Method for preparing L-tertiary leucine based on biological brick tandem double enzymes
A technology of tert-leucine and bio-bricks, which is applied in the direction of introducing foreign genetic material using carriers, recombinant DNA technology, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of low utilization efficiency, unfavorable production costs, and low theoretical yield, and achieve cost savings , low cost, good chiral selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for preparing L-tert-leucine based on biological bricks in series with double enzymes, comprising the steps of:
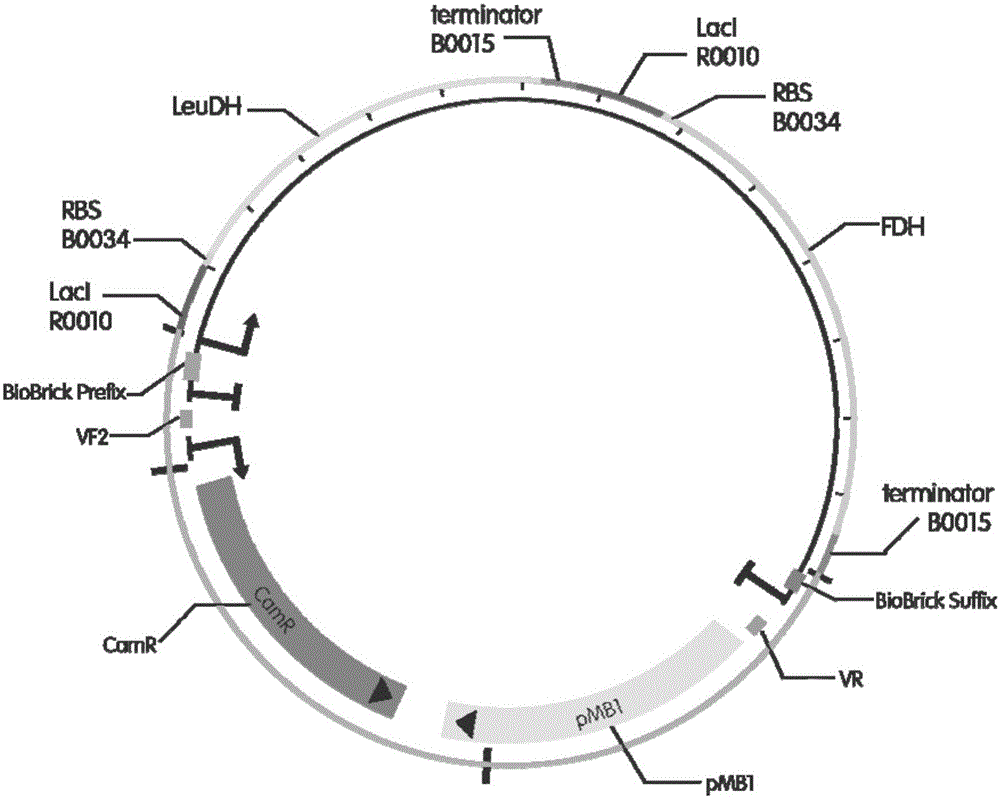
[0038] (1) Construction of tandem biological brick elements capable of tandem expression of leucine dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase (such as figure 1 shown), wherein the gene sequence of leucine dehydrogenase is shown in SEQID01, and the gene sequence of formate dehydrogenase is shown in SEQID02, specifically including:
[0039] 1) constructing the first biological brick element capable of expressing the leucine dehydrogenase alone, specifically:
[0040]a. Using the plasmid pUC18-leudh containing the leucine dehydrogenase gene as a template, PCR amplification was performed with primers LeuDH-F1 and LeuDH-R1 to obtain the leucine dehydrogenase gene sequence, wherein LeuDH-F1 and LeuDH- R1 is shown in SEQID3 and SEQID4 respectively;
[0041] b. Digest the above leucine dehydrogenase gene sequence and terminator B0015 with EcoRI and SpeI res...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Step (1) to step (3) are the same as embodiment 1, and step (4) is as follows:
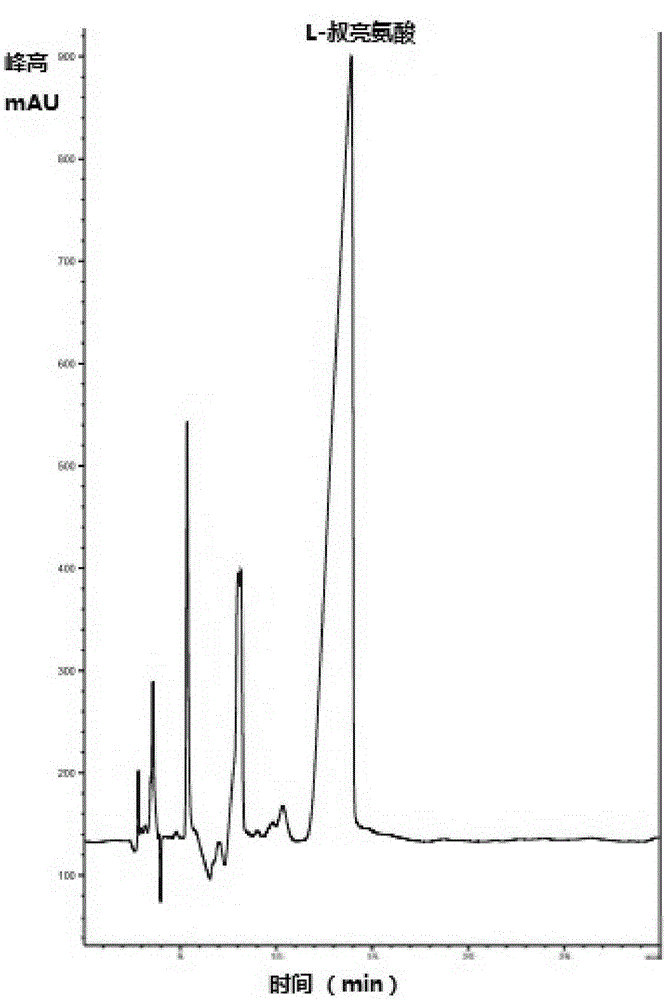
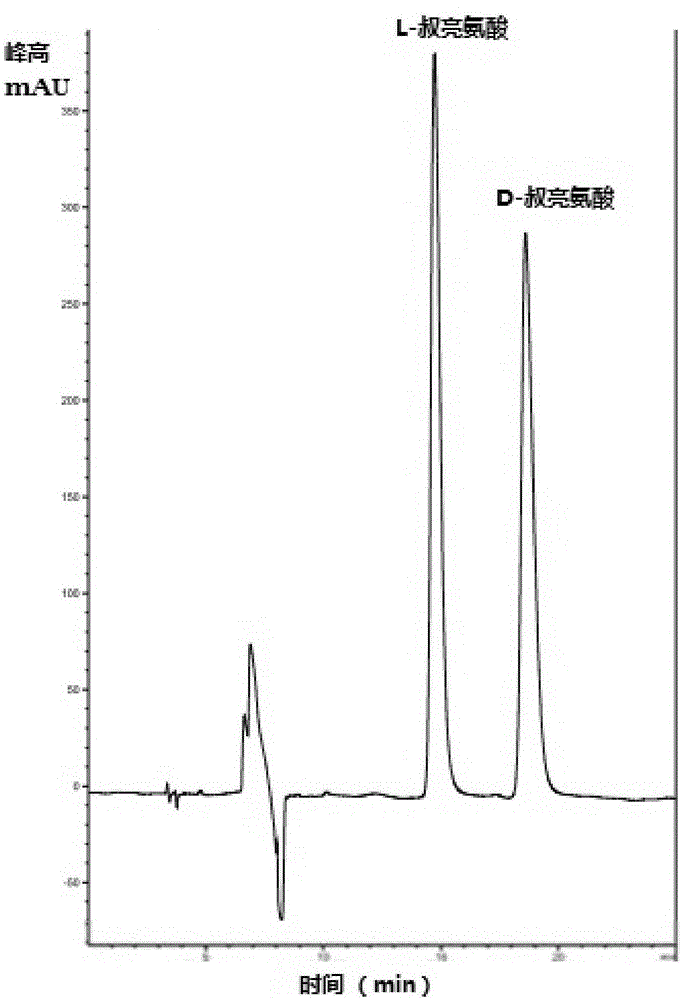
