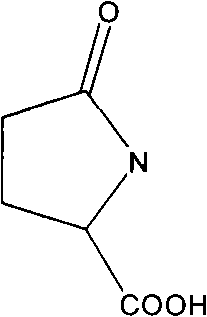
Preparation method for L-pyroglutamic acid
A technology of pyroglutamic acid and glutamic acid, which is applied in the field of biopharmaceuticals and can solve the problems of difficult removal of other impurities and complicated preparation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] High temperature melting:
[0020] Put 200kg of glutenic acid (Hangzhou Xin'anjiang Monosodium Glutamate Factory) into a 500L electric heating reactor with a stirrer, when the temperature rises to 155°C, the glutaric acid melts, keep it warm for 10min, and immediately discharge the reaction solution from the discharge port of the reactor. 175kg of reaction solution was collected.
[0021] Cleaning:
[0022] Add 150L of pure water (500L storage tank) to the above reaction solution, control the temperature at 50°C and keep it warm for 20 minutes and stir until the solution is clear and then lowered to room temperature. The solution cooled to room temperature was filtered to remove solid impurities. The filtrate continued to stand at room temperature for 24h. A small amount of solid appeared and was filtered and the filtrate was collected.
[0023] Decolorization:
[0024] Add 10Kg of activated carbon to the above filtrate, decolorize at 70°C for 1 hour, and filter wh...
Embodiment 2
[0028] High temperature melting:
[0029] Put 150kg of glutenic acid into a 500L electric heating reactor with a stirrer, when the temperature rises to 160°C, the glutaric acid melts, keep it warm for 5 minutes, and immediately discharge the reaction solution from the discharge port of the reactor. 120kg of reaction solution was collected.
[0030] Cleaning:
[0031] Add 108L of pure water (500L storage tank) to the above reaction solution, control the temperature at 60° C. and keep it warm for 20 minutes and stir until the solution is clear and then lowered to room temperature. The solution cooled to room temperature was filtered to remove solid impurities. The filtrate continued to stand at room temperature for 24h. A small amount of solid appeared and was filtered and the filtrate was collected.
[0032] Decolorization:
[0033] Add 5Kg of activated carbon to the above filtrate, decolorize at 65°C for 1 hour, and filter while it is hot. The filtrate can be decolorized ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] High temperature melting:
[0038] Put 180kg of glutenic acid into a 500L electric heating reactor with a stirrer, when the temperature rises to 150°C, the glutaric acid melts, keep it warm for 15min, and immediately discharge the reaction solution from the outlet of the reactor. 155kg of reaction solution was collected.
[0039] Cleaning:
[0040] Add 132L of pure water (500L storage tank) to the above reaction solution, control the temperature at 55°C and keep it warm for 20 minutes and stir until the solution is clear and then lowered to room temperature. The solution cooled to room temperature was filtered to remove solid impurities. The filtrate continued to stand at room temperature for 24h. A small amount of solid appeared and was filtered and the filtrate was collected.
[0041] Decolorization:
[0042] Add 7Kg of activated carbon to the above filtrate, decolorize at 75°C for 1 hour, and filter while it is hot. The filtrate can be decolorized twice accordin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com