the atazanavir intermediate has the advantages of being low in cost, mild in reaction conditions, low in toxicity, convenient to operate, simple in raw material acquisition, high in yield and applicable to industrial production.
Owner:金学芳
A kind of preparation method of N-methoxycarbonyl-l-tert-leucine
ActiveCN103159647BSuitable for industrial productionHigh purityCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationTert-leucineDiastereomer
The invention relates to a preparation method of MOC-L-tertiary leucine, in particular to a method for splitting 2-methoxy group acylamino-3, 3-dimethyl butyric acid to prepare the MOC-L-tertiary leucine. Two kinds of diastereoisomer amine salt of the 2-methoxy group acylamino-3, 3-dimethyl butyric acid are formed through the 2-methoxy group acylamino-3, 3-dimethyl butyric acid and a resolving agent amine compound, MOC-L-tertiary leucine amine salt is obtained through separation, and the MOC-L-tertiary leucine is obtained by utilizing of the free acid MOC-L-tertiary leucine amine salt. The preparation method is low in cost, simple and reasonable in technique, high in product purity and suitable for industrial production of the MOC-L-tertiary leucine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIUZHOU PHARM CO LTD
A kind of method for synthesizing l-tert-leucine with double enzymes
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing L-tertiary leucine through double enzymes. A coenzyme NADH is coupled and mediated by utilizing leucine dehydrogenase and isopropanol dehydrogenase, and NAD+ can be rapidly reduced into NADH through the isopropanol dehydrogenase under the action of isopropanol with the final concentration being about 10 percent in a reaction solution, so that the reaction speed is increased, the reaction time is shortened, the reaction efficiency is improved, the space time yield is increased, the amount of double enzymes is low and is not higher than 3 percent of the mass of substrates, the reaction cost is reduced, the purity of the reaction product is over 99%ee, and recrystallization and resolution are not needed.
Owner:ENZYMASTER NINGBO BIO ENG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






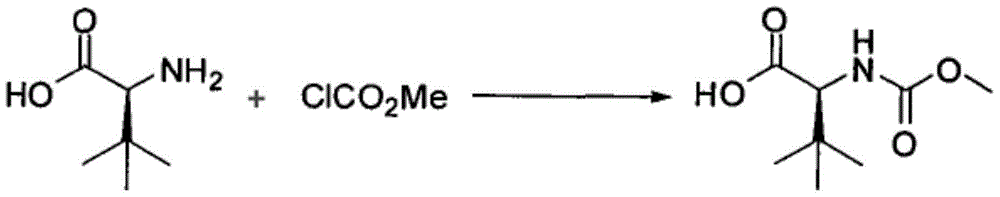

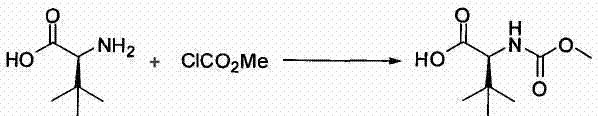
![Method of producing n-[(2S)-sulfanyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl)butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide and intermediate thereof Method of producing n-[(2S)-sulfanyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl)butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide and intermediate thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/148bc1e9-1982-46da-9368-ff4d189dc242/US06960567-20051101-C00001.png)
![Method of producing n-[(2S)-sulfanyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl)butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide and intermediate thereof Method of producing n-[(2S)-sulfanyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl)butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide and intermediate thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/148bc1e9-1982-46da-9368-ff4d189dc242/US06960567-20051101-C00002.png)
![Method of producing n-[(2S)-sulfanyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl)butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide and intermediate thereof Method of producing n-[(2S)-sulfanyl-4-(1,5,5-trimethylhydantoinyl)butanoyl]-L-leucyl-L-tert-leucine N-methylamide and intermediate thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/148bc1e9-1982-46da-9368-ff4d189dc242/US06960567-20051101-C00003.png)