[0054] The above-mentioned cell fluid, trimethylpyruvate, amino donor, coenzyme and auxiliary substrate for coenzyme regeneration are placed in a buffer system with pH = 7.0 for shaking reaction, and the product L-tert. Leucine, the specific reaction system is: 0.030mol / L trimethylpyruvate, 1mol / LNH 4 Cl-NH 3 Buffer system, 0.005mL 1mM NADH, the volume of the above reaction is 15mL, the reaction temperature is 37°C, the reaction time is 8h, and the shaking rate is 180rpm. The reacted material is centrifuged to remove the precipitate, the supernatant is added with an equal volume of methanol, mixed and oscillated evenly, the precipitate is discarded by centrifugation, and the supernatant is diluted for later use. Detected by high performance liquid chromatography, the calculated yield of the product L-tert-leucine is 90.82%, and the e.e. value is greater than 99.0%.
Embodiment 3
[0056] Step (1) to step (3) are the same as embodiment 1, and step (4) is as follows:
[0057] The above-mentioned cell fluid, trimethylpyruvate, amino donor, coenzyme and auxiliary substrate for coenzyme regeneration are placed in a buffer system with pH = 7.0 for shaking reaction, and the product L-tert. Leucine, the specific reaction system is: 5% ammonia water, 0.060mol / L trimethylpyruvate, 1mol / LNH 4 Cl-NH 3 Buffer system, 0.005mL 1mM NADH, the volume of the above reaction is 15mL, the reaction temperature is 37°C, the reaction time is 12h, and the shaking rate is 180rpm. The reacted material is centrifuged to remove the precipitate, the supernatant is added with an equal volume of methanol, mixed and oscillated evenly, the precipitate is discarded by centrifugation, and the supernatant is diluted for later use. Detected by high performance liquid chromatography, the calculated yield of the product L-tert-leucine is 85.39%, and the e.e. value is greater than 99.0%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com